1. 觀察者模式
1.1.?使用場景
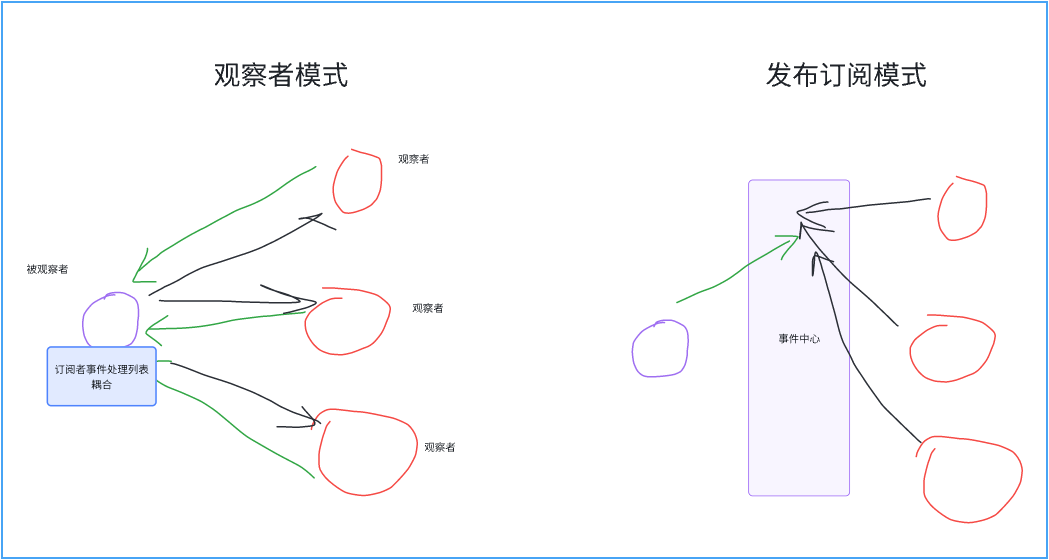
觀察者模式用于對象間的一對多依賴關系,當一個對象的狀態發生變化時,所有依賴于它的對象都能收到通知并自動更新。常用于事件處理、通知系統。在前端中,觀察者模式用于實現事件監聽、數據綁定等功能。
1.2.?代碼實現
class Subject {constructor() {this.observers = [];}addObserver(observer) {this.observers.push(observer);}removeObserver(observer) {this.observers = this.observers.filter(obs => obs !== observer);}notifyObservers(message) {this.observers.forEach(observer => observer.update(message));}
}class Observer {update(message) {console.log('Observer received:', message);}
}// 使用觀察者模式
const subject = new Subject();
const observer1 = new Observer();
const observer2 = new Observer();subject.addObserver(observer1);
subject.addObserver(observer2);subject.notifyObservers('New update available'); // Observer received: New update available1.3.?詳細解釋
Subject:發布者,維護一個觀察者列表,提供方法來添加、移除和通知觀察者。
Observer:觀察者,提供 update 方法來響應發布者的通知。
觀察者模式適合事件系統或數據模型更新的場景。
1.4.?實際應用
觀察者模式常用于事件驅動系統,如 DOM 事件監聽器、Vue 或 React 的響應式系統。
2. 發布訂閱模式
2.1.?使用場景
發布訂閱模式用于實現松耦合的事件驅動系統,發布者(Publisher)和訂閱者(Subscriber)通過事件中心(Event Bus或Broker)進行通信,發布者無需知道誰訂閱了事件,而訂閱者也無需知道事件由誰發布。該模式常用于消息隊列、事件系統、異步處理等場景。
2.2.?代碼實現
// 事件中心(Event Bus)
class EventBus {constructor() {this.subscribers = {}; // 存儲所有事件和其對應的訂閱者}// 訂閱事件subscribe(event, callback) {if (!this.subscribers[event]) {this.subscribers[event] = []; // 如果事件不存在,創建一個新的訂閱者列表}this.subscribers[event].push(callback); // 將訂閱者的回調函數加入列表}// 發布事件publish(event, data) {if (this.subscribers[event]) {this.subscribers[event].forEach(callback => callback(data)); // 通知所有訂閱者}}// 取消訂閱unsubscribe(event, callback) {if (this.subscribers[event]) {this.subscribers[event] = this.subscribers[event].filter(cb => cb !== callback); // 移除指定的訂閱者}}
}// 創建事件中心
const eventBus = new EventBus();// 訂閱者1
const subscriber1 = (data) => {console.log('Subscriber 1 received:', data);
};// 訂閱者2
const subscriber2 = (data) => {console.log('Subscriber 2 received:', data);
};// 訂閱事件
eventBus.subscribe('eventA', subscriber1);
eventBus.subscribe('eventA', subscriber2);// 發布事件
eventBus.publish('eventA', 'This is event A data');
// Subscriber 1 received: This is event A data
// Subscriber 2 received: This is event A data// 取消訂閱者2的訂閱
eventBus.unsubscribe('eventA', subscriber2);// 再次發布事件
eventBus.publish('eventA', 'This is new event A data');
// Subscriber 1 received: This is new event A data2.3.?詳細注釋
EventBus(事件中心):作為中介,維護一個事件和訂閱者的映射關系。負責發布事件、添加訂閱者以及移除訂閱者。
subscribe:用于訂閱某個事件,將訂閱者的回調函數加入到對應事件的訂閱者列表中。
publish:用于發布某個事件,觸發該事件的所有訂閱者的回調函數。
unsubscribe:取消訂閱某個事件,移除指定訂閱者的回調函數。
2.4.?實際應用
在前端開發中,發布訂閱模式常用于事件中心管理事件流,比如在 Vue.js 的 emit和on 中。
消息隊列系統(如 RabbitMQ、Kafka)也是發布訂閱模式的典型應用。
3. 模板方法模式
3.1.?使用場景
模板方法模式定義了一個操作中的算法骨架,而將一些步驟的實現延遲到子類。常用于固定流程中部分步驟需要定制的場景。在前端中,模板方法模式可用于不同頁面之間的結構共享。
3.2.?代碼實現
