文章目錄
- 集合
- Set集合介紹
- HashSet集合的介紹和使用
- LinkedHashSet的介紹以及使用
- 哈希值
- 哈希值的計算方式
- HashSet的存儲去重的過程
- Map集合
- Map的介紹
- HashMap的介紹以及使用
- HashMap的兩種遍歷方式
- 方式1:獲取key,然后再根據key獲取value
- 方式2:同時獲取key和value
- HashMap存儲自定義對象
- Map的練習
- LinkedHashMap
- TreeSet
- TreeMap
- HashTable和Vector集合
- HashTable集合
- Vector集合
- Properties集合(屬性值)
- List嵌套Map
- Map嵌套map
- 哈希表結構存儲過程
- HashMap無參數構造方法的分析
- HashMap有參數的構造方法的分析
- tableSizeFor方法分析
- Node內部類的分析
- 存儲元素的put方法源碼
- putVal方法源碼
- resize方法的擴充計算
- 確定元素存儲的索引
- 遇到重復哈希值的對象
集合
Set集合介紹
1.概述:set是一個接口,是Collection下的子接口
2.使用:
a.所用的方法和Collection接口中的方法一模一樣
b.set接口中的方法并沒有堆Collection中的方法進行任何的擴充
c.set以及下面所有的實現類集合相當是一個傀儡
因為所用的set集合底層都是依靠map集合實現的
HashSet集合的介紹和使用
1.概述:HashSet是Set接口的實現類對象
2.特點
a.元素無序
b.元素不可重復
c.無索引
d.線程不安全
3.數據結構:哈希表
jdk8之前: 哈希表 = 數組+鏈表
jdk8之后:哈希表 = 數組+鏈表+紅黑樹
方法
和Collection一模一樣
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;public class test08 {public static void main(String[] args) {final HashSet<String> set = new HashSet<>();set.add("張三");set.add("李四");set.add("王五");set.add("孫六");System.out.println(set);Iterator<String> iterator = set.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()){System.out.println(iterator.next());}System.out.println("=======================");for (String s : set) {System.out.println(s);}}
}
運行結果

LinkedHashSet的介紹以及使用
概述 LinkedHashSet extends HashSet
特點:
a.元素有序
b.元素布克重復
c.無索引
d.線程不安全
數據結構
哈希表+雙向鏈表
使用 和HashSet一樣
public static void main(String[] args) {final HashSet<String> set = new HashSet<>();set.add("張三");set.add("李四");set.add("王五");set.add("孫六");set.add("張三");System.out.println(set);Iterator<String> iterator = set.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()){System.out.println(iterator.next());}System.out.println("=======================");for (String s : set) {System.out.println(s);}}
哈希值
概述 計算機計算出來的一個十進制數,我們可以理解為是對象的地址值
獲取哈希值:Object類中的
int hashCode()
結論:
如果內容一樣,哈希值一定一樣
如果內容同不用,哈希值也有可能不一樣
public class test10 {public static void main(String[] args) {String s1 = "abc";String s2 = "abc";System.out.println(s1.hashCode());System.out.println(s2.hashCode());System.out.println("==================");String s3 = "通話";String s4 = "重地";System.out.println(s3.hashCode());System.out.println(s4.hashCode());}
}運行結果

哈希值的計算方式
通過進入String的hashCode方法,查看相關的代碼
public int hashCode() {int h = hash;if (h == 0 && value.length > 0) {char val[] = value;for (int i = 0; i < value.length; i++) {h = 31 * h + val[i];}hash = h;}return h;}
從上述代碼中看到31作為常量相乘,31是一個質數,因為31這個數可以盡可能的解決哈希碰撞問題
盡量的不出現,內容不一樣,但是哈希值一樣的問題
HashSet的存儲去重的過程
1.計算元素的哈希值,比較元素哈希值
