🏞? 基于Python+Streamlit的旅游數據分析與預測系統:從數據可視化到機器學習預測的完整實現
📝 前言
在大數據時代,旅游行業的數據分析變得越來越重要。如何從海量的旅游數據中挖掘有價值的信息,并進行準確的銷量預測,是每個數據分析師和產品經理都關心的問題。
本文將詳細介紹一個完整的旅游數據分析與預測系統的設計與實現,該系統集成了數據可視化、地理分析、文本挖掘和機器學習預測等多個功能模塊,采用現代化的Web界面,為用戶提供直觀、交互式的數據分析體驗。
🎯 項目概述
系統功能
- 📊 多維度數據可視化:銷量排行、星級分布、城市分析
- 🗺? 地理數據分析:基于地理坐標的熱力圖展示
- 🔮 智能銷量預測:基于機器學習的景點銷量預測
- ?? 文本數據挖掘:景點簡介詞云分析
- 📈 實時數據概覽:關鍵指標監控面板
技術亮點
- 🚀 現代化Web界面:基于Streamlit構建的響應式界面
- 🎨 自定義UI設計:CSS樣式優化,提升用戶體驗
- ? 性能優化:數據緩存機制,提高加載速度
- 🔧 容錯處理:優雅的依賴包處理和錯誤處理機制
- 📱 多設備適配:支持不同屏幕尺寸的響應式布局
🛠? 技術架構
技術棧選擇
前端框架
streamlit >= 1.28.0 # Web應用框架
選擇理由:Streamlit是專為數據科學和機器學習應用設計的Python Web框架,具有以下優勢:
- 純Python開發,學習成本低
- 內置豐富的數據可視化組件
- 支持實時交互和狀態管理
- 部署簡單,適合快速原型開發
數據處理層
pandas >= 1.5.0 # 數據處理
numpy >= 1.24.0 # 數值計算
可視化層
plotly >= 5.15.0 # 交互式圖表
pydeck >= 0.8.0 # 地理數據可視化
matplotlib >= 3.7.0 # 基礎圖表
機器學習層
scikit-learn >= 1.3.0 # 機器學習算法
文本處理層
wordcloud >= 1.9.2 # 詞云生成
Pillow >= 9.5.0 # 圖像處理
系統架構圖
📊 數據結構設計
原始數據表結構
# tourism_raw_data.csv
columns = ['城市', # 景點所在城市'名稱', # 景點名稱'星級', # 景點星級(如4A、5A等)'評分', # 用戶評分'銷量', # 歷史銷量'價格', # 門票價格'是否免費', # 是否免費景點'具體地址', # 詳細地址'坐標', # 經緯度坐標'簡介' # 景點簡介文本
]
特征工程數據表
# tourism_feature_data.csv
# 經過特征工程處理的數據,用于機器學習訓練
processed_columns = ['城市', # 類別特征'名稱', # 類別特征 '星級', # 數值特征(已處理)'評分', # 數值特征'是否免費', # 布爾特征'銷量' # 目標變量
]
🎨 界面設計與實現
整體布局設計
系統采用側邊欄導航 + 主內容區的經典布局:
# 頁面配置
st.set_page_config(page_title="旅游數據分析與預測系統",page_icon="🏞?",layout="wide", # 寬屏布局initial_sidebar_state="expanded" # 默認展開側邊欄
)
自定義CSS樣式
st.markdown("""
