本章內容
1、socket
2、IO多路復用
3、socketserver
Socket
socket起源于Unix,而Unix/Linux基本哲學之一就是“一切皆文件”,對于文件用【打開】【讀寫】【關閉】模式來操作。socket就是該模式的一個實現,socket即是一種特殊的文件,一些socket函數就是對其進行的操作(讀/寫IO、打開、關閉)
基本上,Socket 是任何一種計算機網絡通訊中最基礎的內容。例如當你在瀏覽器地址欄中輸入 http://www.cnblogs.com/ 時,你會打開一個套接字,然后連接到 http://www.cnblogs.com/ 并讀取響應的頁面然后然后顯示出來。而其他一些聊天客戶端如 gtalk 和 skype 也是類似。任何網絡通訊都是通過 Socket 來完成的。
Python 官方關于 Socket 的函數請看 http://docs.python.org/library/socket.html
socket和file的區別:
1、file模塊是針對某個指定文件進行【打開】【讀寫】【關閉】
2、socket模塊是針對 服務器端 和 客戶端Socket 進行【打開】【讀寫】【關閉】

那我們就先來創建一個socket服務端吧
import socketsk = socket.socket()
sk.bind(("127.0.0.1",8080))
sk.listen(5)conn,address = sk.accept()
sk.sendall(bytes("Hello world",encoding="utf-8"))
server

import socketobj = socket.socket()
obj.connect(("127.0.0.1",8080))ret = str(obj.recv(1024),encoding="utf-8")
print(ret)
View Code
socket更多功能
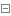
def bind(self, address): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__"""bind(address)Bind the socket to a local address. For IP sockets, the address is apair (host, port); the host must refer to the local host. For raw packetsockets the address is a tuple (ifname, proto [,pkttype [,hatype]])"""
'''將套接字綁定到本地地址。是一個IP套接字的地址對(主機、端口),主機必須參考本地主機。'''passdef close(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__"""close()Close the socket. It cannot be used after this call."""'''關閉socket'''passdef connect(self, address): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__"""connect(address)Connect the socket to a remote address. For IP sockets, the addressis a pair (host, port)."""'''將套接字連接到遠程地址。IP套接字的地址'''passdef connect_ex(self, address): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__"""connect_ex(address) -> errnoThis is like connect(address), but returns an error code (the errno value)instead of raising an exception when an error occurs."""passdef detach(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__"""detach()Close the socket object without closing the underlying file descriptor.The object cannot be used after this call, but the file descriptorcan be reused for other purposes. The file descriptor is returned."""
'''關閉套接字對象沒有關閉底層的文件描述符。'''passdef fileno(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__"""fileno() -> integerReturn the integer file descriptor of the socket."""'''返回整數的套接字的文件描述符。'''return 0def getpeername(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__"""getpeername() -> address infoReturn the address of the remote endpoint. For IP sockets, the addressinfo is a pair (hostaddr, port)."""'''返回遠程端點的地址。IP套接字的地址'''passdef getsockname(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__"""getsockname() -> address infoReturn the address of the local endpoint. For IP sockets, the addressinfo is a pair (hostaddr, port)."""'''返回遠程端點的地址。IP套接字的地址'''passdef getsockopt(self, level, option, buffersize=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__"""getsockopt(level, option[, buffersize]) -> valueGet a socket option. See the Unix manual for level and option.If a nonzero buffersize argument is given, the return value is astring of that length; otherwise it is an integer."""'''得到一個套接字選項'''passdef gettimeout(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__"""gettimeout() -> timeoutReturns the timeout in seconds (float) associated with socket operations. A timeout of None indicates that timeouts on socket operations are disabled."""'''返回的超時秒數(浮動)與套接字相關聯'''return timeoutdef ioctl(self, cmd, option): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__"""ioctl(cmd, option) -> longControl the socket with WSAIoctl syscall. Currently supported 'cmd' values areSIO_RCVALL: 'option' must be one of the socket.RCVALL_* constants.SIO_KEEPALIVE_VALS: 'option' is a tuple of (onoff, timeout, interval)."""return 0def listen(self, backlog=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__"""listen([backlog])Enable a server to accept connections. If backlog is specified, it must beat least 0 (if it is lower, it is set to 0); it specifies the number ofunaccepted connections that the system will allow before refusing newconnections. If not specified, a default reasonable value is chosen."""'''使服務器能夠接受連接。'''passdef recv(self, buffersize, flags=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__"""recv(buffersize[, flags]) -> dataReceive up to buffersize bytes from the socket. For the optional flagsargument, see the Unix manual. When no data is available, block untilat least one byte is available or until the remote end is closed. Whenthe remote end is closed and all data is read, return the empty string."""
