目錄
list的節點(node)
list迭代器
?list 的構造和內存管理
list 的元素操作
-
?list相較于vector連續的線性空間就顯得很復雜,他的存儲空間是不連續的,好處是每次插入和刪除一個元素的時候,只需要配置或者釋放一個元素的空間
- 插入和刪除十分的方便
list的節點(node)
- list 本身和list的節點是不同的結構,需要分開設計
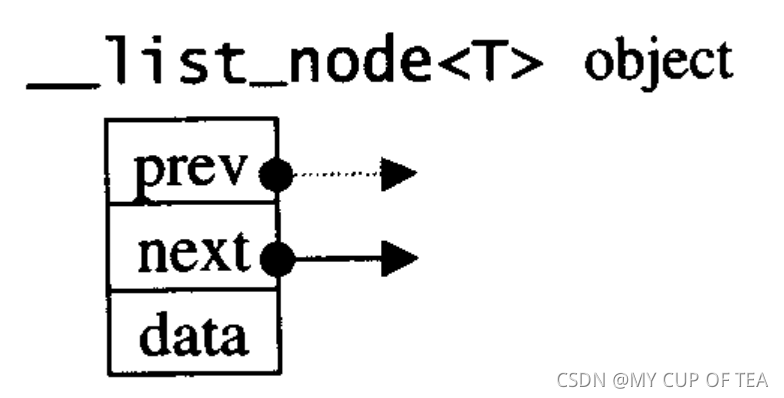
- list節點結構是一個雙向的鏈表
template <class T>
struct __list_node{typedef void* void_pointer;void_pointer prev; //指針的類型是void*,其實可以將其設定為 __list_node<T>void_pointer next; T data;
};
list迭代器
- list迭代器不能像vector一樣使用普通的指針,因為考慮到內存分配的不連續性,list的迭代器必須有能力指向list的的節點,并正確的進行遞增、遞減、取值(獲取成員節點的數據值)、成員的存取(取用的是節點的成員)等操作
- 因為list的迭代器具備前移和后移的能力,所以使用Bidirectional iterators
- list的插入和接合操作(splice)都不會造成原有的list迭代器失效,vector不可以,因為vector插入操作可能造成記憶體的重新配置,會導致原有的迭代器失效
- list刪除元素(erase)也只有指向被刪除元素的那個迭代器會失效,其余的迭代器不會受到任何的影響
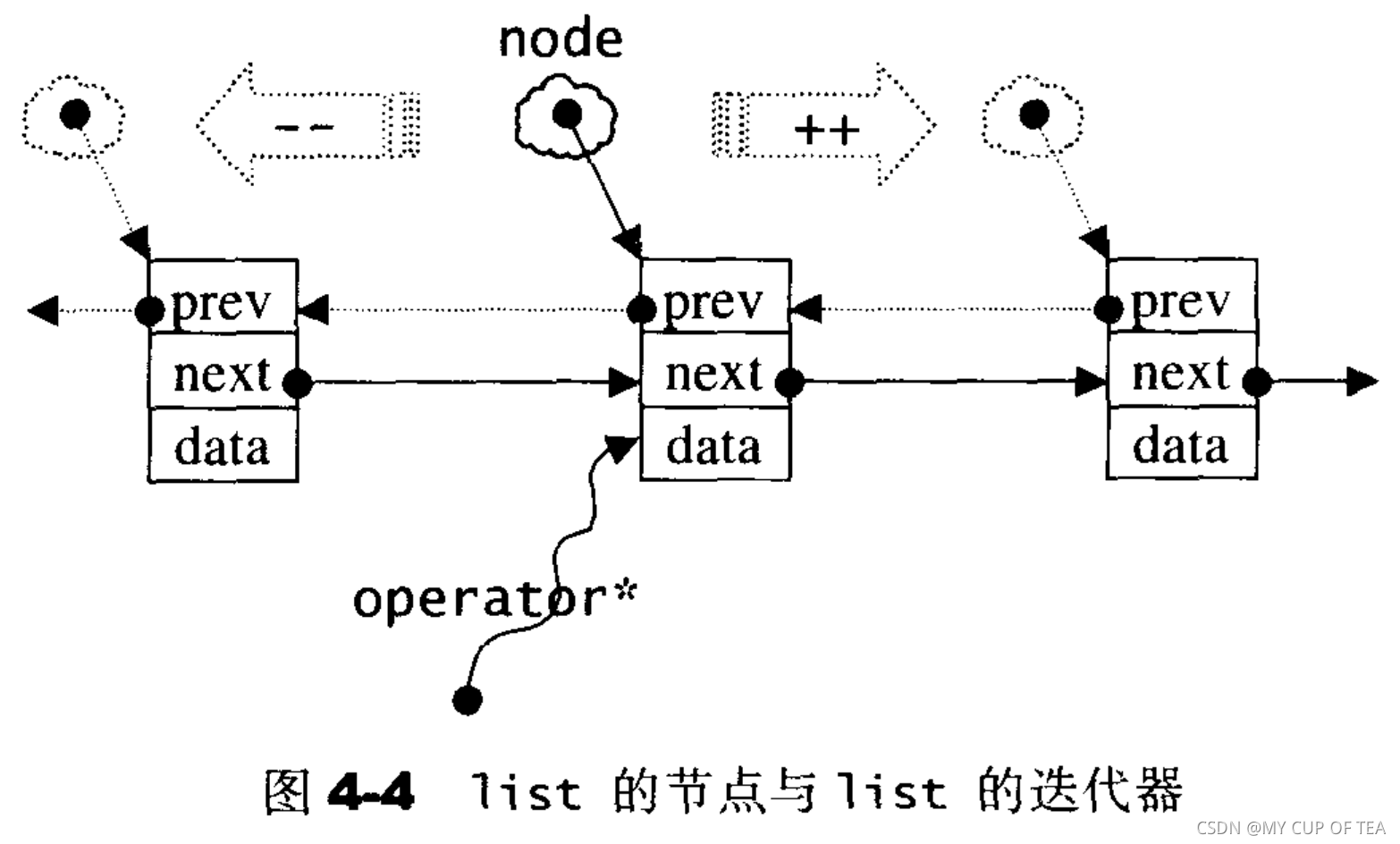
- ?list迭代器設計如下
//list的迭代器設計
template <class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct __list_iterator{typedef __list_iterator<T,T&,T*> iterator;typedef __list_iterator<T,Ref,Ptr> self;typedef std::bidirectional_iterator_tag iterator_category;typedef T value_type;typedef Ptr pointer;typedef Ref reference;typedef __list_node<T>* link_type;typedef std::size_t size_type;typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;link_type node;//迭代器內部需要一個普通的指針,指向list節點//constructor__list_iterator(){}__list_iterator(link_type x):node(x){}__list_iterator(const iterator& x):node(x.node){}bool operator==(const self& x) const{return (node == x.node);}bool operator!=(const self& x) const{return (node != x.node);}//以下對迭代器取值 取得的是節點的數據值reference operator*() const {return (*node).data;}//以下是對迭代器的成員進行存取 (member access) 運算子的標準做法pointer operator->() const {return &(operator*());}//對迭代器進行加一 前進一個節點self& operator++(){node = (link_type)((*node).next);}self operator++(int){self tmp = *this;++*this;return tmp;}//對迭代器進行減一 后退一個節點self& operator--(){node = (link_type)((*node).prev);}self operator--(int){self tmp = *this;--*this;return tmp;}
};list的數據結構
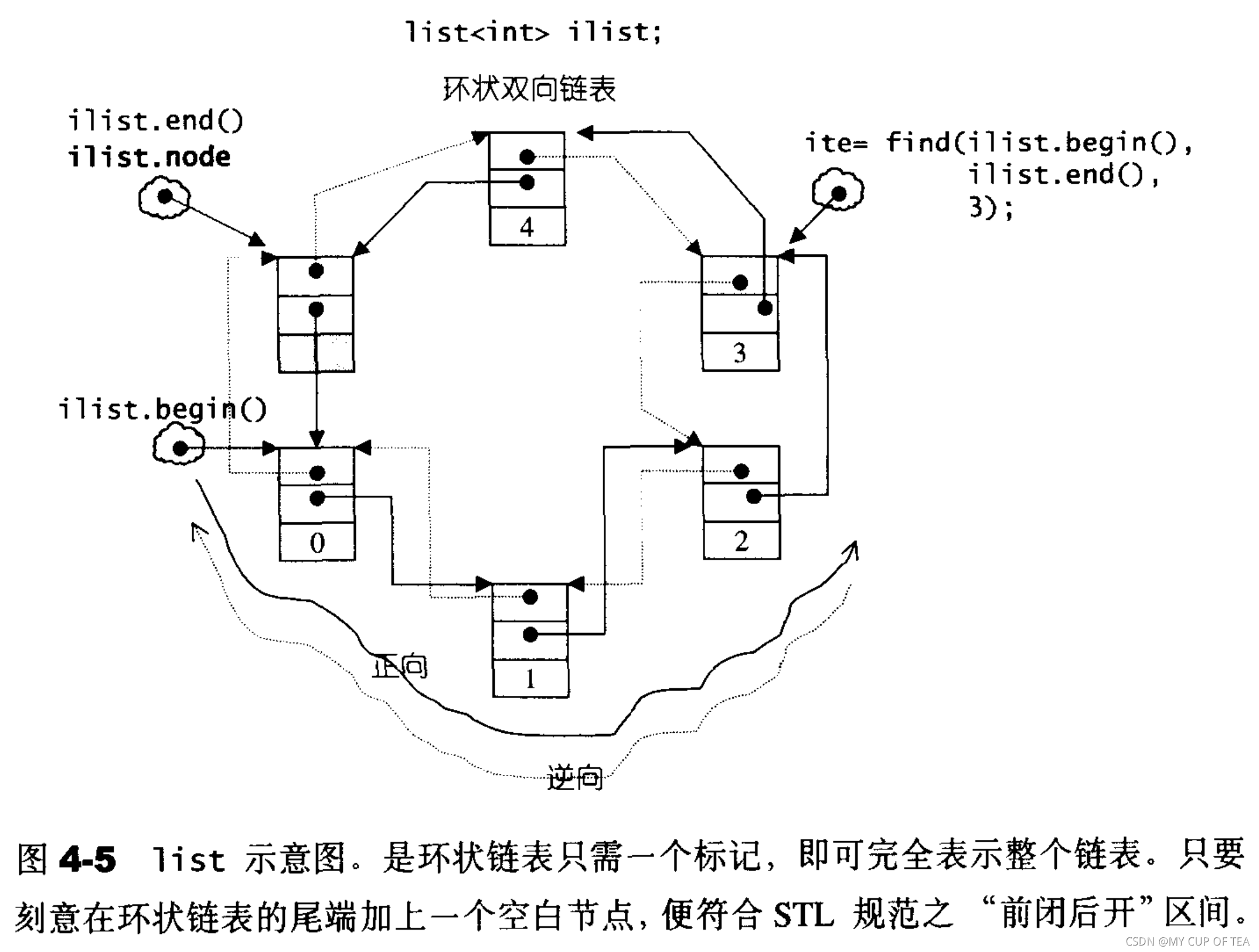
- SGI list不僅僅是雙向鏈表 還是一個環狀雙向鏈表,只需要一個指針就可以完成整個鏈表的遍歷
//list的迭代器設計