<style>.main-header {font-size: 2.5rem;color: #1f77b4;text-align: center;margin-bottom: 2rem;padding: 1rem;background: linear-gradient(90deg, #e3f2fd, #bbdefb);border-radius: 10px;}.section-header {font-size: 1.5rem;color: #2c3e50;margin: 1.5rem 0 1rem 0;padding: 0.5rem;border-left: 4px solid #3498db;background-color: #f8f9fa;}.prediction-container {background-color: #f0f8ff;padding: 1.5rem;border-radius: 10px;border: 1px solid #dde7f0;margin: 1rem 0;}
</style>
""", unsafe_allow_html=True)
功能模塊導航
# 側邊欄導航
page = st.sidebar.selectbox("選擇功能模塊",["🏠 首頁概覽", "📊 數據可視化", "🔮 銷量預測", "🗺? 地理分布", "?? 詞云分析"]
)
📈 數據可視化實現
1. 首頁概覽模塊
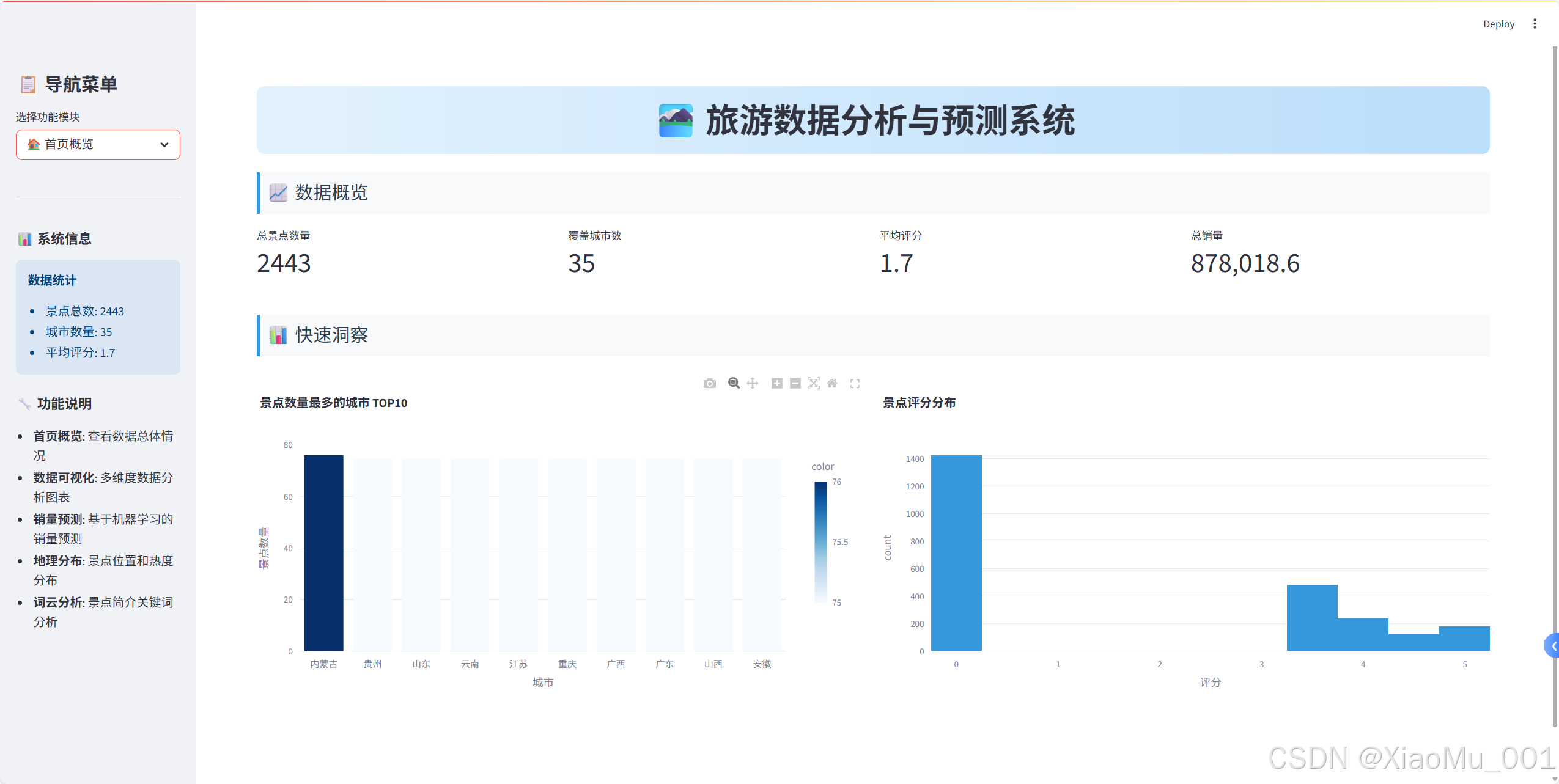
關鍵指標展示
# 創建四列布局顯示關鍵指標
col1, col2, col3, col4 = st.columns(4)with col1:st.metric("總景點數量", len(raw_data))
with col2:st.metric("覆蓋城市數", raw_data['城市'].nunique())
with col3:avg_rating = raw_data['評分'].mean()st.metric("平均評分", f"{avg_rating:.1f}")
with col4:total_sales = raw_data['銷量'].sum()st.metric("總銷量", f"{total_sales:,}")
快速洞察圖表
# 城市景點數量分布
city_counts = raw_data['城市'].value_counts().head(10)
fig_city = px.bar(x=city_counts.index, y=city_counts.values,title="景點數量最多的城市 TOP10",labels={'x': '城市', 'y': '景點數量'},color=city_counts.values,color_continuous_scale='Blues'
)
st.plotly_chart(fig_city, use_container_width=True)
2. 數據可視化模塊
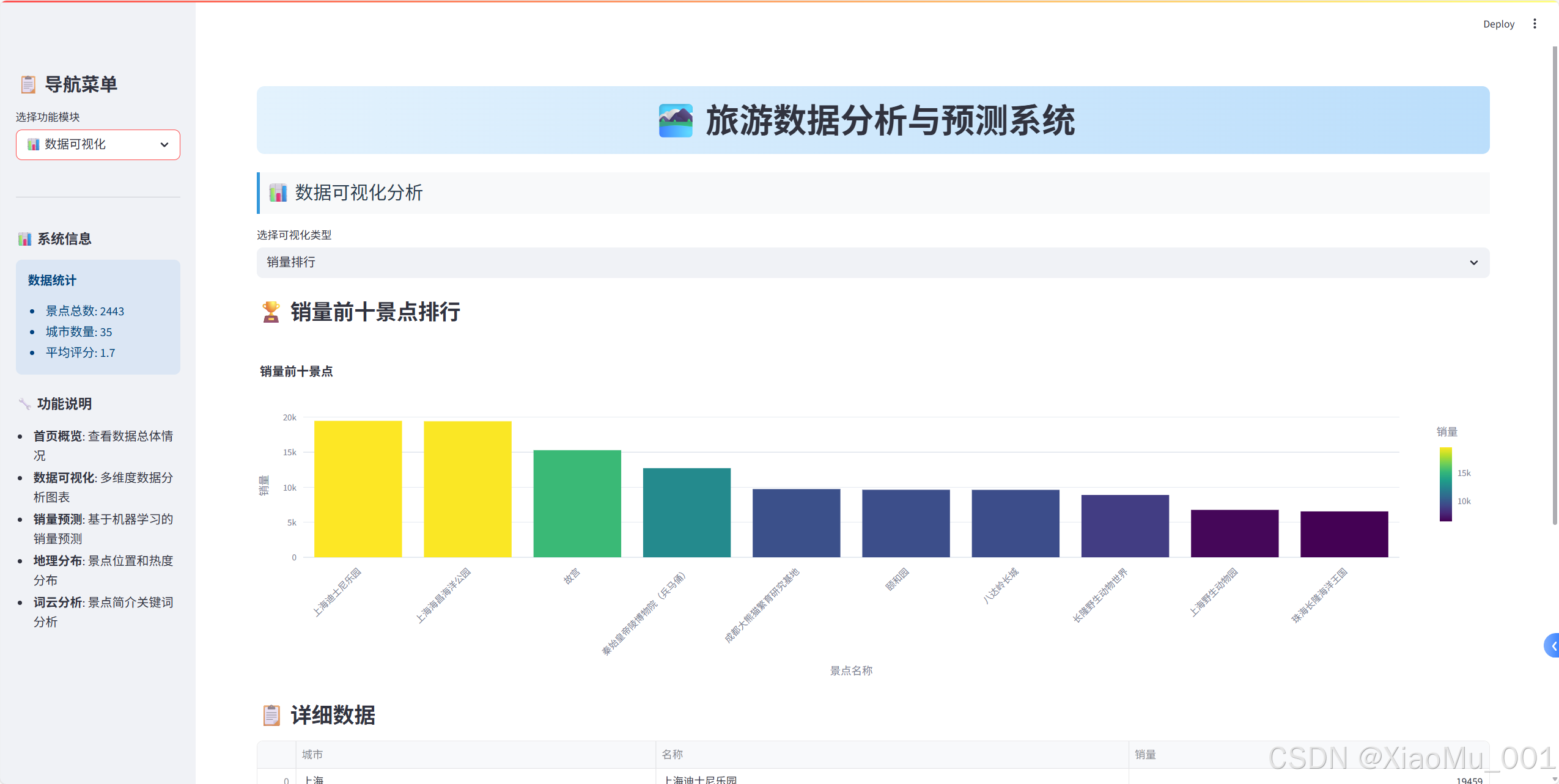
銷量排行分析
