官方鏈接
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Aa_FAA3v22g&t=1s
Task1 Putting It All Together 將所有內容整合在一起
圖片版

文字版
Putting It All Together
將所有內容整合在一起
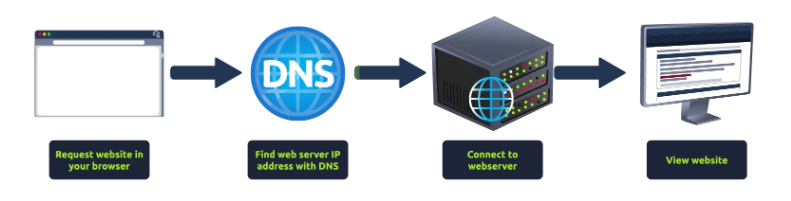
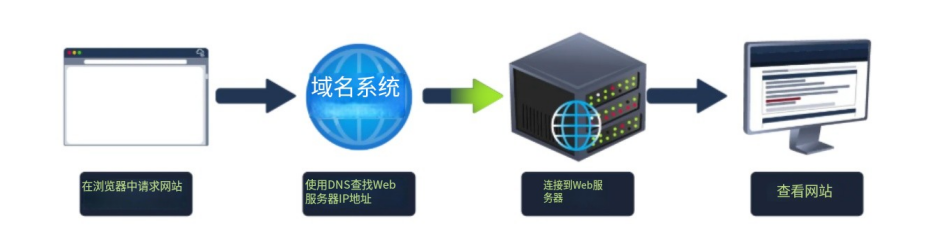
From the previous modules, you'll have learned that quite a lot of things go on behind the scenes when you request a webpage in your browser.
從前面的模塊中,你應該已經了解到,當你在瀏覽器中請求網頁時,背后會發生很多事情。
To summarise, when you request a website, your computer needs to know the server's IP address it needs to talk to; for this, it uses DNS. Your computer then talks to the web server using a special set of commands called the HTTP protocol; the webserver then returns HTML, JavaScript, CSS, Images, etc., which your browser then uses to correctly format and display the website to you.
總結一下,當你請求一個網站時,你的計算機需要知道它需要與之通信的服務器的 IP 地址;為此,它使用 DNS。然后,你的計算機使用一組特殊的命令 (稱為 HTTP 協議) 與 Web 服務器通信;Web 服務器隨后返回 HTML、JavaScript、CSS、圖像等,你的瀏覽器隨后使用這些命令正確地格式化并向你顯示網站。
There are also a few other components that help the web run more efficiently and provide extra features.
還有一些其他組件可以幫助 Web 更高效地運行,并提供額外的功能。
問題
答案
點擊一下就行
Task2 Other Components 其他組件
圖片版

文字版
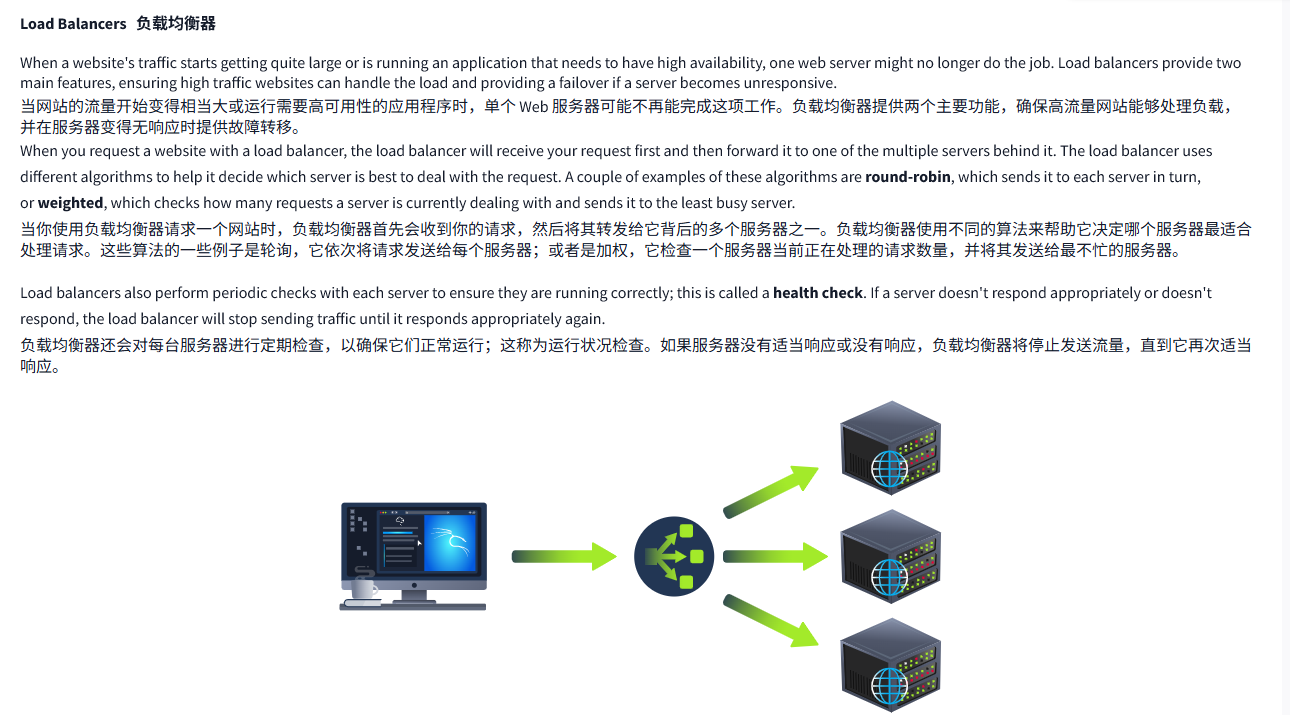
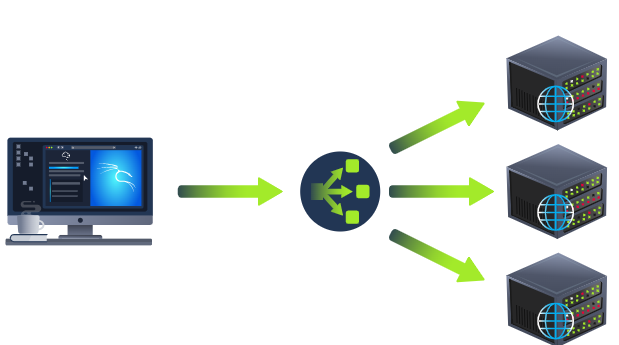
Load Balancers負載均衡器
When a website's traffic starts getting quite large or is running an application that needs to have high availability, one web server might no longer do the job. Load balancers provide two main features, ensuring high traffic websites can handle the load and providing a failover if a server becomes unresponsive.
