深度學習 – 梯度計算及上下文控制
文章目錄
- 深度學習 -- 梯度計算及上下文控制
- 一,自動微分
- 1.1 基礎概念
- 1.2 計算梯度
- 1.2.1 計算標量梯度
- 1.2.2 計算向量梯度
- 1.2.3 多標量梯度計算
- 1.2.4 多向量梯度計算
- 二,梯度上下文控制
- 2.1 控制梯度計算
- 2.2 累計梯度
- 2.3 梯度清零
- 三,案例一----求函數最小值
- 四,案例二----函數參數求解
一,自動微分
自動微分模塊torch.autograd負責自動計算張量操作的梯度,具有自動求導功能。自動微分模塊是構成神經網絡訓練的必要模塊,可以實現網絡權重參數的更新,使得反向傳播算法的實現變得簡單而高效。
1.1 基礎概念
-
張量
Torch中一切皆為張量,屬性requires_grad決定是否對其進行梯度計算。默認是 False,如需計算梯度則設置為True。
-
計算圖:
torch.autograd通過創建一個動態計算圖來跟蹤張量的操作,每個張量是計算圖中的一個節點,節點之間的操作構成圖的邊。
在 PyTorch 中,當張量的 requires_grad=True 時,PyTorch 會自動跟蹤與該張量相關的所有操作,并構建計算圖。每個操作都會生成一個新的張量,并記錄其依賴關系。當設置為
True時,表示該張量在計算圖中需要參與梯度計算,即在反向傳播(Backpropagation)過程中會自動計算其梯度;當設置為False時,不會計算梯度。
- 計算依賴圖
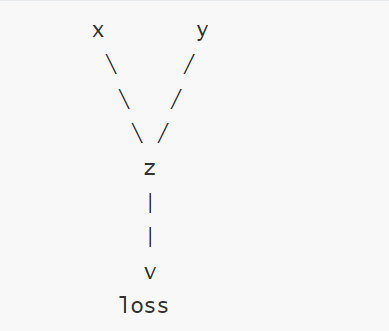
葉子結點判斷方式
x = torch.tensor([1.0, 2.0, 3.0], requires_grad=True) # 葉子節點
y = x ** 2 # 非葉子節點(通過計算生成)
z = y.sum()print(x.is_leaf) # True
print(y.is_leaf) # False
print(z.is_leaf) # False
1.2 計算梯度
使用tensor.backward()方法執行反向傳播,從而計算張量的梯度
1.2.1 計算標量梯度
import torchdef test01():x= torch.tensor(1.0,requires_grad=True)# requires_grad=True表示需要求導y=x**2# 操作張量y.backward() #計算梯度,也就是反向傳播print(x.grad) # 打印梯度if __name__ == '__main__':test01()
1.2.2 計算向量梯度
def test002():# 1. 創建張量:必須為浮點類型x = torch.tensor([1.0, 2.0, 3.0], requires_grad=True)y = x ** 2loss = y.mean()loss.backward()print(x.grad)if __name__ == "__main__":test002()
調用 loss.backward() 從輸出節點 loss 開始,沿著計算圖反向傳播,計算每個節點的梯度。
損失函數loss=mean(y)=1n∑i=1nyiloss=mean(y)=\frac{1}{n}∑_{i=1}^ny_iloss=mean(y)=n1?i=1∑n?yi?,其中 n=3。
對于每個 yiy_iyi?,其梯度為 ?loss?yi=1n=13\frac{?loss}{?y_i}=\frac{1}{n}=\frac13?yi??loss?=n1?=31?。
對于每個 xix_ixi?,其梯度為:
?loss?xi=?loss?yi×?yi?xi=13×2xi=2xi3\frac{?loss}{?x_i}=\frac{?loss}{?y_i}×\frac{?y_i}{?x_i}=\frac1{3}×2x_i=\frac{2x_i}3 ?xi??loss?=?yi??loss?×?xi??yi??=31?×2xi?=32xi??
所以,x.grad 的值為:[2×1.03,2×2.03,2×3.03]=[23,43,2]≈[0.6667,1.3333,2.0000][\frac{2×1.0}3, \frac{2×2.0}3, \frac{2×3.0}3]=[\frac23,\frac43,2]≈[0.6667,1.3333,2.0000][32×1.0?,32×2.0?,32×3.0?]=[32?,34?,2]≈[0.6667,1.3333,2.0000]
1.2.3 多標量梯度計算
#多標量梯度計算
def test03():x1= torch.tensor(1.0,requires_grad=True)x2=torch.tensor(3.0,requires_grad=True)y=x1**2+x2*7z=y.sum()z.backward()print(x1.grad,x2.grad)if __name__ == '__main__':test03()
1.2.4 多向量梯度計算
# 多向量梯度計算
def test04():x1 = torch.tensor([1.0, 2.0], requires_grad=True)x2 = torch.tensor([3.0, 4.0], requires_grad=True)y = x1 ** 2 + x2 * 7z = y.sum()z.backward()print(x1.grad, x2.grad)if __name__ == '__main__':test04()