def create_sales_ranking():"""創建銷量排行圖表"""top_10_sales = raw_data[['城市', '名稱', '銷量']]\.sort_values(by='銷量', ascending=False).head(10)bar_chart = px.bar(top_10_sales, x='名稱', y='銷量',color='銷量',color_continuous_scale='Viridis',title="銷量前十景點",labels={'名稱': '景點名稱', '銷量': '銷量'})bar_chart.update_layout(xaxis_tickangle=-45)return bar_chart
星級分布分析
def create_star_distribution():"""創建星級分布圖表"""star_distribution = raw_data['星級'].value_counts().reset_index()star_distribution.columns = ['星級', '數量']# 餅圖pie_chart = px.pie(star_distribution, names='星級', values='數量',title="星級分布餅圖",color_discrete_sequence=px.colors.qualitative.Set3)# 柱狀圖bar_chart = px.bar(star_distribution,x='星級',y='數量',title="星級分布柱狀圖",color='數量',color_continuous_scale='Blues')return pie_chart, bar_chart
城市評分與價格關聯分析
def create_city_analysis():"""創建城市分析散點圖"""# 排除異常值df_no_sanqing = raw_data[raw_data['名稱'] != '三清山']# 計算城市平均值avg_score_price = df_no_sanqing.groupby('城市').agg({'評分': 'mean', '價格': 'mean'}).reset_index()avg_score_price = avg_score_price.sort_values(by='評分', ascending=False).head(10)scatter_chart = px.scatter(avg_score_price, x='評分', y='價格',color='城市',size='評分',size_max=20,title="平均評分前十城市與價格散點圖",labels={'評分': '平均評分', '價格': '平均價格(元)'},hover_data=['城市'])return scatter_chart
🔮 機器學習預測系統
預測模型設計
1. 特征工程
def process_star(x):"""處理星級特征"""if 'A' in str(x):return int(str(x)[0]) # 提取數字部分else:return 0 # 無星級設為0
2. 數據預處理Pipeline
from sklearn.compose import ColumnTransformer
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder, StandardScaler# 創建預處理器