當網站的流量開始變得相當大或運行需要高可用性的應用程序時,單個 Web 服務器可能不再能完成這項工作。負載均衡器提供兩個主要功能,確保高流量網站能夠處理負載,并在服務器變得無響應時提供故障轉移。
When you request a website with a load balancer, the load balancer will receive your request first and then forward it to one of the multiple servers behind it. The load balancer uses different algorithms to help it decide which server is best to deal with the request. A couple of examples of these algorithms are round-robin, which sends it to each server in turn, or weighted, which checks how many requests a server is currently dealing with and sends it to the least busy server.
當你使用負載均衡器請求一個網站時,負載均衡器首先會收到你的請求,然后將其轉發給它背后的多個服務器之一。負載均衡器使用不同的算法來幫助它決定哪個服務器最適合處理請求。這些算法的一些例子是輪詢,它依次將請求發送給每個服務器;或者是加權,它檢查一個服務器當前正在處理的請求數量,并將其發送給最不忙的服務器。
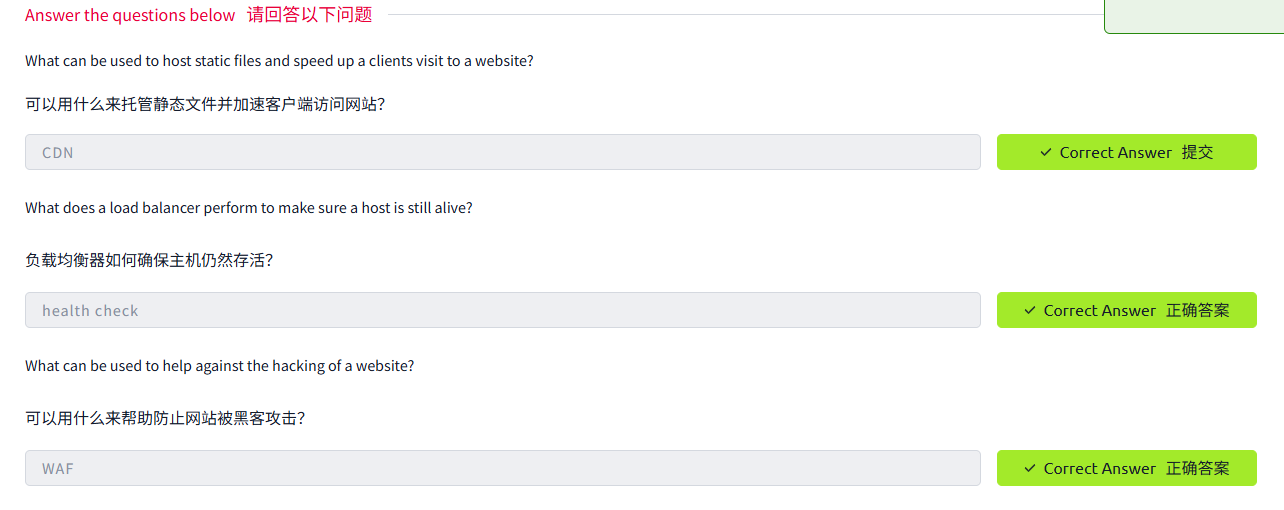
Load balancers also perform periodic checks with each server to ensure they are running correctly; this is called a health check. If a server doesn't respond appropriately or doesn't respond, the load balancer will stop sending traffic until it responds appropriately again.
負載均衡器還會對每臺服務器進行定期檢查,以確保它們正常運行;這稱為運行狀況檢查。如果服務器沒有適當響應或沒有響應,負載均衡器將停止發送流量,直到它再次適當響應。
?
CDN (Content Delivery Networks)CDN (內容分發網絡)
A CDN can be an excellent resource for cutting down traffic to a busy website. It allows you to host static files from your website, such as JavaScript, CSS, Images, Videos, and host them across thousands of servers all over the world. When a user requests one of the hosted files, the CDN works out where the nearest server is physically located and sends the request there instead of potentially the other side of the world.