template <class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct __list_iterator{typedef __list_iterator<T,T&,T*> iterator;typedef __list_iterator<T,Ref,Ptr> self;typedef std::bidirectional_iterator_tag iterator_category;typedef T value_type;typedef Ptr pointer;typedef Ref reference;typedef __list_node<T>* link_type;typedef std::size_t size_type;typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;link_type node;//迭代器內部需要一個普通的指針,指向list節點//constructor__list_iterator(){}__list_iterator(link_type x):node(x){}__list_iterator(const iterator& x):node(x.node){}bool operator==(const self& x) const{return (node == x.node);}bool operator!=(const self& x) const{return (node != x.node);}//以下對迭代器取值 取得的是節點的數據值reference operator*() const {return (*node).data;}//以下是對迭代器的成員進行存取 (member access) 運算子的標準做法pointer operator->() const {return &(operator*());}//對迭代器進行加一 前進一個節點self& operator++(){node = (link_type)((*node).next);}self operator++(int){self tmp = *this;++*this;return tmp;}//對迭代器進行減一 后退一個節點self& operator--(){node = (link_type)((*node).prev);}self operator--(int){self tmp = *this;--*this;return tmp;}//讓指針node刻意指向尾端的一個空白節點,node節點便會符合STL對于前開后閉區間的要求,成為list迭代器iterator begin(){return (link_type)(*node->next);}iterator end(){return node;}bool empty()const{return node->next == node;}size_type size()const{size_type result = 0;std::distance(begin(),end(),result);return result;}//取頭部節點的內容(元素數值)reference front(){return *begin();}//取尾節點的內容(元素數值)reference back(){return *(--end());}
};
//list 環狀雙向鏈表設計如下
template <class T,class Alloc> //缺省使用alloc作為配置器
class list{
protected:typedef __list_node<T> list_node;
public:typedef list_node* link_type;
protected:link_type node; //只需要一個指針,便可以循環遍歷整個環狀的雙向鏈表
};
?list 的構造和內存管理
- 具體內容見代碼注釋
//list 環狀雙向鏈表設計如下
template <class T,class Alloc> //缺省使用alloc作為配置器
class list{protected:typedef __list_node<T> list_node;//專屬空間配置器 每次配置一個節點的大小
public:typedef list_node* link_type;typedef simple_alloc<list_node,Alloc>list_node_allocator;//list_node_allocator(n) 表示分配n個節點空間,以下四個函數分別用來配置、釋放、構造、銷毀一個節點
protected://配置一個節點并返回link_type get_node(){return list_node_allocator::allocate();}//釋放一個節點link_type put_node(){return list_node_allocator::deallocate();}//產生(配置并構造)一個節點 帶有元素數值link_type create_node(const T& x){link_type p = get_node();Chy::allocator<T>::construct(p->data,x); //全局函數 構造/析構基本工具return p;}//銷毀 (析構并釋放) 一個節點void destroy_node(link_type p){Chy::allocator<T>::destroy(&p->data); //全局函數 構造/析構基本工具}public://構造函數//產生一個空的鏈表list(){empty_initialize();} //產生一個空的鏈表