preprocessor = ColumnTransformer(transformers=[# 類別特征:獨熱編碼('cat', OneHotEncoder(handle_unknown='ignore'), ['城市', '名稱']),# 數值特征:標準化('num', StandardScaler(), ['星級', '評分'])])
3. 模型訓練Pipeline
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression# 創建完整的ML Pipeline
model = Pipeline(steps=[('preprocessor', preprocessor),('regressor', LinearRegression())
])# 特征和目標變量
X = df[['城市', '名稱', '星級', '評分', '是否免費']]
y = df['銷量']# 訓練模型
model.fit(X, y)
4. 預測接口實現
def predict_sales(city, spot_name, star_rating, rating, is_free):"""銷量預測函數"""# 構建輸入數據user_input = pd.DataFrame({'城市': [city],'名稱': [spot_name],'星級': [star_rating],'評分': [rating],'是否免費': [is_free]})# 進行預測predicted_sales = model.predict(user_input)return predicted_sales[0]
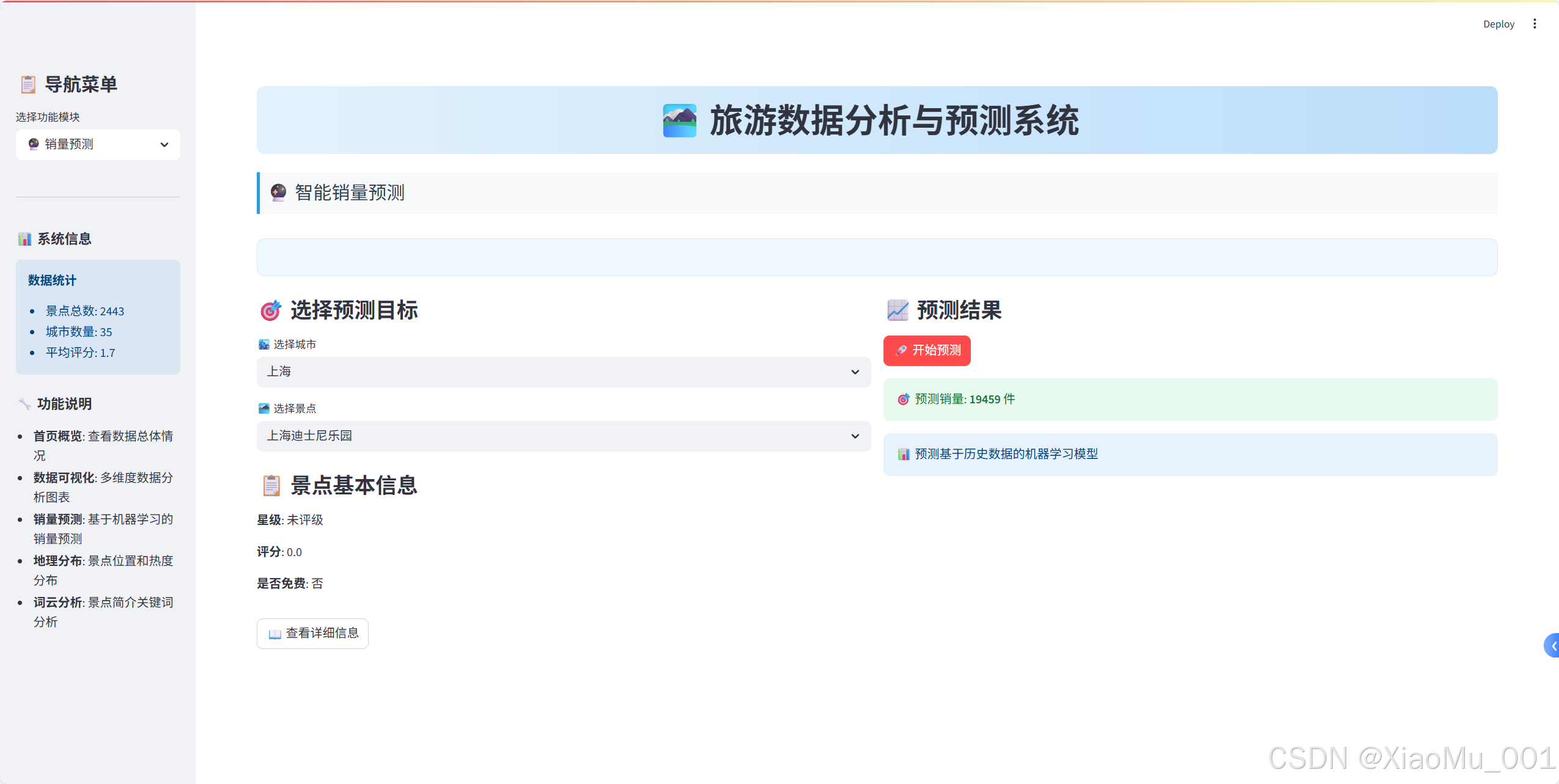
預測界面實現
def create_prediction_interface():"""創建預測界面"""with st.container():col1, col2 = st.columns(2)with col1:st.subheader("🎯 選擇預測目標")# 城市選擇cities = feature_data['城市'].unique()selected_city = st.selectbox('🏙? 選擇城市', cities)# 景點選擇city_spots = feature_data[feature_data['城市'] == selected_city]['名稱'].unique()selected_spot = st.selectbox('🏞? 選擇景點', city_spots)with col2:st.subheader("📈 預測結果")if st.button('🚀 開始預測', type='primary'):# 獲取景點信息spot_data = get_spot_data(selected_city, selected_spot)# 進行預測prediction = predict_sales(selected_city, selected_spot,spot_data['星級'], spot_data['評分'], spot_data['是否免費'])# 顯示結果st.success(f"🎯 預測銷量: **{prediction:.0f}** 件")
🗺? 地理數據可視化
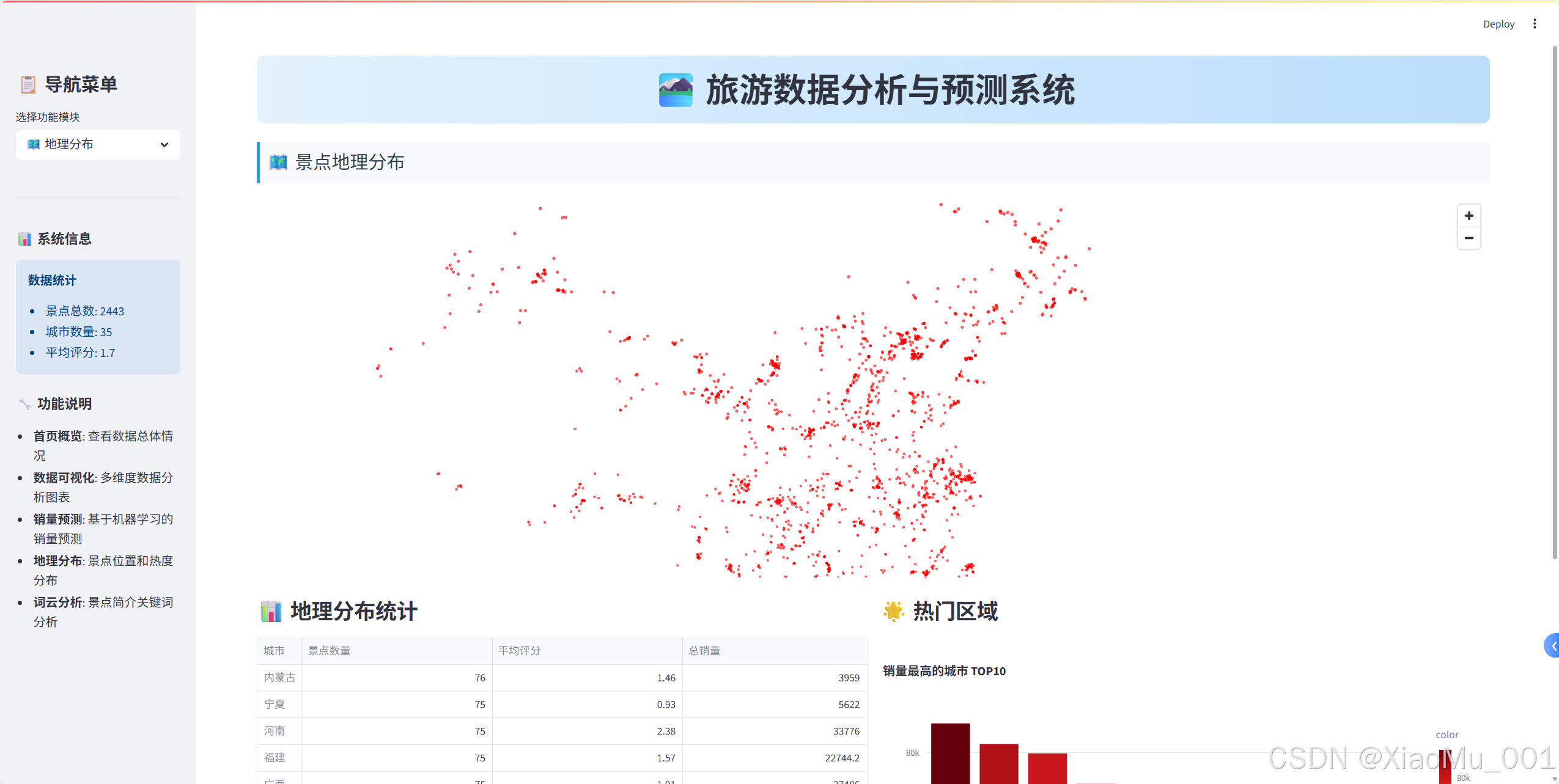