'''當沒有數據可用,阻塞,直到至少一個字節是可用的或遠程結束之前關閉。'''passdef recvfrom(self, buffersize, flags=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__"""recvfrom(buffersize[, flags]) -> (data, address info)Like recv(buffersize, flags) but also return the sender's address info."""passdef recvfrom_into(self, buffer, nbytes=None, flags=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__"""recvfrom_into(buffer[, nbytes[, flags]]) -> (nbytes, address info)Like recv_into(buffer[, nbytes[, flags]]) but also return the sender's address info."""passdef recv_into(self, buffer, nbytes=None, flags=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__"""recv_into(buffer, [nbytes[, flags]]) -> nbytes_readA version of recv() that stores its data into a buffer rather than creating a new string. Receive up to buffersize bytes from the socket. If buffersize is not specified (or 0), receive up to the size available in the given buffer.See recv() for documentation about the flags."""passdef send(self, data, flags=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__"""send(data[, flags]) -> countSend a data string to the socket. For the optional flagsargument, see the Unix manual. Return the number of bytessent; this may be less than len(data) if the network is busy."""'''發送一個數據字符串到套接字。'''passdef sendall(self, data, flags=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__"""sendall(data[, flags])Send a data string to the socket. For the optional flagsargument, see the Unix manual. This calls send() repeatedlyuntil all data is sent. If an error occurs, it's impossibleto tell how much data has been sent."""'''發送一個數據字符串到套接字,直到所有數據發送完成'''passdef sendto(self, data, flags=None, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown; NOTE: unreliably restored from __doc__ """sendto(data[, flags], address) -> countLike send(data, flags) but allows specifying the destination address.For IP sockets, the address is a pair (hostaddr, port)."""passdef setblocking(self, flag): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__"""setblocking(flag)Set the socket to blocking (flag is true) or non-blocking (false).setblocking(True) is equivalent to settimeout(None);setblocking(False) is equivalent to settimeout(0.0)."""
'''是否阻塞(默認True),如果設置False,那么accept和recv時一旦無數據,則報錯。'''passdef setsockopt(self, level, option, value): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__"""setsockopt(level, option, value)Set a socket option. See the Unix manual for level and option.The value argument can either be an integer or a string."""passdef settimeout(self, timeout): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__"""settimeout(timeout)Set a timeout on socket operations. 