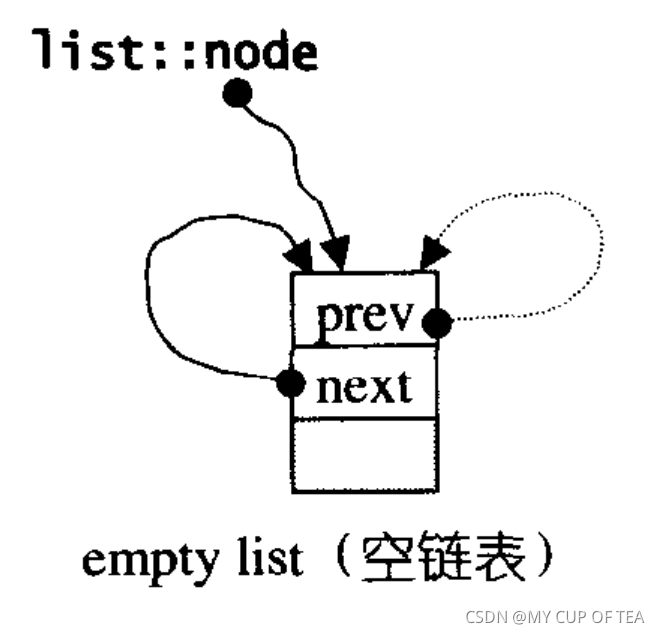
protected:link_type node; //只需要一個指針,便可以循環遍歷整個環狀的雙向鏈表void empty_initialize(){node = get_node(); //配置一個節點空間,令node指向它node->next = node; //令node頭尾指向自己 不設置元素值node->prev = node; }
};
- ?當使用push_back()將新的元素插入到list的尾端的時候 ,這個函數內部調用的是insert();
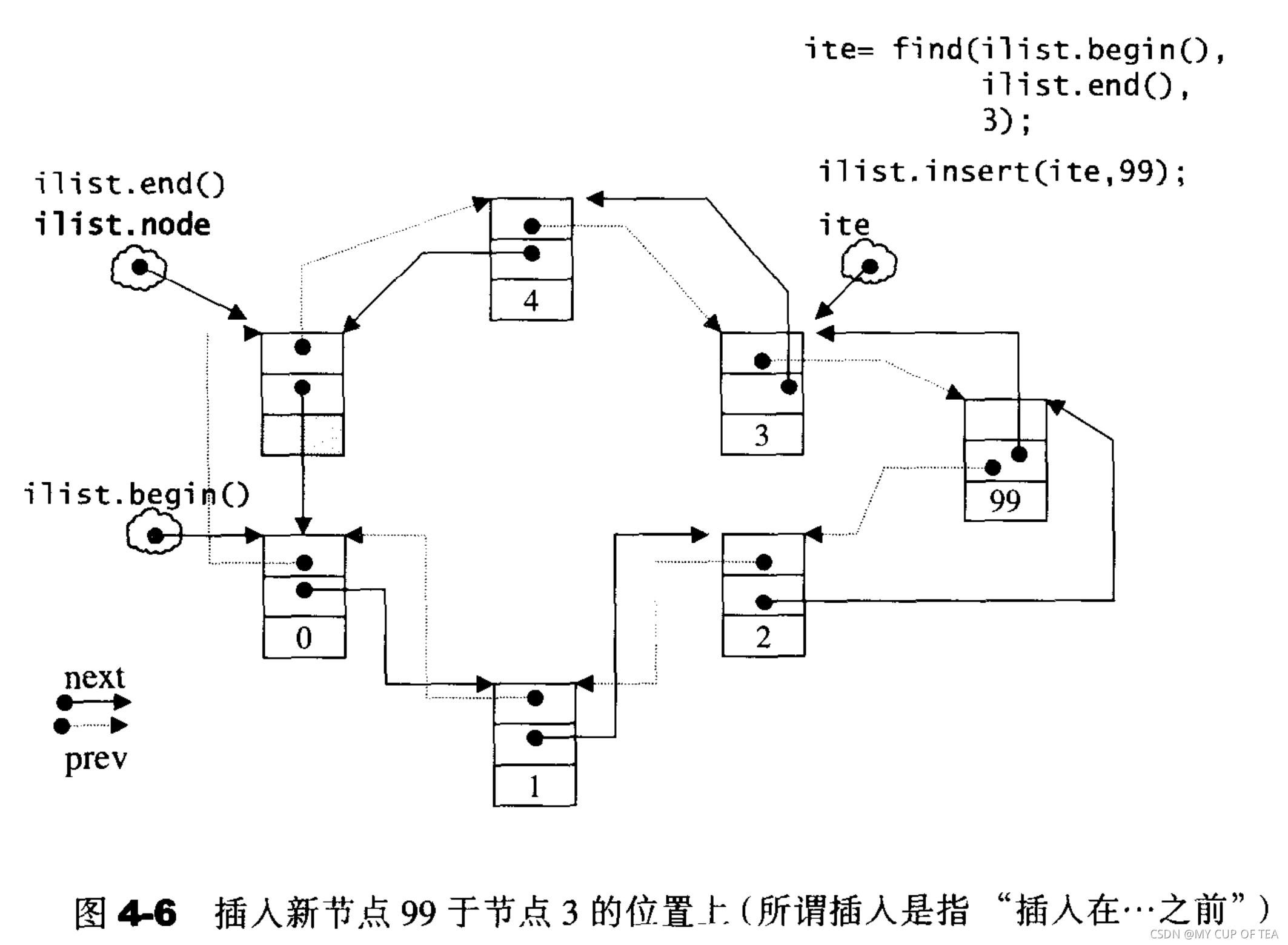
list 的元素操作
//清除所有的節點(整個鏈表)
template <class T,class Alloc>
void list<T,Alloc>::clear() {link_type cur = (link_type)node->next; //begin()while (cur != node){ //遍歷每一個節點link_type tmp = cur;cur = (link_type)cur->next;destroy_node(tmp); //銷毀、析構釋放一個節點}//恢復node的原始狀態node->next = node;node->prev = node;
}//清除數值為value的所有元素
template<class T,class Alloc>
void list<T,Alloc>::remove(const T &value) {typedef typename __list_iterator<T,T&,T*>::iterator iterator;iterator first = __list_iterator<T,T&,T*>::begin();iterator last = __list_iterator<T,T&,T*>::end();while (first != last){iterator next = first;++next;if (*first == value){__list_iterator<T,T&,T*>::erase(value);first = next;}}
}//移除數值相同的連續元素,注意:只有"連續并且相同的元素",才會被刪除只剩一個
template <class T,class Alloc>
void list<T,Alloc>::unique() {typedef typename __list_iterator<T,T&,T*>::iterator iterator;iterator first = __list_iterator<T,T&,T*>::begin();iterator last = __list_iterator<T,T&,T*>::end();if (first == last){return; //空的鏈表 什么都不做}iterator next = first;while(++next != last){ //遍歷每一個節點if (*first == *next){ //如果這個區段中存在相同的元素__list_iterator<T,T&,T*>::erase(next); //移除之} else{first = next; //調整指針}next = first; //修正區段范圍}
}- list是一個雙向的環狀鏈表,只需要處理邊界條件,在頭部和尾部插入和刪除的操作幾乎是一樣的
- 移除(erase) 某個迭代器所指向的元素,只是進行指針移動操作
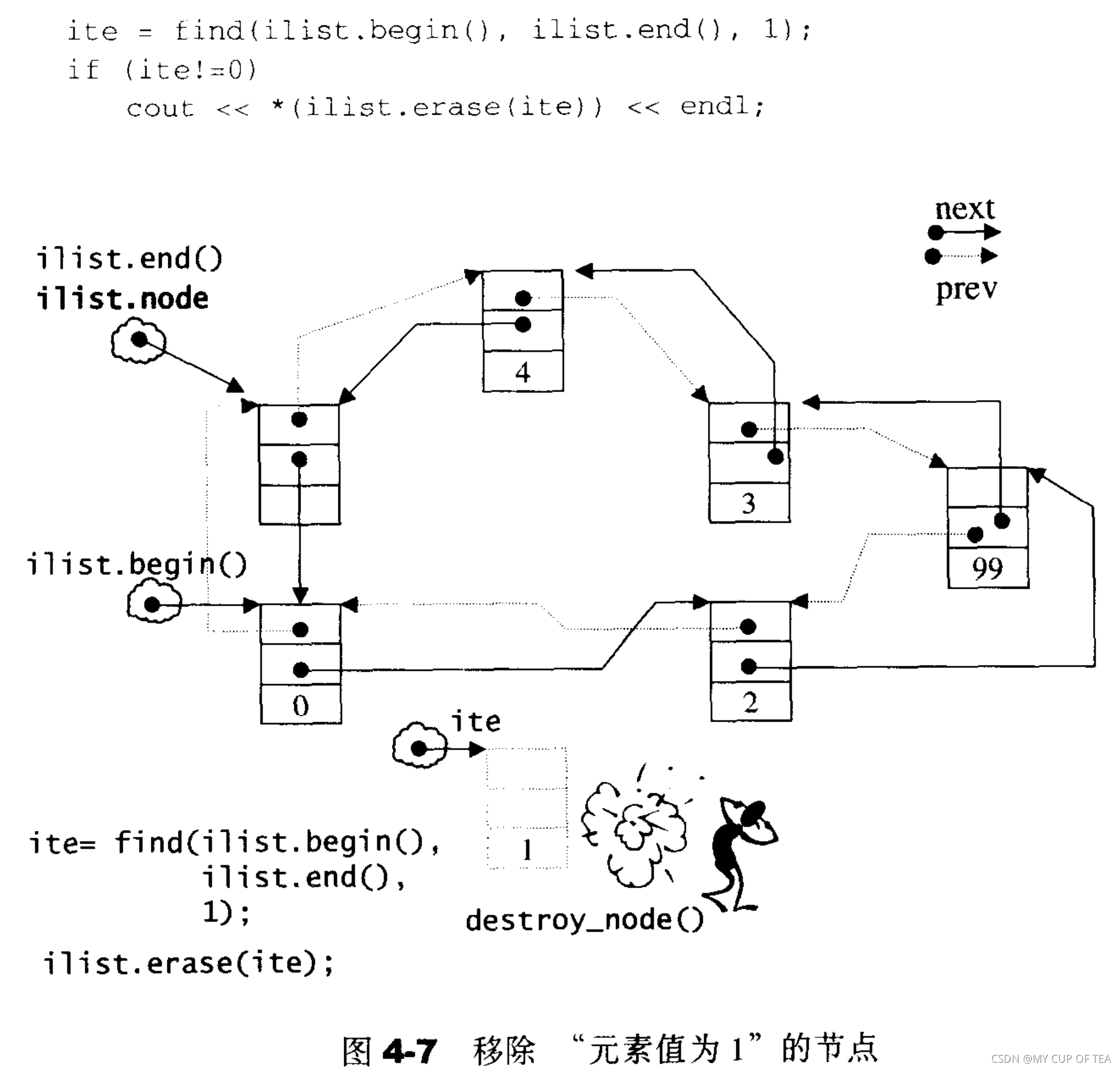
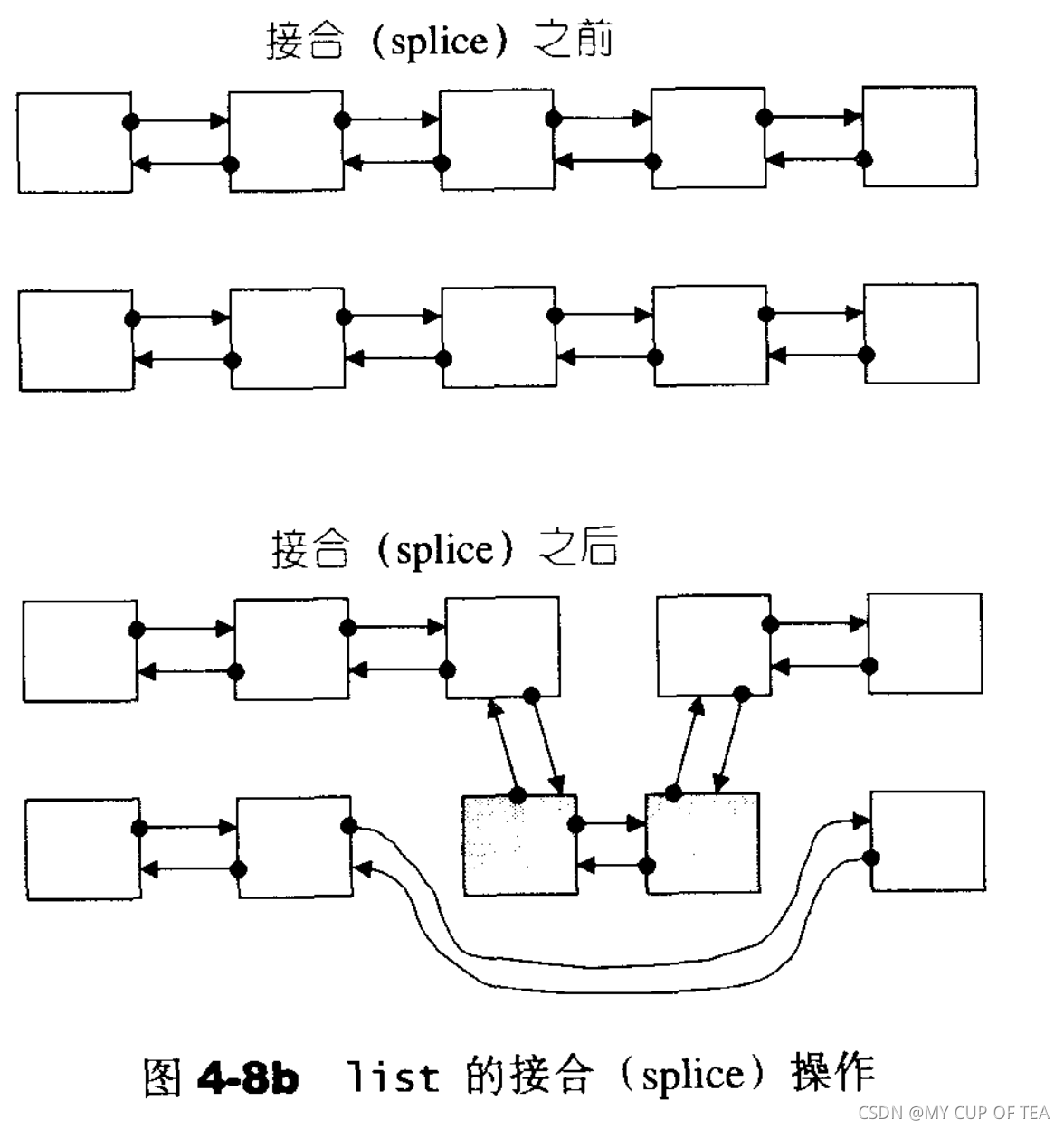
- list提供了一個遷移操作(transfer),將連續范圍的元素遷移到某個特定位置之前,技術角度上講是節點之間的指針移動
- transfer遷移操作 是 其余操作(splice 、 sort 、 merge)的基礎
- transfer的源代碼?

- transfer接收的[first , last)區間可以在同一個list中
- transfer不是公開的接口,list提供的是所謂的接合操作(splice) ,將某聯系范圍的元素從一個list移動到另一個(或者同一個)list的某個定點?