2.如果哈希值不一樣,直接存
3.如果哈希值一樣,再比較內容(equals)
4.如果哈希值不一樣,內容一樣,存
5.如果哈希值一樣,內容一樣,去重復,后面的會把前面的覆蓋掉
Map集合
Map的介紹
概述:雙列集合的頂級接口
組成部分
一個元素是有兩部分構成
key = value ----- 鍵值對
HashMap的介紹以及使用
概述:是Map的實現類
特點:
a.元素無序
b.key唯一,value可重復
c.無索引
d.線程不安全
數據結構:哈希表
常用方法
V put(K key, V value) -> 存儲元素
V remove(Object key) ->根據key刪除對應的鍵值對
V get(Object key) -> 根據key獲取對應的value
boolean containsKey(Object key) ->判斷Map中是否包含指定的key
Collection values() -> 將Map中所有的value存儲到Collection集合中
Set keySet() -> 將Map中所有的key獲取出來存到Set集合中
Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() -> 獲取Map中所有的鍵值對對象,放到set集合中
public class test {public static void main(String[] args) {final HashMap<Integer, String> set = new HashMap<>();//存儲元素set.put(0001,"李云龍");set.put(0002,"丁偉");set.put(0003,"孔捷");System.out.println(set);//根據key刪除對應的鍵值對set.remove(0001);System.out.println(set);//根據key獲取對應的ValueSystem.out.println(set.get(2));//判斷map中是否含有指定的keySystem.out.println(set.containsKey(1));}
}
注意 如果key重復了,后米的會把前面的覆蓋掉,去重復過程和set一模一樣
HashMap的兩種遍歷方式
方式1:獲取key,然后再根據key獲取value
Set keySet() ----- 將Map中所有的key獲取出來存到Set集合中
public class test02 {public static void main(String[] args) {final HashMap<Integer, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();hashMap.put(1,"李云龍");hashMap.put(2,"丁偉");hashMap.put(3,"孔捷");/** 先調用keySet方法,獲取map中所有的key,存儲到Set集合中* 遍歷Set集合,調用map中的get方法,根據key獲取value* */Set<Integer> set = hashMap.keySet();for (Integer key : set) {String value = (String) hashMap.get(key);System.out.println(key + "....." + value);}}
}
方式2:同時獲取key和value
Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() — 獲取Map中所有的鍵值對對象,放到set集合中
1.我們只需要獲取到每個鍵值對的條目就行了
2.拿到條目,就能拿到條目上的key和value
3.記錄key和value的條目, Map中的靜態接口 — Map.Entry
Map.Entry中有兩個方法
getKey() 獲取key
getValue() 獲取value
Set<Map.Entry<Integer, Object>> set1 = hashMap.entrySet();for (Map.Entry<Integer, Object> integerObjectEntry : set1) {Integer key = integerObjectEntry.getKey();String value = (String) integerObjectEntry.getValue();System.out.println(key + "...." + value);}
HashMap存儲自定義對象
1.key存儲自定義對象,value類型隨意
2.需要key重寫hashCode和equals方法
相關代碼
public class Person {private String name;private int age;public Person() {}public Person(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object o) {if (this == o) return true;if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;Person person = (Person) o;return age == person.age && Objects.equals(name, person.name);}@Overridepublic int hashCode() {return Objects.hash(name, age);}
