1. 簡介
在需要輕量級本地持久化的場景中,DataStore 是一個理想的選擇(詳見《Android Jetpack 系列(四)DataStore 全面解析與實踐》)。但當你面臨如下需求時,本地數據庫便顯得尤為重要:
- 復雜的數據模型管理;
- 數據之間存在關聯關系;
- 支持部分字段更新;
- 實現離線緩存與增量更新。
為此,Google 在 Jetpack 架構組件中推出了新一代本地數據庫解決方案:Room。它對原生 SQLite 進行了封裝,提供類型安全、編譯期校驗的數據庫訪問方式,極大簡化了樣板代碼的編寫。
Room 的典型使用場景包括:
- 緩存網絡請求結果,實現離線訪問;
- 管理本地復雜結構化數據;
- 實現高效的增量數據更新及多表關系維護。
主要優勢包括:
- SQL 編譯期校驗:提前發現錯誤,提升穩定性;
- 注解驅動開發:減少冗余代碼;
- 簡化數據遷移:支持版本演進;
- 與 LiveData / Flow 集成:實現響應式 UI 更新。
2. 添加依賴
2.1 添加 Room 依賴項
要在項目中使用 Room,需要在模塊的 build.gradle.kts 或 build.gradle 文件中添加如下依賴項:
dependencies {val room_version = "2.7.2"implementation("androidx.room:room-runtime:$room_version")ksp("androidx.room:room-compiler:$room_version")// Kotlin 擴展與協程支持implementation("androidx.room:room-ktx:$room_version")// 可選 Test helperstestImplementation("androidx.room:room-testing:$room_version")
}
2.2啟用 KSP(Kotlin Symbol Processing)
Room 使用 KSP 編譯時執行注解處理,KSP類似于 kpat,但更高效,特別適合 Kotlin 項目。ksp允許庫開發者創建編譯時代碼生成器,比如自動生成依賴注入代碼、路由代碼、數據庫操作代碼等。
ksp和 kapt 的區別:
| 項目 | ksp | kapt |
| 性能 | 更快、更輕量 | 較慢,尤其在大型項目中 |
| 對 Kotlin 支持 | 原生支持 Kotlin | 本質是處理 Java 注解,Kotlin 兼容性一般 |
| 編譯時間 | 更短 | 更長 |
| 錯誤提示 | 更接近源碼,容易定位問題 | 有時提示不準確 |
下面是啟用 KSP 的方式:
工程級 build.gradle.kts 中添加:
plugins {alias(libs.plugins.android.application) apply falsealias(libs.plugins.kotlin.android) apply falsealias(libs.plugins.kotlin.compose) apply falseid("com.google.devtools.ksp") version "2.0.21-1.0.27" apply false
}
注意?:KSP 的前綴版本需與 Kotlin 版本保持一致。如 Kotlin 版本為 2.0.21,KSP 的版本必須以 2.0.21 開頭。
模塊級 build.gradle.kts 中啟用:
plugins {alias(libs.plugins.android.application)alias(libs.plugins.kotlin.android)alias(libs.plugins.kotlin.compose)id("com.google.devtools.ksp")
}
3. 了解 Room
Room 的架構由三大核心組件構成:
3.1 Entity(實體類)
- 對應數據庫中的一張表;
- 使用 @Entity(tableName = "xxx") 注解聲明;
- 類的每個字段就是表中的一列;
- 至少要有一個主鍵(@PrimaryKey);
- 支持復合主鍵、忽略字段、嵌套對象。
3.2 DAO(數據訪問對象)
- 使用 @Dao 注解聲明;
- 用于定義 SQL 操作(@Query)或封裝常用方法(如 @Insert、@Update、@Delete);
- 支持掛起函數(suspend)、LiveData、Flow 等多種返回類型;
- 可以組合多個操作為一個事務(使用 @Transaction 注解);
- 支持多表查詢與動態SQL構建。
3.3 Database(數據庫類)
- 使用 @Database 注解聲明,并指定 entities、version;
- 必須繼承自 RoomDatabase;
- 是 Room 的核心入口,提供 DAO 實例訪問;
- 建議通過單例或其他線程安全方式創建實現。
三者關系
Room 中,Database 是數據庫的核心入口,負責提供 DAO 實例。而 DAO 提供訪問 Entity 數據的能力。通過 DAO,可以實現對 Entity 對應表的增刪改查操作。如下圖說明了 Room 的不同組件之間的關系。
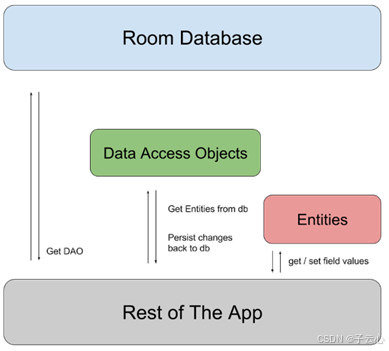
4. 實戰示例
本節將構建一個完整的 Room 使用案例,涉及三個典型數據表:用戶表(User)、商品表(Product)、訂單表(Order)。內容涵蓋了 Entity 注解的多種用法、DAO 接口的定義,以及數據庫的創建與使用。
4.1 數據實體(Entity)
Room 中的實體類(Entity)用于定義數據庫中的數據結構。每個實體類對應數據庫中的一張表,其字段對應表中的列。通過注解即可完成表結構定義,無需手寫 SQL 語句。
用戶表:User
@Entity(tableName = "user",indices = [Index(value = ["username"], unique = true)]