//將[first , last) 內的所有元素 移動到 position之前void transfer(iterator position,iterator first,iterator last){if (last != position){(*(link_type((*last.node).prev))).next = position.node; //1(*(link_type((*first.node).prev))).next = last.node; //2(*(link_type((*position.node).prev))).next = first.node;//3link_type tmp = link_type ((*position.node).prev); //4(*position.node).prev = (*last.node).prev; //5(*last.node).prev = (*first.node).prev; //6(*first.node).prev = tmp; //7}}
- 本質上是節點之間的指針移動,上述splice、reverse、sort函數本身依靠的是transfer函數
- ?完整代碼? 不一定對
#include <iostream>
#include <list>template<class T,class Alloc>
class simple_alloc{
public:static T* allocate(std::size_t n){return 0==n?0:(T*)Alloc::allocate(n * sizeof(T));}static T* allocate(void){return (T*)Alloc::allocate(sizeof (T));}static void deallocate(T* p,size_t n){if (n!=0){Alloc::deallocate(p,n * sizeof(T));}}static void deallocate(T* p){Alloc::deallocate(p,sizeof(T));}
};namespace Chy{template <class T>inline T* _allocate(ptrdiff_t size,T*){std::set_new_handler(0);T* tmp = (T*)(::operator new((std::size_t)(size * sizeof (T))));if (tmp == 0){std::cerr << "out of memory" << std::endl;exit(1);}return tmp;}template<class T>inline void _deallocate(T* buffer){::operator delete (buffer);}template<class T1,class T2>inline void _construct(T1 *p,const T2& value){new(p) T1 (value); //沒看懂}template <class T>inline void _destroy(T* ptr){ptr->~T();}template <class T>class allocator{public:typedef T value_type;typedef T* pointer;typedef const T* const_pointer;typedef T& reference;typedef const T& const_reference;typedef std::size_t size_type;typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;template<class U>struct rebind{typedef allocator<U>other;};pointer allocate(size_type n,const void * hint = 0){return _allocate((difference_type)n,(pointer)0);}void deallocate(pointer p,size_type n){_deallocate(p);}void construct(pointer p,const T& value){_construct(p,value);}void destroy(pointer p){_destroy(p);}pointer address(reference x){return (pointer)&x;}const_pointer const_address(const_reference x){return (const_pointer)&x;}size_type max_size()const{return size_type(UINT_MAX/sizeof (T));}};
}//如果是copy construction 等同于assignment而且destructor 是 trivial以下就會有效
//如果是POD型別 執行的流程就會跳轉到以下函數,這個是通過function template的參數推導機制得到的