class AbstractClass {templateMethod() {this.step1();this.step2();this.step3();}step1() {console.log('AbstractClass: Step 1');}step2() {throw new Error('step2 must be implemented by subclass');}step3() {console.log('AbstractClass: Step 3');}
}class ConcreteClass extends AbstractClass {step2() {console.log('ConcreteClass: Step 2');}
}// 使用模板方法模式
const instance = new ConcreteClass();
instance.templateMethod();
// Output:
// AbstractClass: Step 1
// ConcreteClass: Step 2
// AbstractClass: Step 33.3. 詳細注釋
AbstractClass:提供算法的骨架,定義了 templateMethod 作為算法的模板方法,具體步驟由子類實現。
ConcreteClass:子類實現了模板方法中的具體步驟。
模板方法模式允許子類在不改變算法整體結構的前提下,重新定義算法的某些步驟。
3.4.?實際應用
模板方法模式常用于頁面加載邏輯、復雜流程處理等場景,如表單驗證步驟、數據處理流程等。
4. 策略模式
4.1.?使用場景
策略模式定義了一系列算法,并將每個算法封裝起來,使它們可以互換使用。在前端開發中,策略模式可以用于處理不同的用戶輸入、動態選擇不同的 UI 渲染邏輯等。
4.2.?代碼實現
class StrategyA {execute() {console.log('Executing Strategy A');}
}class StrategyB {execute() {console.log('Executing Strategy B');}
}class Context {setStrategy(strategy) {this.strategy = strategy;}executeStrategy() {this.strategy.execute();}
}// 使用策略模式
const context = new Context();
const strategyA = new StrategyA();
context.setStrategy(strategyA);
context.executeStrategy(); // Executing Strategy Aconst strategyB = new StrategyB();
context.setStrategy(strategyB);
context.executeStrategy(); // Executing Strategy B4.3.?詳細注釋
StrategyA 和 StrategyB:定義了不同的算法實現。
Context:上下文類,維護當前策略,并通過 setStrategy 方法動態切換策略。
策略模式允許在運行時根據條件選擇不同的算法,避免使用大量條件語句。
4.4.?實際應用
- 策略模式常用于表單驗證、輸入處理、動態 UI 渲染等場景。
5. 責任鏈模式
5.1.?使用場景
責任鏈模式用于將請求的處理者串聯起來,多個對象依次處理請求,直到有對象處理它為止。在前端中,責任鏈模式常用于事件處理鏈、表單驗證流程等。
5.2.?代碼實現
class Handler {setNext(handler) {this.nextHandler = handler;}handle(request) {if (this.nextHandler) {return this.nextHandler.handle(request);}return null;}
}class ConcreteHandlerA extends Handler {handle(request) {if (request === 'A') {return 'Handled by A';}return super.handle(request);}
}class ConcreteHandlerB extends Handler {handle(request) {if (request === 'B') {return 'Handled by B';}return super.handle(request);}
}// 使用責任鏈模式
const handlerA = new ConcreteHandlerA();
const handlerB = new ConcreteHandlerB();
handlerA.setNext(handlerB);console.log(handlerA.handle('A')); // Handled by A
console.log(handlerA.handle('B')); // Handled by B5.3.?詳細注釋
Handler:處理者的基類,提供 setNext 方法來設置下一個處理者。
ConcreteHandlerA 和 ConcreteHandlerB:具體處理者,實現了請求處理邏輯。
責任鏈模式使得多個處理者依次處理請求,避免了請求和處理者之間的緊耦合。
5.4.?實際應用
責任鏈模式常用于表單驗證、事件處理鏈、權限管理等場景。
6. 中介者模式
6.1.?使用場景
中介者模式用于定義對象間的通信方式,避免直接交互造成的復雜性。在前端中,中介者模式常用于組件之間的通信、事件總線等。
6.2.?代碼實現
class Mediator {notify(sender, event) {if (event === 'EventA') {console.log('Mediator reacts to EventA and triggers EventB');sender.trigger('EventB');}}
}class Component {constructor(mediator) {this.mediator = mediator;}trigger(event) {console.log(`Component triggered: ${event}`);this.mediator.notify(this, event);}
}// 使用中介者模式
const mediator = new Mediator();
