1.三個法寶
①存儲程序計算機工作模型,計算機系統最最基礎性的邏輯結構;
②函數調用堆棧,堆棧完成了計算機的基本功能:函數的參數傳遞機制和局部變量存取 ;
③中斷,多道程序操作系統的基點,沒有中斷機制程序只能從頭一直運行結束才有可能開始運行其他程序。
2.堆棧的基本功能:
(1)函數調用框架、傳遞參數(32位)、保存返回地址(如eax保存返回值/內存地址)、提供局部變量空間
(2)與堆棧相關的寄存器:esp和ebp
與堆棧相關的操作:push(入棧時esp指針會減4)、pop(出棧時esp指針會加4)
(3)CS:eip總是指向下一條指令的地址
C代碼中嵌入匯編代碼
一、實驗要求
完成一個簡單的時間片輪轉多道程序內核代碼,代碼見視頻中或從mykernel找。
詳細分析該精簡內核的源代碼并給出實驗截圖,撰寫一篇署名博客,并在博客文章中注明“真實姓名(與最后申請證書的姓名務必一致) + 原創作品轉載請注明出處 + 《Linux內核分析》MOOC課程http://mooc.study.163.com/course/USTC-1000029000 ”,博客內容的具體要求如下:
題目自擬,內容圍繞操作系統是如何工作的進行;
博客中需要使用實驗截圖
博客內容中需要仔細分析進程的啟動和進程的切換機制
總結部分需要闡明自己對“操作系統是如何工作的”理解。
二、實驗過程
首先通過cd LinuxKernel/Linux-3.9.4,“cd”表示進入目錄Linux-3.9.4,用rm -rf mykernel命令強力刪除mykernel。使用命令patch -pl< ../mykernel_for_linux3.9.4sc.patch,patch命令用于為特定軟件包打補丁,該命令使用diff命令對源文件進行操作。格式:patch [選項] [原始文件 [補丁文件]
在Linux系統中,專門提供了一個make命令來自動維護目標文件,與手工編譯和連接相比,make命令的優點在于他只更新修改過的文件(在Linux中,一個文件被創建或更新后有一個最后修改時間,make命令就是通過這個最后修改時間來判斷此文件是否被修改),(make還是不太懂)使用命令qemu -kernel arch/x86/boot/bzImage搭建目標環境

通過cd mykernel ,打開mykernel目錄,用ls命令看到目錄內容中包括 mymain.c ,myinterrupt.c,使用命令vi mymain.c以及vi myinterrupt.c可以看到代碼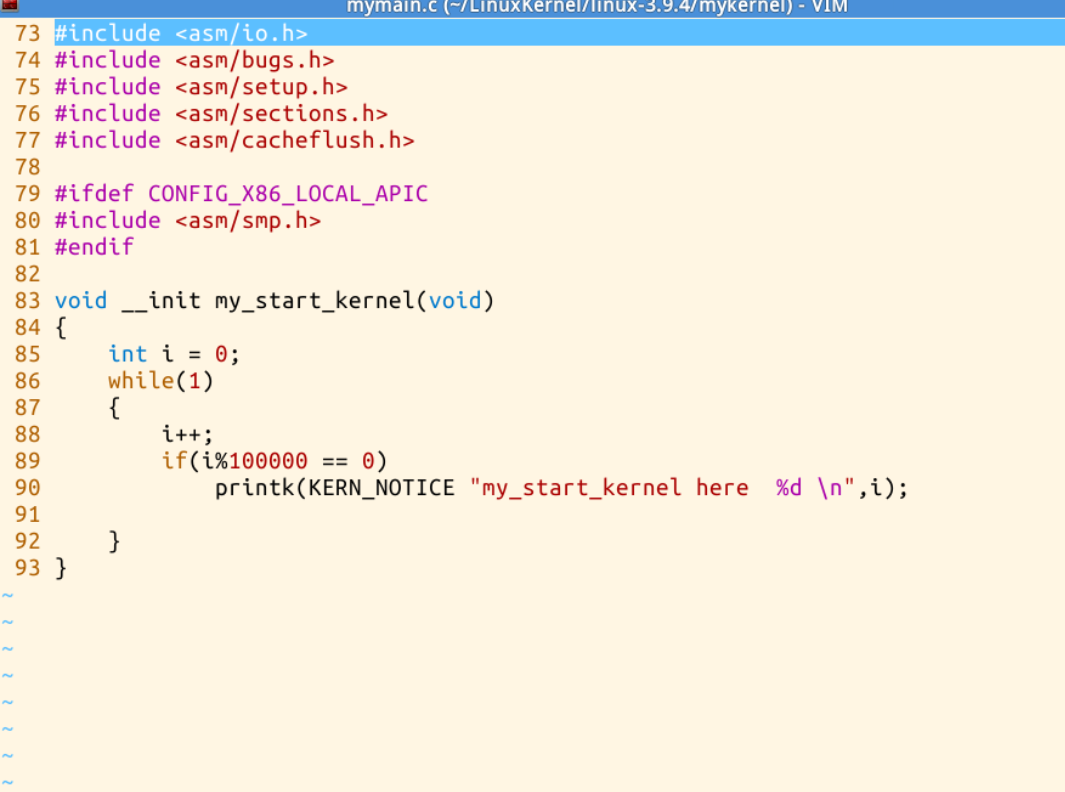
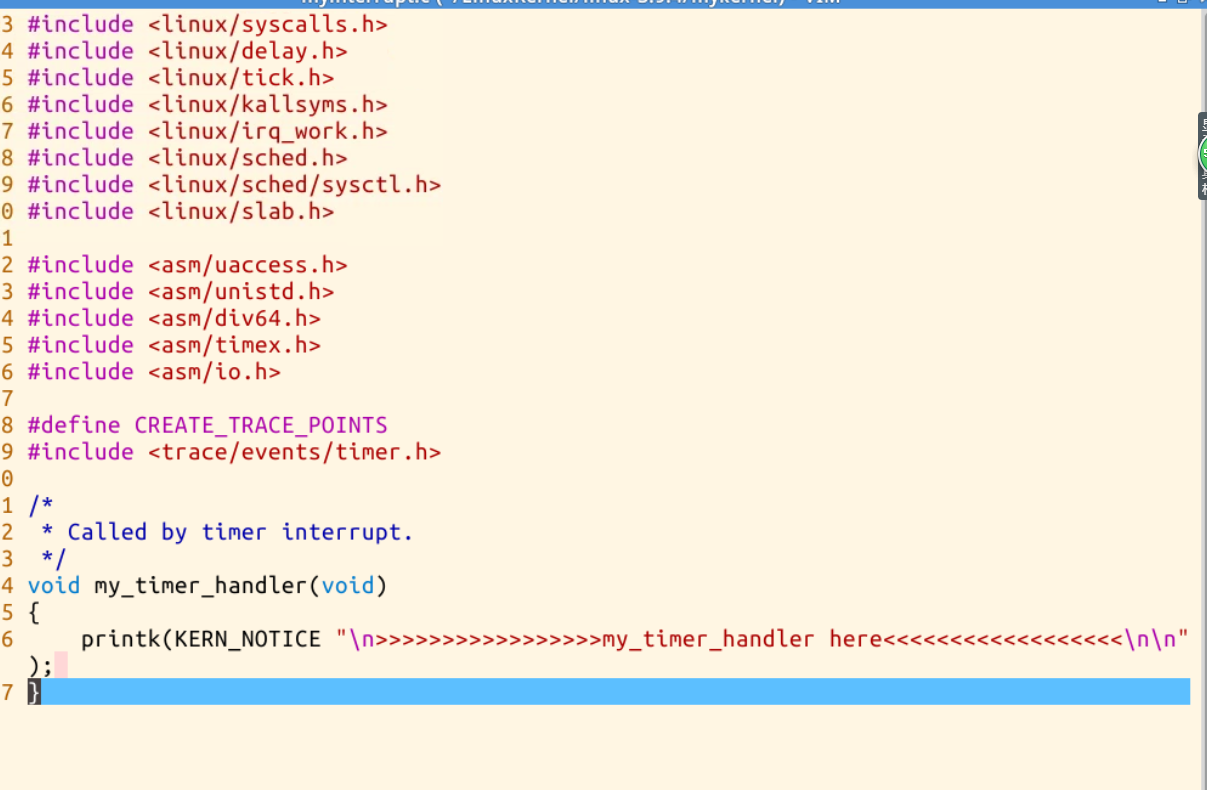
可以看到每當i增加100000會執行(printf函數輸出my_ start_ kernel _ here …)時會觸發一次時鐘中斷,在由時鐘中斷處理函數輸出(>..>>my_timer_handler<<…<)
二 操作系統內核源代碼分析
首先是mypcb.h
+#define MAX_TASK_NUM 10 // max num of task in system //進程參與內核時間片轉,這個系統最多有10個進程
+#define KERNEL_STACK_SIZE 1024*8 //每個進程棧的大小
+#define PRIORITY_MAX 30 //priority range from 0 to 30
