1.樹
1.1概念
樹是一種非線性的數據結構,它是由n個有限節點組成一個具有層次關系。這種結構有以下特點:
- 一個特殊的結點,稱為根節點,根節點沒有前驅節點
- 除根節點以外,其余節點分成M個互不相交的集合。每個集合又是一顆和樹類似的子樹。每顆子樹的根節點有且只有一個前驅,可以有0個或者多個后繼。
- 樹是遞歸定義的。
樹形結構中,子樹之間是不能有交集的,否則就不是樹形結構。除了根節點以外,每一個節點有且只有一個父結點。
一棵樹有N個節點就有N-1條邊。
1.2概念
- 結點的度:一個結點含有子樹的個數。
- 樹的度:一棵樹中,所有結點度最大值稱之為樹的度。
- 葉子結點或終端結點:度為0的結點稱作葉子結點;
- 雙親結點或父結點:若一個結點含有子節點,則稱這個結點為其子節點的父節點。
- 孩子結點或子結點:一個結點含有的子樹的根節點乘坐該結點的子節點。
- 根結點:一棵樹中,沒有雙親結點的結點
- 結點的層次:從根開始定義,根為第一層,根的子結點為第2層
- 樹的高度或深度:樹中結點的最大層次
- 兄弟結點:具有相同父節點的結點互相稱為兄弟結點
- 子孫:以某結點為根的子樹中任一結點都稱為該結點的子孫
- 森林:由m棵互不想接的樹構成的集合稱為森林
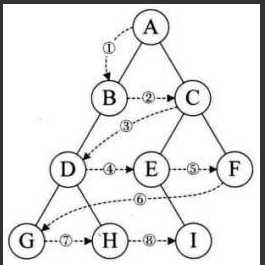
1.3樹的表示形式
2二叉樹
2.1概念
一顆二叉樹是結點的有限集合,該集合:或者為空,或者是由一個根節點加上兩顆別稱為左子樹和右子樹的二叉樹構成。
注意:
- 二叉樹不存在度大于2的結點
- 二叉樹的子樹有左右之分,次序不可顛倒,因此二叉樹是有序樹
2.2兩種特殊的二叉樹
- 滿二叉樹:一顆二叉樹,如果每層的節點數都達到最大值,則這顆二叉樹是滿二叉樹,也就是說如果有一顆二叉樹的層數為K,且結點總數為
,則他是滿二叉樹。
- 完全二叉樹:完全二叉樹是一種效率很高的數據結構,完全二叉樹是由滿二叉樹引申出來的。對于深度為K的,有n個結點的二叉樹,當且僅當其中每一個結點都與深度為K的滿二叉樹中從0到n-1的結點對應時才為完全二叉樹。
2.3二叉樹的性質
- 若根節點的層數為1,則一顆非空二叉樹的第i層上最多有
個結點
- 若只有根節點的二叉樹的深度為1,則深度為K 的二叉樹黨的最大結點數為
。
- 對于任何一棵二叉樹,如果其葉節點個數為n0(度為0),度為2的非葉結點的個數為n2,則有
- 具有n個結點的完全二叉樹的深度k為
向上取整
- 對于具有n個結點的完全二叉樹,如果按照從上至下,從左至右的順序對所有結點從0開始編號,則對于需要為i的結點有:
- 若i>0,雙親的序號為:
;若i=0,i為根節點編號,沒有雙親結點
- 若2i+1<n,左孩子序號為
,否則沒有左孩子
- 若2i+1>n,左孩子序號為
,否則沒有右孩子
2.4二叉樹的存儲
存儲結構分為:順序存儲和類似于鏈表形式的鏈式存儲。二叉樹的鏈式存儲是通過一個一個的節點引用起來的,常見的表示方式有二叉和三叉表示方式,
2.5二叉樹的基本操作
2.1二叉樹的遍歷
1.前中后序遍歷
所謂遍歷是指沿著某條搜索路線,因此對樹種每個結點均做一次且僅做一次的訪問。
- NLR:前序遍歷(Preorder Traversal 亦稱先序遍歷)——訪問根結點--->根的左子樹--->根的右子樹。
- LNR:中序遍歷(Inorder Traversal)——根的左子樹--->根節點--->根的右子樹。
- LRN:后序遍歷(Postorder Traversal)——根的左子樹--->根的右子樹--->根節點。
2.層序遍歷
設二叉樹的根節點所在 層數為1,層序遍歷就是從所在二叉樹的根節點出發,首先訪問第一層的樹根節點,然后從左到右訪問第2層 上的節點,接著是第三層的節點,以此類推,自上而下,自左到右逐層訪問樹的結點的過程就是層序遍歷。
2.5.二叉樹的基本方法
//樹種節點的個數
public void nodeSize(TreeNode root){if(root==null) return ;size++;nodeSize(root.left);nodeSize(root.right);}public int nodeSize2(TreeNode root){if(root==null) return 0;return nodeSize2(root.left)+nodeSize2(root.right)+1;}
// 子問題思路-求葉子結點個數
public int leafSize=0;public void getLeafNodeCount(TreeNode root){if(root==null)return ;if(root.left==null&root.right==null){leafSize++;}getLeafNodeCount(root.left);getLeafNodeCount(root.right);}//左數的葉子+右數的葉子public int getLeafNodeCount2(TreeNode root){if(root==null)return 0;if(root.left==null&&root.right==null){return 1;}return getLeafNodeCount2(root.left)+getLeafNodeCount2(root.right);}
//第K層結點的個數public int getKLevelNodeCount(TreeNode root,int k){if(root==null) return 0;if(k==1){return 1;}return getKLevelNodeCount(root.left,k-1)+getKLevelNodeCount(root.right,k-1);}
