容器的概觀和分類
- array 數組 、list 鏈表、tree樹 、stack堆棧、queue隊列、hash table散列表、set集合、map映射表
- 根據數據在容器中的排列順序,將上述數據結構分為序列式和關聯式兩種類型
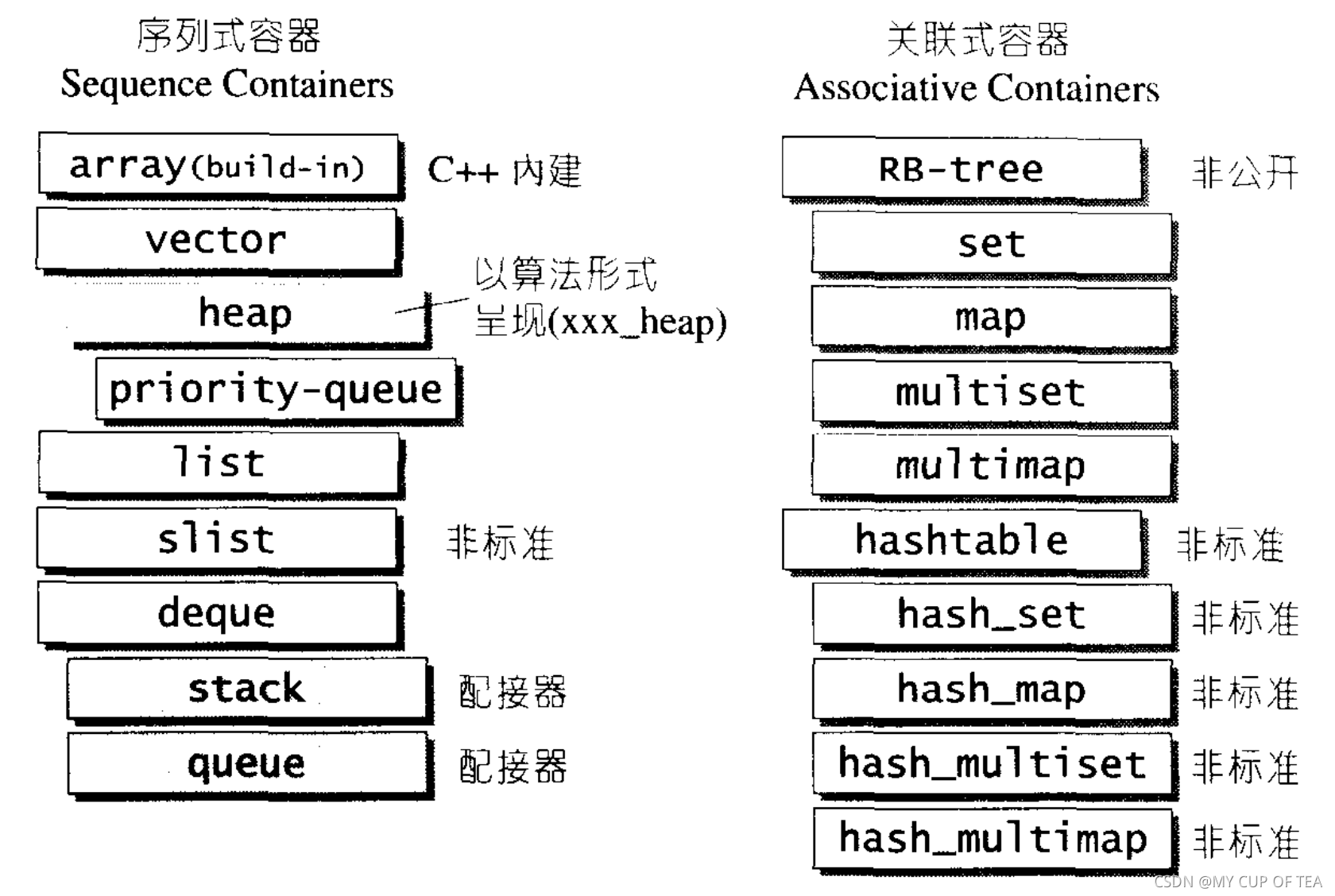
- SGI STL使用內縮方式來表達基層和衍生層之間的關系
- 衍生不是派生,本質上是一種內含的關系,例如heap內含vector,priority-queue內含heap;stack 和 queue都內含deque;set map multiset multimap 內含一個 RB-tree,hash_x都內含hashtable
- 序列式容器,內部元素都可序但是未必有序。C++本身提供了一個序列式容器array,STL提供了vector、list、deque、priority_queue等
- stack 和 queue都是在deque的基礎上改頭換面形成的,技術上將其歸類為一種 配接器
Vector
- vector類似于array,二者唯一的差別在于 空間的運用的靈活性。
- array是靜態空間,一旦配置就不會改變大小,如果存儲空間不夠需要申請空間進行元素的拷貝,這些操作均需要用戶自己來執行,最后還需要釋放先前擁有的區間。? 具體操作:(配置新的空間 | 數據移動 | 釋放先前的內存空間 )
- vector是動態空間,隨著元素的加入,內部的實現機制會自行進行內存空間的擴充從而容納新的元素
- vector的實現技術:關鍵在于其對于大小的控制和重新配置的時候對于數據的移動的效率。第二次申請的內存空間是先前的兩倍
- SGI vector將vector實現于更加底層的<stl_vector.h> ,具體使用的時候直接引入<vector>頭文件即可
#include <iostream>
#include <new> //for placement new
#include <cstddef> //for ptrdiff_t size_t
#include <cstdlib> //for exit
#include <climits> //for UINT_MAXnamespace Chy{template <class T>inline T* _allocate(ptrdiff_t size,T*){std::set_new_handler(0);T* tmp = (T*)(::operator new((std::size_t)(size * sizeof (T))));if (tmp == 0){std::cerr << "out of memory" << std::endl;exit(1);}return tmp;}template<class T>inline void _deallocate(T* buffer){::operator delete (buffer);}template<class T1,class T2>inline void _construct(T1 *p,const T2& value){new(p) T1 (value); //沒看懂}template <class T>inline void _destroy(T* ptr){ptr->~T();}template <class T>class allocator{public:typedef T value_type;typedef T* pointer;typedef const T* const_pointer;typedef T& reference;typedef const T& const_reference;typedef std::size_t size_type;typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;template<class U>struct rebind{typedef allocator<U>other;};pointer