- vector是單向開口的連續線性空間,deque是一種雙向開口的連續線性空間。
- deque可以在頭尾兩端分別進行元素的插入和刪除操作
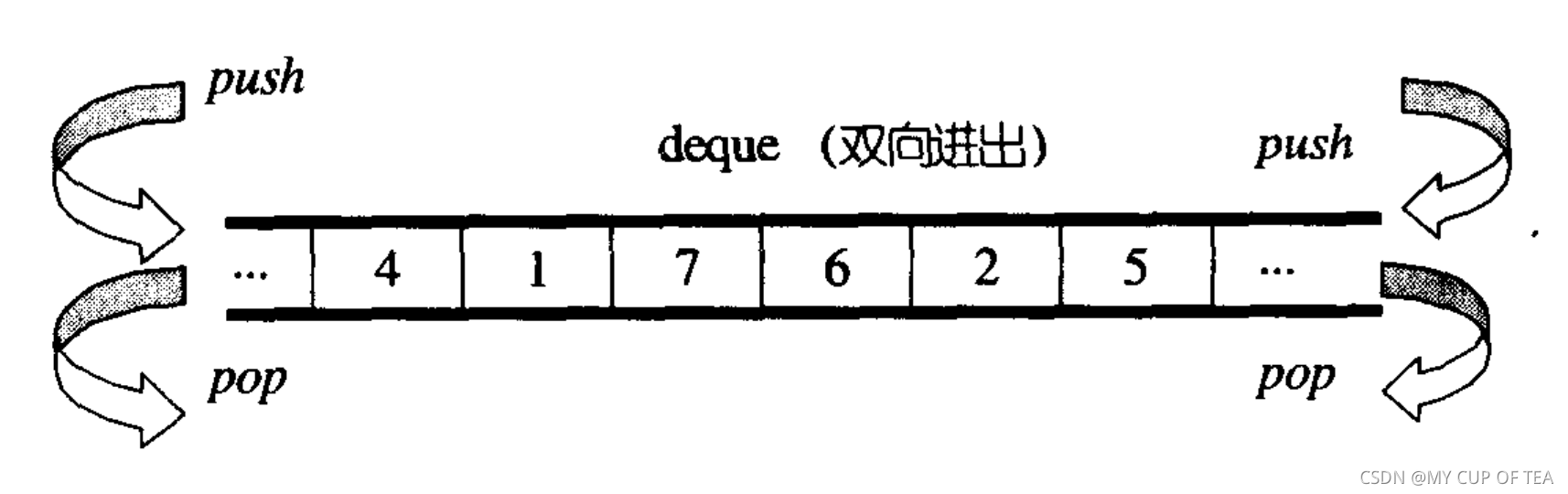
- ?vector和deque的差異
- 1,deque允許常數時間內對于頭端元素進行插入和刪除操作
- 2,deque沒有所謂容量(capacity)的概念,因為它是動態的以分段連續空間組合而成的,隨時可以增加一段空間,將其銜接起來。deque不會發生vector那樣的“因舊的空間不足而重新配置一段內存區間,然后進行元素的復制和舊的空間的釋放”,因此deque不具備所謂的空間保留的能力,也就是reverse
- 雖然deque也提供Random Access Iterator,但是他的迭代器不是普通的指針,其復雜度較高,如果可以使用vector就不要使用deque
- 對于deque進行的排序操作,為了較高的效率,可以將deque先完整復制到一個vector內部,進行排序(STL sort算法) 再復制回deque
- deque由一段一段的定量連續的空間構成。如果需要擴展空間,需要先配置一段定量的連續空間,將其串聯在deque的頭部或者尾部。deque的最大的任務就是在這些分段的定量的連續空間上,維護其整體連續的假象,并提供隨機存取的接口,相較于vector只能向尾端成長的假象,實際需要進行“重新配置、復制、釋放”的輪回操作而言,代價是需要設計 復雜的迭代器架構
- deque使用分段連續性空間,是需要一個中央控制器進行統一調控,但是為了維持整體連續的假象,數據結構的設計和迭代器的前進和后退操作等頗為繁瑣
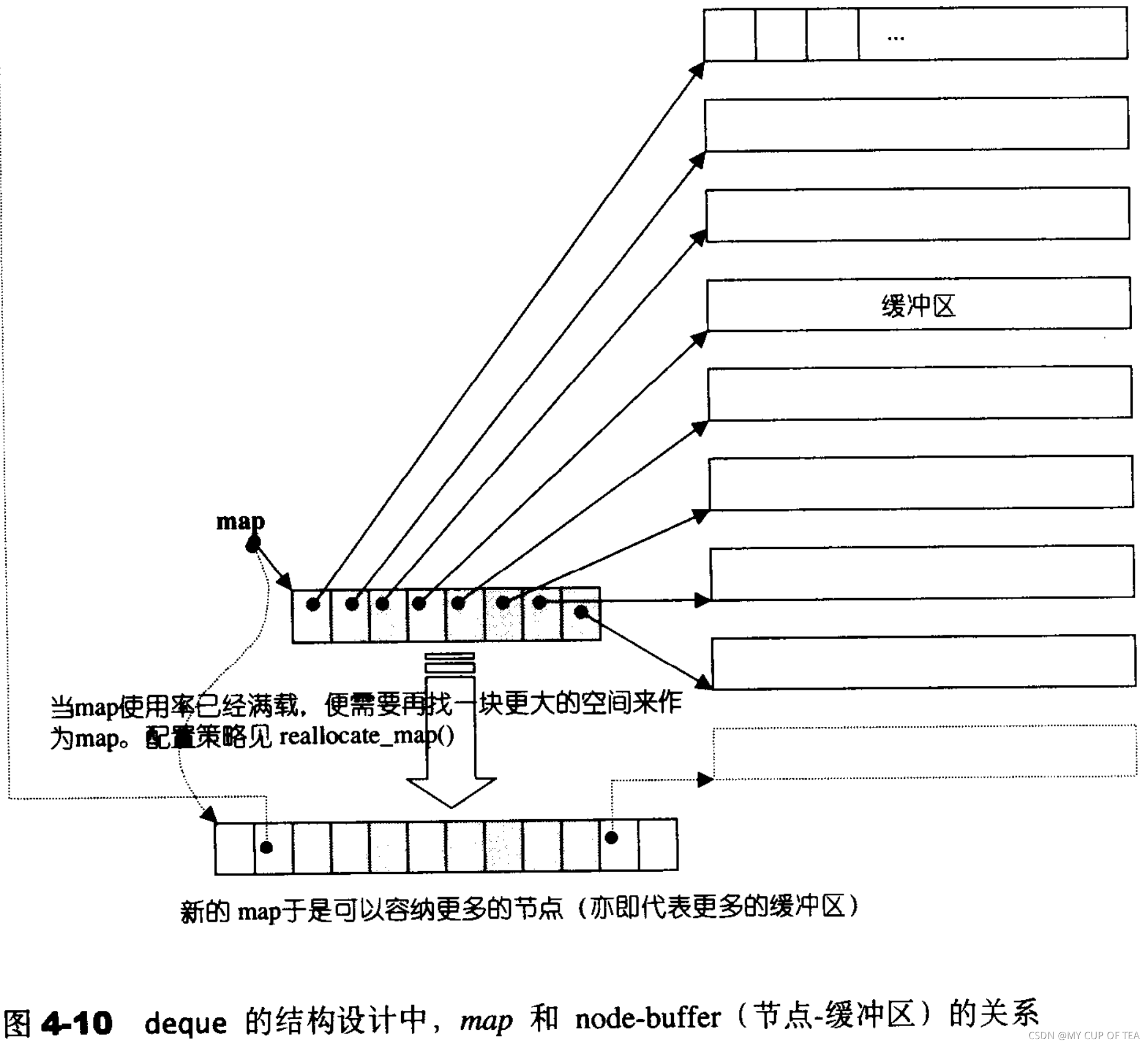
- deque采用一塊所謂的map (這里不是指STL map容器)作為主控,這里的map是指一段連續的空間,其中每個元素(此處稱為一個節點,node)都是指針,指向的是一段(較大的)連續內存空間,稱其為緩沖區。
- deque的存儲空間的主體是 緩沖區
- SGI STL允許我們指定緩沖區的大小,默認值0表示使用512bytes緩沖區
- map本質是 T** ,即指針的指針,指向的是型別為T的一塊空間
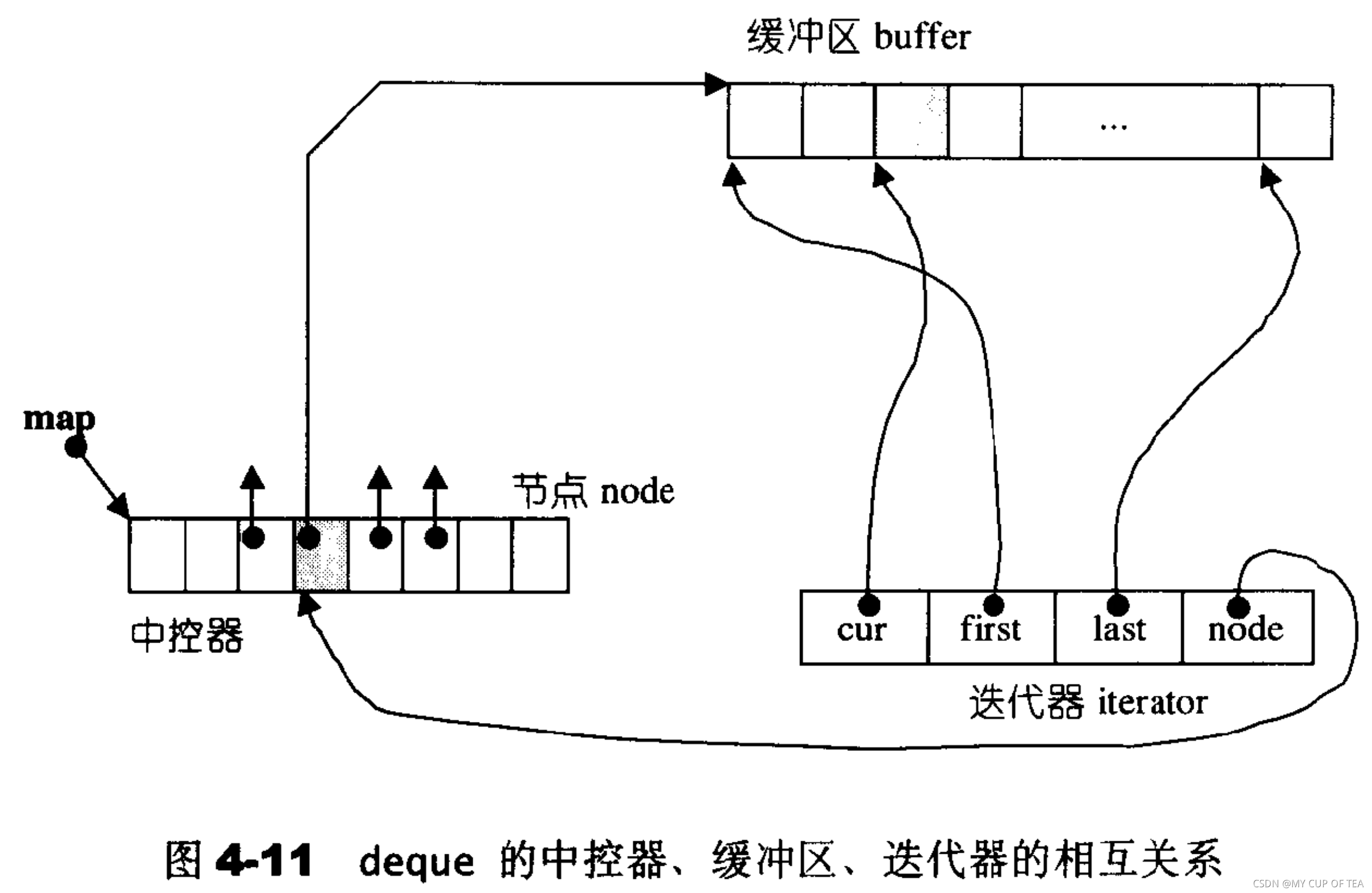
?deque迭代器
- deque是分段連續的空間。需要維持其整體連續的假象的任務是通過operator++和operator--兩個運算子實現的
- 迭代器應該具備什么結構呢?從功能點分析:1,指出分段連續空間(緩沖區)在哪里,從而判斷自己是否已經處于緩沖區的邊界處,一旦前進或者后退就必須跳躍至下一個或者上一個緩沖區。為了可以正確跳躍,需要隨之掌控 控制中心(map)
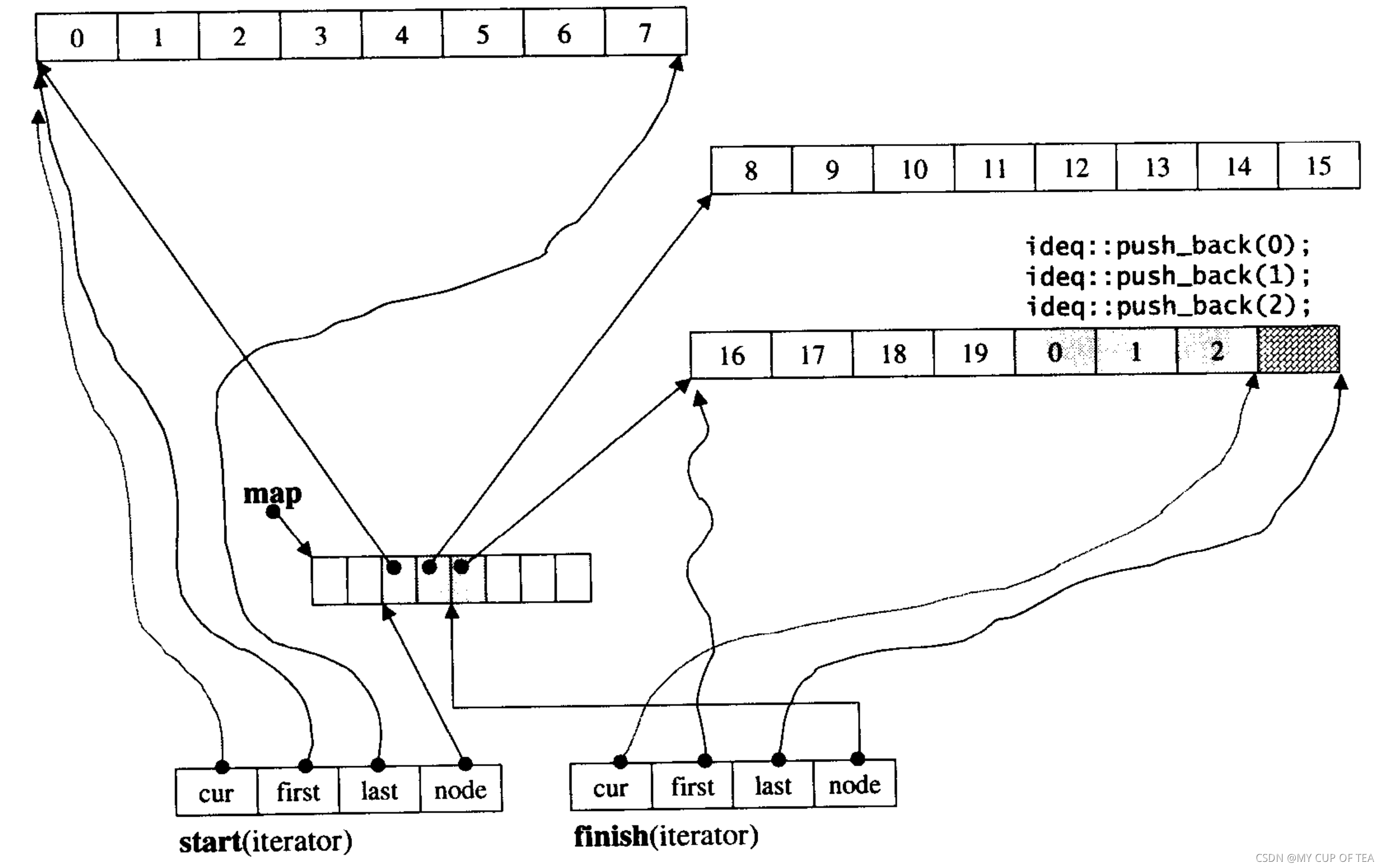
- ?假設產生一個deque<int>令其緩沖區的大小為32,那么每個緩沖區可以容納的元素個數是 32/sizeof(int) =8個元素。假設deque存儲20個元素,需要20/8=3個緩沖區,所以map中控節點需要使用3個節點。
- 迭代器start內的cur指針當然指向緩沖區的第一個元素,迭代器finish內的cur指針指向的是第三個緩沖區的最后元素(的下一個位置)。考慮到最后一個緩沖區尚有備用的空間,如果有新的元素插入到尾端,可以直接使用這個備用空間。
- 陰影區域表示? 還存在四個區域尚未使用
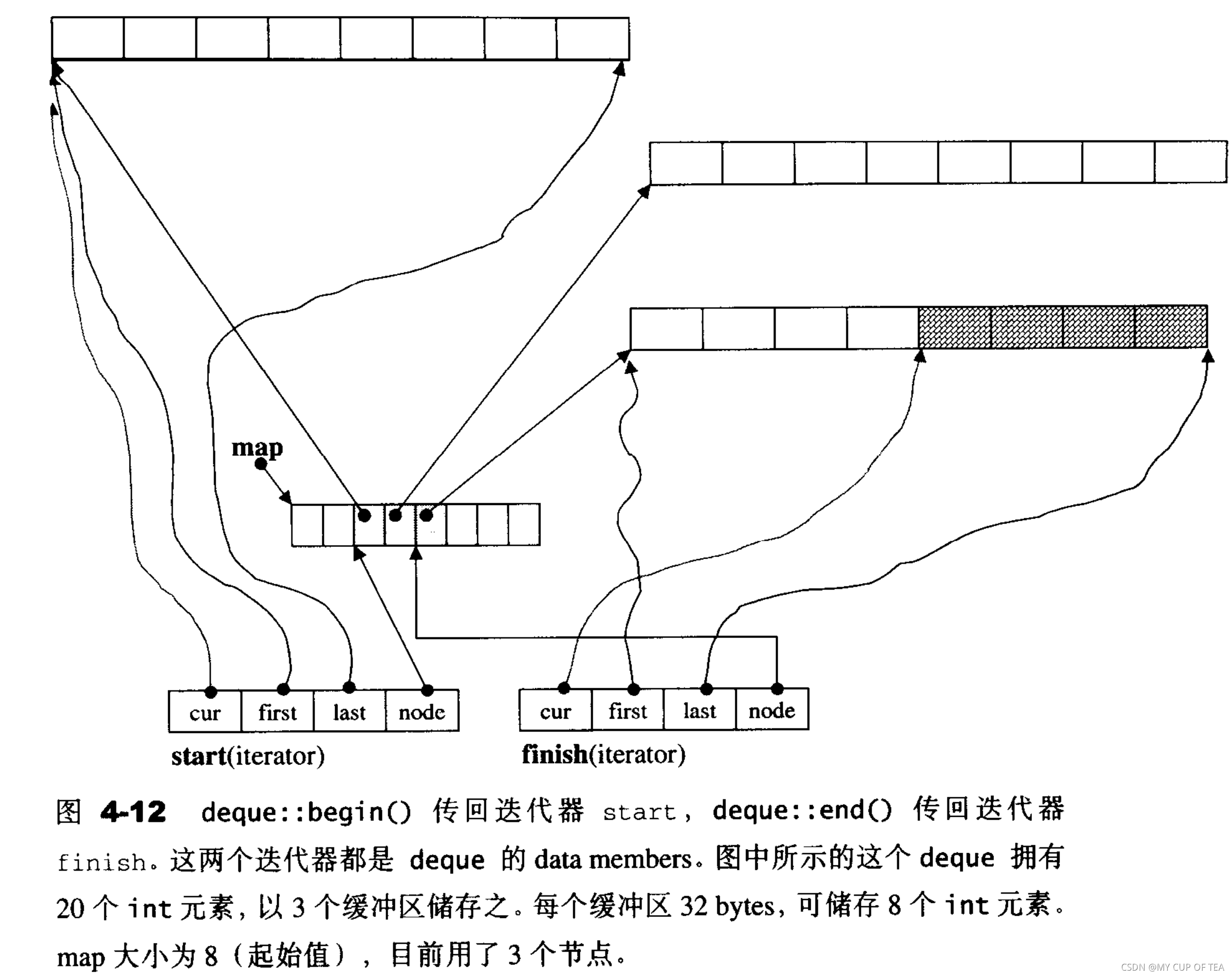
- 對于各個指針的運算比如加、減、前進、后退都不可以直觀看到。
- 最關鍵的是:一旦行進的時候遇到緩沖區邊緣,需要特別當心,需要視前進后退而定,可能需要使用set_node函數跳一個緩沖區
- 雙端隊列的迭代器的代碼
/** 如果n不為0,傳回n,表示buffer size由用戶自定義* 如果n為0,表示buffer size使用的是默認數值,那么* 如果sz(元素的大小,sizeof(value_type))小于512,傳回 512/sz* 如果sz不小于512,傳回1*/
inline std::size_t __deque_buf_size(std::size_t n,std::size_t sz){return n!=0 ? n : (sz < 512 ? std::size_t (512/sz):std::size_t(1));
}//雙端隊列 迭代器
template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr,std::size_t BufSiz>
struct __deque_iterator{ //未繼承 std::iteratortypedef __deque_iterator<T,T&,T*,BufSiz> iterator;typedef __deque_iterator<T,const T&,const T*,BufSiz> const_iterator;static std::size_t buffer_size() {return __deque_buf_size(BufSiz,sizeof (T));}//未繼承 std::iterator,所以需要自行撰寫五個必要的迭代器對應的類別typedef std::random_access_iterator_tag iterator_category;//1typedef T value_type; //2typedef Ptr pointer; //3typedef Ref reference; //4typedef std::size_t size_type;typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type; //5typedef T** map_pointer;typedef __deque_iterator self;//保持和容器的聯結T* cur; //此迭代器所指向的緩沖區的現行(current)元素T* first; //此迭代器所指之緩沖區的頭T* last; //此迭代器所指之緩沖區的尾 (含備用空間)map_pointer node;//指向管控中心public:void set_node(map_pointer new_node){node = new_node;first = *new_node;last = first + difference_type (buffer_size());}//重載各個運算子 __deque_iterator<> 成功運作的關鍵reference operator*() const {return *cur;}pointer operator->() const {return &(operator*());}difference_type operator-(const self& x) const{return difference_type (buffer_size()) * (node - x.node - 1) +(cur - first) + (x.last - x.cur);}//參考More Effective C++//Distinguish between prefix and postfix of increment and decrement operators//注意last指向的是最后一個節點的后面,所以先遞增再判斷self& operator++(){++cur; //切換至下一個元素if (cur==last){ //如果已經到達所在緩沖區的尾端set_node(node+1);//切換至下一個節點 (亦 即緩沖區的第一個元素)cur = first;}return *this;}self& operator++(int){ //后置式 標準寫法self tmp = *this;++*this; //調用self& operator++()return tmp;}//first指向的是最后一個節點,所以需要先進行判斷self& operator--(){if (cur == first){ //如果已經到達所在緩沖區的頭端set_node(node-1);//切換至前一個節點(亦即緩沖區)的最后一個元素cur = last;}--cur; //切換至前一個元素return *this;}self& operator--(int){ //后置式 標準寫法self tmp = *this;--*this;return tmp;}//以下代碼實現隨機存取,迭代器直接跳過 n 個距離self& operator+=(difference_type n){difference_type offset = n + (cur - first);if (offset >= 0 && offset < difference_type(buffer_size())){//目標位置在同一緩沖區內cur += n;} else{//目標位置不在同一個緩沖區內difference_type node_offset = offset > 0 ? offset / difference_type(buffer_size()): -difference_type ((-offset - 1) / buffer_size()) - 1;//切換到正確的節點(即對應的緩沖區)set_node(node+node_offset);//切換至正確的元素cur = first+(offset - node_offset * difference_type(buffer_size()));}return *this;}//參考More Effective C++ item22//consider using op= instead of stand-alone opself operator+(difference_type n) const{self tmp = *this;return tmp += n; //調用operator+=}//通過使用operator+= 完成operator-=self& operator-=(difference_type n){return *this += -n;}self operator-(difference_type n)const{self tmp = *this;return tmp -= n;//調用operator-=}//以下實現隨機存取,迭代器可以直接跳躍n個距離reference operator[](difference_type n)const {//以上調用operator* ,operator+return *(*this + n);}bool operator==(const self& x)const{ return cur == x.cur;}bool operator!=(const self& x)const{ return cur != x.cur;}bool operator< (const self& x)const{return (node == x.node) ? (cur < x.cur) : (node < x.node);}
};deque的數據結構
- deque除了需要維護一個先前說過的指向map的指針外,也需要維護start和finish兩個迭代器,分別指向第一緩沖區的第一個元素和最后緩沖區的最后一個元素(的下一個位置)
- 注意:還需要記住此刻的map的大小,因為一旦map所提供的節點不足,就需要重新配置更大的一塊map
//雙端隊列
template<class T,class Alloc,std::size_t BufSiz = 0>
class deque{
public: //Basic typestypedef T value_type;typedef value_type* pointer;typedef value_type& reference;typedef std::size_t size_type;typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type; public:typedef __deque_iterator<T,T&,T*,BufSiz> iterator;protected: //Internal typedefs//元素的指針的指針 (pointer of pointer of T)typedef pointer* map_pointer;protected: //Data membersmap_pointer map; //指向map,map是塊連續空間,其內部的每個元素都是一個指針(稱為節點),//指向的是一塊緩沖區std::size_t map_size; //map內可以容納多少指針iterator start; //指向的是第一個節點iterator finish; //指向的是最后一個節點
public: //Basic accessorsiterator begin(){ return start; }iterator end(){ return finish; }reference operator[](size_type n){//調用__deque_iterator<>::operator[]return start[difference_type(n)];}//調用__deque_iterator<>::operator*reference front(){return *start;}reference back(){iterator tmp = finish;--tmp; //調用__deque_iterator<>::operator--return *tmp; //調用__deque_iterator<>::operator*/** 以上三行為何不使用 return *(finish-1); 替代* 書上給出的理由是:因為__deque_iterator<>沒有為(finish-1)定義運算子*/}//調用__deque_iterator<>::operator-size_type size() const{return finish - start;}//不理解size_type max_size()const{return size_type (-1);}bool empty(){return finish == start;}
};

 ?
?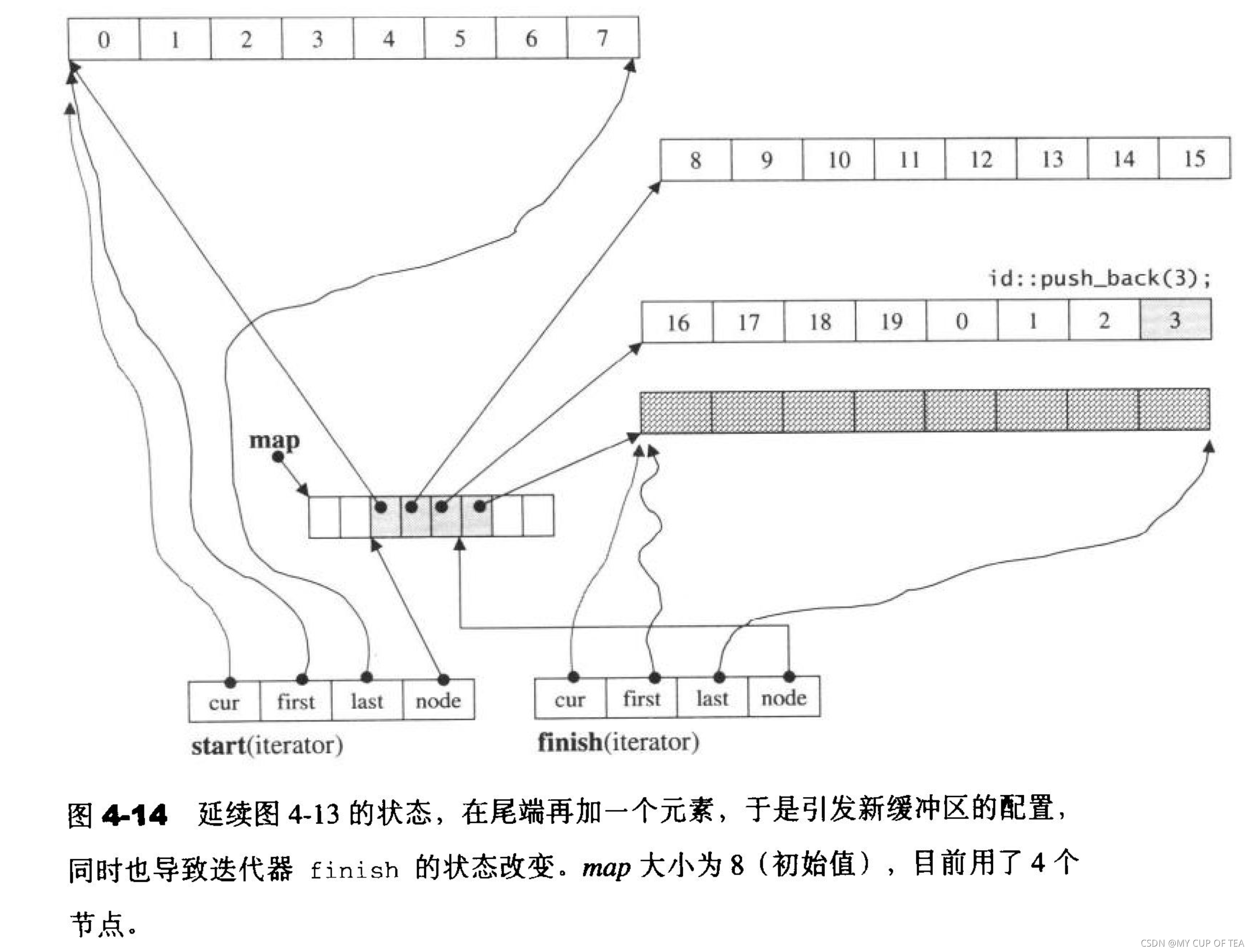
//負責產生并安排好deque的結構void create_map_and_nodes(size_type num_elements){//需要節點的個數 = (元素的個數 / 每個緩沖區容納的元素的個數) + 1;//如果剛好整除 會多為其分配一=一個節點size_type num_nodes = num_elements / buffer_size() + 1;//一個map需要管理幾個節點。