- +/* CPU-specific state of this task */
+struct Thread { - unsigned long ip;//point to cpu run address //用于eip的保存
- unsigned long sp;//point to the thread stack's top address //用于esp的保存
- //todo add other attrubte of system thread
+};
+//PCB Struct
+typedef struct PCB{ //用于表示一個進程,定義了進程管理相關的數據結構 - int pid; // pcb id //進程編號
- volatile long state; /* -1 unrunnable, 0 runnable, >0 stopped */
- char stack[KERNEL_STACK_SIZE];// each pcb stack size is 1024*8
- /* CPU-specific state of this task */
- struct Thread thread;
- unsigned long task_entry;//the task execute entry memory address 進程第一次執行開始的地方
- struct PCB *next;//pcb is a circular linked list //用于構造進程鏈表
- unsigned long priority;// task priority
- //todo add other attrubte of process control block
+}tPCB; - +//void my_schedule(int pid);
+void my_schedule(void); //調用了my_schedule
接下來是mymain.c
+tPCB task[MAX_TASK_NUM];
+tPCB * my_current_task = NULL;
+volatile int my_need_sched = 0; //定義一個標志,用來判斷是否需要調度 - +void my_process(void);
+unsigned long get_rand(int ); - +void sand_priority(void)
+{ - int i;
- for(i=0;i<MAX_TASK_NUM;i++)
+}task[i].priority=get_rand(PRIORITY_MAX);
+void __init my_start_kernel(void)
+{- int pid = 0; 初始化一個進程0
- /* Initialize process 0*/
- task[pid].pid = pid;
- task[pid].state = 0;/* -1 unrunnable, 0 runnable, >0 stopped */
- // set task 0 execute entry address to my_process
- task[pid].task_entry = task[pid].thread.ip = (unsigned long)my_process;