Pydeck地圖實現
1. 坐標數據處理
def process_coordinates(df):"""處理坐標數據"""# 分離經緯度df[['longitude', 'latitude']] = df['坐標'].str.split(',', expand=True)df['longitude'] = pd.to_numeric(df['longitude'], errors='coerce')df['latitude'] = pd.to_numeric(df['latitude'], errors='coerce')# 過濾無效坐標return df.dropna(subset=['longitude', 'latitude'])
2. 地圖視圖配置
import pydeck as pdk# 設置地圖視圖
view_state = pdk.ViewState(latitude=35.8617, # 中國中心緯度longitude=104.1954, # 中國中心經度zoom=3, # 縮放級別pitch=0, # 俯仰角度
)
3. 散點圖層創建
# 創建散點圖層
layer = pdk.Layer("ScatterplotLayer",df_map,get_position=["longitude", "latitude"],get_radius=10000, # 點的半徑get_color=[255, 0, 0, 160], # 紅色半透明pickable=True, # 可點擊
)
4. 交互式地圖組裝
# 創建地圖對象
deck = pdk.Deck(layers=[layer],initial_view_state=view_state,tooltip={"text": "{名稱}\n城市: {城市}\n評分: {評分}\n銷量: {銷量}"},map_style="mapbox://styles/mapbox/light-v10" # 淺色主題
)# 在Streamlit中顯示
st.pydeck_chart(deck, use_container_width=True)
地理統計分析
def create_geographic_stats(df_map):"""創建地理統計信息"""# 按城市統計region_stats = df_map.groupby('城市').agg({'名稱': 'count', # 景點數量'評分': 'mean', # 平均評分'銷量': 'sum' # 總銷量}).round(2)region_stats.columns = ['景點數量', '平均評分', '總銷量']# 熱門區域分析hot_regions = df_map.groupby('城市')['銷量'].sum()\.sort_values(ascending=False).head(10)return region_stats, hot_regions
?? 文本數據挖掘
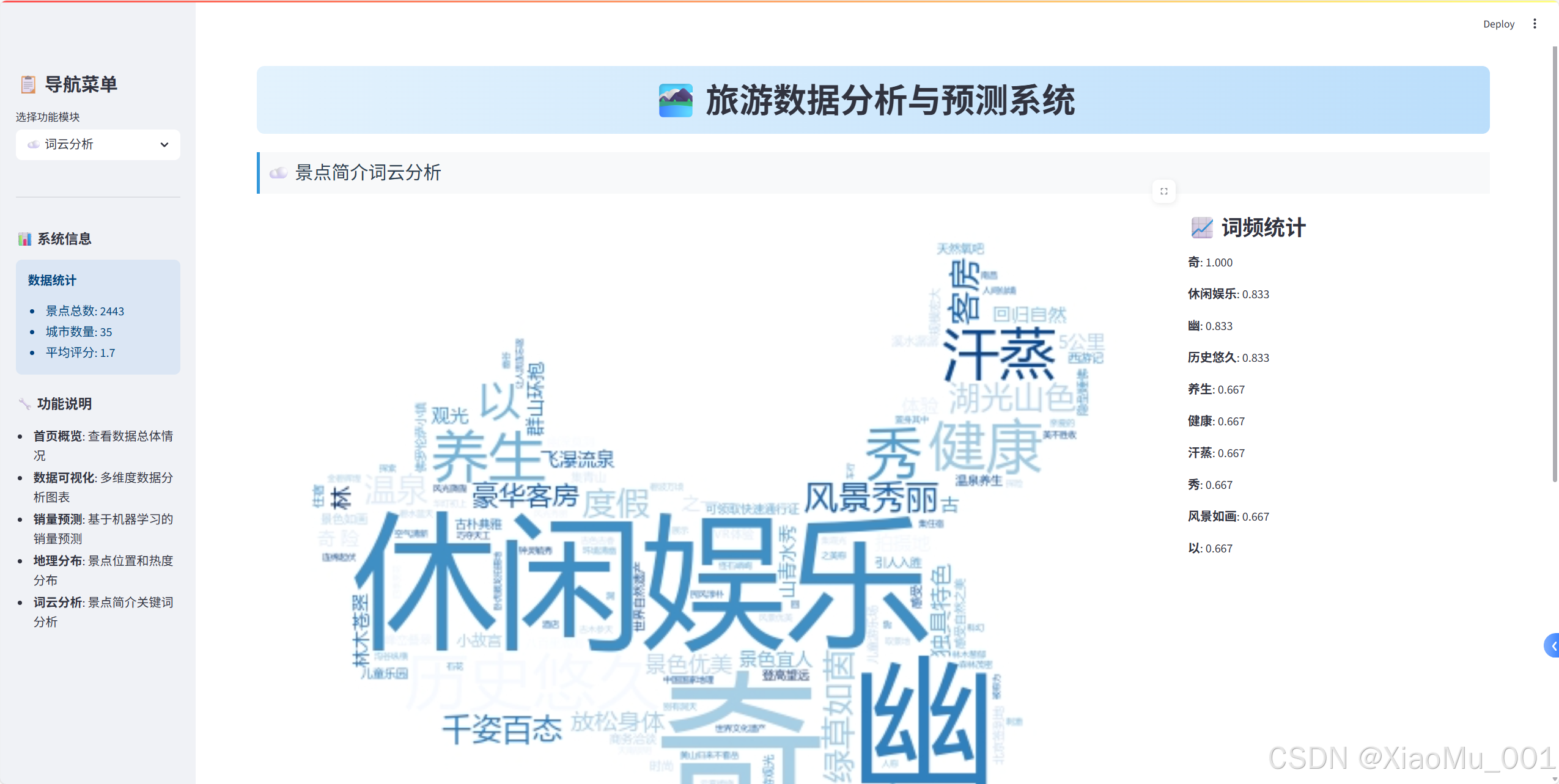
詞云生成實現
1. 文本預處理