最少是8個,最多是 "所需要的節點數 + 2"//前后各預留一個 擴充的時候使用map_size = std::max(initial_map_size(),num_nodes + 2);//配置一個具有map_size的個節點的mapmap = map_allocator::allocate(map_size);//以下是讓nstart和nfinish指向的map所擁有的全部節點的最中央區段//保持在最中央的目的是為了保證頭尾兩端擴充的能量一樣大,每個節點對應一個緩沖區map_pointer nstart = map + (map_size - num_nodes) / 2;map_pointer nfinish = nstart + num_nodes -1;map_pointer cur;try {//為map內的每一個現用節點配置緩沖區,所有緩沖區加起來就是deque的可用空間//最后一個緩沖區可能存在一些富裕for (cur = nstart;cur<=finish;++cur) {*cur = allocate_node();}} catch (std::exception ) {//使用catch捕捉異常//"commit or rollback" 如非全部成功 就一個不要保留}//為deque內的兩個迭代器start和end設定正確的內容start.set_node(nstart);finish.set_node(nfinish);start.cur = start.first; //first、cur都是public//如果剛好整除,會多分配一個節點//令cur指向這多分配的一個節點(所對映之緩沖區)的起始處finish.cur = finish.first + num_elements % buffer_size();}//push_back()void push_back(const value_type& t){if (finish.cur != finish.last - 1){//最后尚有一個以上的備用空間//直接在備用空間上進行元素的構造Chy::allocator<T>::construct(finish.cur,t);//調整最后緩沖區的使用狀態++finish.cur;} else{//最后緩沖區已經 無(或者只剩下一個)元素的備用空間push_back_aux(t);}}//當尾端只剩下一個元素作為備用的空間,于是會調用push_back_aux()//先分配一整塊新的緩沖區,再設置新的元素的內容,然后更改迭代器finish的狀態//只有當 finish.cur == finish.last - 1 的時候才會調用void push_back_aux(const value_type& t){value_type t_copy = t;reverse_map_at_back(); //符合某種條件則必須重換一個map*(finish.node + 1) = allocate_node(); //配置一個新的節點 (緩沖區)try {Chy::allocator<T>::construct(finish.cur,t_copy);//針對標的元素設定初值finish.set_node(finish.node+1);//改變finish令其指向新的節點finish.cur = finish.first; //設定finish的狀態}catch (std::exception){Chy::allocator<T>::deallocate(*(finish.node + 1));}}void push_front(const value_type& t){if (start.cur != start.first){ //第一緩沖區尚有備用的空間Chy::allocator<T>::construct(start.cur - 1,t); //直接在備用空間上構造元素--start.cur; //調整第一緩沖區的使用狀態} else{ //第一緩沖區已經無備用空間push_back_aux(t);}}//當start.cur == start.first時才會被調用//當第一個緩沖區沒有任何備用元素的時候才會被調用void push_front_aux(const value_type& t){value_type t_copy = t;reverse_map_at_front(); //如果滿足條件則必須要重新換一個map*(start.node - 1) = allocate_node(); //配置一個新的節點(緩沖區)try{start.set_node(start.node - 1); //改變start,另其指向新的節點start.cur = start.cur - 1; //設定start的狀態Chy::allocator<T>::construct(start.cur,t_copy);}catch (std::exception){//commit or rollbackstart.set_node(start.node + 1);start.cur = start.first;Chy::allocator<T>::deallocate(*(start.node - 1));throw ;}}//整治的實際操作是通過調用 reallocate_map()函數 來實現的void reallocate_map(size_type nodes_to_add,bool add_at_front){size_type old_num_nodes = finish.node - start.node + 1;size_type new_num_nodes = old_num_nodes + nodes_to_add;map_pointer new_nstart;if (map_size > 2 * new_num_nodes){new_nstart = map + (map_size - new_num_nodes)/2 + (add_at_front ? nodes_to_add : 0);if (new_nstart < start.node){std::copy(start.node,finish.node+1,new_nstart);} else{std::copy_backward(start.node,finish.node+1,new_nstart + old_num_nodes);}} else{size_type new_map_size = map_size + std::max(map_size,nodes_to_add) + 2;//配置一塊新的內存 給map使用map_pointer new_map = map_allocator::allocate(new_map_size);new_nstart = new_map + (new_map_size - new_num_nodes)/2 + (add_at_front ? nodes_to_add : 0);//將原map內容拷貝過來std::copy(start.node,finish.node+1,new_nstart);//釋放原mapmap_allocator::deallocate(map,map_size);map = new_map;map_size = new_map_size;}//重新設定 迭代器 start 和 finishstart.set_node(new_nstart);finish.set_node(new_nstart + old_num_nodes - 1);}//reverse_map_at_front() 和 reverse_map_at_back()負責整治 mapvoid reverse_map_at_back(size_type nodes_to_add = 1){if (nodes_to_add + 1 > map_size - (finish.node - map)){//如果map節點備用空間不足//符合上述條件則必須重新替換一個map (配置更大的內存,拷貝先前的舊的區間,釋放先前的舊的空間)reallocate_map(nodes_to_add, false);}}void reverse_map_at_front(size_type nodes_to_add = 1){if (nodes_to_add > start.node - map){//如果map的前端節點備用空間不足//符合上述條件則必須重新替換一個map (配置更大的內存,拷貝先前的舊的區間,釋放先前的舊的空間)reallocate_map(nodes_to_add, true);}}?改編版 代碼