'timeout' can be a float,giving in seconds, or None. Setting a timeout of None disablesthe timeout feature and is equivalent to setblocking(1).Setting a timeout of zero is the same as setblocking(0)."""passdef share(self, process_id): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__"""share(process_id) -> bytesShare the socket with another process. The target process idmust be provided and the resulting bytes object passed to the targetprocess. There the shared socket can be instantiated by callingsocket.fromshare()."""return b""def shutdown(self, flag): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__"""shutdown(flag)Shut down the reading side of the socket (flag == SHUT_RD), the writing sideof the socket (flag == SHUT_WR), or both ends (flag == SHUT_RDWR)."""passdef _accept(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__"""_accept() -> (integer, address info)Wait for an incoming connection. Return a new socket file descriptorrepresenting the connection, and the address of the client.For IP sockets, the address info is a pair (hostaddr, port)."""pass
更多功能
注:擼主知道大家懶,所以把全部功能的中文標記在每個功能的下面啦。下面擼主列一些經常用到的吧
sk.bind(address)
s.bind(address) 將套接字綁定到地址。address地址的格式取決于地址族。在AF_INET下,以元組(host,port)的形式表示地址。
sk.listen(backlog)
開始監聽傳入連接。backlog指定在拒絕連接之前,可以掛起的最大連接數量。
backlog等于5,表示內核已經接到了連接請求,但服務器還沒有調用accept進行處理的連接個數最大為5
這個值不能無限大,因為要在內核中維護連接隊列
sk.setblocking(bool)
是否阻塞(默認True),如果設置False,那么accept和recv時一旦無數據,則報錯。
sk.accept()
接受連接并返回(conn,address),其中conn是新的套接字對象,可以用來接收和發送數據。address是連接客戶端的地址。
接收TCP 客戶的連接(阻塞式)等待連接的到來
sk.connect(address)
連接到address處的套接字。一般,address的格式為元組(hostname,port),如果連接出錯,返回socket.error錯誤。
sk.connect_ex(address)
同上,只不過會有返回值,連接成功時返回 0 ,連接失敗時候返回編碼,例如:10061
sk.close()
關閉套接字
sk.recv(bufsize[,flag])
接受套接字的數據。數據以字符串形式返回,bufsize指定 最多 可以接收的數量。flag提供有關消息的其他信息,通常可以忽略。
sk.recvfrom(bufsize[.flag])
與recv()類似,但返回值是(data,address)。其中data是包含接收數據的字符串,address是發送數據的套接字地址。
sk.send(string[,flag])
將string中的數據發送到連接的套接字。返回值是要發送的字節數量,該數量可能小于string的字節大小。即:可能未將指定內容全部發送。
sk.sendall(string[,flag])
將string中的數據發送到連接的套接字,但在返回之前會嘗試發送所有數據。成功返回None,失敗則拋出異常。
內部通過遞歸調用send,將所有內容發送出去。
sk.sendto(string[,flag],address)
將數據發送到套接字,address是形式為(ipaddr,port)的元組,指定遠程地址。返回值是發送的字節數。該函數主要用于UDP協議。
sk.settimeout(timeout)
設置套接字操作的超時期,timeout是一個浮點數,單位是秒。值為None表示沒有超時期。一般,超時期應該在剛創建套接字時設置,因為它們可能用于連接的操作(如 client 連接最多等待5s )
sk.getpeername()
返回連接套接字的遠程地址。返回值通常是元組(ipaddr,port)。
sk.getsockname()
返回套接字自己的地址。通常是一個元組(ipaddr,port)
sk.fileno()
套接字的文件描述符
TCP:

import socketserver
服務端class Myserver(socketserver.BaseRequestHandler):def handle(self):conn = self.requestconn.sendall(bytes("你好,我是機器人",encoding="utf-8"))while True:ret_bytes = conn.recv(1024)ret_str = str(ret_bytes,encoding="utf-8")if ret_str == "q":breakconn.sendall(bytes(ret_str+"你好我好大家好",encoding="utf-8"))if __name__ == "__main__":server = socketserver.ThreadingTCPServer(("127.0.0.1",8080),Myserver)server.serve_forever()客戶端import socketobj = socket.socket()obj.connect(("127.0.0.1",8080))ret_bytes = obj.recv(1024)
ret_str = str(ret_bytes,encoding="utf-8")
print(ret_str)while True:inp = input("你好請問您有什么問題? \n >>>")if inp == "q":obj.sendall(bytes(inp,encoding="utf-8"))breakelse:obj.sendall(bytes(inp, encoding="utf-8"))ret_bytes = obj.recv(1024)ret_str = str(ret_bytes,encoding="utf-8")print(ret_str)
案例一 機器人聊天

服務端import socketsk = socket.socket()sk.bind(("127.0.0.1",8080))
sk.listen(5)while True:conn,address = sk.accept()conn.sendall(bytes("歡迎光臨我愛我家",encoding="utf-8"))size = conn.recv(1024)size_str = str(size,encoding="utf-8")file_size = int(size_str)conn.sendall(bytes("開始傳送", encoding="utf-8"))has_size = 0f = open("db_new.jpg","wb")while True:if file_size == has_size:breakdate = conn.recv(1024)f.write(date)has_size += len(date)f.close()客戶端import socket