}public class test03 {public static void main(String[] args) {HashMap<Person, String> hashMap = new HashMap<>();hashMap.put(new Person("李云龍",18),"獨立團");hashMap.put(new Person("孔捷",26),"新一團");hashMap.put(new Person("丁偉",26),"新二團");System.out.println(hashMap);}
}Map的練習
需求:用Map集合統計字符串中每一個字符出現的次數
步驟
1.創建Scanner對象,調用next方法錄入字符串
2.創建HashMap集合,key為String用于存儲字符串,value作為Integer用于存儲字符對應的個數
3.遍歷字符串,判斷,集合中有沒有該字符
4.如果沒有,將該字符以及對用的1存到Map集合中
5.如果有,根據該字符獲取對用的value,對value進行加一
6.將該字符以及對用的value值存進去
7.輸出
public class test03 {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("請輸入字符串");final Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);String data = scanner.next();final HashMap<String, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<>();char[] chars = data.toCharArray();for (char aChar : chars) {String achar = aChar + "";if (!hashMap.containsKey(achar)){hashMap.put(achar,1);}else {int value = hashMap.get(achar);value ++;hashMap.put(achar,value);}}System.out.println(hashMap);}
}
LinkedHashMap
概述 LinkedHashMap extends HashMap
特點:
a.有序
b.無索引
c.key唯一,value可重復
d.線程不安全
數據結構
哈希表+雙向鏈表
用法:和HashMap一樣
public class test04 {public static void main(String[] args) {final LinkedHashMap<String, String> hashMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();hashMap.put("001","李云龍");hashMap.put("002","丁偉");hashMap.put("003","孔捷");System.out.println(hashMap);//使用keyset方式遍歷final Set<String> set = hashMap.keySet();for (String s : set) {final String s1 = hashMap.get(s);System.out.println(s+"...."+s1);}//使用entrySet方式遍歷final Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> entries = hashMap.entrySet();for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : entries) {System.out.println(entry.getKey()+ "...." +entry.getValue());}}
}
TreeSet
1.概述:ThreeSet是Set接口的實現類
2.特點:
a.可以對元素進行排序
b.元素唯一
c.無索引
d.線程不安全
3.數據結構
紅黑樹
4.方法 和HashSet一樣
構造
TreeSet() — 對元素進行自然排序 ---- ASCII
TreeSet(Comparator<? suoer E> comparator) ----------- 按照指定規則進行排序
相關練習代碼
public class Person {private String name;private int age;public Person() {}public Person(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Person{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object o) {if (this == o) return true;if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;Person person = (Person) o;return age == person.age && Objects.equals(name, person.name);}@Overridepublic int hashCode() {return Objects.hash(name, age);}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}
}
