From what I have seen so far, CSV seems to be the most popular format to store data among data scientists. And that’s understandable, it gets the job done and it’s a quite simple format; in Python, even without any library, one can build a simple CSV parser in under 10 lines of code.
從目前為止我所看到的,CSV似乎是數據科學家中最流行的存儲數據格式。 這是可以理解的,它可以完成工作,而且格式非常簡單; 在Python中,即使沒有任何庫,也可以用不到10行代碼構建一個簡單的CSV解析器。
But you may not always find the data that you need in CSV format. Sometimes the only available format may be an Excel file. Like, for example, this dataset on ons.gov.uk about crime in England and Wales, which is only in xlsx format; dataset that I will use in the examples below.
但是您可能并不總是以CSV格式找到所需的數據。 有時,唯一可用的格式可能是Excel文件。 例如, ons.gov.uk上有關英格蘭和威爾士犯罪的數據集,僅采用xlsx格式; 我將在以下示例中使用的數據集。
讀取Excel文件 (Reading Excel files)
The simplest way to read Excel files into pandas data frames is by using the following function (assuming you did import pandas as pd):
將Excel文件讀入pandas數據幀的最簡單方法是使用以下函數(假設您確實import pandas as pd ):
df = pd.read_excel(‘path_to_excel_file’, sheet_name=’…’)
df = pd.read_excel('path_to_excel_file', sheet_name='…')
Where sheet_name can be the name of the sheet we want to read, it’s index, or a list with all the sheets we want to read; the elements of the list can be mixed: sheet names or indices. If we want all the sheets, we can use sheet_name=None. In the case in which we want more sheets to be read, they will be returned as a dictionary of data frames. The keys of such a dictionary will be either the index or name of a sheet, depending on how we specified in sheet_name; in the case of sheet_name=None, the keys will be sheet names.
其中sheet_name可以是我們要讀取的工作表的名稱,索引或包含我們要讀取的所有工作表的列表; 列表中的元素可以混合使用:工作表名稱或索引。 如果我們需要所有圖紙,可以使用sheet_name=None 。 在我們希望讀取更多圖紙的情況下,它們將作為數據幀的字典返回。 這樣的字典的鍵將是工作表的索引或名稱,這取決于我們在sheet_name指定sheet_name ; 在sheet_name=None的情況下,鍵將是工作表名稱。
Now, if we use it to read our Excel file we get:
現在,如果我們使用它來讀取我們的Excel文件,則會得到:

That’s right, an error! It turns out that pandas cannot read Excel files on its own, so we need to install another python package to do that.
是的,這是一個錯誤! 事實證明,熊貓無法自行讀取Excel文件,因此我們需要安裝另一個python軟件包來做到這一點。
There are 2 options that we have: xlrd and openpyxl. The package xlrd can open both Excel 2003 (.xls) and Excel 2007+ (.xlsx) files, whereas openpyxl can open only Excel 2007+ (.xlsx) files. So, we will install xlrd as it can open both formats:
我們有2個選項: xlrd和openpyxl 。 包xlrd可以同時打開Excel 2003(.xlsx)和Excel 2007+(.xlsx)文件,而openpyxl只能打開Excel 2007+(.xlsx)文件。 因此,我們將安裝xlrd因為它可以打開兩種格式:
pip install xlrd
pip install xlrd
Now, if we try to read the same data again:
現在,如果我們嘗試再次讀取相同的數據:

It works!
有用!
But Excel files can be a little bit messier. Besides data, they may have other comments/explanations in the first and/or last couple of rows.
但是Excel文件可能有點混亂。 除數據外,它們在第一和/或最后幾行中可能還有其他注釋/解釋。
To tell pandas to start reading an Excel sheet from a specific row, use the argument header = 0-indexed row where to start reading. By default, header=0, and the first such row is used to give the names of the data frame columns.
要告訴熊貓開始從特定行讀取Excel工作表,請使用參數header = 0索引行開始讀取。 默認情況下,header = 0,并且第一個這樣的行用于給出數據框列的名稱。
To skip rows at the end of a sheet, use skipfooter = number of rows to skip.
要跳過工作表末尾的行,請使用skipfooter =要跳過的行數。
For example:
例如:
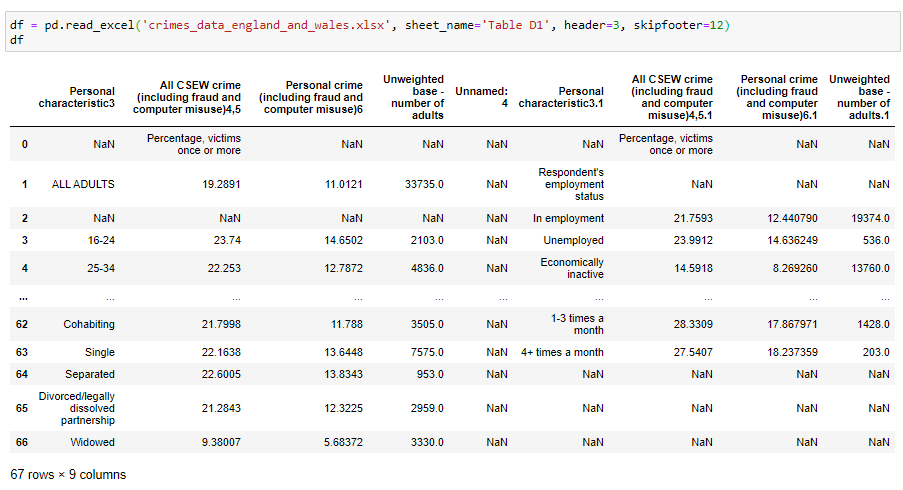
This is a little better. There are still some issues that are specific to this data. Depending on what we want to achieve we may also need to rearrange the data values into another way. But in this article, we will focus only on reading and writing to and from data frames.
這樣好一點了。 仍然存在一些特定于此數據的問題。 根據我們要實現的目標,我們可能還需要將數據值重新排列為另一種方式。 但是在本文中,我們將僅專注于讀寫數據幀。
Another way to read Excel files besides the one above is by using a pd.ExcelFile object. Such an object can be constructed by using the pd.ExcelFile(‘excel_file_path’) constructor. An ExcelFile object can be used in a couple of ways. Firstly, it has a .sheet_names attribute which is a list of all the sheet names inside the opened Excel file.
除上述方法外,另一種讀取Excel文件的方法是使用pd.ExcelFile對象。 可以使用pd.ExcelFile('excel_file_path')構造函數構造此類對象。 ExcelFile對象可以通過兩種方式使用。 首先,它具有.sheet_names屬性,該屬性是打開的Excel文件中所有工作表名稱的列表。

Then, this ExcelFile object also has a .parse() method that can be used to parse a sheet from the file and return a data frame. The first parameter of this method can be the index of the sheet we want to parse or its name. The rest of the parameters are the same as in the pd.read_excel() function.
然后,此ExcelFile對象還具有.parse()方法,該方法可用于從文件中解析工作表并返回數據框。 此方法的第一個參數可以是我們要解析的工作表的索引或其名稱。 其余參數與pd.read_excel()函數中的參數相同。
An example of parsing the second sheet (index 1):
解析第二張紙(索引1)的示例:

… and here we parse the same sheet using its name instead of an index:
…在這里,我們使用其名稱而不是索引來解析同??一張紙:

ExcelFiles can also be used inside with … as … statements, and if you want to do something a little more elaborate, like parsing only sheets with 2 words in their name, you can do something like:
ExcelFile也可以with … as …語句一起使用,如果您想做一些更復雜的事情,例如僅解析名稱中帶有2個單詞的工作表,則可以執行以下操作:

The same thing you can do by using pd.read_excel() instead of .parse() method, like this:
您可以使用pd.read_excel()而不是.parse()方法來執行相同的操作,如下所示:

… or, if you simply want all the sheets, you can do:
…或者,如果您只想要所有工作表,則可以執行以下操作:

編寫Excel文件 (Writing Excel Files)
Now that we know how to read excel files, the next step for us is to be able to also write a data frame to an excel file. We can do that by using the data frame method .to_excel(‘path_to_excel_file’, sheet_name=’…’).
現在我們知道了如何讀取excel文件,對我們來說,下一步就是能夠將數據幀寫入excel文件。 我們可以通過使用數據框方法.to_excel('path_to_excel_file', sheet_name='…') 。
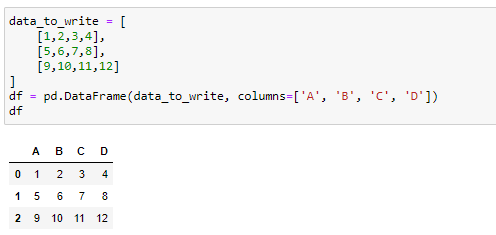
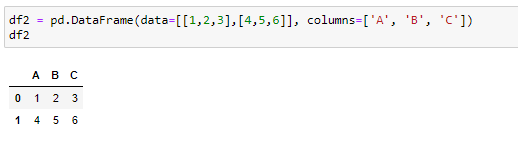
Let’s first create a simple data frame for writing to an excel file:
首先,讓我們創建一個簡單的數據框架以寫入excel文件:
Now we want to write it to an excel file:
現在我們想將其寫入一個excel文件:
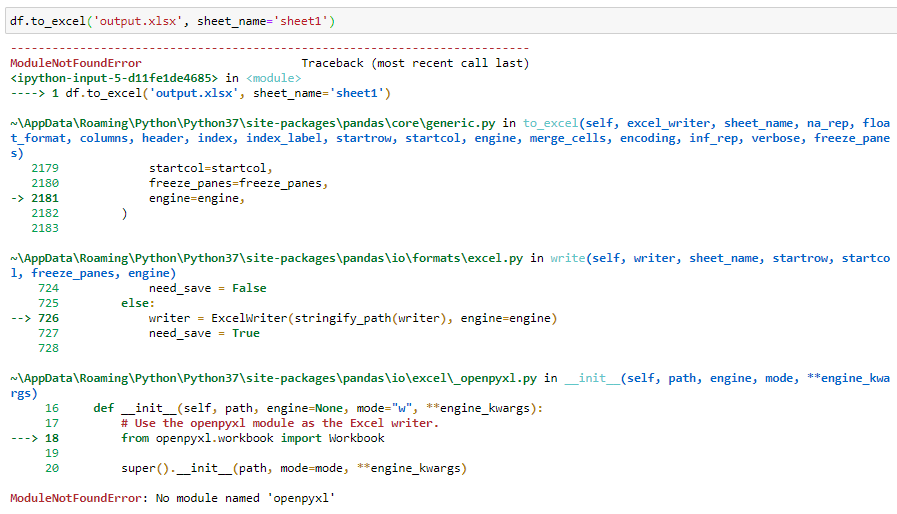
… and we got an error.
……我們遇到了一個錯誤。
Again, pandas can’t write to excel files on its own; we need another package for that. The main options that we have are:
同樣,熊貓不能自己寫入excel文件。 我們需要另一個軟件包。 我們提供的主要選項是:
xlwt— works only with Excel 2003 (.xls) files; append mode not supportedxlwt僅適用于Excel 2003(.xls)文件; 不支持追加模式xlsxwriter— works only with Excel 2007+ (.xlsx) files; append mode not supportedxlsxwriter僅適用于Excel 2007+(.xlsx)文件; 不支持追加模式openpyxl— works only with Excel 2007+ (.xlsx) files; supports append modeopenpyxl僅適用于Excel 2007+(.xlsx)文件; 支持追加模式
If we want to be able to write to the old .xls format we should install xlwt as it is the only that handles those files. For .xlsx files, we will choose openpyxl as it also supports the append mode.
如果我們希望能夠寫入舊的.xls格式,則應該安裝xlwt因為它是唯一處理那些文件的文件。 對于.xlsx文件,我們將選擇openpyxl因為它也支持附加模式。
pip install xlwt openpyxl
pip install xlwt openpyxl
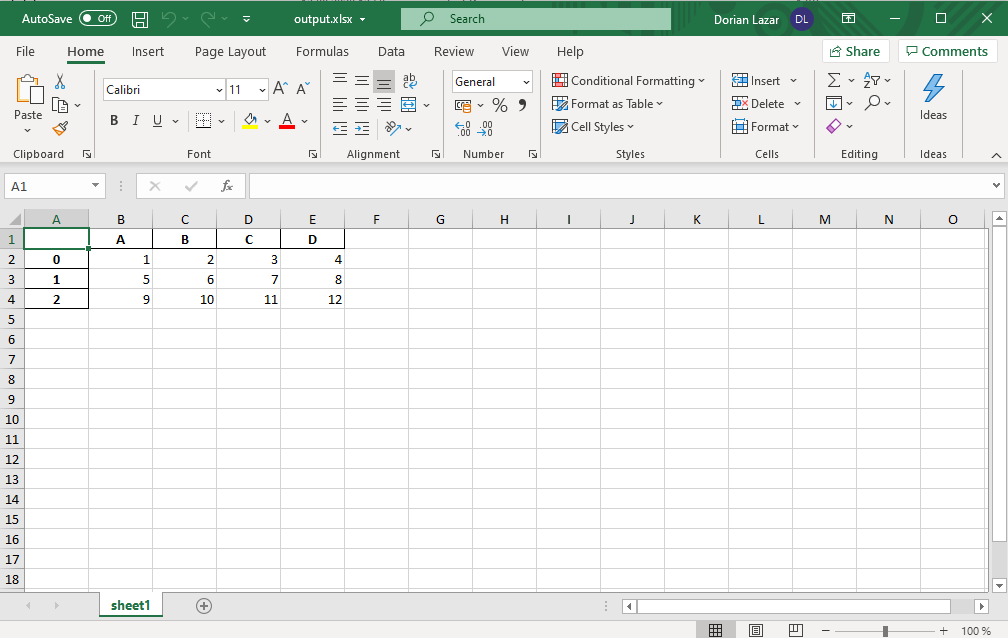
Now if we run again the above code, it works; an excel file was created:
現在,如果我們再次運行上面的代碼,它可以工作; 創建了一個excel文件:
By default, pandas also writes the index column along with our columns. To get rid of it, use index=False like in the code below:
默認情況下,pandas還會將索引列與我們的列一起寫入。 要擺脫它,請使用index=False如下面的代碼所示:

The index column isn’t there now:
索引列現在不存在:

What if we want to write more sheets? If we want to add a second sheet to the previous file, do you think that the below code will work?
如果我們想寫更多的圖紙怎么辦? 如果我們想在先前的文件中添加第二張紙,您認為以下代碼可以工作嗎?

The answer is no. It will just overwrite the file with only one sheet: sheet2.
答案是否定的 。 它將僅用一張紙覆蓋該文件:sheet2。
To write more sheets to an Excel file we need to use a pd.ExcelWriter object as shown below. First, we create another data frame for sheet2, then we open an Excel file as an ExcelWriter object in which we write the 2 data frames:
要將更多工作表寫入Excel文件,我們需要使用pd.ExcelWriter對象,如下所示。 首先,我們為sheet2創建另一個數據框,然后打開一個Excel文件作為ExcelWriter對象,在其中寫入2個數據框:

Now our Excel file should have 2 sheets. If we then want to add another sheet to it, we need to open the file in append mode and run code similar to the previous one. For example:
現在我們的Excel文件應該有2張紙。 然后,如果要向其添加另一張紙,則需要以附加模式打開文件,并運行與上一張相似的代碼。 例如:

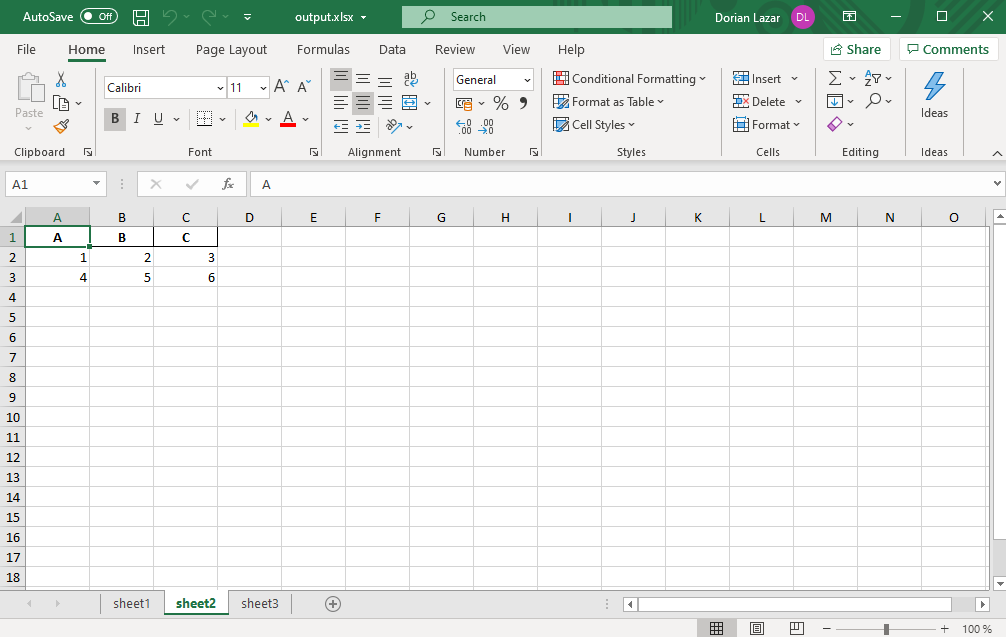
Our Excel file, now, has 3 sheets and looks like this:
我們的Excel文件現在有3張紙,看起來像這樣:
使用Excel公式 (Working with Excel Formulas)
Probably you are wondering, at this point, about Excel formulas. What about them? How to read from files that have formulas? How to write them to Excel files?
此時,您可能想知道有關Excel公式的信息。 那他們呢 如何從具有公式的文件中讀取? 如何將它們寫入Excel文件?
Well… good news. It is quite easy. Writing formulas to Excel files is as simple as just writing the string of the formula, and these strings will be automatically interpreted by Excel as formulas.
好吧...好消息。 這很容易。 將公式寫入Excel文件就像編寫公式的字符串一樣簡單,并且Excel將自動將這些字符串解釋為公式。
As an example:
舉個例子:

The Excel file produced by the code above is:
上面的代碼生成的Excel文件是:

Now, if we want to read an Excel file with formulas in it, pandas will read into data frames the result of those formulas.
現在,如果我們要讀取其中包含公式的Excel文件,則大熊貓會將這些公式的結果讀入數據框。
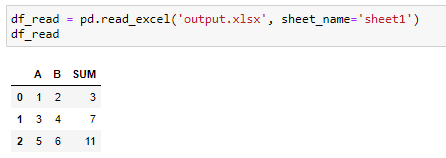
For example, let’s read our previously created file:
例如,讓我們閱讀之前創建的文件:
Sometimes you need to save the Excel file manually for this to work and not get zeros instead of the result of formulas (hit CTRL+S before executing the above code).
有時,您需要手動保存Excel文件才能使其正常工作,而不是獲取零而不是公式的結果(執行上述代碼之前,請按CTRL + S)。
Below is the code as a Jupyter notebook:
以下是Jupyter筆記本的代碼:
That’s all for this article. Thanks for reading!
這就是本文的全部內容。 謝謝閱讀!
翻譯自: https://towardsdatascience.com/how-to-work-with-excel-files-in-pandas-c584abb67bfb
本文來自互聯網用戶投稿,該文觀點僅代表作者本人,不代表本站立場。本站僅提供信息存儲空間服務,不擁有所有權,不承擔相關法律責任。 如若轉載,請注明出處:http://www.pswp.cn/news/391718.shtml 繁體地址,請注明出處:http://hk.pswp.cn/news/391718.shtml 英文地址,請注明出處:http://en.pswp.cn/news/391718.shtml
如若內容造成侵權/違法違規/事實不符,請聯系多彩編程網進行投訴反饋email:809451989@qq.com,一經查實,立即刪除!







)



)