template<class ForwardIterator,class Size,class T>
inline ForwardIterator __uninitizlized_fill_n_aux(ForwardIterator first,Size n,const T&x){return fill_n(first,n,x); //交給高階函數執行
}struct __true_type{};
struct __false_type{};template<class T>
struct __type_traits {typedef __true_type this_dummy_member_must_be_first;typedef __false_type has_trivial_default_constructor;typedef __false_type has_trivial_copy_constructor;typedef __false_type has_trivial_assignment_constructor;typedef __false_type has_trivial_destructor;typedef __false_type is_POD_type;
};//函數的邏輯是
//首先萃取出 迭代器first的value type,然后判斷這個型別是否是POD類型
template<class ForwardIterator,class Size,class T,class T1>
inline ForwardIterator __uninitizlized_fill_n(ForwardIterator first,Size n,const T&x,T1*){//以下使用的是__type_traits<T1>::is_POD_type is _PODtypedef typename __type_traits<T1>::is_POD_type is_POD;return __uninitizlized_fill_n_aux(first,n,x,is_POD());
}template<class ForwardIterator,class Size,class T>
ForwardIterator uninitialized_fill_n(ForwardIterator first,Size n,const T&x){return __uninitizlized_fill_n(first,n,x,value_type(first));//使用value_type()判斷first的value type
}//list的節點結構設計
template <class T>
struct __list_node{typedef void* void_pointer;void_pointer prev; //指針的類型是void*,其實可以將其設定為 __list_node<T>void_pointer next;T data;
};//list的迭代器設計
template <class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct __list_iterator{typedef __list_iterator<T,T&,T*> iterator;typedef __list_iterator<T,Ref,Ptr> self;typedef std::bidirectional_iterator_tag iterator_category;typedef T value_type;typedef Ptr pointer;typedef Ref reference;typedef __list_node<T>* link_type;typedef std::size_t size_type;typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;link_type node;//迭代器內部需要一個普通的指針,指向list節點//constructor__list_iterator(){}__list_iterator(link_type x):node(x){}__list_iterator(const iterator& x):node(x.node){}bool operator==(const self& x) const{return (node == x.node);}bool operator!=(const self& x) const{return (node != x.node);}//以下對迭代器取值 取得的是節點的數據值reference operator*() const {return (*node).data;}//以下是對迭代器的成員進行存取 (member access) 運算子的標準做法pointer operator->() const {return &(operator*());}//對迭代器進行加一 前進一個節點self& operator++(){node = (link_type)((*node).next);}self operator++(int){self tmp = *this;++*this;return tmp;}//對迭代器進行減一 后退一個節點self& operator--(){node = (link_type)((*node).prev);}self operator--(int){self tmp = *this;--*this;return tmp;}};//list 環狀雙向鏈表設計如下