const component = new Component(mediator);component.trigger('EventA');/* Output:
Component triggered: EventA
Mediator reacts to EventA and triggers EventB
Component triggered: EventB
*/6.3.?詳細注釋
Mediator:中介者類,負責協調不同組件之間的交互。
Component:組件類,負責觸發事件并通過中介者進行通信。
中介者模式通過集中化的中介者,避免了多個組件之間的復雜依賴關系。
6.4.?實際應用
- 中介者模式常用于組件通信、消息總線、事件系統等場景。
7. 訪問者模式
7.1.?使用場景
訪問者模式用于在不改變數據結構的前提下,定義對數據結構中元素的操作。在前端中,訪問者模式適用于復雜結構的遍歷和操作,如 DOM 樹操作等。
7.2.?代碼實現
class Element {accept(visitor) {visitor.visit(this);}
}class ConcreteElementA extends Element {operationA() {console.log('Operation A');}
}class ConcreteElementB extends Element {operationB() {console.log('Operation B');}
}class Visitor {visit(element) {if (element instanceof ConcreteElementA) {element.operationA();} else if (element instanceof ConcreteElementB) {element.operationB();}}
}// 使用訪問者模式
const elements = [new ConcreteElementA(), new ConcreteElementB()];
const visitor = new Visitor();
elements.forEach(element => element.accept(visitor));7.3.?詳細注釋
Element:元素基類,定義 accept 方法來接受訪問者。
Visitor:訪問者類,提供 visit 方法處理不同的元素類型。
訪問者模式允許在不修改數據結構的前提下,動態為結構中的每個元素定義新的操作。
7.4.?實際應用
訪問者模式常用于對樹形結構、DOM 元素的遍歷操作。
8. 命令模式
8.1.?使用場景
命令模式用于將請求封裝為對象,從而實現請求的參數化、隊列化。在前端中,命令模式適用于實現操作歷史、撤銷功能等場景。
8.2.?代碼實現
class Command {execute() {throw new Error('execute method must be implemented');}
}class ConcreteCommand extends Command {constructor(receiver) {super();this.receiver = receiver;}execute() {this.receiver.action();}
}class Receiver {action() {console.log('Receiver action executed');}
}class Invoker {setCommand(command) {this.command = command;}executeCommand() {this.command.execute();}
}// 使用命令模式
const receiver = new Receiver();
const command = new ConcreteCommand(receiver);
const invoker = new Invoker();invoker.setCommand(command);
invoker.executeCommand(); // Receiver action executed8.3. 詳細注釋
Command:命令的基類,定義 execute 方法。
ConcreteCommand:具體命令,執行對接收者的操作。
Invoker:調用者,負責執行命令。
命令模式通過封裝請求,將請求處理邏輯與請求發出者解耦。
8.4.?實際應用
命令模式常用于實現操作歷史、撤銷重做、宏命令等場景。
9. 解釋器模式
9.1.?使用場景
解釋器模式用于給定語言的語法表達式,并解析其中的語句。在前端中,解釋器模式可用于解析自定義的模板語言、腳本等。
9.2.?代碼實現
class Expression {interpret(context) {throw new Error('interpret method must be implemented');}
}class NumberExpression extends Expression {constructor(value) {super();this.value = value;}interpret() {return this.value;}
}class AddExpression extends Expression {constructor(left, right) {super();this.left = left;this.right = right;}interpret() {return this.left.interpret() + this.right.interpret();}
}// 使用解釋器模式
const left = new NumberExpression(3);
const right = new NumberExpression(5);
const addExpr = new AddExpression(left, right);console.log(addExpr.interpret()); // 89.3.?詳細注釋
Expression:解釋器基類,定義 interpret 方法。
NumberExpression 和 AddExpression:具體的解釋器,解析數字和加法操作。
解釋器模式允許定義一個簡單的語言或規則,并通過解釋器解析和執行。
9.4.?實際應用
解釋器模式常用于處理模板引擎、正則表達式解析等場景。