import osobj = socket.socket()obj.connect(("127.0.0.1",8080))ret_bytes = obj.recv(1024)
ret_str = str(ret_bytes,encoding="utf-8")
print(ret_str)size = os.stat("yan.jpg").st_size
obj.sendall(bytes(str(size),encoding="utf-8"))obj.recv(1024)with open("yan.jpg","rb") as f:for line in f:obj.sendall(line)
案例二 上傳文件
UdP

import socket
ip_port = ('127.0.0.1',9999)
sk = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_DGRAM,0)
sk.bind(ip_port)while True:data = sk.recv(1024)print dataimport socket
ip_port = ('127.0.0.1',9999)sk = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_DGRAM,0)
while True:inp = input('數據:').strip()if inp == 'exit':breaksk.sendto(bytes(inp,encoding = "utf-8"),ip_port)sk.close()
udp傳輸
WEB服務應用:
#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding:utf-8
import socketdef handle_request(client):buf = client.recv(1024)client.send("HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n\r\n")client.send("Hello, World")def main():sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)sock.bind(('localhost',8080))sock.listen(5)while True:connection, address = sock.accept()handle_request(connection)connection.close()if __name__ == '__main__':main()
IO多路復用
I/O(input/output),即輸入/輸出端口。每個設備都會有一個專用的I/O地址,用來處理自己的輸入輸出信息 首先什么是I/O:
I/O分為磁盤io和網絡io,這里說的是網絡io
IO多路復用:
I/O多路復用指:通過一種機制,可以監視多個描述符(socket),一旦某個描述符就緒(一般是讀就緒或者寫就緒),能夠通知程序進行相應的讀寫操作。
Linux
Linux中的 select,poll,epoll 都是IO多路復用的機制。
Linux下網絡I/O使用socket套接字來通信,普通I/O模型只能監聽一個socket,而I/O多路復用可同時監聽多個socket.
I/O多路復用避免阻塞在io上,原本為多進程或多線程來接收多個連接的消息變為單進程或單線程保存多個socket的狀態后輪詢處理.
Python
Python中有一個select模塊,其中提供了:select、poll、epoll三個方法,分別調用系統的 select,poll,epoll 從而實現IO多路復用。
Windows Python:提供: selectMac Python:提供: selectLinux Python:提供: select、poll、epoll
對于select模塊操作的方法:
句柄列表11, 句柄列表22, 句柄列表33 = select.select(句柄序列1, 句柄序列2, 句柄序列3, 超時時間)參數: 可接受四個參數(前三個必須)
返回值:三個列表select方法用來監視文件句柄,如果句柄發生變化,則獲取該句柄。
1、當 參數1 序列中的句柄發生可讀時(accetp和read),則獲取發生變化的句柄并添加到 返回值1 序列中
2、當 參數2 序列中含有句柄時,則將該序列中所有的句柄添加到 返回值2 序列中
3、當 參數3 序列中的句柄發生錯誤時,則將該發生錯誤的句柄添加到 返回值3 序列中
4、當 超時時間 未設置,則select會一直阻塞,直到監聽的句柄發生變化
5、當 超時時間 = 1時,那么如果監聽的句柄均無任何變化,則select會阻塞 1 秒,之后返回三個空列表,如果監聽的句柄有變化,則直接執行。

import socket
import selectsk1 = socket.socket()
sk1.bind(("127.0.0.1",8001))
sk1.listen()sk2 = socket.socket()
sk2.bind(("127.0.0.1",8002))
sk2.listen()sk3 = socket.socket()
sk3.bind(("127.0.0.1",8003))
sk3.listen()li = [sk1,sk2,sk3]while True:r_list,w_list,e_list = select.select(li,[],[],1) # r_list可變化的for line in r_list: conn,address = line.accept()conn.sendall(bytes("Hello World !",encoding="utf-8"))
利用select監聽終端操作實例
服務端:
sk1 = socket.socket()
sk1.bind(("127.0.0.1",8001))
sk1.listen()inpu = [sk1,]while True:r_list,w_list,e_list = select.select(inpu,[],[],1)for sk in r_list:if sk == sk1:conn,address = sk.accept()inpu.append(conn)else:try:ret = str(sk.recv(1024),encoding="utf-8")sk.sendall(bytes(ret+"hao",encoding="utf-8"))except Exception as ex:inpu.remove(sk)客戶端