#include <iostream>template<class T,class Alloc>
class simple_alloc{
public:static T* allocate(std::size_t n){return 0==n?0:(T*)Alloc::allocate(n * sizeof(T));}static T* allocate(void){return (T*)Alloc::allocate(sizeof (T));}static void deallocate(T* p,size_t n){if (n!=0){Alloc::deallocate(p,n * sizeof(T));}}static void deallocate(T* p){Alloc::deallocate(p,sizeof(T));}
};namespace Chy{template <class T>inline T* _allocate(ptrdiff_t size,T*){std::set_new_handler(0);T* tmp = (T*)(::operator new((std::size_t)(size * sizeof (T))));if (tmp == 0){std::cerr << "out of memory" << std::endl;exit(1);}return tmp;}template<class T>inline void _deallocate(T* buffer){::operator delete (buffer);}template<class T1,class T2>inline void _construct(T1 *p,const T2& value){new(p) T1 (value); //沒看懂}template <class T>inline void _destroy(T* ptr){ptr->~T();}template <class T>class allocator{public:typedef T value_type;typedef T* pointer;typedef const T* const_pointer;typedef T& reference;typedef const T& const_reference;typedef std::size_t size_type;typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;template<class U>struct rebind{typedef allocator<U>other;};pointer allocate(size_type n,const void * hint = 0){return _allocate((difference_type)n,(pointer)0);}void deallocate(pointer p,size_type n){_deallocate(p);}void construct(pointer p,const T& value){_construct(p,value);}void destroy(pointer p){_destroy(p);}pointer address(reference x){return (pointer)&x;}const_pointer const_address(const_reference x){return (const_pointer)&x;}size_type max_size()const{return size_type(UINT_MAX/sizeof (T));}};
}//如果是copy construction 等同于assignment而且destructor 是 trivial以下就會有效
//如果是POD型別 執行的流程就會跳轉到以下函數,這個是通過function template的參數推導機制得到的
template<class ForwardIterator,class Size,class T>
inline ForwardIterator __uninitizlized_fill_n_aux(ForwardIterator first,Size n,const T&x){return fill_n(first,n,x); //交給高階函數執行
}struct __true_type{};
struct __false_type{};template<class T>
struct __type_traits {typedef __true_type this_dummy_member_must_be_first;typedef __false_type has_trivial_default_constructor;typedef __false_type has_trivial_copy_constructor;typedef __false_type has_trivial_assignment_constructor;typedef __false_type has_trivial_destructor;typedef __false_type is_POD_type;
};//函數的邏輯是
//首先萃取出 迭代器first的value type,然后判斷這個型別是否是POD類型
template<class ForwardIterator,class Size,class T,class T1>
inline ForwardIterator __uninitizlized_fill_n(ForwardIterator first,Size n,const T&x,T1*){//以下使用的是__type_traits<T1>::is_POD_type is _PODtypedef typename __type_traits<T1>::is_POD_type is_POD;return __uninitizlized_fill_n_aux(first,n,x,is_POD());
}//如果是copy construction 等同于assignment而且destructor 是 trivial以下就會有效
//如果是POD型別 執行的流程就會跳轉到以下函數,這個是通過function template的參數推導機制得到的
template <class ForwardIterator,class T>
inline void __uninitialized_fill_aux(ForwardIterator first,ForwardIterator last,const T& x,__true_type){fill(first,last,x);//調用STL算法 fill()
}
//如果不是POD型別 執行的流程就會轉向以下函數 這個是通過function template的參數推導機制得到的
template <class ForwardIterator,class T>
inline void __uninitialized_fill_aux(ForwardIterator first,ForwardIterator last,const T& x,__false_type){ForwardIterator cur = first;//為了簡化 省略了異常處理for(;cur != last;++cur){Chy::_construct(&*cur,x);}
}template<class ForwardIterator,class T,class T1>
inline void __uninitialized_fill(ForwardIterator first,ForwardIterator last,const T&x,T1*){typedef typename __type_traits<T1>::is_POD_type is_POD;__uninitialized_fill_aux(first,last,x,is_POD());