)
data class User(@PrimaryKey(autoGenerate = true)@ColumnInfo(name = "user_id")val userId: Long = 0,val username: String,val password: String,@ColumnInfo(name = "full_name")val fullName: String,@Embedded(prefix = "addr_")val address: Address
) {@Ignoreval isOnline: Boolean = false
}
地址嵌套類:Address
data class Address(val province:String,val city: String,val zipCode: String
)
商品表:Product
@Entity(tableName = "products",indices = [Index(value = ["name"], unique = true)]
)
data class Product(@PrimaryKey(autoGenerate = true)@ColumnInfo(name = "product_id")val productId: Long = 0L,val name: String,val price: Double
)
訂單表:Order
@Entity(tableName = "orders",foreignKeys = [ForeignKey(entity = User::class,parentColumns = ["user_id"],childColumns = ["user_owner_id"],onDelete = ForeignKey.CASCADE),ForeignKey(entity = Product::class,parentColumns = ["product_id"],childColumns = ["product_id"],onDelete = ForeignKey.NO_ACTION)],indices = [Index(value = ["user_owner_id"]),Index(value = ["product_id"])]
)
data class Order(@PrimaryKey(autoGenerate = true)@ColumnInfo(name = "order_id")val orderId: Long = 0L,@ColumnInfo(name = "user_owner_id")val userOwnerId: Long, @ColumnInfo(name = "product_id")val productId: Long, val quantity: Int
)
注意:SQLite 表名和列名稱不區分大小寫。
常用注解說明:
| 注解 | 說明 |
| @Entity | 聲明表結構,可設置表名、索引、外鍵、主鍵等。 |
| tableName 參數表示表名,為空則 Room 將類名稱用作數據庫表名稱 | |
| indices?參數表示為某一個表字段加上索引,其中value表示字段名;unique表示是否唯一。 | |
| ForeignKeys 參數用于聲明多個外鍵。ForeignKey內的參數: entity 參數表示外鍵指向的實體類; parentColumns 參數表示指向實體類的表字段名; childColumns 表示當前表中的字段名; onDelete 表示主表刪除后是否會自動刪除本表的數據,CASCADE 會刪除;NO_ACTION不刪除。 | |
| primaryKeys 參數可設置多個列的組合對實體實例進行唯一標識,也就是通過多個列定義一個復合主鍵。例如: data class User( ??? val firstName: String?, ??? val lastName: String? ) | |
| ignoredColumns 參數用于指定某字段是忽略字段,例如實體繼承了父實體的字段,則通過該參數進行指定。例如: ??? var picture: Bitmap? = null } @Entity(ignoredColumns = ["picture"]) data class RemoteUser( ??? @PrimaryKey val id: Int, ??? val hasVpn: Boolean ) : User() | |
| @ColumnInfo | 映射字段名稱到數據庫列名,name參數為空或者省略該注解,Room 默認使用字段名稱作為數據庫中的列名稱。 |
| @PrimaryKey | 聲明列字段為表主鍵,若autoGenerate參數為true,則表示可自動遞增生成。 |
| @Embedded | 聲明字段為嵌套字段,字段類型對應類內的字段同樣會存儲在數據庫。prefix參數表示為內部字段加上前綴。例如上面User的address字段,它在數據庫實際上是對應三個字段:addr_province、addr_city 和 addr_zipCode。 |
| @Ignore | 聲明字段僅用于類本身,但不會創建數據庫列。 |
4.2 數據訪問對象(DAO)
DAO(Data Access Object)是訪問數據庫的核心接口。Room 會在編譯時自動生成其實現代碼,保障類型安全。
推薦將 DAO 定義為接口(也可為抽象類),并始終使用 @Dao 注解標記。
用戶Dao:UserDao
@Dao