def preprocess_text(descriptions):"""文本預處理"""# 合并所有簡介文本text = " ".join(descriptions.dropna().values)# 定義停用詞stopwords = set(["被譽為", "有", "之稱", "和", "是", "的", "在", "為", "一", "名", "景點", "素有", "餐飲", "中國", "世界", "最", "大", "多", "被", "包含", "這", "些", "該", "多個", "此", "風景", "之譽", "在這里", "旅游", "娛樂"])return text, stopwords
2. 詞云參數配置
def create_wordcloud_config(text, stopwords, mask=None):"""創建詞云配置"""config = {'width': 800,'height': 400,'max_words': 200,'max_font_size': 100,'contour_width': 1,'contour_color': 'white','colormap': 'Blues','background_color': 'white','font_path': "C:/Windows/Fonts/msyh.ttc", # 中文字體'stopwords': stopwords}# 添加自定義形狀if mask is not None:config['mask'] = maskreturn config
3. 詞云生成與展示
def generate_and_display_wordcloud():"""生成并顯示詞云"""try:# 加載自定義形狀custom_mask = np.array(Image.open('map_copy.png'))mask_available = Trueexcept:mask_available = Falsest.warning("未找到自定義形狀文件,將使用默認形狀")# 生成詞云wordcloud_params = create_wordcloud_config(text, stopwords, custom_mask if mask_available else None)wordcloud = WordCloud(**wordcloud_params).generate(text)# 雙列布局展示col1, col2 = st.columns([3, 1])with col1:st.image(wordcloud.to_array(), use_container_width=True)with col2:st.subheader("📈 詞頻統計")word_freq = wordcloud.words_top_words = dict(list(word_freq.items())[:10])for word, freq in top_words.items():st.write(f"**{word}**: {freq:.3f}")
替代方案:詞頻統計圖表
def create_word_frequency_chart(text, stopwords):"""創建詞頻統計圖表(WordCloud不可用時的替代方案)"""from collections import Counter# 簡單分詞和過濾words = text.split()filtered_words = [word for word in words if word not in stopwords and