allocate(size_type n,const void * hint = 0){return _allocate((difference_type)n,(pointer)0);}void deallocate(pointer p,size_type n){_deallocate(p);}void construct(pointer p,const T& value){_construct(p,value);}void destroy(pointer p){_destroy(p);}pointer address(reference x){return (pointer)&x;}const_pointer const_address(const_reference x){return (const_pointer)&x;}size_type max_size()const{return size_type(UINT_MAX/sizeof (T));}};
}template<class T,class Alloc>
class simple_alloc{
public:static T* allocate(std::size_t n){return 0==n?0:(T*)Alloc::allocate(n * sizeof(T));}static T* allocate(void){return (T*)Alloc::allocate(sizeof (T));}static void deallocate(T* p,size_t n){if (n!=0){Alloc::deallocate(p,n * sizeof(T));}}static void deallocate(T* p){Alloc::deallocate(p,sizeof(T));}
};//如果是copy construction 等同于assignment而且destructor 是 trivial以下就會有效
//如果是POD型別 執行的流程就會跳轉到以下函數,這個是通過function template的參數推導機制得到的
template<class ForwardIterator,class Size,class T>
inline ForwardIterator __uninitizlized_fill_n_aux(ForwardIterator first,Size n,const T&x){return fill_n(first,n,x); //交給高階函數執行
}struct __true_type{};
struct __false_type{};template<class T>
struct __type_traits {typedef __true_type this_dummy_member_must_be_first;typedef __false_type has_trivial_default_constructor;typedef __false_type has_trivial_copy_constructor;typedef __false_type has_trivial_assignment_constructor;typedef __false_type has_trivial_destructor;typedef __false_type is_POD_type;
};//函數的邏輯是
//首先萃取出 迭代器first的value type,然后判斷這個型別是否是POD類型
template<class ForwardIterator,class Size,class T,class T1>
inline ForwardIterator __uninitizlized_fill_n(ForwardIterator first,Size n,const T&x,T1*){//以下使用的是__type_traits<T1>::is_POD_type is _PODtypedef typename __type_traits<T1>::is_POD_type is_POD;return __uninitizlized_fill_n_aux(first,n,x,is_POD());