interface UserDao {// 增@Insertfun insertUser(user: User): Long// 增@Insertfun insertUsers(vararg users: User): List<Long>// 增@Insertfun insertBothUsers(user1: User, user2: User)// 增@Insertfun insertUsersAndFriends(user: User, friends: List<User>)// 刪@Deletefun deleteUser(user: User): Int// 刪@Deletefun deleteUsers(vararg users: User) : Int// 改@Updatefun updateUser(user: User): Int// 改@Updatefun updateUsers(vararg users: User) : Int// 更改用戶密碼@Query("UPDATE user SET password = :newPassword WHERE username = :username")fun updatePassword(username: String, newPassword: String): Int// 根據用戶ID查詢用戶@Query("SELECT * FROM user WHERE user_id = :userId")fun getUserByUserId(userId: Long): User?// 無條件查詢所有用戶@Query("SELECT * FROM user")fun getAllUserList(): List<User>// 支持LiveData@Query("SELECT * FROM user")fun getAllUsersLiveData(): LiveData<List<User>>// 支持響應式流@Query("SELECT * FROM user")fun getAllUsersFlow(): Flow<List<User>>// 輸入用戶數組查詢包含的結果@Query("SELECT * FROM user WHERE user_id IN (:userIds)")fun getUsersByUserIds(userIds: IntArray): List<User>// 根據用戶名查詢用戶@Query("SELECT * FROM user WHERE username LIKE :username LIMIT 1")fun getUserByUsername(username: String): User?// 根據全名模糊查找用戶@Query("SELECT * FROM user WHERE full_name LIKE '%' || :fullName || '%'")fun findUsersByFullName(fullName: String): List<User>// 強制插入用戶,通過事務方式先刪除再插入新的@Transactionfun forceInstallUser(user: User): Long {val newUser = getUserByUsername(user.username)newUser?.let {val result = deleteUser(it)if (result > 0) {val userId = insertUser(user)return userId}}return 0}
}
商品Dao:ProductDao
@Dao
interface ProductDao {// 若已存在則替換@Insert(onConflict = OnConflictStrategy.REPLACE)fun insert(product: Product): Long@Query("SELECT * FROM products WHERE name LIKE :name LIMIT 1")fun getProduct(name: String): Product@Query("SELECT * FROM products")fun getAllProducts(): List<Product>
}
訂單Dao:OrderDao
@Dao
interface OrderDao {@Insertfun insert(order: Order): Long@Query("SELECT * FROM orders WHERE user_owner_id = :userId")fun getOrdersByUser(userId: Long): List<Order>@Query("SELECT * FROM user JOIN orders ON user.user_id = orders.user_owner_id")fun loadUserAndOrders(): Map<User, List<Order>>
}
Dao注解說明:
| 注解 | 說明 |
| @Dao | 聲明針于數據表的增刪改查操作。 |
| @Insert | 插入數據方法,onConflict 參數可設置若新增數據主鍵或索引存在沖突時的處理方法:REPLACE 替換;ABORT 中止;IGNORE 忽略。 |
| @Delete | 刪除數據方法 |
| @Update | 更新數據方法 |
| @Query | 根據SQL語句執行操作的方法,大多情況下用于查詢單表或聯表數據,也可以用于更復雜的刪除、更新或插入數據操作。 |
| 用于查詢返回多個結果時,還可以配合LiveData或Flow 返回。 | |
| 注意:Room 會在編譯時驗證 SQL 查詢。這意味著,如果查詢出現問題,則會出現編譯錯誤,而不是運行時失敗。 | |
| @Transaction | 標記方法在數據庫中作為一個事務執行,方法中所有的數據庫操作要么全部成功執行并提交,要么在中途出錯時全部回滾,以保障數據一致性。 |
4.3 數據庫類:AppDatabase
數據庫類需繼承自 RoomDatabase,并使用 @Database 注解指定實體類與版本。
@Database(entities = [User::class, Product::class, Order::class], version = 1)