CDN 可以是減少繁忙網站流量的絕佳資源。它允許你托管網站的靜態文件,如 JavaScript、CSS、圖像、視頻,并將它們托管在全球數千臺服務器上。當用戶請求其中一個托管文件時,CDN 會計算出最近的服務器的物理位置,并將請求發送到那里,而不是潛在的世界另一端。
Databases
數據庫
Often websites will need a way of storing information for their users. Webservers can communicate with databases to store and recall data from them. Databases can range from just a simple plain text file up to complex clusters of multiple servers providing speed and resilience. You'll come across some common databases: MySQL, MSSQL, MongoDB, Postgres, and more; each has its specific features.
網站通常需要一種為用戶存儲信息的方式。Web 服務器可以與數據庫通信,以存儲和調用數據。數據庫可以從簡單的純文本文件到復雜的多個服務器集群,提供速度和彈性。你會遇到一些常見的數據庫:MySQL、MSSQL、MongoDB、Postgres 等,每個都有其獨特的特性。
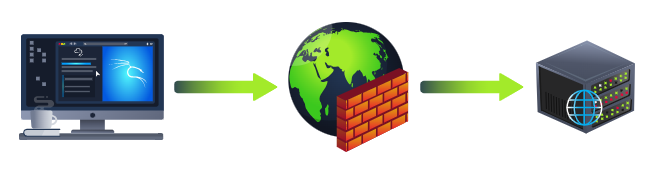
WAF (Web Application Firewall)WAF (Web 應用層防火墻)
A WAF sits between your web request and the web server; its primary purpose is to protect the webserver from hacking or denial of service attacks. It analyses the web requests for common attack techniques, whether the request is from a real browser rather than a bot. It also checks if an excessive amount of web requests are being sent by utilising something called rate limiting, which will only allow a certain amount of requests from an IP per second. If a request is deemed a potential attack, it will be dropped and never sent to the webserver.
WAF 位于你的 Web 請求和 Web 服務器之間;它的主要目的是保護 Web 服務器免受黑客攻擊或拒絕服務攻擊。它分析 Web 請求以了解常見的攻擊技術,包括請求是否來自真實瀏覽器而非機器人。它還會檢查是否使用所謂的速率限制來發送過多的 Web 請求,這種限制每秒只允許來自一定數量的 IP 的請求。如果一個請求被認為是潛在的攻擊,它將被丟棄,并且永遠不會發送到 Web 服務器。
問題
答案
Task3 How Web Servers WorkWeb 服務器如何工作
圖片版



文字版
How Web servers work.Web 服務器是如何工作的。
What is a Web Server?