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.TreeSet;public class test05 {public static void main(String[] args) {final TreeSet<String> treeSet = new TreeSet<>();treeSet.add("d");treeSet.add("a");treeSet.add("v");treeSet.add("c");treeSet.add("e");System.out.println(treeSet);System.out.println("=================");final TreeSet<Person> people = new TreeSet<>(new Comparator<Person>() {@Overridepublic int compare(Person o1, Person o2) {return o1.getAge() - o2.getAge();}});people.add(new Person("李云龍",30));people.add(new Person("丁偉",21));people.add(new Person("孔捷",42));System.out.println(people);}
}
TreeMap
1.概述:TreeMap是Map接口的實現類
2.特點:
a.可以對key進行排序
b.無索引
c.線程不安全
3.數據結構:
紅黑樹
4.方法:
和HashMao一樣
1.構造:
TreeMap() -> 按照自然順序對key進行排序
TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator)-> 按照指定規則對key進行排序
public class test06 {public static void main(String[] args) {final TreeMap<String, String> treeMap = new TreeMap<>();treeMap.put("a","寶兒姐");treeMap.put("b","張之維");treeMap.put("c","王也");treeMap.put("e","張楚嵐");System.out.println(treeMap);System.out.println("====================");final TreeMap<Person, String> treeMap1 = new TreeMap<>(new Comparator<Person>() {@Overridepublic int compare(Person o1, Person o2) {return o1.getAge() - o2.getAge();}});treeMap1.put(new Person("李云龍",32),"獨立團");treeMap1.put(new Person("丁偉",42),"新一團");treeMap1.put(new Person("孔捷",33),"新二團");System.out.println(treeMap1);}
}
HashTable和Vector集合
HashTable集合
1.概述:是Map的實現類
2.特點:
a.無序
b.key唯一,value可重復
c.無索引
d.線程安全
3.數據結構
哈希表
4.用法
和HashMap一樣
public class test07 {public static void main(String[] args) {final Hashtable<String, String> hashtable = new Hashtable<>();hashtable.put("老天師","張之維");hashtable.put("不要碧蓮","張楚嵐");hashtable.put("土豪道士","王也");System.out.println(hashtable);}
}
Vector集合
1.概述 是Collection的實現類
2.特點
a.有序
b.有索引
c.元素可重復
d.線程安全
3.數據結構
數組
4.用法 和ArrayList一樣
5.底層分析:
a.Vector ---- new底層會直接產生一個長度為10 的空數組
b.數組擴容 Arrays.copyof 擴容兩倍
public class test08 {public static void main(String[] args) {final Vector<String> vector = new Vector<>();vector.add("李云龍");vector.add("丁偉");vector.add("孔捷");System.out.println("vector = " + vector);}
}
HashMap和Hashtable的區別
1.相同點
key唯一,無索引,元素無序,底層都是哈希表
2.不同點
HashMap線程不安全,允許有null鍵null值
Hashtable線程安全,不允許有null鍵null值
Properties集合(屬性值)
1.概述:Properties是Hashtable的子類
2.特點
a.無序
b.key唯一,value可重復
c.無索引
d.線程安全
e.Properties的key的value類型默認是String
f.不允許有null鍵null值
3.數據結構
哈希表
4.用法:
可以使用HashMap的方法
5.特有方法
Object setProperty(String key, String value) -> 存儲鍵值對
String getProperty(String key) -> 根據key獲取value
Set stringPropertyNames() -> 獲取所有的key,存放到Set集合中
void load(InputStream inStream) -> 將流中的數據信息加載到Properties集合中