abstract class AppDatabase : RoomDatabase() {abstract fun userDao(): UserDaoabstract fun productDao(): ProductDaoabstract fun orderDao(): OrderDaocompanion object {@Volatileprivate var INSTANCE: AppDatabase? = nullfun getInstance(context: Context): AppDatabase {return INSTANCE ?: synchronized(this) {INSTANCE ?: Room.databaseBuilder(context.applicationContext, AppDatabase::class.java, "app_database").build().also { INSTANCE = it }}}}
}
數據庫類必須滿足以下條件:
- 該類必須帶有?@Database?注解,該注解包含列出所有與數據庫關聯的數據實體的?entities?數組。
- 該類必須是一個抽象類,用于擴展?RoomDatabase。
- 對于與數據庫關聯的每個 DAO 類,數據庫類必須定義返回其實例的抽象方法。
注解說明:
| 注解 | 說明 |
| @Database | 聲明數據庫。 |
| entities 參數用于聲明數據庫中的表。 | |
| version 參數用于聲明數據庫版本。 |
注意:
Room 實例化成本較高,建議采用單例模式避免重復創建。
多進程支持:
如需支持多進程訪問數據庫,請調用 .enableMultiInstanceInvalidation()。這樣每個進程中都有一個?AppDatabase?實例,可以在一個進程中使共享數據庫文件失效,并且這種失效會自動傳播到其他進程中?AppDatabase?的實例。
Room.databaseBuilder(context.applicationContext, AppDatabase::class.java, "app_database").enableMultiInstanceInvalidation().build()數據庫文件說明:
databaseBuilder方法中name 參數指定數據庫文件名,數據庫文件默認保存在 app 私有目錄的 databases/ 子目錄下,完整路徑如下:
/data/data/<應用包名>/databases/<數據庫名>.db
如果你想將數據庫放在自定義路徑,可以使用:
Room.databaseBuilder(context,AppDatabase::class.java,File(context.filesDir, "custom/path/app_database").absolutePath
)
可以通過以下方式獲取數據庫文件的絕對路徑:
val dbFile: File = context.getDatabasePath("app_database")
Log.d(TAG, "數據庫路徑為:${dbFile.absolutePath}")
如果你在測試或調試中想確認數據庫是否存在,可以這樣判斷:
if (dbFile.exists()) {Log.d(TAG, "數據庫已存在")
} else {Log.d(TAG, "數據庫尚未創建")
}
注意:
只有在你第一次訪問數據庫(如調用 db.userDao().getAll())或顯式觸發數據庫操作后,數據庫文件才會真正創建。
4.4 調用示例
suspend fun test(context: Context) = withContext(Dispatchers.IO) {val db = AppDatabase.getInstance(context)val dbFile: File = context.getDatabasePath("app_database")Log.d(TAG, "數據庫路徑為:${dbFile.absolutePath}")if (dbFile.exists()) {Log.d(TAG, "數據庫已存在")} else {Log.d(TAG, "數據庫尚未創建")}// 插入用戶val user = User(username = "zyx",password = "123456",fullName = "子云心",address = Address("廣東省", "廣州市", "510000"))val userId = db.userDao().insertUser(user)Log.d(TAG, "insert result, userId: $userId")if (dbFile.exists()) {Log.d("DB_PATH", "數據庫已存在")} else {Log.d("DB_PATH", "數據庫尚未創建")}// 更新全名val updatedUser = user.copy(userId = userId, fullName = "馬戶")val updateUserNumber = db.userDao().updateUser(updatedUser)Log.d(TAG, "update user result, number: $updateUserNumber")// 更改用戶密碼val updatePasswordResult = db.userDao().updatePassword("zyx", "9527")Log.d(TAG, "update password result, number: $updatePasswordResult")// 根據用戶名查詢用戶val userResult = db.userDao().getUserByUsername("zyx")Log.d(TAG, "getUserByUsername result: $userResult")// 根據全名模糊查找用戶val usersResult = db.userDao().findUsersByFullName("馬")Log.d(TAG, "getUsersByFullName result: $usersResult")// 無條件查詢所有用戶val usersList = db.userDao().getAllUserList()Log.d(TAG, "getAllUserList result: $usersList")
