
1. 概述
JavaScript面向對象比較難理解的點是類的繼承。不管是es5寫法還是es6寫法,JavaScript繼承的本質是原型鏈。具體可看我的上一篇文章:
田浩:詳解原型、原型鏈、構造函、實例、new?zhuanlan.zhihu.com
因為es6有專門的語法,寫法很簡單且容易理解,所以本文將著重介紹es5的實現繼承不同方式及其原理。
再閱讀本文之前,一定要注意區分幾個名詞:父類、子類、子類的實例。
2.類的聲明和實例化:
/*** 類的聲明*/
var Animal = function () {this.name = 'Animal';
};/*** es6中class的聲明*/
class Animal2 {constructor () {this.name = 'Animal2';}
}/*** 實例化方式相同*/
let dog = new Animal();
let dog2 = new Animal2();
2. ES5中類的繼承:
2.1 借助構造函數實現繼承(部分繼承)
function Parent1 () {this.name = 'parent1';
}Parent1.prototype.say = function () {
}; // 不會被子類繼承function Child1 () {Parent1.call(this);this.type = 'child1';
}
原理:
核心在于:Parent1.call(this)
改變Parant1運行時的this的指向,指向子構造函數,所以父類中有的屬性,子類中也有。
缺點:
父類原型鏈上的屬性方法并沒有被子類繼承。 所以這種方式不能成為繼承,只能叫做部分繼承。
2.2 借助原型鏈實現繼承
function Parent2 () {this.name = 'parent2';this.array = [1,2,3];
}
function Child2 () {this.type = 'child2';
}
Child2.prototype = new Parent2();
原理:
核心在于: Child2.prototype =new Parent2();
將Parent2的一個實例作為Child2的prototype。訪問Child2的實例時候,實例可以通過__proto__訪問Parent2中的屬性。
缺點:
試想,如果Child2實例兩個對象s1、s2,他們通過__proto__訪問的父類上的屬性實際上是同一個引用(s1.__proto__ === s2.__proto__)。這樣,比如s1修改array,s2的array也會跟著變。這是我們所不想看到的。
2.3 組合方式
將上兩種組合:
function Parent3 () {this.name = 'parent3';this.array = [1, 2, 3];
}
function Child3 () {Parent3.call(this); this.type = 'child3';
}
Child3.prototype = new Parent3();
原理:
核心在于: 將上兩種方式結合。實際上,子類的實例中,Parent3上的屬性會存在兩份,一份在實例中,一份在實例的__proto__上:
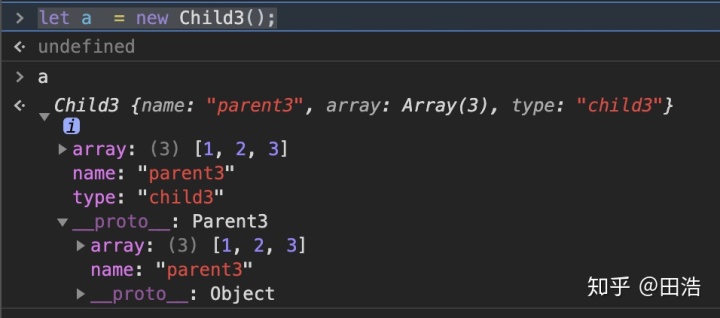
缺點:
實例化子類的時候,父類執行了兩次,且子類實例中存在冗余數據。這些都是沒有必要的。
2.4 組合繼承的優化1
function Parent4 () {this.name = 'parent4';this.play = [1, 2, 3];
}
function Child4 () {Parent4.call(this);this.type = 'child4';
}
Child4.prototype = Parent4.prototype;
原理:
核心在于: 將 Parent4的prototype直接賦給Child4.prototype。此時父類只執行一次。
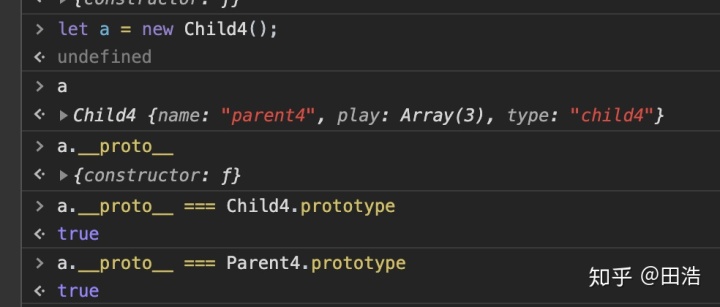
缺點:
子類實例的constructor會指向父類:a的constructor會指向Parent4,不符合預期,無法區分這個實例是父類創造的還是子類創造的。當然這個缺點在2.3中也存在。原因是constructor屬性來自原型對象中,上述方法子類的實例訪問constructor 實際訪問的事父類的prototype中的constructor。
2.5 組合繼承的優化2
function Parent5 () {this.name = 'parent5';this.play = [1, 2, 3];
}
function Child5 () {Parent5.call(this);this.type = 'child5';
}
Child5.prototype = Object.create(Parent5.prototype);
// 手動修改constructor指向,由于父類的prototype和子類的prototype已經隔離開,可以放心修改。
Child5.prototype.constructor = Child5;
原理:
核心在于: Object.create(Parent5.prototype);
Object.create()方法創建一個新對象,使用現有的對象來提供新創建的對象的__proto__。

)











)