public class test01 {public static void main(String[] args) {final Properties properties = new Properties();//將鍵值對存入集合properties.setProperty("username","root");properties.setProperty("password","1234");System.out.println("properties = " + properties);//根據key獲取相應的valueSystem.out.println(properties.getProperty("username"));//獲取所有的key,存放到set集合中和keyset方法效果一致final Set<String> set = properties.stringPropertyNames();for (String s : set) {System.out.println(properties.getProperty(s)+"...."+s);}}
}
List嵌套Map
需求:
一班有四名同學。學號和姓名分別為:
1=張楚嵐,2=馮寶寶,3=王也,4=諸葛青
二班有三名同學,分別為:
1=張之維,2=張靈玉 3=夏禾
將同學的信息以鍵值對形式存入到2個Map集合中,再將2個map集合存儲到list集合中
public class test02 {public static void main(String[] args) {final HashMap<Integer, String> hashMap = new HashMap<>();final HashMap<Integer, String> hashMap1 = new HashMap<>();hashMap.put(1,"張楚嵐");hashMap.put(2,"馮寶寶");hashMap.put(3,"王也");hashMap.put(4,"諸葛青");hashMap1.put(1,"張之維");hashMap1.put(2,"張靈玉");hashMap1.put(3,"夏禾");final ArrayList<HashMap<Integer,String>> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add(hashMap);list.add(hashMap1);//遍歷列表for (HashMap<Integer, String> integerStringHashMap : list) {final Set<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> entries = integerStringHashMap.entrySet();for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : entries) {System.out.println(entry.getKey()+"..."+entry.getValue());}}}
}
Map嵌套map
javaSE集合存儲的是學號 鍵,值學生姓名
1 張三
2 李四
javaEE 結合存儲的是學號 鍵,值學生姓名
1 王五
2 趙六
public class test03 {public static void main(String[] args) {final HashMap<Integer, String> hashMap = new HashMap<>();final HashMap<Integer, String> hashMap1 = new HashMap<>();hashMap.put(1,"張三");hashMap.put(2,"李四");hashMap1.put(1,"王五");hashMap1.put(2,"田六");final HashMap<HashMap<Integer,String>, String> map = new HashMap<>();map.put(hashMap,"javaSE");map.put(hashMap1,"javaEE");//遍歷大mapfinal Set<Map.Entry<HashMap<Integer, String>, String>> entries = map.entrySet();for (Map.Entry<HashMap<Integer, String>, String> entry : entries) {System.out.println(entry.getKey()+"...."+entry.getValue());}}
}
哈希表結構存儲過程
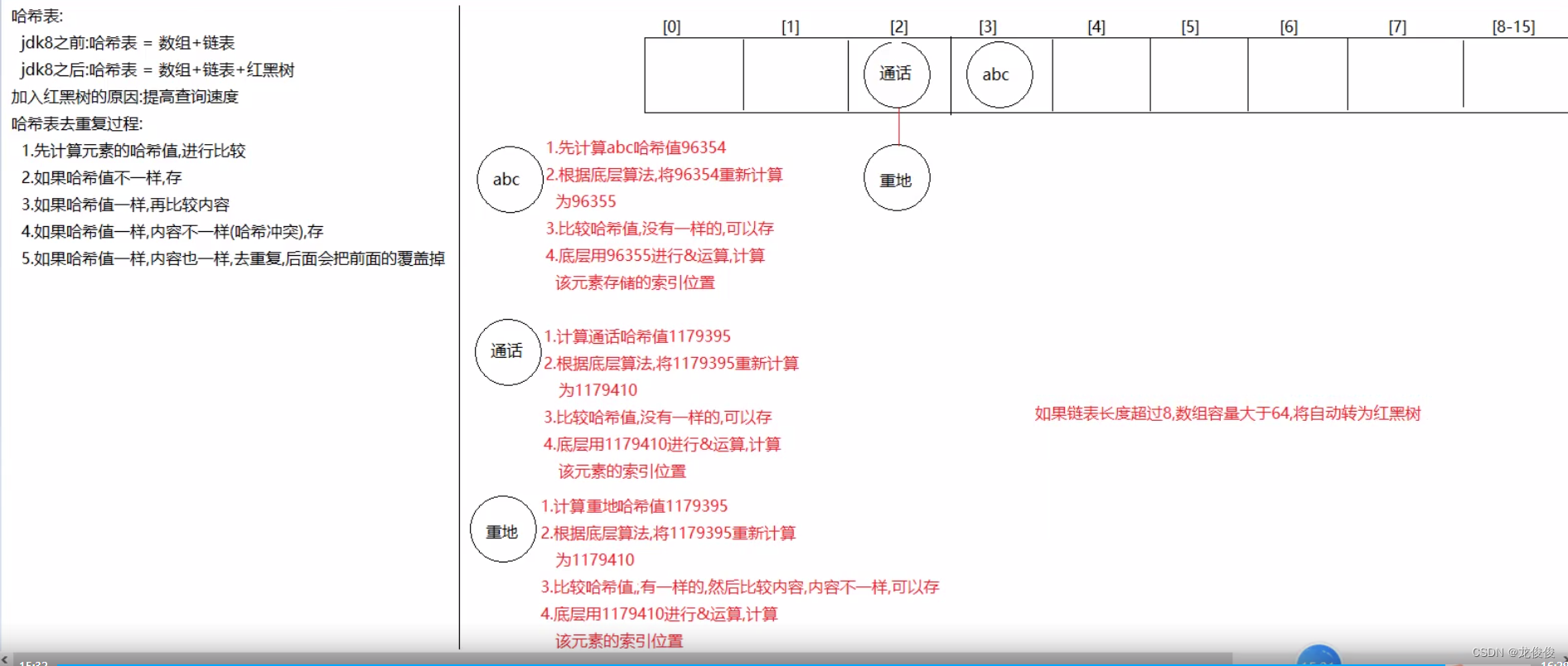
要知道的點
a.在不指定長度時,哈希表中的數組默認長度為16,HashMap創建出來,一開始沒有床架長度為16的數組
b.在第一次put的時候,底層會創建出來長度為16的數組
c.哈希表中有一個數據加【加載因子】---- 默認為0.75(加載因子)---- 代表當元素存儲到百分之七十五的時候要擴容了—0–2倍
d.如果元素的哈希值出現相同,內容不一樣時,就會在同一個索引上以鏈表的形式存儲,當鏈表長度達到8,并且當前數組長度>64時,鏈表就會改成使用紅黑樹存儲
e.加入紅黑樹目的:查詢快
面試時可能會問到的變量
default_initial_capacity:HashMap默認容量 16
defaul_load_factor:HashMap默認加載因子 0.75f
threshold 擴充的臨界值 等于 容量8*0.75 =12 第一次擴容
threeify_threshold: 鏈表長度默認值,轉為紅黑樹:8
min_treeify_capacity: 鏈表被樹化時最小的數組容量 64
HashMap無參數構造方法的分析
HashMap中的靜態成員變量
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