}/** 迭代器first指向輸出端 (欲初始化空間) 起始處* 迭代器last指向的輸出端 (欲初始化空間) 結尾處 前閉后開區間* x 表示初始數值*/
template<class ForwardIterator,class T>
ForwardIterator uninitialized_fill(ForwardIterator first,ForwardIterator last,const T&x){__uninitialized_fill(first,last,x,value_type(first));
}/** 如果n不為0,傳回n,表示buffer size由用戶自定義* 如果n為0,表示buffer size使用的是默認數值,那么* 如果sz(元素的大小,sizeof(value_type))小于512,傳回 512/sz* 如果sz不小于512,傳回1*/
inline std::size_t __deque_buf_size(std::size_t n,std::size_t sz){return n!=0 ? n : (sz < 512 ? std::size_t (512/sz):std::size_t(1));
}//雙端隊列 迭代器
template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr,std::size_t BufSiz>
struct __deque_iterator{ //未繼承 std::iteratortypedef __deque_iterator<T,T&,T*,BufSiz> iterator;typedef __deque_iterator<T,const T&,const T*,BufSiz> const_iterator;static std::size_t buffer_size() {return __deque_buf_size(BufSiz,sizeof (T));}//未繼承 std::iterator,所以需要自行撰寫五個必要的迭代器對應的類別typedef std::random_access_iterator_tag iterator_category;//1typedef T value_type; //2typedef Ptr pointer; //3typedef Ref reference; //4typedef std::size_t size_type;typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type; //5typedef T** map_pointer;typedef __deque_iterator self;//保持和容器的聯結T* cur; //此迭代器所指向的緩沖區的現行(current)元素T* first; //此迭代器所指之緩沖區的頭T* last; //此迭代器所指之緩沖區的尾 (含備用空間)map_pointer node;//指向管控中心public:void set_node(map_pointer new_node){node = new_node;first = *new_node;last = first + difference_type (buffer_size());}//重載各個運算子 __deque_iterator<> 成功運作的關鍵reference operator*() const {return *cur;}pointer operator->() const {return &(operator*());}difference_type operator-(const self& x) const{return difference_type (buffer_size()) * (node - x.node - 1) +(cur - first) + (x.last - x.cur);}//參考More Effective C++//Distinguish between prefix and postfix of increment and decrement operators//注意last指向的是最后一個節點的后面,所以先遞增再判斷self& operator++(){++cur; //切換至下一個元素if (cur==last){ //如果已經到達所在緩沖區的尾端set_node(node+1);//切換至下一個節點 (亦 即緩沖區的第一個元素)cur = first;}return *this;}self& operator++(int){ //后置式 標準寫法self tmp = *this;++*this; //調用self& operator++()return tmp;}//first指向的是最后一個節點,所以需要先進行判斷self& operator--(){if (cur == first){ //如果已經到達所在緩沖區的頭端set_node(node-1);//切換至前一個節點(亦即緩沖區)的最后一個元素cur = last;}--cur; //切換至前一個元素return *this;}self& operator--(int){ //后置式 標準寫法self tmp = *this;--*this;return tmp;}//以下代碼實現隨機存取,迭代器直接跳過 n 個距離self& operator+=(difference_type n){difference_type offset = n + (cur - first);if (offset >= 0 && offset < difference_type(buffer_size())){//目標位置在同一緩沖區內cur += n;} else{//目標位置不在同一個緩沖區內difference_type node_offset =offset > 0 ? offset / difference_type(buffer_size()): -difference_type ((-offset - 1) / buffer_size()) - 1;//切換到正確的節點(即對應的緩沖區)set_node(node+node_offset);//切換至正確的元素cur = first+(offset - node_offset * difference_type(buffer_size()));}return *this;}//參考More Effective C++ item22//consider using op= instead of stand-alone opself operator+(difference_type n) const{self tmp = *this;return tmp += n; //調用operator+=}//通過使用operator+= 完成operator-=self& operator-=(difference_type n){return *this += -n;}self operator-(difference_type n)const{self tmp = *this;return tmp -= n;//調用operator-=}//以下實現隨機存取,迭代器可以直接跳躍n個距離reference operator[](difference_type n)const {//以上調用operator* ,operator+return *(*this + n);}bool operator==(const self& x)const{ return cur == x.cur;}bool operator!=(const self& x)const{ return cur != x.cur;}bool operator< (const self& x)const{return (node == x.node) ? (cur < x.cur) : (node < x.node);}