len(word) > 1]# 統計詞頻word_counts = Counter(filtered_words).most_common(20)# 創建DataFramewords_df = pd.DataFrame(word_counts, columns=['詞語', '頻次'])# 創建柱狀圖fig = px.bar(words_df, x='詞語', y='頻次',title="關鍵詞頻率統計 TOP20",color='頻次',color_continuous_scale='Blues')fig.update_layout(xaxis_tickangle=-45)return fig, words_df
? 性能優化策略
1. 數據緩存機制
@st.cache_data
def load_data():"""緩存數據加載"""raw_data = pd.read_csv('tourism_raw_data.csv')feature_data = pd.read_csv('tourism_feature_data.csv')return raw_data, feature_data@st.cache_resource
def train_model(feature_data):"""緩存模型訓練"""# 模型訓練代碼# ...return model
緩存策略說明:
@st.cache_data:用于緩存數據加載操作@st.cache_resource:用于緩存資源密集型操作(如模型訓練)- 避免重復計算,顯著提升應用響應速度
2. 條件導入處理
# 優雅處理可選依賴
try:from wordcloud import WordCloudWORDCLOUD_AVAILABLE = True
except ImportError:WORDCLOUD_AVAILABLE = Falsest.warning("WordCloud 庫未安裝,詞云功能將不可用。")
3. 異步加載策略
def lazy_load_components():"""延遲加載組件"""if 'model_trained' not in st.session_state:with st.spinner('正在訓練模型...'):st.session_state.model_trained = train_model(feature_data)return st.session_state.model_trained
🔧 容錯處理與用戶體驗
1. 錯誤處理機制
def safe_execute(func, error_msg="操作失敗"):"""安全執行函數"""try:return func()except Exception as e:st.error(f"{error_msg}: {str(e)}")return None
2. 用戶反饋系統
def show_loading_progress():"""顯示加載進度"""progress_bar = st.progress(0)status_text = st.empty()for i in range(100):progress_bar.progress(i + 1)status_text.text(f'加載中... {i+1}%')time.sleep(0.01)status_text.text('加載完成!')