}template<class ForwardIterator,class Size,class T>
ForwardIterator uninitialized_fill_n(ForwardIterator first,Size n,const T&x){return __uninitizlized_fill_n(first,n,x,value_type(first));//使用value_type()判斷first的value type
}//alloc 是SGI STL默認的空間配置器
template <class T,class Alloc>
class vector{
public://vector的嵌套型別定義typedef T value_type;typedef value_type * pointer;typedef value_type * iterator;typedef value_type & reference;typedef std::size_t size_type;typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;
protected://simple_alloc 是SGI STL的空間配置器typedef simple_alloc<value_type,Alloc>data_allocator;iterator start; //表示目前使用空間的頭部iterator finish; //表示目前使用空間的尾部iterator end_of_storage; //表示目前可用空間的尾部void insert_aux(iterator position,const T&x);void deallocate(){if (start){data_allocator ::deallocate(start,end_of_storage - start);}}void fill_initialize(size_type n,const T& value){start = allocate_and_fill(n,value);finish = start+n;end_of_storage = finish;}public:iterator begin(){return start;}iterator end(){return finish;}size_type size() const {return size_type(end() - begin());}size_type capacity() const{return size_type (end_of_storage - begin());}bool empty(){return begin() == end();}reference operator[] (size_type n){return (*(begin() + n));}vector():start(0),finish(0),end_of_storage(0){};vector(size_type n,const T& value){fill_initialize(n,value);}vector(int n,const T& value){fill_initialize(n,value);}vector(long n,const T& value){fill_initialize(n,value);}explicit vector(size_type n){fill_initialize(n,T());}~vector(){Chy::allocator<T>::destroy(start,finish); //全局函數deallocate(); //vector的成員函數}reference front(){return *begin();} //第一個元素reference