二,梯度上下文控制
梯度計算的上下文控制和設置對于管理計算圖、內存消耗、以及計算效率至關重要。下面我們學習下Torch中與梯度計算相關的一些主要設置方式。
2.1 控制梯度計算
簡單的運算不需要梯度
import torchdef test01():x=torch.tensor(11.5,requires_grad=True)print(x.requires_grad)# Truey=x**2print(y.requires_grad)# Truewith torch.no_grad():z=x**2print(z.requires_grad)#使用裝飾器@torch.no_grad()def test():return x**2y=test()print(y.requires_grad)if __name__ == '__main__':test01()
2.2 累計梯度
默認情況下,當我們重復對一個自變量進行梯度計算時,梯度是累加的
import torchdef test002():x = torch.tensor([1.0, 2.0, 5.3], requires_grad=True)# 2. 累計梯度:每次計算都會累計梯度for i in range(3):y = x**2 + 2 * x + 7z = y.mean()z.backward()print(x.grad)if __name__ == "__main__":test002()
2.3 梯度清零
大多數情況下是不需要梯度累加的
#梯度清零
def test002():x = torch.tensor([1.0, 2.0, 5.3], requires_grad=True)# 2. 累計梯度:每次計算都會累計梯度for i in range(3):y = x**2 + 2 * x + 7z = y.mean()# 2.1 反向傳播之前先對梯度進行清零if x.grad is not None:x.grad.zero_()z.backward()print(x.grad)if __name__ == "__main__":test002()
三,案例一----求函數最小值
import torch
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as npdef test01():x = np.linspace(-10, 10, 100)y = x ** 2plt.plot(x, y)plt.show()def test02():# 初始化自變量Xx = torch.tensor([3.0], requires_grad=True, dtype=torch.float)# 迭代輪次epochs = 50# 學習率lr = 0.1list = []for i in range(epochs):# 計算函數表達式y = x ** 2# 梯度清零if x.grad is not None:x.grad.zero_()# 反向傳播y.backward()with torch.no_grad():x -= lr * x.gradprint('epoch:', i, 'x:', x.item(), 'y:', y.item())list.append((x.item(), y.item()))# 散點圖,觀察收斂效果x_list = [l[0] for l in list]y_list = [l[1] for l in list]plt.scatter(x=x_list, y=y_list)plt.show()if __name__ == "__main__":test01()test02()
四,案例二----函數參數求解
import torchdef test02():x = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], dtype=torch.float)y = torch.tensor([3, 5, 7, 9, 11], dtype=torch.float)a = torch.tensor([1.0], dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)b = torch.tensor([1.0], dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)lr = 0.05epochs = 1000for epoch in range(epochs):y_pred = a * x + bloss = ((y_pred - y) ** 2).mean()if a.grad is not None:a.grad.zero_()if b.grad is not None:b.grad.zero_()loss.backward()with torch.no_grad():a -= lr * a.gradb -= lr * b.gradif (epoch + 1) % 100 == 0:print(f'Epoch [{epoch + 1}/{epochs}], Loss: {loss.item():.4f}')print(f'a: {a.item():.4f}, b: {b.item():.4f}')if __name__ == '__main__':test02()

)



)









解題報告 | 珂學家)

- 首頁數據業務視圖)