- task[pid].thread.sp = (unsigned long)&task[pid].stack[KERNEL_STACK_SIZE-1];
- task[pid].next = &task[pid];
- /fork more process /
- for(pid=1;pid<MAX_TASK_NUM;pid++)
- {
memcpy(&task[pid],&task[0],sizeof(tPCB));task[pid].pid = pid;task[pid].state = -1;task[pid].thread.sp = (unsigned long)&task[pid].stack[KERNEL_STACK_SIZE-1];- task[pid].priority=get_rand(PRIORITY_MAX);//each time all tasks get a random priority //每個進程都有自己的堆棧,把創建好的新進程放到進程列表的尾部
- }
- task[MAX_TASK_NUM-1].next=&task[0];
- printk(KERN_NOTICE "\n\n\n\n\n\n system begin :>>>process 0 running!!!<<<\n\n");
- /* start process 0 by task[0] */
- pid = 0;
- my_current_task = &task[pid];
+asm volatile( "movl %1,%%esp\n\t" /* set task[pid].thread.sp to esp */"pushl %1\n\t" /* push ebp */"pushl %0\n\t" /* push task[pid].thread.ip */"ret\n\t" /* pop task[pid].thread.ip to eip */"popl %%ebp\n\t":
+);: "c" (task[pid].thread.ip),"d" (task[pid].thread.sp) /* input c or d mean %ecx/%edx*/
+}
+void my_process(void) //定義所有進程的工作,if語句表示循環1000萬次才有機會判斷是否需要調度。
+{- int i = 0;
- while(1)
- {
i++;if(i%10000000 == 0){if(my_need_sched == 1){my_need_sched = 0;sand_priority();my_schedule();}}- }
+}//end of my_process - +//produce a random priority to a task
+unsigned long get_rand(max)
+{ - unsigned long a;
- unsigned long umax;
- umax=(unsigned long)max;
- get_random_bytes(&a, sizeof(unsigned long ));
- a=(a+umax)%umax;
- return a;
+}






)










SYN flood 攻擊)