public HashMap() {this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; // all other fields defaulted
}
解析:使用無參數構造方法創建HashMap對象,將加載因子設置成默認的加載因子,loadfactor=0.75
HashMap有參數的構造方法的分析
解析 如果帶有參數構造方法,傳遞哈希表的初始化容量和加載因子
HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) ->創建Map集合的時候指定底層數組長度以及加載因子public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
//如果初始化容量小于0,直接拋出異常if (initialCapacity < 0)throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +initialCapacity);
//如果初始化容量大于最大容量,初始化容量直接等于最大容量if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
//如果loadFactor(加載因子)小于等于0,直接拋出異常if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +loadFactor);this.loadFactor = loadFactor;this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity);//10
tableSizeFor方法分析
tableSizeFor(initCapacity)方法計算哈希表的初始化容量
注意 哈希表是進行計算得出的容量,而初始化容量不直接等于我們傳遞的參數。
8 4 2 1規則—無論指定了多少容量,最終經過tableSizeFor這個方法計算以后,都會遵守8421規則去初始化列表容量
解析:該方法對我們傳遞的初始化容量進行位移運算,位移的結果是8421碼
例如傳遞2,結果還是2,傳遞的是4,結果還是4
傳遞3,結果傳遞4,傳遞5,結果是8,傳遞20,結果是32
Node內部類的分析
哈希表是采用數組加鏈表的實現方法
HashMap中的內部類Node非常重要,證明HashSet是一個單向鏈表
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {final int hash;final K key;V value;Node<K,V> next;Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {this.hash = hash;this.key = key;this.value = value;this.next = next;
}
解析:內部類Node中具有四個成員變量
hash 對象的哈希值
key 作為鍵的對象
value 作為值的對象
next,下一個節點對象
存儲元素的put方法源碼
public V put(K key, V value) {return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
解析:put方法中調用putVal方法,putVal方法中調用hash方法
hash(key)方法;傳遞要存儲的元素,獲取對象的哈希值
putVal方法:傳遞對象哈希值和要存儲的對象key
putVal方法源碼
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)n = (tab = resize()).length;
解析,方法中進行Node對象數組的判斷,如果數組是null或者長度等于0,那么就會調用resize()方法進行數組的擴充
resize方法的擴充計算
if (oldCap > 0) {if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;return oldTab;}else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold
}
解析:計算結果,新的數組容量 = 原始數組容量 <<1,也就是乘以2
確定元素存儲的索引
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
解析:i = (數組長度-1) & 對象的哈希值,會得到一個索引,然后在此索引下tab[i],創建鏈表對象。不同的哈希值的對象,也是有可能存儲在同一個數組索引下
遇到重復哈希值的對象
Node<K,V> e; K k;if (p.hash == hash &&((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))e = p;
解析 如果對象的哈希值相同,對象的equals方法返回true,判斷為一個對象,進行覆蓋操作
else {for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {if ((e = p.next) == null) {p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1sttreeifyBin(tab, hash);break;}
解析:如果對象哈希值相同嗎,但是對象的equals方法返回false,將對此鏈表進行遍歷
當鏈表沒有下一個節點的時候,創建下一個節點存儲對象

:Docker CLI 基本用法解析)


)



)




)


處理高光譜及多光譜遙感數據)