// 獲取二叉樹的高度
public int getHeight(TreeNode root){if(root==null) return 0;int leftHeight=getHeight(root.left);int rightHeight=getHeight(root.right);return (leftHeight>rightHeight? leftHeight+1:rightHeight+1);}
// 檢測值為value的元素是否存在public boolean find(TreeNode root,char key){if(root==null)return false;if(root.val==key){return true;}boolean leftVal=find(root.left,key);if (leftVal==true){return true;}boolean rightVal=find(root.right,key);if(rightVal==true){return true;}return false;}
//層序遍歷
public void levelOrder1(TreeNode root){//層序遍歷if(root==null){return;}Queue<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);while(!queue.isEmpty()){TreeNode cur=queue.poll();System.out.println(cur.val+" ");if(cur.left!=null){queue.offer(cur.left);}if(cur.right!=null){queue.offer(cur.right);}}}
public List<List<TreeNode>> levelOrder2(TreeNode root){//層序遍歷List<List<TreeNode>> ret=new ArrayList<>();if(root==null){return ret;}Queue<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);while(!queue.isEmpty()){int size= queue.size();//當前隊列的大小List<TreeNode> tmp=new ArrayList<>();while (size!=0){TreeNode cur=queue.poll();tmp.add(cur);size--;if(cur.left!=null){queue.offer(cur.left);}if(cur.right!=null){queue.offer(cur.right);}}ret.add(tmp);}return ret;}
2.5.3常見0j
判斷一棵樹是否是完全二叉樹
// 判斷一棵樹是不是完全二叉樹
public boolean isCompleteTree(TreeNode root){if(root==null) return false;Queue<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);while(!queue.isEmpty()){TreeNode cur=queue.poll();if (cur!=null){queue.offer(root.left);queue.offer(root.right);}else {break;}}while (!queue.isEmpty()){TreeNode cur=queue.poll();if(cur==null){return false;}}return true;}思路:先把當前節點放入隊列中,再彈出元素判斷是否為空節點,若不為空將該節點的左右節點再入隊,一直到隊列中都為空。再挨個彈出隊列中所剩下的元素,遇到null就說明不是完全二叉樹。若非空說明元素都是按序排列的。
100. 相同的樹
class Solution {public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if(p==null&&q!=null||p!=null&&q==null){return false;}if(p==null&&q==null){return true;}if(p.val!=q.val){return false;}return isSameTree(p.left,q.left)&&isSameTree(p.right,q.right);}
}思路:定義兩個節點位于兩棵樹,若一個節點為空一個不為空,說明不是相同的樹。若兩個節點都為空,說明是兩顆空樹,則相同。若兩個節點的值不相同,則不相同。遍歷兩樹的左子樹和右子樹,只有當左右子樹都相同的時候才是相同的樹。
572. 另一棵樹的子樹
class Solution {public boolean isSubtree(TreeNode root, TreeNode subRoot) {if(root==null){return false;} if(isSameTree(root,subRoot)){return true;}return isSubtree(root.left,subRoot)||isSubtree(root.right,subRoot);}private boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p,TreeNode q){if(p==null&&q!=null||p!=null&&q==null){return false;}if(p==null&&q==null){return true;}if(p.val!=q.val){return false;}return isSameTree(p.left,q.left)&&isSameTree(p.right,q.right);}