什么是 Web 服務器?
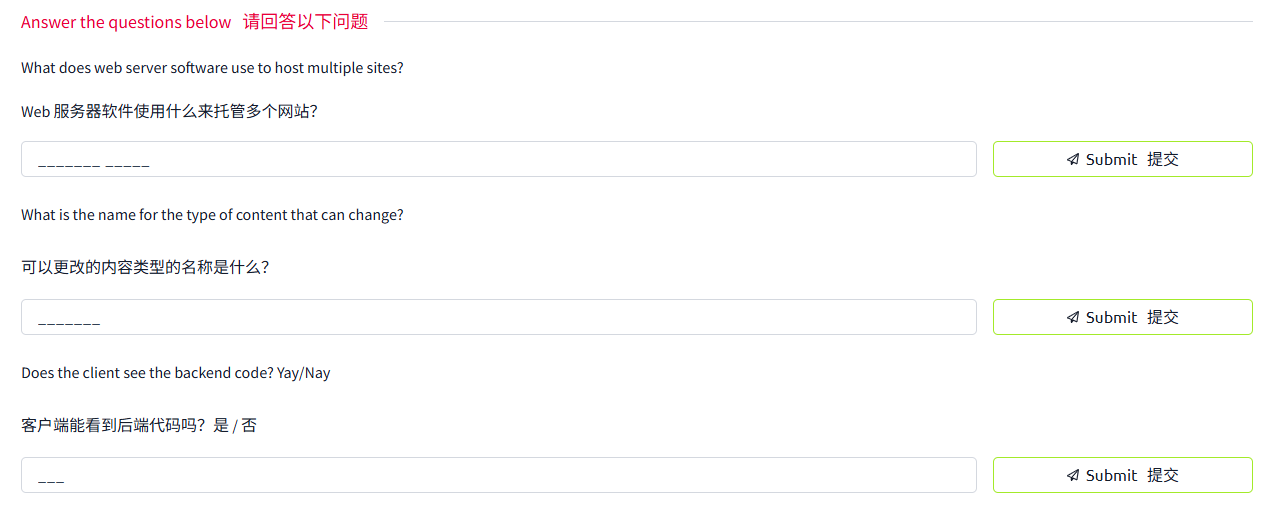
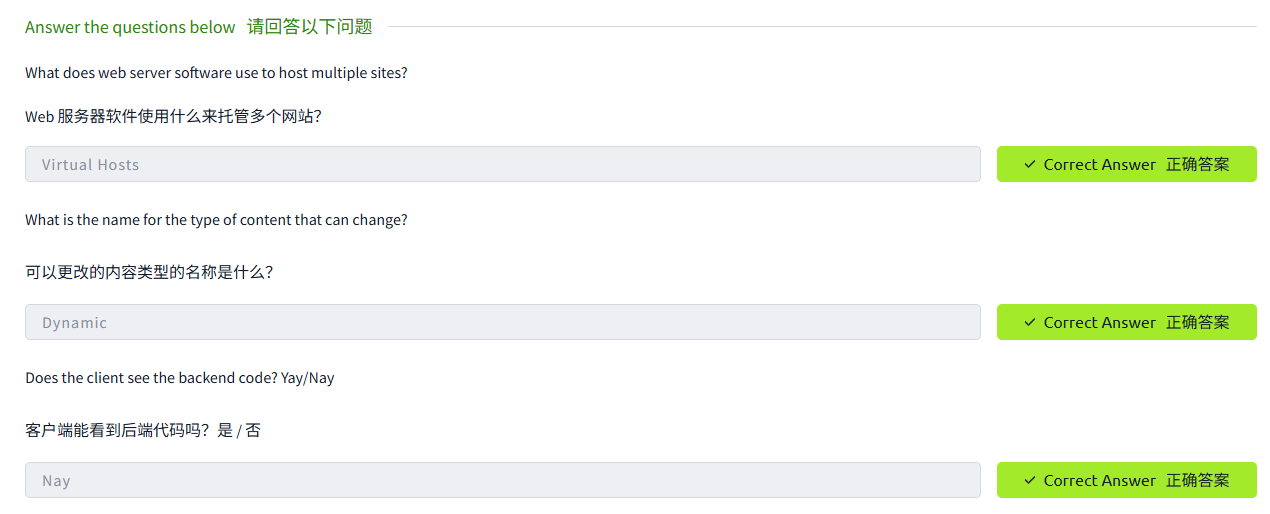
A web server is a software that listens for incoming connections and then utilises the HTTP protocol to deliver web content to its clients. The most common web server software you'll come across is Apache, Nginx, IIS and NodeJS. A Web server delivers files from what's called its root directory, which is defined in the software settings. For example, Nginx and Apache share the same default location of /var/www/html in Linux operating systems, and IIS uses C:\inetpub\wwwroot for the Windows operating systems. So, for example, if you requested the file http://www.example.com/picture.jpg, it would send the file /var/www/html/picture.jpg from its local hard drive.