import socketobj = socket.socket()obj.connect(('127.0.0.1',8001))while True:inp = input("Please(q\退出):\n>>>")obj.sendall(bytes(inp,encoding="utf-8"))if inp == "q":breakret = str(obj.recv(1024),encoding="utf-8")print(ret)
利用select實現偽同時處理多個Socket客戶端請求
服務端:
import socket
sk1 = socket.socket()
sk1.bind(("127.0.0.1",8001))
sk1.listen()
inputs = [sk1]
import select
message_dic = {}
outputs = []
while True:r_list, w_list, e_list = select.select(inputs,[],inputs,1)print("正在監聽的socket對象%d" % len(inputs))print(r_list)for sk1_or_conn in r_list:if sk1_or_conn == sk1:conn,address = sk1_or_conn.accept()inputs.append(conn)message_dic[conn] = []else:try:data_bytes = sk1_or_conn.recv(1024)data_str = str(data_bytes,encoding="utf-8")sk1_or_conn.sendall(bytes(data_str+"好",encoding="utf-8"))except Exception as ex:inputs.remove(sk1_or_conn)else:data_str = str(data_bytes,encoding="utf-8")message_dic[sk1_or_conn].append(data_str)outputs.append(sk1_or_conn)for conn in w_list:recv_str = message_dic[conn][0]del message_dic[conn][0]conn.sendall(bytes(recv_str+"好",encoding="utf-8"))for sk in e_list:inputs.remove(sk)客戶端:
import socketobj = socket.socket()obj.connect(('127.0.0.1',8001))while True:inp = input("Please(q\退出):\n>>>")obj.sendall(bytes(inp,encoding="utf-8"))if inp == "q":breakret = str(obj.recv(1024),encoding="utf-8")print(ret)
利用select實現偽同時處理多個Socket客戶端請求讀寫分離
socketserver
 SocketServer內部使用 IO多路復用 以及 “多線程” 和 “多進程” ,從而實現并發處理多個客戶端請求的Socket服務端。即:每個客戶端請求連接到服務器時,Socket服務端都會在服務器是創建一個“線程”或者“進程” 專門負責處理當前客戶端的所有請求。
SocketServer內部使用 IO多路復用 以及 “多線程” 和 “多進程” ,從而實現并發處理多個客戶端請求的Socket服務端。即:每個客戶端請求連接到服務器時,Socket服務端都會在服務器是創建一個“線程”或者“進程” 專門負責處理當前客戶端的所有請求。
ThreadingTCPServer
ThreadingTCPServer實現的Soket服務器內部會為每個client創建一個 “ 線程 ”,該線程用來和客戶端進行交互。
1、ThreadingTCPServer基礎
使用ThreadingTCPServer:
- 創建一個繼承自 SocketServer.BaseRequestHandler 的類
- 類中必須定義一個名稱為 handle 的方法
- 啟動ThreadingTCPServer

import socketserverclass Myserver(socketserver.BaseRequestHandler):def handle(self):conn = self.requestconn.sendall(bytes("你好,我是機器人",encoding="utf-8"))while True:ret_bytes = conn.recv(1024)ret_str = str(ret_bytes,encoding="utf-8")if ret_str == "q":breakconn.sendall(bytes(ret_str+"你好我好大家好",encoding="utf-8"))if __name__ == "__main__":server = socketserver.ThreadingTCPServer(("127.0.0.1",8080),Myserver)server.serve_forever()
服務端


import socketobj = socket.socket()obj.connect(("127.0.0.1",8080))ret_bytes = obj.recv(1024)
ret_str = str(ret_bytes,encoding="utf-8")
print(ret_str)while True:inp = input("你好請問您有什么問題? \n >>>")if inp == "q":obj.sendall(bytes(inp,encoding="utf-8"))breakelse:obj.sendall(bytes(inp, encoding="utf-8"))ret_bytes = obj.recv(1024)ret_str = str(ret_bytes,encoding="utf-8")print(ret_str)
客戶端
2、ThreadingTCPServer源碼剖析
ThreadingTCPServer的類圖關系如下:
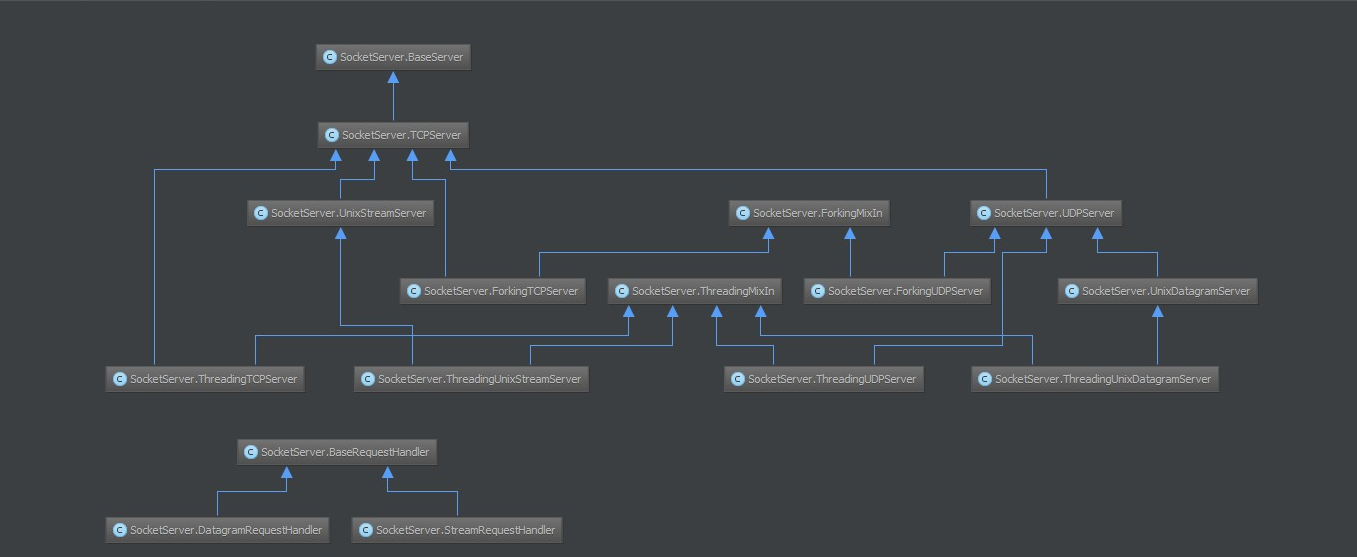
內部調用流程為:
- 啟動服務端程序
- 執行 TCPServer.init 方法,創建服務端Socket對象并綁定 IP 和 端口
- 執行 BaseServer.init 方法,將自定義的繼承自SocketServer.BaseRequestHandler 的類 MyRequestHandle賦值給 self.RequestHandlerClass
- 執行 BaseServer.server_forever 方法,While 循環一直監聽是否有客戶端請求到達 …
- 當客戶端連接到達服務器
- 執行 ThreadingMixIn.process_request 方法,創建一個 “線程” 用來處理請求
- 執行 ThreadingMixIn.process_request_thread 方法