};//雙端隊列
template<class T,class Alloc,std::size_t BufSiz = 0>
class deque{
public: //Basic typestypedef T value_type;typedef value_type* pointer;typedef value_type& reference;typedef std::size_t size_type;typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;public:typedef __deque_iterator<T,T&,T*,BufSiz> iterator;protected: //Internal typedefs//元素的指針的指針 (pointer of pointer of T)typedef pointer* map_pointer;protected: //Data membersmap_pointer map; //指向map,map是塊連續空間,其內部的每個元素都是一個指針(稱為節點),//指向的是一塊緩沖區std::size_t map_size; //map內可以容納多少指針iterator start; //指向的是第一個節點iterator finish; //指向的是最后一個節點public: //Basic accessorsiterator begin(){ return start; }iterator end(){ return finish; }reference operator[](size_type n){//調用__deque_iterator<>::operator[]return start[difference_type(n)];}//調用__deque_iterator<>::operator*reference front(){return *start;}reference back(){iterator tmp = finish;--tmp; //調用__deque_iterator<>::operator--return *tmp; //調用__deque_iterator<>::operator*/** 以上三行為何不使用 return *(finish-1); 替代* 書上給出的理由是:因為__deque_iterator<>沒有為(finish-1)定義運算子*/}//調用__deque_iterator<>::operator-size_type size() const{return finish - start;}//不理解size_type max_size()const{return size_type (-1);}bool empty(){return finish == start;}protected: //Internal typedef//專屬配置器 每次配置一個元素的大小typedef simple_alloc<value_type,Alloc>data_allocator;//專屬配置器 每次配置一個指針大小typedef simple_alloc<pointer,Alloc>map_allocator;static size_type initial_map_size() { return 8; }static size_type buffer_size() {//返回return __deque_buf_size(BufSiz, sizeof(value_type));}void allocate_node() { return data_allocator::allocate(buffer_size()); }void deallocate_node() {return data_allocator::deallocate(buffer_size());}//構造器deque(int n,const value_type& value):start(),finish(),map(0),map_size(0){fill_initialize(n,value);}
protected://負責產生并安排好deque的結構,并設定元素數值void fill_initialize(size_type n,const value_type& value){//把deque的結構轉備好create_map_and_nodes(n);map_pointer cur;try {//為每個節點的緩沖區設定初始值for (cur = start.node;cur < finish.node;++cur) {uninitialized_fill(*cur,*cur + buffer_size(),value);}//最后一個節點的設定稍微有些不同(因為尾端可能有備用空間,不必為其設定初值)uninitialized_fill(finish.first,finish,cur,value);}catch (std::exception) {}}//負責產生并安排好deque的結構void create_map_and_nodes(size_type num_elements){//需要節點的個數 = (元素的個數 / 每個緩沖區容納的元素的個數) + 1;//如果剛好整除 會多為其分配一=一個節點size_type num_nodes = num_elements / buffer_size() + 1;//一個map需要管理幾個節點。最少是8個,最多是 "所需要的節點數 + 2"//前后各預留一個 擴充的時候使用map_size = std::max(initial_map_size(),num_nodes + 2);//配置一個具有map_size的個節點的mapmap = map_allocator::allocate(map_size);//以下是讓nstart和nfinish指向的map所擁有的全部節點的最中央區段//保持在最中央的目的是為了保證頭尾兩端擴充的能量一樣大,每個節點對應一個緩沖區map_pointer nstart = map + (map_size - num_nodes) / 2;map_pointer nfinish = nstart + num_nodes -1;map_pointer cur;try {//為map內的每一個現用節點配置緩沖區,所有緩沖區加起來就是deque的可用空間//最后一個緩沖區可能存在一些富裕for (cur = nstart;cur<=finish;++cur) {*cur = allocate_node();}} catch (std::exception ) {//使用catch捕捉異常//"commit or rollback" 如非全部成功 就一個不要保留}//為deque內的兩個迭代器start和end設定正確的內容start.set_node(nstart);finish.set_node(nfinish);start.cur = start.first; //first、cur都是public//如果剛好整除,會多分配一個節點//令cur指向這多分配的一個節點(所對映之緩沖區)的起始處finish.cur = finish.first + num_elements % buffer_size();}//push_back()void push_back(const value_type& t){if (finish.cur != finish.last - 1){//最后尚有一個以上的備用空間//直接在備用空間上進行元素的構造Chy::allocator<T>::construct(finish.cur,t);//調整最后緩沖區的使用狀態++finish.cur;} else{//最后緩沖區已經 