Web 服務器是一種軟件,它會監聽傳入的連接,然后使用 HTTP 協議將 Web 內容傳遞給客戶端。你會遇到的最常見的 Web 服務器軟件是 Apache、Nginx、IIS 和 NodeJS。Web 服務器從其根目錄 (root directory) 傳遞文件,該目錄在軟件設置中定義。例如,Nginx 和 Apache 在 Linux 操作系統中共享相同的默認位置 /var/www/html, 而 IIS 在 Windows 操作系統中使用 C:inetpubwwwroot。因此,例如,如果你請求文件 http://www.example.com/picture.jpg, 它會從其本地硬盤驅動器發送文件 /var/www/html/picture.jpg。
Virtual Hosts虛擬主機
Web servers can host multiple websites with different domain names; to achieve this, they use virtual hosts. The web server software checks the hostname being requested from the HTTP headers and matches that against its virtual hosts (virtual hosts are just text-based configuration files). If it finds a match, the correct website will be provided. If no match is found, the default website will be provided instead.
Web 服務器可以托管具有不同域名的多個網站;為了實現這一點,它們使用虛擬主機。Web 服務器軟件會檢查 HTTP 首部請求的主機名,并將其與其虛擬主機進行匹配 (虛擬主機只是基于文本的配置文件)。如果找到匹配,就會提供正確的網站。如果沒有找到匹配,就會提供默認網站。
Virtual Hosts can have their root directory mapped to different locations on the hard drive. For example, one.com being mapped to /var/www/website_one, and two.com being mapped to /var/www/website_two
虛擬主機可以將其根目錄映射到硬盤驅動器上的不同位置。例如,one.com 映射到 /var/www/website_one,two.com 映射到 /var/www/web site_two。
There's no limit to the number of different websites you can host on a web server.
你可以在一個 Web 服務器上托管的不同網站數量沒有限制。
Static Vs Dynamic Content靜態內容與動態內容
Static content, as the name suggests, is content that never changes. Common examples of this are pictures, javascript, CSS, etc., but can also include HTML that never changes. Furthermore, these are files that are directly served from the webserver with no changes made to them.
靜態內容,顧名思義,是永遠不變的內容。常見的例子包括圖片、javascript、CSS 等,但也可以包括永遠不變的 HTML。此外,這些文件是直接從 Web 服務器提供的,不需要對其進行任何修改。
Dynamic content, on the other hand, is content that could change with different requests. Take, for example, a blog. On the homepage of the blog, it will show you the latest entries. If a new entry is created, the home page is then updated with the latest entry, or a second example might be a search page on a blog. Depending on what word you search, different results will be displayed.
另一方面,動態內容是指可能隨著不同請求而變化的內容。以一個博客為例。在博客的主頁上,它會顯示最新條目。如果創建了一個新條目,主頁就會更新為最新條目,或者第二個例子可能是博客的搜索頁面。根據你搜索的詞,將顯示不同的結果。
These changes to what you end up seeing are done in what is called the Backend with the use of programming and scripting languages. It's called the Backend because what is being done is all done behind the scenes. You can't view the websites' HTML source and see what's happening in the Backend, while the HTML is the result of the processing from the Backend. Everything you see in your browser is called the Frontend.