- 執行 BaseServer.finish_request 方法,執行 self.RequestHandlerClass() 即:執行 自定義 MyRequestHandler 的構造方法(自動調用基類BaseRequestHandler的構造方法,在該構造方法中又會調用 MyRequestHandler的handle方法)
相對應的源碼如下:


class BaseServer:"""Base class for server classes.Methods for the caller:- __init__(server_address, RequestHandlerClass)- serve_forever(poll_interval=0.5)- shutdown()- handle_request() # if you do not use serve_forever()- fileno() -> int # for select()Methods that may be overridden:- server_bind()- server_activate()- get_request() -> request, client_address- handle_timeout()- verify_request(request, client_address)- server_close()- process_request(request, client_address)- shutdown_request(request)- close_request(request)- handle_error()Methods for derived classes:- finish_request(request, client_address)Class variables that may be overridden by derived classes orinstances:- timeout- address_family- socket_type- allow_reuse_addressInstance variables:- RequestHandlerClass- socket"""timeout = Nonedef __init__(self, server_address, RequestHandlerClass):"""Constructor. May be extended, do not override."""self.server_address = server_addressself.RequestHandlerClass = RequestHandlerClassself.__is_shut_down = threading.Event()self.__shutdown_request = Falsedef server_activate(self):"""Called by constructor to activate the server.May be overridden."""passdef serve_forever(self, poll_interval=0.5):"""Handle one request at a time until shutdown.Polls for shutdown every poll_interval seconds. Ignoresself.timeout. If you need to do periodic tasks, do them inanother thread."""self.__is_shut_down.clear()try:while not self.__shutdown_request:# XXX: Consider using another file descriptor or# connecting to the socket to wake this up instead of# polling. Polling reduces our responsiveness to a# shutdown request and wastes cpu at all other times.r, w, e = _eintr_retry(select.select, [self], [], [],poll_interval)if self in r:self._handle_request_noblock()finally:self.__shutdown_request = Falseself.__is_shut_down.set()def shutdown(self):"""Stops the serve_forever loop.Blocks until the loop has finished. This must be called whileserve_forever() is running in another thread, or it willdeadlock."""self.__shutdown_request = Trueself.__is_shut_down.wait()# The distinction between handling, getting, processing and# finishing a request is fairly arbitrary. Remember:## - handle_request() is the top-level call. It calls# select, get_request(), verify_request() and process_request()# - get_request() is different for stream or datagram sockets# - process_request() is the place that may fork a new process# or create a new thread to finish the request# - finish_request() instantiates the request handler class;# this constructor will handle the request all by itselfdef handle_request(self):"""Handle one request, possibly blocking.Respects self.timeout."""