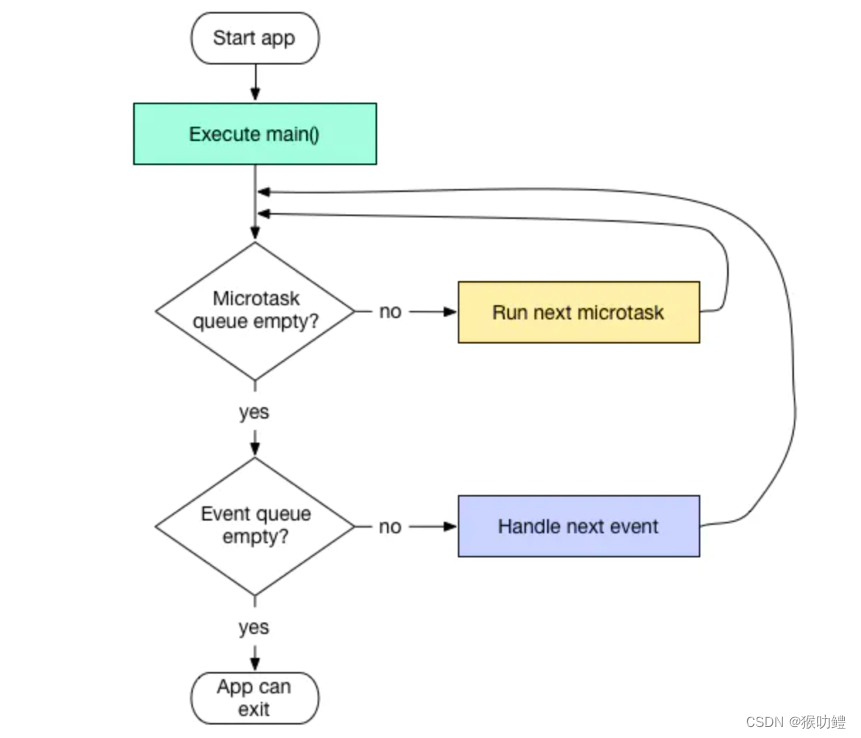
????????事件隊列(event?queue),包含所有的外來事件:I/O、mouse?events、drawing?events、timers、isolate之間的信息傳遞。
? ? ? ? Future中的任務會加入下一輪的任務隊列,then中的任務則是也會加入同樣的任務隊列。?Future中的任務和then后的任務可以理解為同步任務,因此,若Future嵌套微任務,會優先執行then中的代碼, 然后分別是微任務隊列中的代碼、事件隊列中的代碼。
? ? ? ? 當前事件循環中的微任務,會在這一輪中繼續執行。當前事件循環中嵌套的Future中的代碼,?才會在下一輪事件循環中執行。
? ? ? ? ?Future?是鏈式調用,意味著Future?的?then?未執行完,下一個then?不會執行。
? ? ? ? 看一個簡單的例子:
void testFuture(){print('外部代碼1');Future(()=>print('A')).then((value) => print('A結束'));Future(()=>print('B')).then((value) => print('B結束'));scheduleMicrotask((){print('微任務A');});sleep(Duration(seconds: 1));print('外部代碼2');
}????????打印結果:
? ? ? ? 外部代碼1
? ? ? ? 外部代碼2
? ? ? ? 微任務A
? ? ? ? ?A
? ? ? ? ?A結束
? ? ? ? ?B
? ? ? ? ?B結束
????????再看一個復雜點的例子:
void testFuture4(){Future x1 = Future(()=>null);x1.then((value){print('6');scheduleMicrotask(()=>print('7'));}).then((value) => print('8'));Future x = Future(()=>print('1'));x.then((value){print('4');Future(()=>print('9'));}).then((value) => print('10'));Future(()=>print('2'));scheduleMicrotask(()=>print('3'));print('5');
}
????????打印結果:
????????5,3, ?6,8,7,?1,4,10,2 ?,9
????????注意: 8先于7執行,因為已經調度到了當前隊列中,8在6之后是立刻執行的,而7是異步執行的。 ?
????????注意: 9不是在10之后執行,因為9是在嵌套中下一層的隊列中,因此需要等下一個消息循環才會執行。
? ? ? ? 再看一個例子:
void testFuture() {Future f1 = new Future(() => print('f1'));Future f2 = new Future(() => null);Future f3 = new Future.delayed(Duration(seconds: 1) ,() => print('f2'));Future f4 = new Future(() => null);Future f5 = new Future(() => null);f5.then((_) => print('f3'));f4.then((_) {print('f4');new Future(() => print('f5'));f2.then((_) {print('f6');});});f2.then((m) {print('f7');});print('f8');
}????????執行順序:?f8?、f1?、f7?、f4、f6、f3、f5、f2
????????因此可以解釋:f4之后為什么直接是f6? 因為f2在前面已經執行過了,所以f6可以理解為一個同步任務,會被立刻執行。
? ? ? ? 再看一個更復雜的例子:
void testScheduleMicrotatsk() {scheduleMicrotask(() => print('1'));
//1.0new Future.delayed(new Duration(seconds: 1), () => print('2'));
//2.0new Future(() => print('3')).then((_) {print('4');scheduleMicrotask(() => print('5'));}).then((_) => print('6'));
//3.0new Future(() => print('7')).then((_) => new Future(() => print('8'))).then((_) => print('9'));
//3.1
//new Future(() => print('7'))
// .then( (_) { new Future( () => print('8') );})
// .then( (_) => print('9') ) ;
//4.0new Future(() => print('10'));scheduleMicrotask(() => print('11'));print('12');
}
????????注意:如果按照3.0的寫法,?執行完7后,?由于then是直接返回一個Future,而不是嵌套一個新Future,9將被阻塞,?因此執行順序為:12、1、11、3、4?、6、5、7、10、8、9?、2
? ? ? ? 3.0的寫法等同于下述寫法, then中是返回一個Future,而不是嵌套一個新的Future
new Future(() => print('7')).then( (_) { Future f = new Future( () => print('8') );return f;}).then( (_) => print('9') ) ;
????????而如果是3.1的寫法,則不會阻塞。?因為3.1這里then是嵌套了一個新的Future,?與then直接返回一個Future不同。?其,執行順序為12,1,11,3,4,6,5,7,9,10,8,2。


![[NSSCTF 2nd] web復現](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[NSSCTF 2nd] web復現)



![在Redhat 7 Linux上安裝llama.cpp [ 錯誤stdatomic.h: No such file or directory]](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/在Redhat 7 Linux上安裝llama.cpp [ 錯誤stdatomic.h: No such file or directory])

)
)




![Bulingbuling - 《歷史的教訓》 [ The Lessons of History ]](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/Bulingbuling - 《歷史的教訓》 [ The Lessons of History ])

)