}思路與相同樹類似。只不過可能從根結點處開始相同,也有可能與左右子樹中任意一棵子樹相同。
226. 翻轉二叉樹
class Solution {public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {if(root==null){return null;}TreeNode tmp=root.left;root.left=root.right;root.right=tmp;invertTree(root.left);invertTree(root.right);return root;}
}110. 平衡二叉樹
class Solution {public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {return getHeight(root) != -1;}private int getHeight(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) {return 0;}int leftHeight = getHeight(root.left);if (leftHeight == -1) {return -1; // 左子樹不平衡}int rightHeight = getHeight(root.right);if (rightHeight == -1) {return -1; // 右子樹不平衡}if (Math.abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1) {return -1; // 當前節點不平衡}return Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1;}
}思路:平衡二叉樹的概念是:平衡二叉樹是指該樹所有節點的左右子樹的高度相差不超過 1。基本思路與求樹的高度相同,遍歷左右子樹計算子樹的高度,比較高度并加1。但是這里為預防重復計算高度設置一個-1值說明該子樹已經不平衡了。
101. 對稱二叉樹
class Solution {public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {if(root==null){return true;}return isSymmetricChild(root.left,root.right);}public boolean isSymmetricChild(TreeNode p,TreeNode q){if(p==null&&q!=null||p!=null&&q==null){return false;}if(p==null&&q==null){return true;}if(p.val!=q.val){return false;}return isSymmetricChild(p.left,q.right)&&isSymmetricChild(p.right,q.left);}
}思路:遍歷左右子樹,當p.left==q.right且p.right==q.left時才滿足對稱。
給定一個字符串生成一個二叉樹
編一個程序,讀入用戶輸入的一串先序遍歷字符串,根據此字符串建立一個二叉樹(以指針方式存儲)。 例如如下的先序遍歷字符串: ABC##DE#G##F### 其中“#”表示的是空格,空格字符代表空樹。
public static int i = 0;public static TreeNode creatrTree(String str) {TreeNode root = null;if(str.charAt(i) != '#') {root = new TreeNode(str.charAt(i));i++;root.left = creatrTree(str);root.right = creatrTree(str);}else {i++;}return root;}
}
思路:按照先序遍歷的方式創建二叉樹。
236. 二叉樹的最近公共祖先
class Solution {public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if(root==null)return null;if(root==p||root==q){return root;}TreeNode left=lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);TreeNode right=lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);if(left!=null&&right!=null){return root;}else if(left==null){return right;}else{return left;}}
}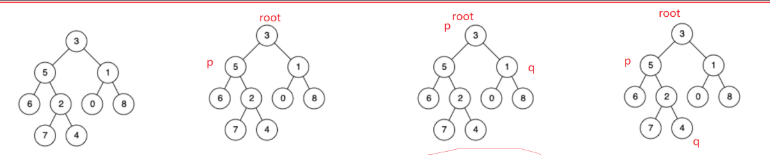
思路:p,q若分別位于左右子樹上那么最近公共祖先一定是根節點。若一個位于左或右子樹上,一個位于根節點,那么根節點就是最近公共祖先。?