這些對你最終看到的內容的修改是在所謂的后端中使用編程和腳本語言完成的。它之所以被稱為后端,是因為所有正在進行的操作都是在幕后進行的。你無法查看網站的 HTML 源代碼,也無法看到后端中發生的事情,而 HTML 是后端處理的結果。你在瀏覽器中看到的所有內容都被稱為前端。
Scripting and Backend Languages腳本語言和后端語言
There's not much of a limit to what a backend language can achieve, and these are what make a website interactive to the user. Some examples of these languages (in no particular order :p) are
后端語言可以實現的功能并沒有太多限制,這些是使網站與用戶交互的因素。這些語言的一些例子 (不按特定順序:p) 如下:PHP, Python, Ruby, NodeJS, Perl and many more. These languages can interact with databases, call external services, process data from the user, and so much more. A very basic
、Python、Ruby、NodeJS、Perl 等。這些語言可以與數據庫交互、調用外部服務、處理用戶數據等。一個非常基本的PHP example of this would be if you requested the website
例如,如果你請求網站http://example.com/index.php?name=adamHttp://example.com/index.php?name=adam
If index.php was built like this:
如果 index.php 是這樣構建的:
<html><body>Hello <?php echo $_GET["name"]; ?></body></html>
It would output the following to the client:
它會向客戶端輸出以下內容:
<html><body>Hello adam</body></html>
You'll notice that the client doesn't see any PHP code because it's on the Backend. This interactivity opens up a lot more security issues for web applications that haven't been created securely, as you learn in further modules.