3. 響應式設計
def create_responsive_layout():"""創建響應式布局"""# 根據屏幕寬度調整列數if st.session_state.get('mobile_view', False):col1, col2 = st.columns(1), st.columns(1)else:col1, col2 = st.columns(2)
📦 部署與配置
1. 依賴管理
# requirements.txt
streamlit
pandas
numpy
plotly
pydeck
matplotlib
scikit-learn
Pillow
wordcloud
collections-extended
2. 啟動腳本
#!/bin/bash
# run_app.sh
echo "啟動旅游數據分析系統..."
streamlit run streamlit_integrated_app.py --server.port 8501
3. Docker部署(可選)
FROM python:3.9-slimWORKDIR /app
COPY requirements.txt .
RUN pip install -r requirements.txtCOPY . .
EXPOSE 8501CMD ["streamlit", "run", "streamlit_integrated_app.py"]
🚀 項目運行指南
環境準備
# 1. 克隆項目
git clone <repository-url>
cd tourism-analysis-system# 2. 安裝依賴
pip install -r requirements.txt# 3. 準備數據文件
# 確保以下文件存在:
# - tourism_raw_data.csv
# - tourism_feature_data.csv
# - map_copy.png (可選)# 4. 啟動應用
streamlit run streamlit_integrated_app.py
使用流程
- 數據概覽:查看整體數據情況
- 可視化分析:深入分析各維度數據
- 銷量預測:選擇景點進行銷量預測
- 地理分析:查看景點地理分布
- 文本挖掘:分析景點描述特征
📊 技術特色與創新點
1. 模塊化設計
- 清晰的功能分離
- 可擴展的架構設計
- 易于維護和升級
2. 用戶體驗優化
- 直觀的導航設計
- 豐富的交互功能
- 美觀的視覺效果
3. 性能優化
- 智能緩存機制
- 異步加載策略
- 資源使用優化
4. 容錯能力
- 優雅的錯誤處理
- 依賴包兼容性處理
- 用戶友好的提示信息
🔮 未來擴展方向
1. 功能擴展
- 添加時間序列分析
- 集成更多ML算法對比
- 支持數據導出功能
- 添加用戶管理系統
2. 技術優化
- 數據庫集成
- 實時數據更新
- 移動端適配優化
- 性能監控系統
3. 業務拓展
- 多數據源集成
- 定制化報告生成
- API接口開發
- 第三方系統集成
💡 經驗總結
技術選型心得
- Streamlit vs Flask/Django:對于數據分析應用,Streamlit的開發效率更高
- Plotly vs Matplotlib:Plotly的交互性更好,用戶體驗更佳
- 緩存策略:合理使用緩存可以顯著提升應用性能
開發最佳實踐
- 模塊化開發:將功能拆分為獨立模塊,便于維護
- 錯誤處理:預見性地處理各種異常情況
- 用戶體驗:始終從用戶角度考慮界面設計
- 性能優化:在開發初期就考慮性能問題
項目管理經驗
- 版本控制:使用Git進行代碼版本管理
- 文檔編寫:詳細的文檔是項目成功的關鍵
- 測試策略:多環境測試確保應用穩定性
- 用戶反饋:及時收集和處理用戶反饋
🎯 總結
本項目成功實現了一個完整的旅游數據分析與預測系統,集成了數據可視化、機器學習預測、地理分析和文本挖掘等多個功能模塊。通過現代化的Web界面設計和優化的用戶體驗,為旅游行業的數據分析提供了一個實用的解決方案。
項目亮點:
- 🏗? 完整的技術棧:從數據處理到模型部署的全流程實現
- 🎨 現代化界面:美觀、直觀、易用的Web界面
- ? 高性能設計:緩存機制和性能優化策略
- 🔧 容錯能力強:完善的錯誤處理和用戶提示
- 📈 實用價值高:真實業務場景的完整解決方案
這個項目不僅展示了Python在數據分析和Web開發方面的強大能力,也為類似的數據分析應用提供了一個很好的參考模板。希望本文的詳細介紹能夠幫助讀者理解現代數據分析應用的開發流程和技術要點。

:面向鏈接預測的知識圖譜表示學習方法綜述)
,規則(Rules))

![前沿重器[74] | 淘寶RecGPT:大模型推薦框架,打破信息繭房](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/前沿重器[74] | 淘寶RecGPT:大模型推薦框架,打破信息繭房)

的崛起——為什么“會寫Prompt”成了新技能?)

)


)