105. 從前序與中序遍歷序列構造二叉樹
class Solution {public int preindex=0;public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {return buildTreeChild(preorder,inorder,0,inorder.length-1);}private TreeNode buildTreeChild(int[] preorder,int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend){if(inbegin>inend){return null;}TreeNode root=new TreeNode(preorder[preindex]);int rootIndex=findIdex(inorder,inbegin, inend,preorder[preindex] );if(rootIndex==-1){return null;}preindex++;root.left=buildTreeChild(preorder,inorder,inbegin,rootIndex-1);root.right=buildTreeChild(preorder,inorder,rootIndex+1,inend);return root;}private int findIdex(int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend,int key){for(int i=inbegin;i<=inend;i++){if(inorder[i]==key){return i;}}return -1;}
}思路:按照手動畫樹的思路,前序遍歷第一個數就是根節點,而中序遍歷以這個數分作左右兩棵子樹。那么遍歷前序遍歷數組,并在中序遍歷數組中找到對應下標,構建根節點。同時按照中序遍歷順序先構建左子樹再構建右邊子樹。在中序遍歷數組定義一個數組開頭和結尾。調用是改變結尾或者開頭的位置,一直到開頭下標大于結尾下標時,說明子樹構建完成。
?106. 從中序與后序遍歷序列構造二叉樹
class Solution {public int postIndex;public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {postIndex=postorder.length-1;return buildTreeChild(postorder,inorder,0,inorder.length-1);}private TreeNode buildTreeChild(int[] postorder,int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend){if(inbegin>inend){return null;}TreeNode root=new TreeNode(postorder[postIndex]);int rootIndex=findIdex(inorder,inbegin, inend,postorder[postIndex]);if(rootIndex==-1){return null;}postIndex--;root.right=buildTreeChild(postorder,inorder,rootIndex+1,inend);root.left=buildTreeChild(postorder,inorder,inbegin,rootIndex-1);return root;}private int findIdex(int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend,int key){for(int i=inbegin;i<=inend;i++){if(inorder[i]==key){return i;}}return -1;}}思路:與前中序遍歷創建子樹同理。后序遍歷最后一個節點為根節點。且子樹創建順序應該是先右子樹后左子樹。
606. 根據二叉樹創建字符串
class Solution {public String tree2str(TreeNode root) {StringBuilder stringBuider=new StringBuilder();tree2strChild(root,stringBuider);return stringBuider.toString();}private void tree2strChild(TreeNode t,StringBuilder stringBuider){if(t==null){return;}stringBuider.append(t.val);if(t.left!=null){stringBuider.append("(");tree2strChild(t.left,stringBuider);stringBuider.append(")");}else{if(t.right==null){return ;}else{stringBuider.append("()");}}if(t.right!=null){stringBuider.append("(");tree2strChild(t.right,stringBuider);stringBuider.append(")");}else{return ;}}
}思路:左子樹不為空的時候添加左括號,在添加字符后添加右括號。若右子樹節點為空那么添加左右括號。可以將情況分為:1左邊不為空(右邊為空,右邊不為空)2.左邊為空(右邊為空,右邊不為空)3.右邊空4.右邊不為空。
145. 二叉樹的后序遍歷
(非遞歸遍歷)
class Solution {public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> res=new ArrayList<Integer>();if(root==null) return res;Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<>();TreeNode cur=root;TreeNode top=null;TreeNode prev=null;while(cur!=null||!stack.isEmpty()){while(cur!=null){stack.push(cur);cur=cur.left;}top=stack.peek();if(top.right==null||top.right==prev){stack.pop();res.add(top.val);prev=top;//當前結點被打印過了}else{cur=top.right;}} return res;}
}


 邏輯備份實操)

 運行HelloWorld)
區別)

)








常用類)