你會注意到,客戶端看不到任何 PHP 代碼,因為它位于后端。這種交互性為那些尚未安全創建的 Web 應用程序帶來了更多安全問題,你將在后續模塊中學習。
問題
答案
Task4 Quiz 小測驗
圖片版
文字版
The Quiz
小測驗
Click the "View Site" button on the right. Using everything you've learnt from the other modules, drag and drop the tiles into the correct order of how a request to a website works to reveal the flag.
點擊右側的 “查看網站” 按鈕。使用您從其他模塊中學到的所有知識,按照向網站發出請求以顯示標志的正確順序拖放磁貼。
Note: When placing a tile in the correct position, it will highlight in green. When a tile is in the wrong spot, it will highlight in red. Make sure not to refresh the page, as it will reset the tiles all to blank again!
注意:當將方塊放置在正確位置時,它將以綠色突出顯示。當方塊放置錯誤位置時,它將以紅色突出顯示。請確保不要刷新頁面,因為它會將所有方塊重置為空白!
問題
答案

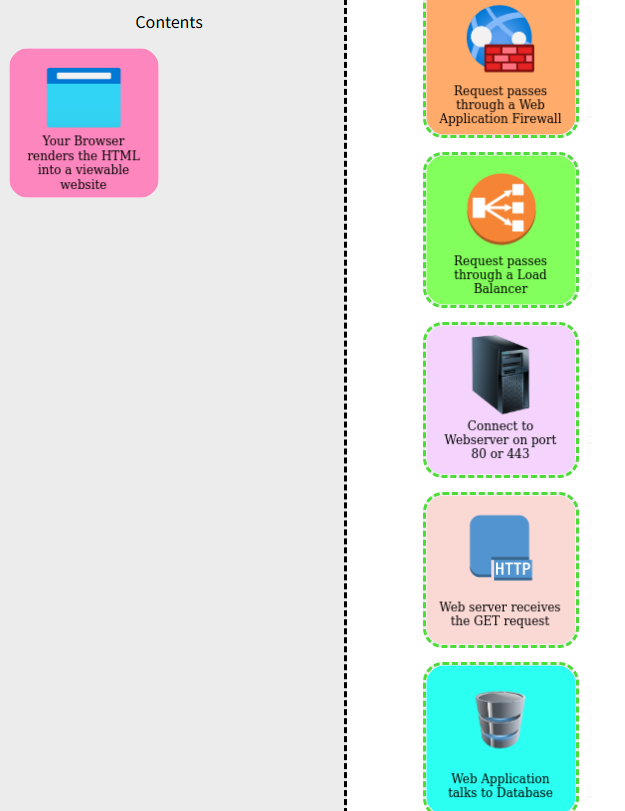
理解
所以訪問網頁的大概流程是這樣的(用文字敘述)
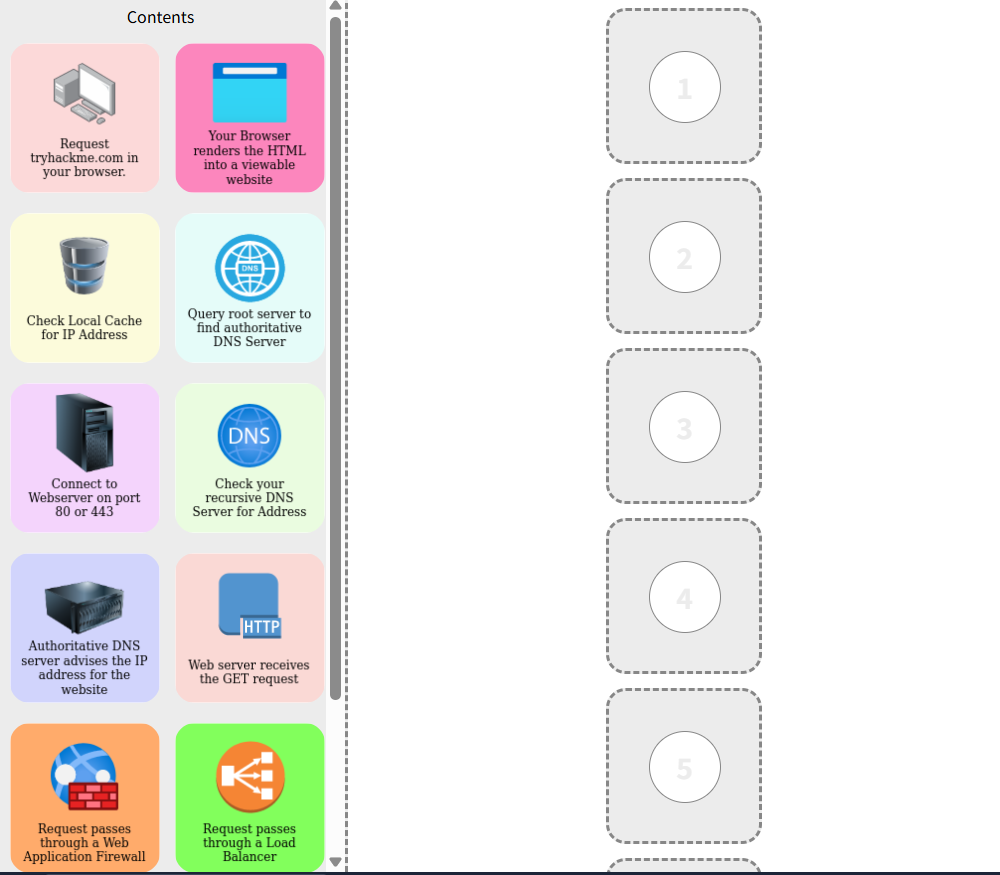
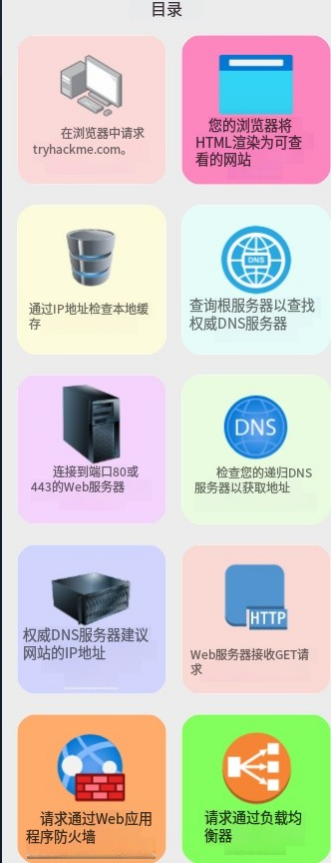
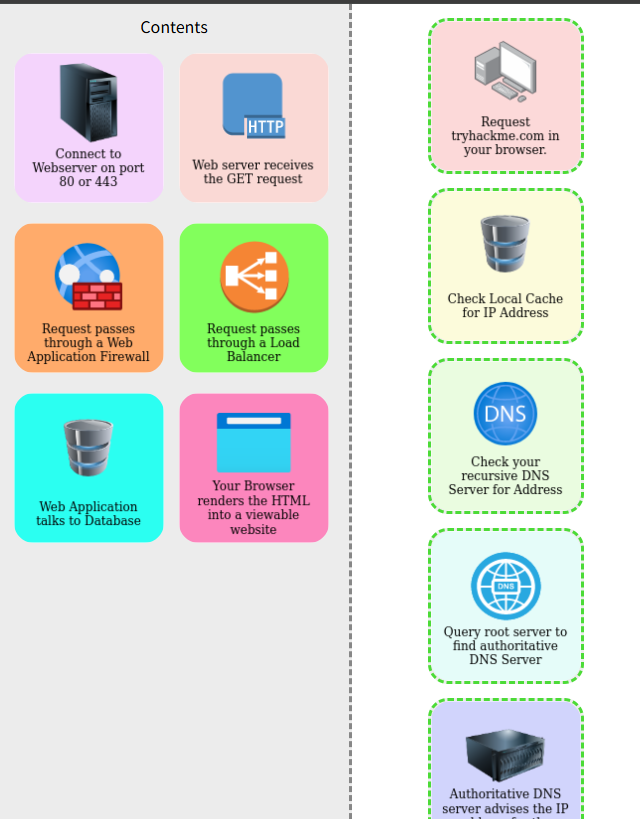
1 在網頁上搜索網站
2 通過ip地址來檢查本地的緩存
3 檢查你的遞歸DNS服務器以獲取地址
4 查詢跟服務器以查找權威的DNS服務器
5 權威DNS服務器建議網站的ip地址
6 請求通過web應用程序防火墻
7 請求通過負載均衡器
8 連接到端口為80或443的web服務器
9 web服務器接收GET請求
10 web應用程序和數據庫通信
11 您的瀏覽器將HTML渲染為可查看到的網站
以下是訪問網頁的專業化流程描述
- 用戶發起請求
用戶在瀏覽器地址欄輸入目標URL(統一資源定位符)并回車,或通過搜索引擎導航至目標網站。 - 本地DNS緩存查詢
瀏覽器首先檢查本地DNS緩存(包括操作系統緩存及瀏覽器緩存),若存在有效域名解析記錄(域名→IP映射),則直接使用該IP地址,跳過后續DNS解析步驟。 - 遞歸DNS服務器查詢