back(){return *(end()-1);} //最后一個元素void push_back(const T& x){if (finish != end_of_storage){Chy::allocator<T>::construct(finish,x);++finish;} else{insert_aux(end(),x);// vector的成員函數}}void pop_back(){ //將最尾端的元素取出--finish;Chy::allocator<T>::destroy(finish);}iterator erase(iterator position){ //清除某個位置上的元素if (position+1 != end()){std::copy(position+1,finish,position); //后續元素向前移動 進行元素的覆蓋}--finish;Chy::allocator<T>::destroy(finish);return position;}void resize(size_type new_size,const T& x){if (new_size < size()){erase(begin()+new_size,end());} else{std::inserter(end(),new_size - size(),x);}}void resize(size_type new_size){resize(new_size,T());}void clear(){erase(begin(),end());}
protected://配置空間并填滿內容iterator allocate_and_fill(size_type n,const T&x){iterator result = data_allocator ::allocate(n);uninitialized_fill_n(result,n,x); //全局函數return result;}
};vector迭代器
- vector維護的是一個連續的線性空間,所以不論其元素的的型別是怎樣,普通的指針都可以作為vector的迭代器從而滿足所有的必要的條件
- 因為vector迭代器所需要的操作,比如 operator*??operator->?operator++?operator--?operator+?operator-?operator+=?operator-= 是普通指針天生就具備的能力
- 普通指針支持隨機存取,正因為普通指針具備這樣的能力,所以vector提供的是random Access iterators
- vector的迭代器是普通的指針
- 例子
std::vector<int>::iterator i_vite; //i_vite的型別本質上是int*
std::vector<Shape>::iterator s_vite; //s_vite的型別本質上是Shape*Vector數據結構
- 數據結構很簡單:線性連續空間
- 使用start和finish指向配置的連續空間中的已經使用的范圍區間
- 使用迭代器end_of_storage指向的是整個一塊連續的空間(包含備用空間)的尾端
iterator start; //表示目前使用空間的頭部iterator finish; //表示目前使用空間的尾部iterator end_of_storage; //表示目前可用空間的尾部- vector分配的內存空間實際上是大于客戶端申請的內存空間,主要是為了防止以后內存的擴充,這個便是容量的概念。
- 即容量的概念 永遠大于或者等于其大小,一旦容量等于大小,即是滿載。
- 使用三個迭代器,完成 vector的首尾標定、使用空間的大小、容量、空容器的判斷、注標[]的運算子、最前端的元素 和最末尾的元素等等
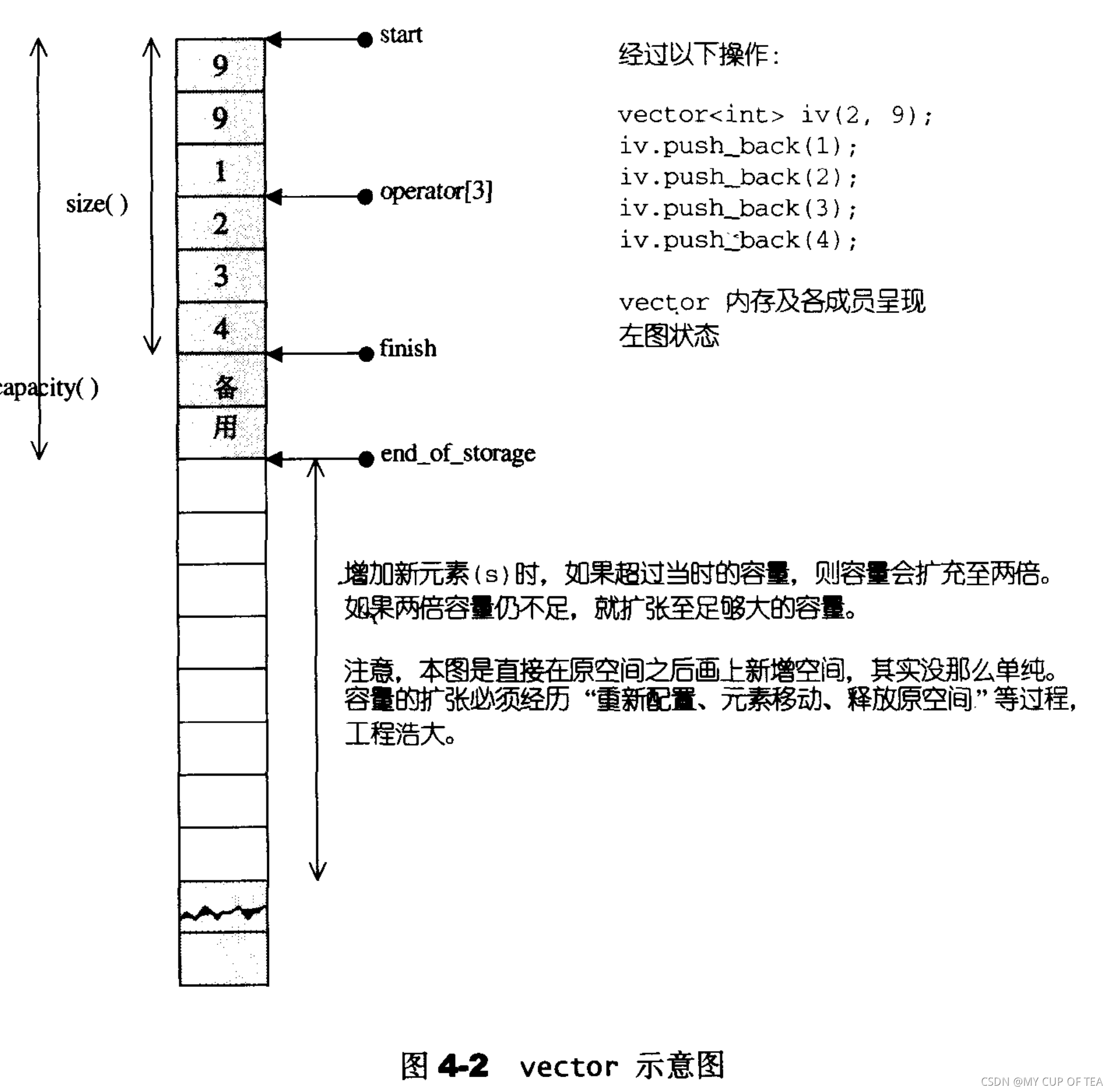
Vector的構造和內存管理
- //vector缺省使用alloc作為空間配置器,并據此另外定義了data_allocator,為的是更方便的以元素大小作為配置單位
