大家好,我是蘇貝,本篇博客帶大家了解棧,如果你覺得我寫的還不錯的話,可以給我一個贊👍嗎,感謝??
目錄
- 一 .棧的概念及結構
- 二 .棧的實現
- 棧的結構體
- 初始化
- 銷毀
- 棧頂插入
- 棧頂刪除
- 顯示棧頂元素
- 是否為空
- 棧的大小
- 三. 模塊化代碼實現
- Stack.h
- Stack.c
- Test.c
- 結果演示
一 .棧的概念及結構
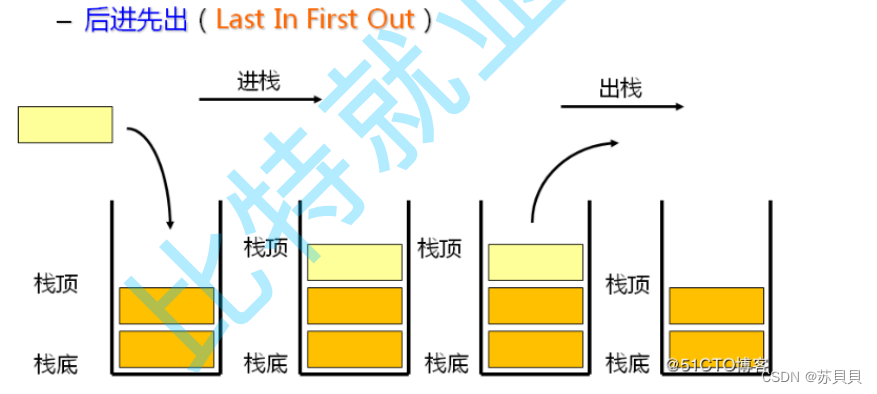
棧:一種特殊的線性表,其只允許在固定的一端進行插入和刪除元素操作。進行數據插入和刪除操作的一端稱為棧頂,另一端稱為棧底。棧中的數據元素遵守后進先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原則。
壓棧:棧的插入操作叫做進棧/壓棧/入棧,入數據在棧頂。
出棧:棧的刪除操作叫做出棧,出數據也在棧頂。
二 .棧的實現
棧的實現一般可以使用數組或者鏈表實現,相對而言數組的結構實現更優一些,因為數組在尾上插入數據的代價比較小(數組的尾插、尾刪很方便)。所以下面我們用數組來實現
1
棧的結構體
typedef int STDataType;
#define N 10
typedef struct Stack
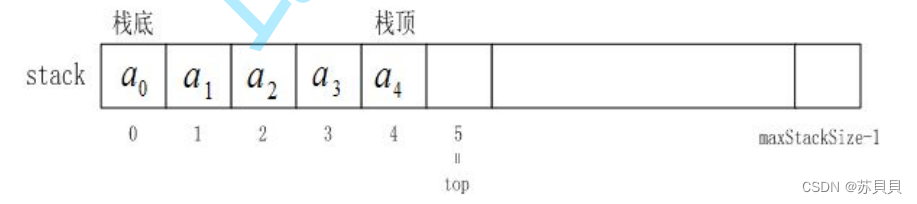
{STDataType _a[N];int top; // 棧頂
}ST;
上面是定長的靜態棧的結構,實際中一般不實用,所以我們主要實現下面的支持動態增長的棧
typedef int STDataType;typedef struct Stack
{STDataType* a;int top;//棧頂int capacity;//容量
}ST;
2
初始化
因為我們要對ST類型的變量進行初始化,所以實參要傳ST類型變量的地址,用一級指針來接收。因為實參(ST類型變量的地址)不可能為NULL,所以對它斷言(下面的接口同理)。
注意:我們這里的top指的是棧頂元素的下一個,而非棧頂元素,所以將它初始化為0
void STInit(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);pst->a = NULL;pst->capacity = 0;pst->top = 0;//指向棧頂元素的下一個
}
3
銷毀
注意:在這里我們使用的是動態開辟內存,所以要在銷毀時釋放掉動態開辟的內存,也就是pst->a指向的那個數組
void STDestroy(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);if (pst->a != NULL){free(pst->a);pst->a = NULL;pst->capacity = 0;pst->top = 0;}
}
4
棧頂插入
再插入元素之前我們要先判斷是否要增容,因為在初始化時我們將pst->capacity初始化為0,所以在增容時要特別注意將pst->capacity==0的情況。還要注意對realloc的結果進行判斷,防止realloc失敗返回NULL,又直接將NULL賦值給pst->a,這樣就再找不到開辟的數組了。
最后不要忘記pst->top++
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x)
{assert(pst);//判斷是否需要增容if (pst->top == pst->capacity){int newcapacity = (pst->capacity == 0) ? 4 : 2 * pst->capacity;ST* tmp = (ST*)realloc(pst->a, newcapacity * sizeof(ST));if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");return;}pst->a = tmp;pst->capacity = newcapacity;}//插入數據pst->a[pst->top] = x;pst->top++;
}
5
棧頂刪除
刪除時我們必須保證棧內有元素,所以要對pst->top>0斷言,如果top==0,表示棧內已無元素,返回錯誤信息,下面的顯示棧頂元素同理
void STPop(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);assert(pst->top > 0);pst->top--;
}
6
顯示棧頂元素
STDataType STTop(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);assert(pst->top > 0);return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}
7
是否為空
bool STEmpty(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);return pst->top == 0;
}
8
棧的大小
int STSize(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);return pst->top;
}
三. 模塊化代碼實現
Stack.h
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>typedef int STDataType;typedef struct Stack
{STDataType* a;int top;int capacity;
}ST;//初始化
void STInit(ST* pst);
//銷毀
void STDestroy(ST* pst);
//棧頂插入
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x);
//棧頂刪除
void STPop(ST* pst);
//顯示棧頂元素
STDataType STTop(ST* pst);
//是否為空
bool STEmpty(ST* pst);
//大小
int STSize(ST* pst);
Stack.c
#include"Stack.h"//初始化
void STInit(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);pst->a = NULL;pst->capacity = 0;pst->top = 0;//指向棧頂元素的下一個
}//銷毀
void STDestroy(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);if (pst->a != NULL){free(pst->a);pst->a = NULL;pst->capacity = 0;pst->top = 0;}
}//棧頂插入
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x)
{assert(pst);//判斷是否需要增容if (pst->top == pst->capacity){int newcapacity = (pst->capacity == 0) ? 4 : 2 * pst->capacity;ST* tmp = (ST*)realloc(pst->a, newcapacity * sizeof(ST));if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");return;}pst->a = tmp;pst->capacity = newcapacity;}//插入數據pst->a[pst->top] = x;pst->top++;
}//棧頂刪除
void STPop(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);assert(pst->top > 0);pst->top--;
}//顯示棧頂元素
STDataType STTop(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);assert(pst->top > 0);return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}//是否為空
bool STEmpty(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);return pst->top == 0;
}//大小
int STSize(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);return pst->top;
}
Test.c
#include"Stack.h"int main()
{ST s;STInit(&s);STPush(&s, 1);STPush(&s, 2);STPush(&s, 3);STPush(&s, 4);STPush(&s, 5);while (!STEmpty(&s)){printf("%d ", STTop(&s));STPop(&s);}printf("\n");return 0;
}
結果演示

好了,那么本篇博客就到此結束了,如果你覺得本篇博客對你有些幫助,可以給個大大的贊👍嗎,感謝看到這里,我們下篇博客見??





![[計算機網絡]--五種IO模型和select](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[計算機網絡]--五種IO模型和select)





)

)
)

)