10. 迭代器模式
10.1.?使用場景
迭代器模式用于順序訪問集合對象的元素,而無需暴露其內部結構。在前端中,迭代器模式常用于遍歷數組、集合等數據結構。
10.2.?代碼實現
class Iterator {constructor(collection) {this.collection = collection;this.index = 0;}hasNext() {return this.index < this.collection.length;}next() {return this.collection[this.index++];}
}// 使用迭代器模式
const collection = [1, 2, 3, 4];
const iterator = new Iterator(collection);while (iterator.hasNext()) {console.log(iterator.next()); // 1 2 3 4
}10.3.?詳細注釋
Iterator:迭代器類,提供 hasNext 和 next 方法來順序訪問集合中的元素。
迭代器模式允許分離集合對象的遍歷邏輯,使得遍歷和數據結構解耦。
10.4.?實際應用
迭代器模式常用于處理數組、鏈表、樹等數據結構的遍歷。
11. 備忘錄模式
11.1.?使用場景
備忘錄模式用于保存對象的狀態,以便在需要時恢復。在前端中,備忘錄模式可用于實現撤銷功能、保存表單狀態等。
11.2.?代碼實現
class Memento {constructor(state) {this.state = state;}getState() {return this.state;}
}class Originator {setState(state) {console.log('Setting state to:', state);this.state = state;}saveStateToMemento() {return new Memento(this.state);}getStateFromMemento(memento) {this.state = memento.getState();}
}class Caretaker {constructor() {this.mementoList = [];}
}// 使用備忘錄模式
const originator = new Originator();
const caretaker = new Caretaker();originator.setState('State 1');
caretaker.add(originator.saveStateToMemento());originator.setState('State 2');
caretaker.add(originator.saveStateToMemento());originator.setState('State 3');
console.log('Current State:', originator.state); // Current State: State 3originator.getStateFromMemento(caretaker.get(0));
console.log('Restored State:', originator.state); // Restored State: State 111.3.?詳細注釋
Memento:備忘錄類,保存狀態。
Originator:原始對象,提供保存和恢復狀態的方法。
Caretaker:管理備忘錄列表。
備忘錄模式通過保存對象的狀態,允許在需要時恢復之前的狀態。
11.4.?實際應用
- 備忘錄模式常用于實現撤銷功能、表單狀態恢復等場景。
12. 狀態模式
12.1.?使用場景
狀態模式允許對象在內部狀態發生改變時,改變其行為。在前端中,狀態模式可用于管理復雜的組件狀態,如表單驗證、UI 狀態管理等。
12.2.?代碼實現
class State {handle(context) {throw new Error('handle method must be implemented');}
}class ConcreteStateA extends State {handle(context) {console.log('State A, transitioning to State B');context.setState(new ConcreteStateB());}
}class ConcreteStateB extends State {handle(context) {console.log('State B, transitioning to State A');context.setState(new ConcreteStateA());}
}class Context {constructor() {this.state = new ConcreteStateA();}setState(state) {this.state = state;}request() {this.state.handle(this);}
}// 使用狀態模式
const context = new Context();
context.request(); // State A, transitioning to State B
context.request(); // State B, transitioning to State A12.3.?詳細注釋
State:狀態基類,定義 handle 方法。
ConcreteStateA 和 ConcreteStateB:具體狀態類,實現了狀態切換邏輯。
Context:上下文類,負責在不同狀態下切換并調用狀態行為。
狀態模式允許對象在狀態變化時改變其行為,使得狀態切換透明化。
12.4.?實際應用
- 狀態模式常用于處理復雜的狀態邏輯,如表單的驗證狀態、UI 的顯示狀態等。














![【LCA 樹上倍增】P9245 [藍橋杯 2023 省 B] 景區導游|普及+](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/【LCA 樹上倍增】P9245 [藍橋杯 2023 省 B] 景區導游|普及+)


:面向鏈接預測的知識圖譜表示學習方法綜述)
,規則(Rules))