無(或者只剩下一個)元素的備用空間push_back_aux(t);}}//當尾端只剩下一個元素作為備用的空間,于是會調用push_back_aux()//先分配一整塊新的緩沖區,再設置新的元素的內容,然后更改迭代器finish的狀態//只有當 finish.cur == finish.last - 1 的時候才會調用void push_back_aux(const value_type& t){value_type t_copy = t;reverse_map_at_back(); //符合某種條件則必須重換一個map*(finish.node + 1) = allocate_node(); //配置一個新的節點 (緩沖區)try {Chy::allocator<T>::construct(finish.cur,t_copy);//針對標的元素設定初值finish.set_node(finish.node+1);//改變finish令其指向新的節點finish.cur = finish.first; //設定finish的狀態}catch (std::exception){deallocate_node(*(finish.node + 1));}}void push_front(const value_type& t){if (start.cur != start.first){ //第一緩沖區尚有備用的空間Chy::allocator<T>::construct(start.cur - 1,t); //直接在備用空間上構造元素--start.cur; //調整第一緩沖區的使用狀態} else{ //第一緩沖區已經無備用空間push_back_aux(t);}}//當start.cur == start.first時才會被調用//當第一個緩沖區沒有任何備用元素的時候才會被調用void push_front_aux(const value_type& t){value_type t_copy = t;reverse_map_at_front(); //如果滿足條件則必須要重新換一個map*(start.node - 1) = allocate_node(); //配置一個新的節點(緩沖區)try{start.set_node(start.node - 1); //改變start,另其指向新的節點start.cur = start.cur - 1; //設定start的狀態Chy::allocator<T>::construct(start.cur,t_copy);}catch (std::exception){//commit or rollbackstart.set_node(start.node + 1);start.cur = start.first;deallocate_node(*(start.node - 1));throw ;}}//整治的實際操作是通過調用 reallocate_map()函數 來實現的void reallocate_map(size_type nodes_to_add,bool add_at_front){size_type old_num_nodes = finish.node - start.node + 1;size_type new_num_nodes = old_num_nodes + nodes_to_add;map_pointer new_nstart;if (map_size > 2 * new_num_nodes){new_nstart = map + (map_size - new_num_nodes)/2 + (add_at_front ? nodes_to_add : 0);if (new_nstart < start.node){std::copy(start.node,finish.node+1,new_nstart);} else{std::copy_backward(start.node,finish.node+1,new_nstart + old_num_nodes);}} else{size_type new_map_size = map_size + std::max(map_size,nodes_to_add) + 2;//配置一塊新的內存 給map使用map_pointer new_map = map_allocator::allocate(new_map_size);new_nstart = new_map + (new_map_size - new_num_nodes)/2 + (add_at_front ? nodes_to_add : 0);//將原map內容拷貝過來std::copy(start.node,finish.node+1,new_nstart);//釋放原mapmap_allocator::deallocate(map,map_size);map = new_map;map_size = new_map_size;}//重新設定 迭代器 start 和 finishstart.set_node(new_nstart);finish.set_node(new_nstart + old_num_nodes - 1);}//reverse_map_at_front() 和 reverse_map_at_back()負責整治 mapvoid reverse_map_at_back(size_type nodes_to_add = 1){if (nodes_to_add + 1 > map_size - (finish.node - map)){//如果map節點備用空間不足//符合上述條件則必須重新替換一個map (配置更大的內存,拷貝先前的舊的區間,釋放先前的舊的空間)reallocate_map(nodes_to_add, false);}}void reverse_map_at_front(size_type nodes_to_add = 1){if (nodes_to_add > start.node - map){//如果map的前端節點備用空間不足//符合上述條件則必須重新替換一個map (配置更大的內存,拷貝先前的舊的區間,釋放先前的舊的空間)reallocate_map(nodes_to_add, true);}}void pop_back(){if (finish.cur != finish.first){//最后一個緩沖區存在一個 或者 更多的元素--finish.cur; //調整指針,相當于排除了最后的元素Chy::allocator<T>::destroy(finish.cur); //析構最后的元素} else{pop_back_aux();}}//finish.cur == finish.firstvoid pop_back_aux(){deallocate_node(finish.first); //釋放最后一個緩沖區finish.set_node(finish.node - 1);//調整finish的狀態finish.cur = finish.last - 1;//將finish的cur指針指向最后一個元素Chy::allocator<T>::destroy(finish.cur);//進行元素的析構}void pop_front(){if (start != start.last - 1){//第一緩沖區有一個或者多個元素Chy::allocator<T>::destroy(start.cur);//析構當前的元素++start.cur; //調整指針,相當于排除了第一個元素} else{pop_back_aux(); //這里將進行緩沖區的釋放工作}}//當start.cur == start.last-1被調用void