- ? ? typedef simple_alloc<value_type,Alloc>data_allocator; 所以data_allocator::allocate(n)? ; 表示配置n個元素的空間
- vector提供了很多的構造器


- uninitialized_fill_n 根據第一個參數的特性(使用type_traits 進行類型推導),決定使用fill_n() 還是通過反復調用 construct() 來完成任務
- 使用push_back()將元素插入到vector的尾端的時候,函數檢查是否存在備用的空間,如果有直接在備用空間進行元素的構造,并且調整迭代器finish使得vector變大
- 如果沒有備用空間就需要進行元素的擴充(配置 、移動數據、釋放空間)
void push_back(const T& x){if (finish != end_of_storage){ //還存在備用空間Chy::allocator<T>::construct(finish,x); //直接進行元素的構造++finish; //調整水位高度} else{ //無備用空間insert_aux(end(),x);// vector的成員函數}}//insert_aux 偽代碼
template<class T,class Alloc>
void vector<T,Alloc>::insert_aux(iterator position, const T &x) {if (finish != end_of_storage){ //還有備用空間//在備用空間起始處構造一個元素,并使用vector最后一個元素數值為其初始化Chy::allocator<T>::construct(finish,*(finish-1));//調整水位++finish;T x_copy = x;copy_backward(position,finish-2,finish-1);*position = x_copy;} else{ //無備用空間const size_type old_size = size();const size_type len = old_size != 0 ? 2*old_size:1;//配置原則://如果原大小為0 則配置1 (單位是 元素的大小)//如果原大小不為0 配置內存大小是先前的兩倍//前半段用于放置先前的數據,后半段用于存儲新的數據iterator new_start = data_allocator::allocate(len); //實際配置內存iterator new_finish = new_start;try{//進行先前元素的拷貝,將原vector的內容拷貝到新的vectornew_finish = unintialized_copy(start,position,new_start);//為新的元素設定初始數值 xChy::allocator<T>::construct(new_finish,x);//調整水位++new_finish;//將原vector的備用空間中的內容也忠實拷貝過來new_finish = unintialized_copy(position,finish,new_finish);}catch (){//commit or rollbackChy::allocator<T>::destroy(new_start,new_finish);data_allocator::allocate(new_start,len);throw ;}//析構并且釋放原有的vectorChy::allocator<T>::destroy(begin(),end());deallocate();//調整迭代器 指向新的vectorstart = new_start;finish = new_finish;end_of_storage = new_start + len;}
}
- ?動態增加大小 不是在現有的內存空間后面接入新的空間 (? 無法保證原有空間之后是否還尚有可以配置的空間?)