template <class T,class Alloc> //缺省使用alloc作為配置器
class list{protected:typedef typename __list_iterator<T,T&,T*>::iterator iterator;typedef typename __list_iterator<T,T&,T*>::value_type value_type;typedef typename __list_iterator<T,T&,T*>::reference reference;typedef typename __list_iterator<T,T&,T*>::size_type size_type;typedef __list_node<T> list_node;//專屬空間配置器 每次配置一個節點的大小
public:typedef list_node* link_type;typedef simple_alloc<list_node,Alloc>list_node_allocator;//list_node_allocator(n) 表示分配n個節點空間,以下四個函數分別用來配置、釋放、構造、銷毀一個節點
protected://配置一個節點并返回link_type get_node(){return list_node_allocator::allocate();}//釋放一個節點link_type put_node(){return list_node_allocator::deallocate();}//產生(配置并構造)一個節點 帶有元素數值link_type create_node(const T& x){link_type p = get_node();Chy::allocator<T>::construct(p->data,x); //全局函數 構造/析構基本工具return p;}//銷毀 (析構并釋放) 一個節點void destroy_node(link_type p){Chy::allocator<T>::destroy(&p->data); //全局函數 構造/析構基本工具}public://讓指針node刻意指向尾端的一個空白節點,node節點便會符合STL對于前開后閉區間的要求,成為list迭代器iterator begin(){return (link_type)(*node->next);}iterator end(){return node;}bool empty()const{return node->next == node;}size_type size()const{size_type result = 0;std::distance(begin(),end(),result);return result;}//取頭部節點的內容(元素數值)reference front(){return *begin();}//取尾節點的內容(元素數值)reference back(){return *(--end());}//插入元素 供push_back()函數調用//insert函數 需要配置并構造一個節點,然后在尾端進行指針操作,將新的節點插入進去//函數的目的是為了在迭代器指定的位置插入一個節點,內容為xiterator insert(iterator position,const T&x){ //產生一個節點,默認初始化元素數值為xlink_type tmp = create_node(x);//調整雙指針 將tmp插入進去tmp->next = position.node;tmp->prev = position.node->prev;(link_type(position.node->prev))->next = tmp;position.node->prev = tmp;return tmp;}//插入一個節點 作為頭部節點void push_front(const T& x){insert(begin(),x);}//插入一個節點 作為尾節點void push_back(const T& x){insert(end(),x);}//移除迭代器position指向的節點iterator erase(iterator position){link_type next_node = link_type (position.node->next);link_type