# Support people who used socket.settimeout() to escape# handle_request before self.timeout was available.timeout = self.socket.gettimeout()if timeout is None:timeout = self.timeoutelif self.timeout is not None:timeout = min(timeout, self.timeout)fd_sets = _eintr_retry(select.select, [self], [], [], timeout)if not fd_sets[0]:self.handle_timeout()returnself._handle_request_noblock()def _handle_request_noblock(self):"""Handle one request, without blocking.I assume that select.select has returned that the socket isreadable before this function was called, so there should beno risk of blocking in get_request()."""try:request, client_address = self.get_request()except socket.error:returnif self.verify_request(request, client_address):try:self.process_request(request, client_address)except:self.handle_error(request, client_address)self.shutdown_request(request)def handle_timeout(self):"""Called if no new request arrives within self.timeout.Overridden by ForkingMixIn."""passdef verify_request(self, request, client_address):"""Verify the request. May be overridden.Return True if we should proceed with this request."""return Truedef process_request(self, request, client_address):"""Call finish_request.Overridden by ForkingMixIn and ThreadingMixIn."""self.finish_request(request, client_address)self.shutdown_request(request)def server_close(self):"""Called to clean-up the server.May be overridden."""passdef finish_request(self, request, client_address):"""Finish one request by instantiating RequestHandlerClass."""self.RequestHandlerClass(request, client_address, self)def shutdown_request(self, request):"""Called to shutdown and close an individual request."""self.close_request(request)def close_request(self, request):"""Called to clean up an individual request."""passdef handle_error(self, request, client_address):"""Handle an error gracefully. May be overridden.The default is to print a traceback and continue."""print '-'*40print 'Exception happened during processing of request from',print client_addressimport tracebacktraceback.print_exc() # XXX But this goes to stderr!print '-'*40
Baseserver

class TCPServer(BaseServer):"""Base class for various socket-based server classes.Defaults to synchronous IP stream (i.e., TCP).Methods for the caller:- __init__(server_address, RequestHandlerClass, bind_and_activate=True)- serve_forever(poll_interval=0.5)- shutdown()- handle_request() # if you don't use serve_forever()- fileno() -> int # for select()Methods that may be overridden:- server_bind()- server_activate()- get_request() -> request, client_address- handle_timeout()- verify_request(request, client_address)- process_request(request, client_address)- shutdown_request(request)- close_request(request)- handle_error()Methods for derived classes:- finish_request(request, client_address)Class variables that may be overridden by derived classes orinstances:- timeout- address_family- socket_type- request_queue_size (only for stream sockets)- allow_reuse_addressInstance variables:- server_address- RequestHandlerClass- socket"""address_family = socket.AF_INETsocket_type = socket.SOCK_STREAMrequest_queue_size = 5allow_reuse_address = Falsedef __init__(self, server_address, RequestHandlerClass, bind_and_activate=True):"""Constructor. May be extended, do not override."""BaseServer.