}
注意:
Room 所有數據庫操作必須在主線程之外執行,例如使用 Dispatchers.IO。
5. Room 的進階使用
5.1 類型轉換(TypeConverter)
Room 支持的字段類型是有限的,比如:
- 不支持直接存儲 Date、List、Map、Enum 等類型;
- 如果你的實體類中包含這些類型的字段,就會報錯。
此時,可以使用 @TypeConverter 注解來自定義轉換邏輯,讓 Room 知道如何將這些類型轉換為數據庫支持的類型進行存儲和讀取。
以 User 實體為例,我們為其新增一個 Date 類型的 birthday 字段:
@Entity(tableName = "user",indices = [Index(value = ["username"], unique = true)]
)
data class User(@PrimaryKey(autoGenerate = true)@ColumnInfo(name = "user_id")val userId: Long = 0,val username: String,val password: String,@ColumnInfo(name = "full_name")val fullName: String,@Embedded(prefix = "addr_")val address: Address,val birthday: Date
) {@Ignoreval isOnline: Boolean = false
}
創建類型轉換器:
class Converters {@TypeConverterfun fromTimestamp(value: Long?): Date? {return value?.let { Date(it) }}@TypeConverterfun dateToTimestamp(date: Date?): Long? {return date?.time}
}
然后在數據庫類中注冊該轉換器:
@TypeConverters(Converters::class)
@Database(entities = [User::class, Product::class, Order::class], version = 1)
abstract class AppDatabase : RoomDatabase() {abstract fun userDao(): UserDaoabstract fun productDao(): ProductDaoabstract fun orderDao(): OrderDaocompanion object {@Volatileprivate var INSTANCE: AppDatabase? = nullfun getInstance(context: Context): AppDatabase {return INSTANCE ?: synchronized(this) {INSTANCE ?: Room.databaseBuilder(context.applicationContext, AppDatabase::class.java, "app_database").build().also { INSTANCE = it }}}}
}
這樣,Room 會自動將 Date 類型轉換為 Long 存儲到數據庫中,再反向轉換回來,整個過程無需手動干預。
同理:支持 List<String> 類型
Room 同樣不支持直接存儲集合類型,如 List<String>。可以將其序列化為逗號拼接的字符串:
@TypeConverter
fun fromString(value: String): List<String> {return if (value.isEmpty()) emptyList() else value.split(",")
}@TypeConverter
fun fromList(list: List<String>): String {return list.joinToString(",")
}
5.2 數據庫版本升級(Migration)
在上一節中我們為 User 表新增了 birthday 字段,運行時會遇到如下異常:
java.lang.IllegalStateException: Room cannot verify the data integrity. Looks like you've changed schema but forgot to update the version number. You can simply fix this by increasing the version number. Expected identity hash: xxx, found: xxx
這是因為修改了數據庫結構但未更新版本號。更新版本后如果未提供遷移邏輯,又會出現:
java.lang.IllegalStateException: A migration from 1 to 2 was required but not found. Please provide the necessary Migration path via RoomDatabase.Builder.addMigration(...) or allow for destructive migrations via one of the RoomDatabase.Builder.fallbackToDestructiveMigration* functions.