prev_node = link_type (position.node->prev);prev_node->next = next_node;next_node->prev = prev_node;destroy_node(position.node);return iterator (next_node);}//移除頭部節點void pop_front(){erase(begin());}//移除尾部節點void pop_back(){iterator tmp = end();erase(--tmp);}//將[first , last) 內的所有元素 移動到 position之前void transfer(iterator position,iterator first,iterator last){if (last != position){(*(link_type((*last.node).prev))).next = position.node; //1(*(link_type((*first.node).prev))).next = last.node; //2(*(link_type((*position.node).prev))).next = first.node;//3link_type tmp = link_type ((*position.node).prev); //4(*position.node).prev = (*last.node).prev; //5(*last.node).prev = (*first.node).prev; //6(*first.node).prev = tmp; //7}}public://構造函數//產生一個空的鏈表list(){empty_initialize();} //產生一個空的鏈表void clear();void remove(const T& value);void unique();protected:link_type node; //只需要一個指針,便可以循環遍歷整個環狀的雙向鏈表//空初始化void empty_initialize(){node = get_node(); //配置一個節點空間,令node指向它node->next = node; //令node頭尾指向自己 不設置元素值node->prev = node;}public://將x結合于position所指定位置之前 x必須不同于*thisvoid splice(__list_iterator<T, T &, T *>, list &x);//將i指向的元素結合于position所指定的位置之前。position和i可以指向同一個listvoid splice(iterator position,list& ,iterator i){iterator j = i;++j;if (position == i || position == j){return;}transfer(position,i,j);}//將[first,last)內的元素接合于position指定的位置之前//position 和 [first,last)內可能指向的是同一個list//但是position 不能位于 [first,last)內部void splice(iterator position,list &,iterator first,iterator last){if (first != last){transfer(position,first,last);}}//merage() 將x合并到*this身上,但是兩個lists的內容都必須要先經過遞增排序void meage(list& x){iterator first1 = begin();iterator last1 = end();iterator first2 = x.begin();iterator last2 = x.end();//兩個list實現需要經過排序while (first1 != last1 && first2 != last2){if (*first2 < *first1){iterator next = first2;transfer(first1,first2,++next);first2 = next;} else{++first1;}if (first2 != last2){transfer(last1,first2,last2);}}}//reverse() 將this的內容 逆向重置void reverse(){//以下判斷,如果是空的鏈表,或者僅僅只有一個元素,就不進行任何的操作//使用size() == 0 || size() == 1 判斷,速度較慢if (node->next == node ||link_type(node->next)->next == node)return;iterator first = begin();++first;while (first != end()){iterator old = first;++first;transfer(begin(),old,first);}}//list不能使用STL算法的sort() 因為STL算法只接受randomAccessIterator//本函數使用快速排序void sort(){//以下判斷,如果是空的鏈表,或者僅僅只有一個元素,就不進行任何的操作//使用size() == 0 || size() == 1 判斷,速度較慢if (node->next == node ||link_type(node->next)->next == node)return;//使用一些新的lists 作為中介數據存儲區list carry;list counter[64];int fill = 0;while (!empty()){carry.splice(carry.begin(),*this,begin());int i = 0;while (i < fill && !counter[i].empty()){counter[i].merage(carry);carry.swap(counter[i++]);}carry.swap(counter[i]);if (i == fill){++fill;}}for (int i = 1; i < fill; ++i) {counter[i].merage(counter[i-1]);}std::swap(counter[fill-1]);}
};//清除所有的節點(整個鏈表)
template <class T,class Alloc>
void list<T,Alloc>::clear() {link_type cur = (link_type)node->next; //begin()while (cur != node){ //遍歷每一個節點link_type tmp = cur;cur = (link_type)cur->next;destroy_node(tmp); //銷毀、析構釋放一個節點}//恢復node的原始狀態node->next = node;node->prev = node;
}//清除數值為value的所有元素
template<class T,class Alloc>
void list<T,Alloc>::remove(const T &value) {typedef typename __list_iterator<T,T&,T*>::iterator iterator;iterator first = __list_iterator<T,T&,T*>::begin();iterator last = __list_iterator<T,T&,T*>::end();while (first != last){iterator next = first;++next;if (*first == value){__list_iterator<T,T&,T*>::erase(value);first = next;}}
}//移除數值相同的連續元素,注意:只有"連續并且相同的元素",才會被刪除只剩一個
template <class T,class Alloc>
void list<T,Alloc>::unique() {typedef typename __list_iterator<T,T&,T*>::iterator iterator;iterator first = __list_iterator<T,T&,T*>::begin();iterator last = __list_iterator<T,T&,T*>::end();if (first == last){return; //空的鏈表 什么都不做}iterator next = first;while(++next != last){ //遍歷每一個節點if (*first == *next){ //如果這個區段中存在相同的元素__list_iterator<T,T&,T*>::erase(next); //移除之} else{first = next; //調整指針}next = first; //修正區段范圍}
}template <class T,class Alloc>
void list<T,Alloc>::splice(__list_iterator<T, T &, T *>position, list<T, Alloc> &x) {if (!x.empty()){transfer(position,x.begin(),x.end());}
}- 涉及到transfer的相關函數的代碼 理解不是很透徹 垃圾











作為stack的底層容器)







![python從小白到大牛百度云盤_Java從小白到大牛 (關東升著) 中文pdf+mobi版[36MB]](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/python從小白到大牛百度云盤_Java從小白到大牛 (關東升著) 中文pdf+mobi版[36MB])