- 需要在背的地方申請空間
- 因此一旦造成空間的重新配置,指向原有vector的所有迭代器就會失效了
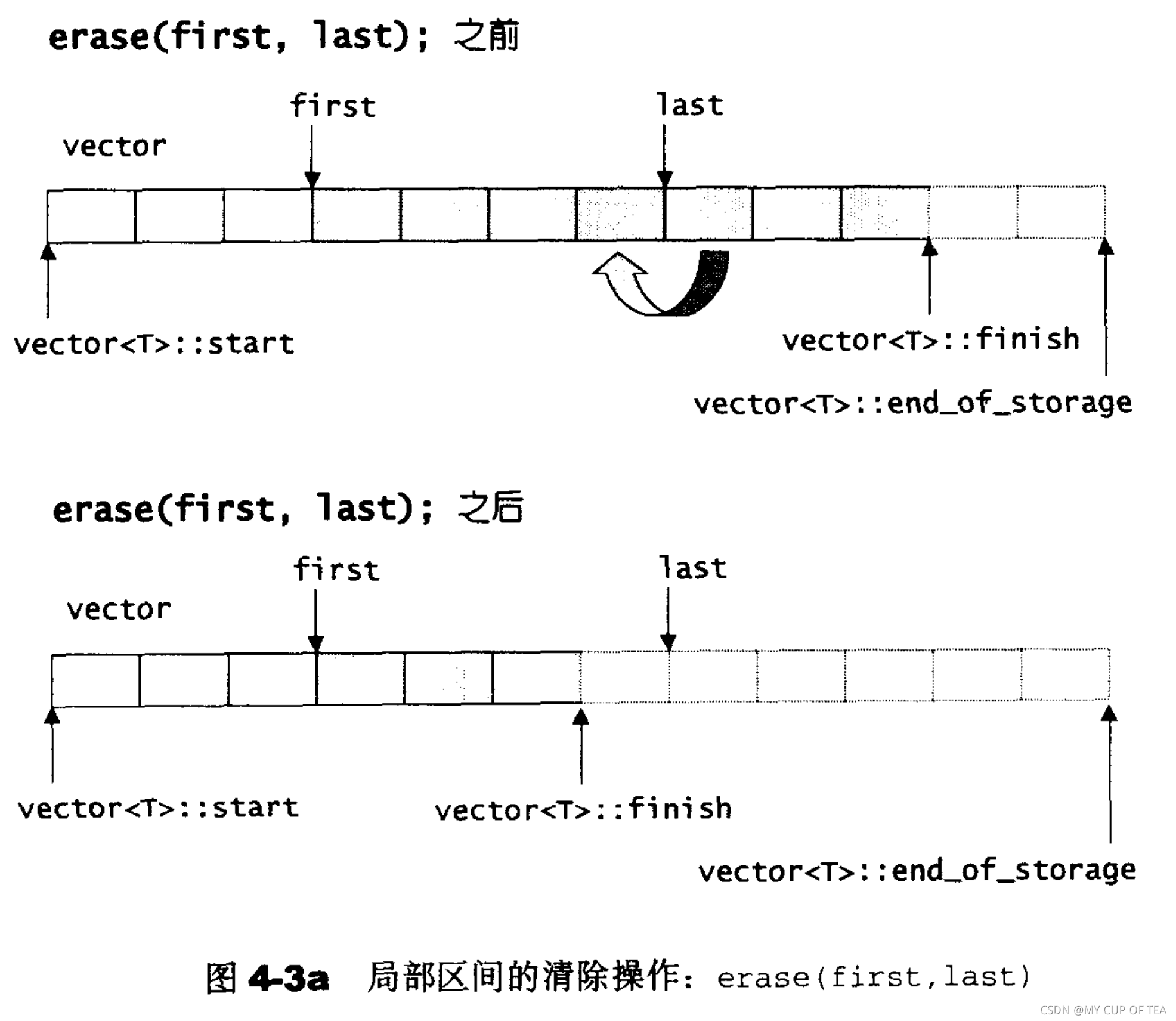
void pop_back(){ //將最尾端的元素取出--finish; //將尾端標記往前移動一格,表示放棄尾端元素Chy::allocator<T>::destroy(finish);} void pop_back(){ //將最尾端的元素取出--finish; //將尾端標記往前移動一格,表示放棄尾端元素Chy::allocator<T>::destroy(finish);}//清除[first ,last)內部所有元素iterator erase(iterator first,iterator last){iterator i = copy(last,finish,first);Chy::allocator<T>::destroy(i,finish);finish = finish - (last - first);return first;}//清除某個特定位置上的元素iterator erase(iterator position){ //清除某個位置上的元素if (position+1 != end()){std::copy(position+1,finish,position); //后續元素向前移動 進行元素的覆蓋}--finish;Chy::allocator<T>::destroy(finish);return position;}void clear(){erase(begin(),end());}
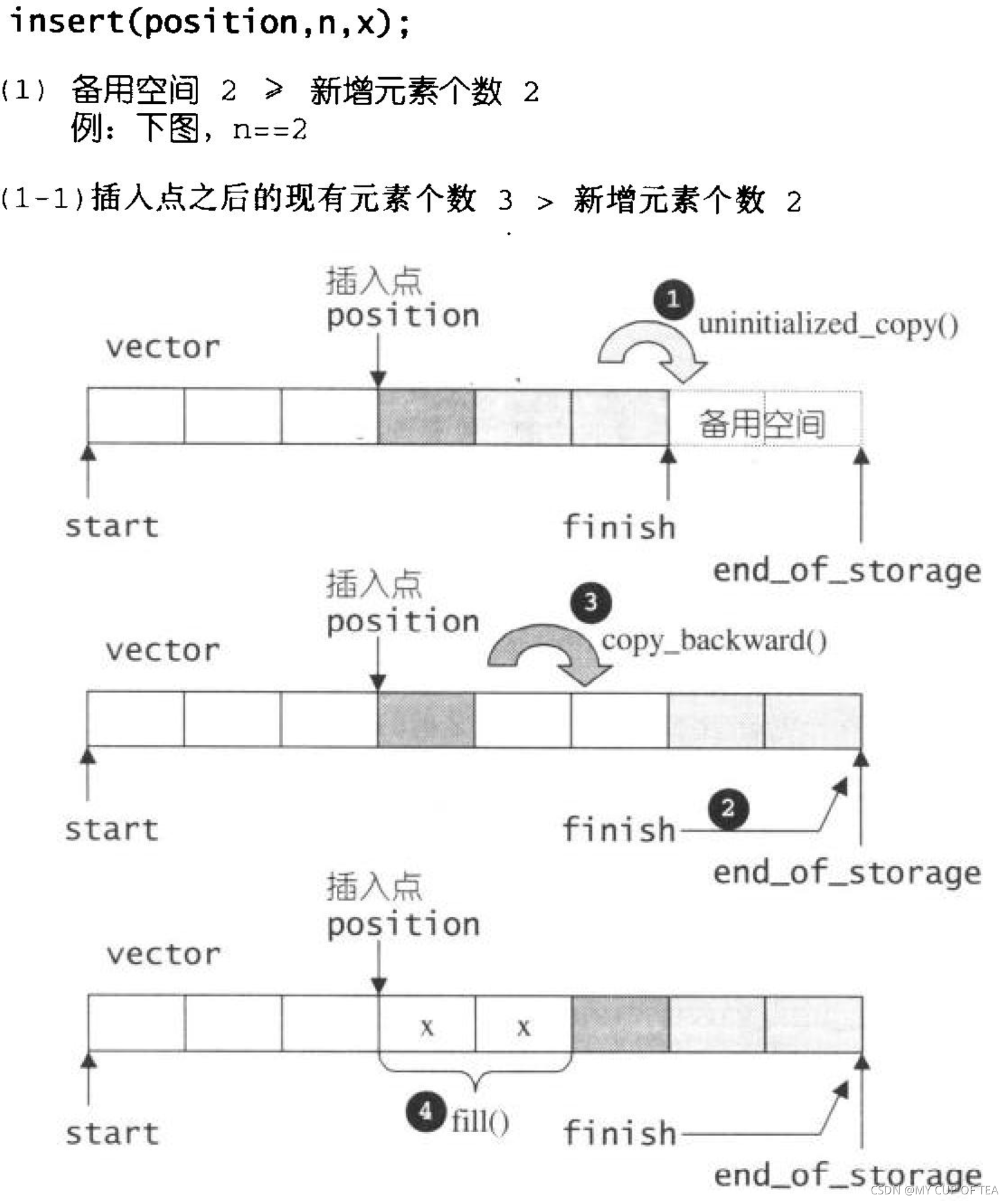
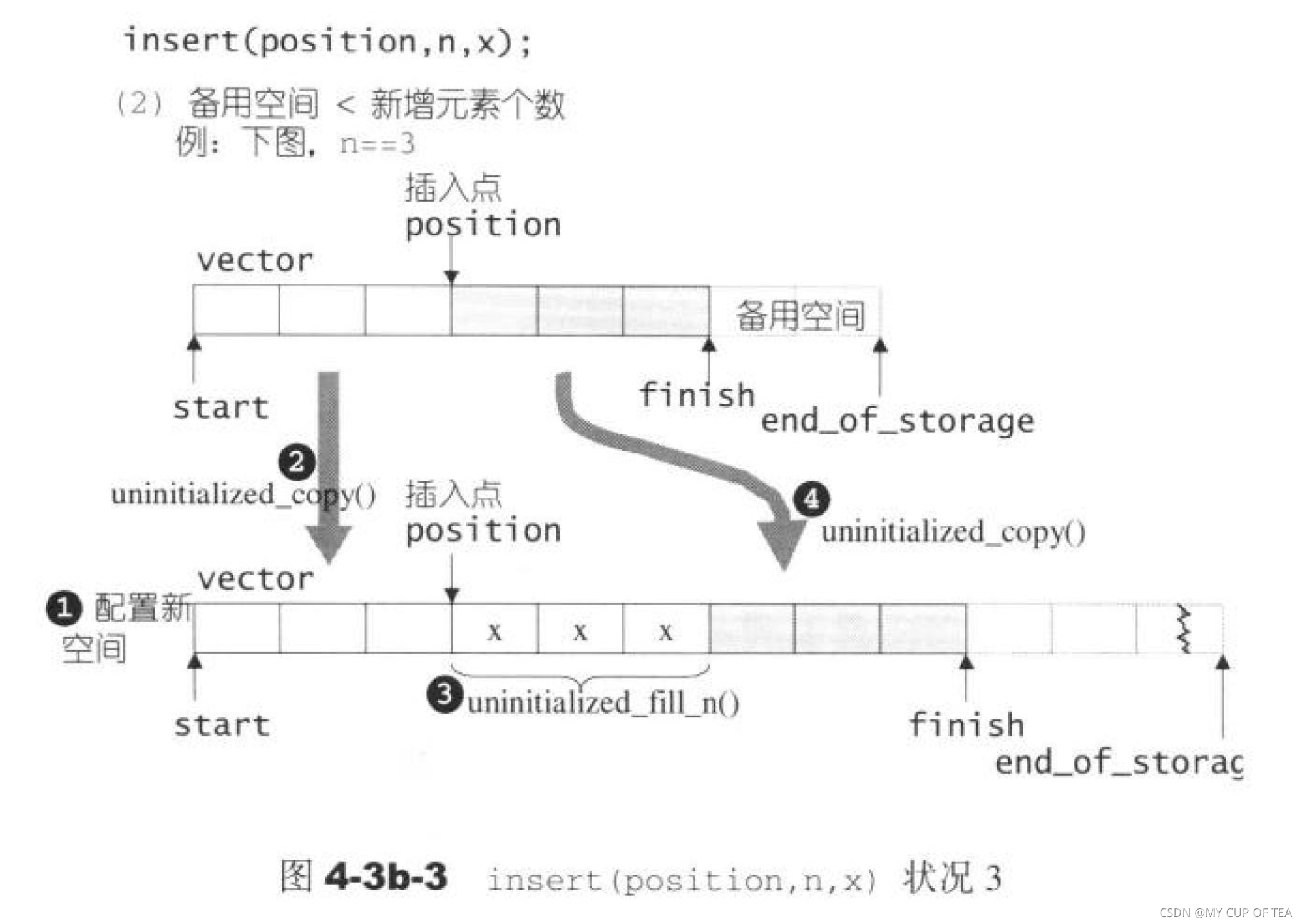
- 這一塊還不是很清晰 需要進一步完善 insert(position,n,x)














作為stack的底層容器)