若本地無緩存,客戶端向配置的遞歸DNS服務器(Local DNS)發起查詢請求。遞歸DNS服務器檢查自身緩存,若有記錄則返回IP;若無則代表客戶端進行全球DNS層級查詢。 - 根域名與權威DNS服務器定位
遞歸DNS服務器從根域名服務器開始迭代查詢,依次獲取頂級域(如.com)、二級域(如example.com)的權威DNS服務器地址,最終定位到目標域名的權威DNS服務器。 - 權威DNS服務器響應解析記錄
權威DNS服務器返回目標域名的解析記錄(A記錄或CNAME記錄),包含其托管服務器的IP地址。遞歸DNS服務器緩存該記錄并返回至客戶端。 - 請求經過安全防護層
客戶端向目標IP發送的請求首先經過Web應用防火墻(WAF),進行安全策略檢測(如SQL注入/XSS攻擊防護),過濾惡意流量。 - 負載均衡器路由分發
合法請求抵達負載均衡器(如LVS、Nginx)。負載均衡器依據預設算法(輪詢、最小連接數等)將請求分發至后端多臺Web服務器中的一臺,確保集群高可用。 - 與Web服務器建立連接
客戶端與目標Web服務器通過TCP三次握手建立連接。HTTP協議默認使用端口80,HTTPS(TLS加密)使用端口443。 - Web服務器處理請求
Web服務器(如Apache、Nginx)接收HTTP GET請求,解析請求頭/請求路徑,定位靜態資源或轉發動態請求至應用服務器(如Tomcat、Node.js)。 - 應用層與數據庫交互
動態請求由Web應用程序(如PHP/Python程序)執行業務邏輯,包括查詢/更新數據庫(如MySQL、Redis),生成動態內容(如用戶數據、實時信息)。 - 客戶端渲染與呈現
瀏覽器接收響應(HTML/CSS/JS),執行以下流程:
-
- 解析HTML → 構建DOM樹
- 解析CSS → 構建CSSOM樹
- 執行JavaScript → 動態修改DOM/CSSOM
- 合并渲染樹 → 布局(Layout) → 繪制(Paint) → 最終呈現可視化網頁。
關鍵協議與技術說明
- DNS解析:分層查詢機制(根→頂級域→權威域)確保全球域名可管理;
- HTTPS安全擴展:在TCP握手后增加TLS協商(證書驗證+密鑰交換),加密傳輸數據;
- 連接復用:HTTP/1.1默認Keep-Alive復用TCP連接,HTTP/2支持多路復用減少握手開銷;
- 渲染阻塞:JS執行會暫停DOM/CSSOM構建,需優化加載策略。












)


:音頻重采樣)

![【[特殊字符][特殊字符] 協變與逆變:用“動物收容所”講清楚 PHP 類型的“靈活繼承”】](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/【[特殊字符][特殊字符] 協變與逆變:用“動物收容所”講清楚 PHP 類型的“靈活繼承”】)