__init__(self, server_address, RequestHandlerClass)self.socket = socket.socket(self.address_family,self.socket_type)if bind_and_activate:try:self.server_bind()self.server_activate()except:self.server_close()raisedef server_bind(self):"""Called by constructor to bind the socket.May be overridden."""if self.allow_reuse_address:self.socket.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1)self.socket.bind(self.server_address)self.server_address = self.socket.getsockname()def server_activate(self):"""Called by constructor to activate the server.May be overridden."""self.socket.listen(self.request_queue_size)def server_close(self):"""Called to clean-up the server.May be overridden."""self.socket.close()def fileno(self):"""Return socket file number.Interface required by select()."""return self.socket.fileno()def get_request(self):"""Get the request and client address from the socket.May be overridden."""return self.socket.accept()def shutdown_request(self, request):"""Called to shutdown and close an individual request."""try:#explicitly shutdown. socket.close() merely releases#the socket and waits for GC to perform the actual close.request.shutdown(socket.SHUT_WR)except socket.error:pass #some platforms may raise ENOTCONN hereself.close_request(request)def close_request(self, request):"""Called to clean up an individual request."""request.close()
TCP server

class ThreadingMixIn:"""Mix-in class to handle each request in a new thread."""# Decides how threads will act upon termination of the# main processdaemon_threads = Falsedef process_request_thread(self, request, client_address):"""Same as in BaseServer but as a thread.In addition, exception handling is done here."""try:self.finish_request(request, client_address)self.shutdown_request(request)except:self.handle_error(request, client_address)self.shutdown_request(request)def process_request(self, request, client_address):"""Start a new thread to process the request."""t = threading.Thread(target = self.process_request_thread,args = (request, client_address))t.daemon = self.daemon_threadst.start()
ThreadingMixIn

class BaseRequestHandler:"""Base class for request handler classes.This class is instantiated for each request to be handled. Theconstructor sets the instance variables request, client_addressand server, and then calls the handle() method. To implement aspecific service, all you need to do is to derive a class whichdefines a handle() method.The handle() method can find the request as self.request, theclient address as self.client_address, and the server (in case itneeds access to per-server information) as self.server. Since aseparate instance is created for each request, the handle() methodcan define arbitrary other instance variariables."""def __init__(self, request, client_address, server):self.request = requestself.client_address = client_addressself.server = serverself.setup()try:self.handle()finally:self.finish()def setup(self):passdef handle(self):passdef finish(self):pass
SocketServer.BaseRequestHandler
SocketServer的ThreadingTCPServer之所以可以同時處理請求得益于 select 和 Threading 兩個東西,其實本質上就是在服務器端為每一個客戶端創建一個線程,當前線程用來處理對應客戶端的請求,所以,可以支持同時n個客戶端鏈接(長連接)。

















——圖像基本處理(二))