pop_front_aux(){Chy::allocator<T>::destroy(start.cur); //將第一緩沖區僅剩的一個元素析構deallocate_node(start.first); //釋放第一個緩沖區start.set_node(start.node + 1);//調整start的狀態start.cur = start.first; //將start指向緩沖區的第一個元素}//清除整個deque//需要注意的是 deque的最初狀態(無任何元素的時候) 保證有一個緩沖區void clear(){//針對頭尾指針以外的每一個緩沖區,都應該是飽滿的for(map_pointer node = start.node + 1;node < finish.node - 1;++node){//將緩沖區內的所有元素全部析構//調用destroy()的第二版本Chy::allocator<T>::deallocate(*node,buffer_size());}if (start.node != finish.node){//至少有頭尾兩個緩沖區Chy::allocator<T>::destroy(start.cur,start.last); //將頭緩沖區目前所有的元素析構Chy::allocator<T>::destroy(finish.first,finish.cur); //將尾緩沖區目前所有的元素析構//釋放尾緩沖區的的物理內存,但是保留頭部緩沖區data_allocator::deallocate(finish.first,buffer_size());} else{//只有一個緩沖區//將唯一緩沖區內的所有元素析構//注意:并不釋放緩沖區的空間,將這唯一的緩沖區保留Chy::allocator<T>::destroy(start.cur,finish.cur);}//調整狀態finish = start;}//使用erase消除特定位置上的元素//消除pos指向的元素,pos為清除點iterator erase(iterator pos){iterator next = pos;++next;difference_type index = pos - start; //清除點之前的元素的個數if(index < (size() >> 1)){ //如果清除點之前的元素比較少std::copy_backward(start,pos,next);//移動清除點之前的元素pop_front(); //移動完畢,將最前一個元素刪除} else{//清除點之后的元素較少std::copy(next,finish,pos);//移動清除點之后的元素pop_back();//移動完畢 將最后一個冗余的元素刪除}return start+index;}//使用erase刪除[first,last)區間內的所有元素// 也就是刪除指定范圍內的一段元素iterator erase(iterator first,iterator last){if (first == start && last == finish){//如果刪除的是整段內存空間,直接調用clear()clear();return finish;} else{difference_type n = last - first; //清除區間的長度difference_type elements_before = first - start; //清除區間前方的元素個數if (elements_before < (size() - n)/2){ //如果前方的元素比較少//copy_backward和copy函數類似,只是逆向對元素進行復制std::copy_backward(start,first,last); //向后移動前方的元素(覆蓋清除區間)iterator new_start = start + n; //標記deque的新的起點Chy::allocator<T>::destroy(start,new_start); //移動完畢之后,將冗余的元素析構//以下將冗余的緩沖區釋放for (map_pointer cur = start.node; cur < new_start.node;++cur){data_allocator::deallocate(*cur,buffer_size());}start = new_start;//設定deque的新起點} else{//如果刪除區間的后方的元素比較少std::copy(last,finish,first); //向前移動后方的元素 (覆蓋清除區間)iterator new_finish = finish - n; //標記finish的新的尾巴Chy::allocator<T>::destroy(new_finish,finish); //移動完畢,將冗余的元素進行析構//以下將釋放冗余的緩沖區for(map_pointer cur = new_finish.node +1;cur <= finish.node;++cur){data_allocator::deallocate(cur,buffer_size());}//設定新的尾節點finish = new_finish;}return start + elements_before;}}//在某個點之前插入一個元素,并設定其值iterator insert(iterator position,const value_type& x){if (position.cur == start.cur){ //如果插入點是deque的最前端push_front(x);return start;}else if(position.cur == finish.cur){ //如果插入點是deque的最后端pop_back(x);iterator tmp = finish;--tmp;return tmp;} else{return insert_aux(position,x);}}iterator insert_aux(iterator pos,const value_type& x){difference_type index = pos - start;//插入點之前的元素的個數value_type x_copy = x;if (index < (size() / 2)){//如果插入節點之前的元素的個數比較少push_front(front());//在最前端加上和第一個元素數值相同的元素iterator front1 = start;//以下標記記號,然后進行元素的移動++front1;iterator front2 = front1;++front2;pos = start + index;iterator pos1 = pos;++pos1;std::copy(front2,pos1,front1);//元素的移動} else{push_back(back());iterator back1 = finish;--back1;iterator back2 = back1;--back2;pos = start + index;std::copy_backward(pos,back2,back1);}//在插入點上設定新值*pos = x_copy;return pos;}};?參考鏈接
- STL之deque實現詳解_一個菜鳥的博客-CSDN博客_deque
- C++ copy_backward(STL copy_backward)算法詳解


作為stack的底層容器)







![python從小白到大牛百度云盤_Java從小白到大牛 (關東升著) 中文pdf+mobi版[36MB]](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/python從小白到大牛百度云盤_Java從小白到大牛 (關東升著) 中文pdf+mobi版[36MB])







:40+個依賴子模塊之ActionBarShadow)
