matlab:涉及復雜函數圖像的交點求解
在MATLAB中求解兩個圖像的交點是一個常見的需求。本文將通過一個示例,展示如何求解兩個圖像的交點,并提供相應的MATLAB代碼。
畫出圖像
首先,我們需要繪制兩個圖像,以便直觀地看到它們的交點。以下是繪制圖像的MATLAB代碼:
% 定義符號變量
syms x1 x2;% 上邊界方程
eq1 = 10 + 110 * (0.8 + 0.05 + 0.4 * sin(4 * atan2(x2, x1))^16)^2 - (x1 + x2) == 0;% 繪制圖形
figure;% 使用 fimplicit 繪制上邊界
fimplicit(@(x1, x2) 10 + 110 * (b + 0.05 + 0.4 * sin(4 * atan2(x2, x1))^16)^2 - (x1 + x2), [0, 100, 0, 100]);
hold on;% 使用 fimplicit 繪制 y = 100 - x1
fimplicit(@(x1, x2) x1 + x2 - 100, [0, 100, 0, 100]);% 設置圖例和標題
legend('Upper Boundary', 'y = 100 - x1');
title('Plot of Equations');
xlabel('x1');
ylabel('x2');
hold off;
繪制的圖像如下所示:
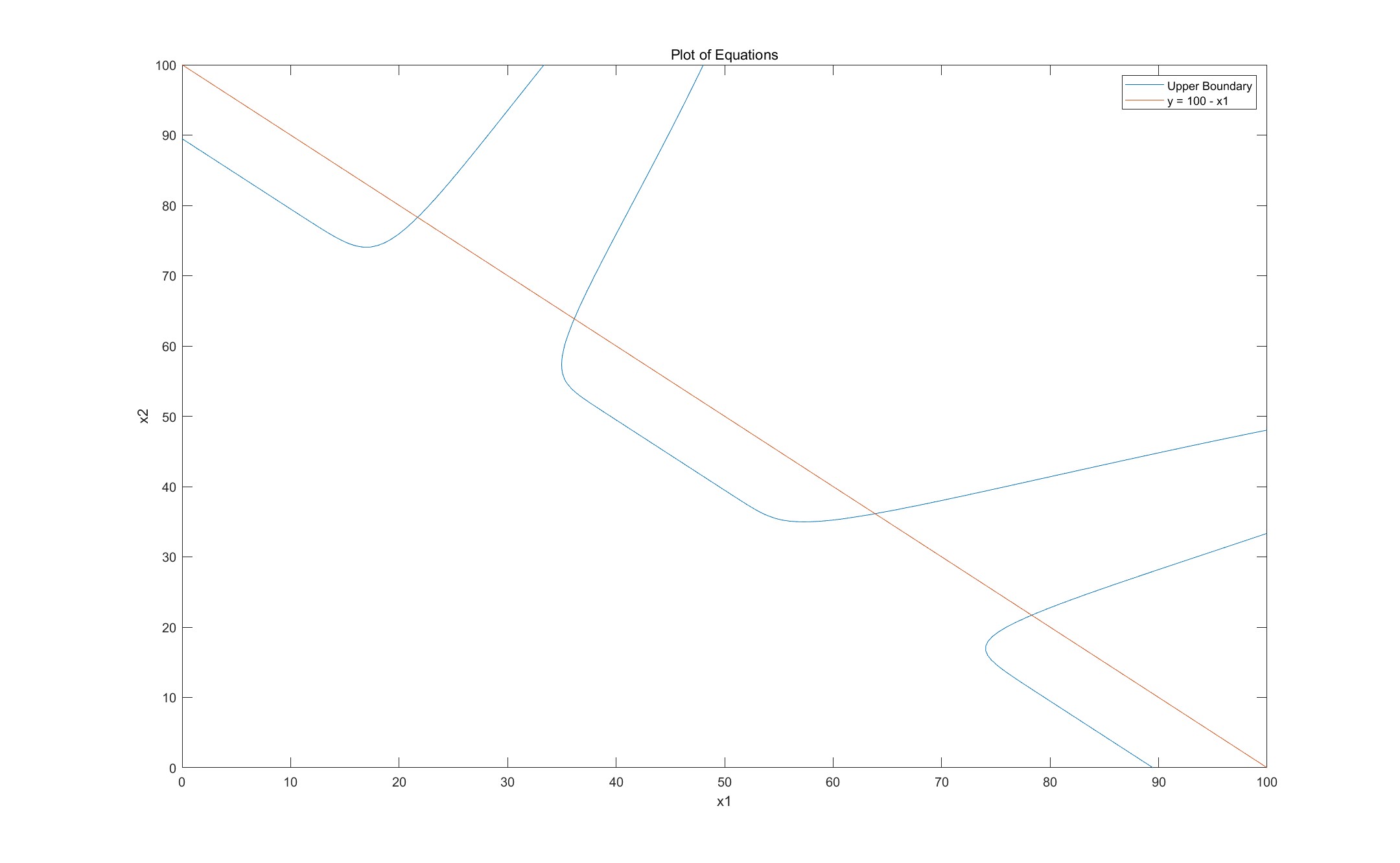
從圖中可以看出,存在四個實數域交點。
求解交點方法1:solve不加求解范圍(失敗)
首先嘗試使用solve函數來求解交點:
% 定義符號變量
syms x1 x2;% 定義參數
b = 0.8;
l = atan2(x2, x1);% 定義方程組
eq1 = 10 + 110 * (b + 0.05 + 0.4 * sin(4 * l)^16)^2 - (x1 + x2);
eq2 = x1 + x2 - 100;% 解方程組
[sol_x1, sol_x2] = solve([eq1 == 0, eq2 == 0], [x1, x2]);% 轉換為數值解
sol_x1 = double(sol_x1);
sol_x2 = double(sol_x2);% 篩選實數解
real_solutions = [sol_x1, sol_x2];
real_solutions = real_solutions(imag(real_solutions(:, 1)) == 0 & imag(real_solutions(:, 2)) == 0, :);% 輸出實數解
disp('Real solutions (x1, x2):');
disp(real_solutions);
輸出為空值,這表明在解的過程中遇到了問題。
求解交點方法2:solve加求解范圍(成功)
% 定義符號變量
syms x1 x2;% 求解范圍
assume(x1>=0&x1<=100)
assume(x2>=0&x2<=100)% 定義參數
b = 0.8;
l = atan2(x2, x1);% 定義方程組
eq1 = 10 + 110 * (b + 0.05 + 0.4 * sin(4 * l)^16)^2 - (x1 + x2);
eq2 = x1 + x2 - 100;% 解方程組
[sol_x1, sol_x2] = solve([eq1 == 0, eq2 == 0], [x1, x2]);% 轉換為數值解
sol_x1 = double(sol_x1);
sol_x2 = double(sol_x2);% 篩選實數解
real_solutions = [sol_x1, sol_x2];
real_solutions = real_solutions(imag(real_solutions(:, 1)) == 0 & imag(real_solutions(:, 2)) == 0, :);% 輸出實數解
disp('Real solutions (x1, x2):');
disp(real_solutions);
輸出:

求解交點方法3:fsolve(成功)
下面通過數值方法而不是符號方法來找到解,使用 fsolve(數值求解函數):
% 定義匿名函數
func = @(x) [10 + 110 * (b + 0.05 + 0.4 * sin(4 * atan2(x(2), x(1)))^16)^2 - (x(1) + x(2)), x(1) + x(2) - 100];% 設置選項以使用較大的初始搜索范圍
options = optimoptions('fsolve', 'Display', 'off', 'MaxFunctionEvaluations', 6000, 'MaxIterations', 4000);% 存儲解
solutions = [];% 嘗試多個隨機初始猜測
for i = 1:100initial_guess = rand(1, 2) * 100; % 生成0到100之間的隨機初始猜測[sol, fval, exitflag, output] = fsolve(func, initial_guess, options);% 只有當fsolve成功收斂時才記錄解if exitflag > 0 && all(abs(fval) < 1e-6)solutions = [solutions; sol];end
end% 去除重復的解,考慮數值誤差
solutions = round(solutions, 3); % 四舍五入到三位小數
solutions = unique(solutions, 'rows', 'stable');% 過濾掉不在感興趣區域的解
solutions = solutions(all(solutions >= 0 & solutions <= 100, 2), :);% 輸出數值解
disp('Numerical solutions (x1, x2):');
disp(solutions);
輸出:
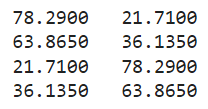
這表明成功找到了交點的坐標,不過誤差稍大一些。
總結
- 使用solve時,限制求解范圍是重要的
- 當solve無能為力的時候,可以試試fsolve



)





為什么基帶有I和Q路?)
)
】)
-弱電網)