這個錯誤說明 Room 發現版本變化但無法找到遷移路徑。
5.2.1 推薦方案:添加 Migration(數據保留)
定義版本 1 → 2 的遷移邏輯:
val MIGRATION_1_2 = object : Migration(1, 2) {override fun migrate(db: SupportSQLiteDatabase) {db.execSQL("ALTER TABLE user ADD COLUMN birthday INTEGER DEFAULT 0 NOT NULL")}
}
使用addMigrations注冊遷移:
Room.databaseBuilder(context.applicationContext, AppDatabase::class.java, "app_database").addMigrations(MIGRATION_1_2).build()
注意:
- ALTER TABLE 僅支持新增字段,但不支持刪除或修改字段類型。
- 如需修改列或結構,需要手動新建臨時表轉存數據,關于 SQL 語句的相關知識,這里就不作過多演示。
- 一般情況下已發布版本的數據庫,盡量不進行修改結構和刪除字段。
5.2.2 替換方案:破壞性遷移(開發期可用,數據會被清除)
使用 fallbackToDestructiveMigration 設置破壞遷移:
Room.databaseBuilder(context, AppDatabase::class.java, "app_database").fallbackToDestructiveMigration(true) // 每次版本變動就清空舊庫重建.build()
注意:
此方式會清空舊數據并重建數據庫,不推薦在正式環境使用。
5.3 多表聯查
5.3.1 使用 SQL JOIN(靈活強大)
定義結果數據類:
data class OrderInfo(val orderId: Long,val quantity: Int,val username: String,val fullName: String,val productName: String,val productPrice: Double
)
在 OrderDao 中書寫 JOIN 查詢語句:
@Dao
interface OrderDao {// ……@Query("""SELECT o.order_id AS orderId,o.quantity AS quantity,u.username AS username,u.full_name AS fullName,p.name AS productName,p.price AS productPriceFROM orders oINNER JOIN user u ON o.user_owner_id = u.user_idINNER JOIN products p ON o.product_id = p.product_id""")fun getOrderInfoList(): List<OrderInfo>
}
優點:靈活、可控、支持復雜篩選。
缺點:字段映射需手動維護,代碼稍顯冗長。
5.3.2 使用 @Relation(結構清晰)
定義嵌套數據類:
data class OrderDetail(@Embedded val order: Order,@Relation(parentColumn = "user_owner_id",entityColumn = "user_id")val user: User,@Relation(parentColumn = "product_id",entityColumn = "product_id")val product: Product
)
說明:
- @Relation 會自動根據外鍵字段將 User 和 Product 加載進來;
- @Embedded val order: Order 是基礎訂單表本身。
在 OrderDao 中添加查詢方法:
@Dao
interface OrderDao {//……@Query("SELECT * FROM orders")fun getOrderDetailList(): List<OrderDetail>
}
優點:類型安全、自動加載。
缺點:不支持復雜過濾或自定義字段,性能略低于原生 JOIN。
5.4數據庫加密
5.4.1 使用SQLCipher
如果你存儲在本地的數據較為敏感,不希望數據庫文件被導出后被 SQLite工具直接打開,可以集成 SQLCipher 版本的 Room,實現數據庫加密。
添加依賴:
dependencies {// ……implementation ("net.zetetic:android-database-sqlcipher:4.5.4")
}
創建加密數據庫:
import net.sqlcipher.database.SQLiteDatabase
import net.sqlcipher.database.SupportFactoryval passphrase: ByteArray = SQLiteDatabase.getBytes("your-secure-password".toCharArray())
val factory = SupportFactory(passphrase)Room.databaseBuilder(context.applicationContext, AppDatabase::class.java, "app_database").openHelperFactory(factory) // 使用加密支持工廠.build()
注意:
- 密碼必須妥善保管,否則數據無法恢復。
- 性能相較未加密數據庫略有下降,但一般可接受。
5.4.2 使用 Android Keystore 管理密碼
在上述示例中,雖然使用了SQLCipher對數據庫文件進行了加密,但是密碼明文定義在代碼中,這樣會被攻擊者通過反編譯代碼從而獲取密碼,加密的動作就變得形同虛設。一般希望對本地數據加密保護時,會將密碼通過 Android Keystore動態生成和存儲。
Keystore 是 Android 系統提供的一套安全機制,用于在設備上安全地生成、存儲和使用加密密鑰,而不讓應用本身直接接觸密鑰的原始內容。這有助于防止密鑰被反編譯、提取或泄露。
創建 Keystore 加密解密輔助類:
object KeystoreHelper {private const val KEY_ALIAS = "my_db_key_alias"private const val ANDROID_KEYSTORE = "AndroidKeyStore"private const val TRANSFORMATION = "AES/GCM/NoPadding"fun encrypt(plainText: String): Pair<String, String> {generateSecretKeyIfNeeded()val cipher = Cipher.getInstance(TRANSFORMATION)cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, getSecretKey())val iv = cipher.ivval encrypted = cipher.doFinal(plainText.toByteArray())return Base64.encodeToString(encrypted, Base64.NO_WRAP) to Base64.encodeToString(iv, Base64.NO_WRAP)}fun decrypt(encryptedBase64: String, ivBase64: String): String {val encrypted = Base64.decode(encryptedBase64, Base64.NO_WRAP)val iv = Base64.decode(ivBase64, Base64.NO_WRAP)val cipher = Cipher.getInstance(TRANSFORMATION)val spec = GCMParameterSpec(128, iv)cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, getSecretKey(), spec)return String(cipher.doFinal(encrypted))}private fun generateSecretKeyIfNeeded() {val keyStore = KeyStore.getInstance(ANDROID_KEYSTORE).apply { load(null) }if (!keyStore.containsAlias(KEY_ALIAS)) {val keyGen = KeyGenerator.getInstance(KeyProperties.KEY_ALGORITHM_AES, ANDROID_KEYSTORE)val parameterSpec = KeyGenParameterSpec.Builder(KEY_ALIAS, KeyProperties.PURPOSE_ENCRYPT or KeyProperties.PURPOSE_DECRYPT).setBlockModes(KeyProperties.BLOCK_MODE_GCM).setEncryptionPaddings(KeyProperties.ENCRYPTION_PADDING_NONE).build()keyGen.init(parameterSpec)keyGen.generateKey()}}private fun getSecretKey(): SecretKey {val keyStore = KeyStore.getInstance(ANDROID_KEYSTORE).apply { load(null) }return keyStore.getKey(KEY_ALIAS, null) as SecretKey}
}
定義獲取密碼方法:
fun getDatabasePassword(context: Context): String {val prefs: SharedPreferences = context.getSharedPreferences("secure_prefs", Context.MODE_PRIVATE)// 獲取上次生成的 encrypted 和 ivval encrypted = prefs.getString("encrypted", null)val iv = prefs.getString("iv", null)if (encrypted != null && iv != null) {// 解密出密碼return KeystoreHelper.decrypt(encrypted, iv)}// 生成隨機密碼val password = UUID.randomUUID().toString()// 加密密碼獲取 encrypted 和 ivval (newEncrypted, newIv) = KeystoreHelper.encrypt(password)// 保存 encrypted 和 ivprefs.edit { putString("encrypted", newEncrypted).putString("iv", newIv) }return password
}
替換明文密碼創建加密數據庫:
import net.sqlcipher.database.SQLiteDatabase
import net.sqlcipher.database.SupportFactoryval password = getDatabasePassword(context)
val passphrase: ByteArray = SQLiteDatabase.getBytes(password.toCharArray())
val factory = SupportFactory(passphrase)Room.databaseBuilder(context.applicationContext, AppDatabase::class.java, "app_database").openHelperFactory(factory) // 使用加密支持工廠.build()
Keystore 的優勢:
- 密鑰保護:密鑰被存儲在專用的硬件或系統區域中(如 TEE 或 StrongBox),不暴露給應用層。
- 受限使用:密鑰只能通過特定操作使用,不能直接導出,避免明文或反編譯暴露。
- 生命周期控制:可以設置使用限制,比如只允許解鎖設備時使用、綁定到生物識別認證、設定失效時間等。
- 綁定安全環境:即使 APK 被反編譯,也無法還原出 Keystore 中的密鑰。因為 Keystore 里的密鑰是綁定到包名 + 簽名 + 用戶空間的,如上述示例,就算通過ROOT手機后導出 SharedPreferences,獲取到 encrypted 和 iv并且反編譯后看到KeystoreHelper.decrypt() 的代碼邏輯,在別的設備上也會解密失敗。或者就算同樣的設備同樣的APK反編譯后重打包,因為簽名不一樣,無會解失敗。
6. 總結
Room 作為 Jetpack 架構組件中本地數據庫解決方案,擁有良好的類型安全、編譯時校驗與響應式擴展能力。
- 推薦搭配 Paging、WorkManager 等組件構建現代 Android 應用架構;
- 對于需要結構化緩存、本地持久化、關系數據管理等場景尤其適合;
- 實際開發中應重視數據庫升級策略與數據安全保護。
更多詳細的 Room 介紹,請訪問?Android 開發者官網。





)



:冒泡排序、快速排序)







 加權稀疏迭代最近點算法(matlab版))

