CAS
全稱(Compare And Swap),比較交換
Unsafe類是CAS的核心類,提供硬件級別的原子操作。
?
// 對象、對象的地址、預期值、修改值
public final native boolean compareAndSwapInt(Object var1, long var2, int var4, int var5);
缺點:
- 開銷大:在并發量比較高的情況下,如果反復嘗試更新某個變量,卻又一直更新不成功,會給CPU帶來較大的壓力
- ABA問題:當變量從A修改為B在修改回A時,變量值等于期望值A,但是無法判斷是否修改,CAS操作在ABA修改后依然成功。
- 如何避免:Java提供了AtomicStampedReference和AtomicMarkableReference來解決。AtomicStampedReference通過包裝[E,Integer]的元組來對對象標記版本戳stamp,對于ABA問題其解決方案是加上版本號,即在每個變量都加上一個版本號,每次改變時加1,即A —> B —> A,變成1A —> 2B —> 3A。
- 不能保證代碼塊的原子性:CAS機制所保證的只是一個變量的原子性操作,而不能保證整個代碼塊的原子性。
?
public class Test {private static AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(100);private static AtomicStampedReference atomicStampedReference = new AtomicStampedReference(100,1);public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {//AtomicIntegerThread at1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {atomicInteger.compareAndSet(100,110);atomicInteger.compareAndSet(110,100);}});Thread at2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); // at1,執行完} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("AtomicInteger:" + atomicInteger.compareAndSet(100,120));}});at1.start();at2.start();at1.join();at2.join();//AtomicStampedReferenceThread tsf1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {try {//讓 tsf2先獲取stamp,導致預期時間戳不一致TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}// 預期引用:100,更新后的引用:110,預期標識getStamp() 更新后的標識getStamp() + 1atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(100,110,atomicStampedReference.getStamp(),atomicStampedReference.getStamp() + 1);atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(110,100,atomicStampedReference.getStamp(),atomicStampedReference.getStamp() + 1);}});Thread tsf2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {int stamp = atomicStampedReference.getStamp();try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); //線程tsf1執行完} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("AtomicStampedReference:" +atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(100,120,stamp,stamp + 1));}});tsf1.start();tsf2.start();}}
AQS(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer)
維護一個volatile int state(代表共享資源狀態)和一個FIFO線程等待隊列。
模板方法基本分為三類:
- 獨占鎖
- 共享鎖
- 釋放鎖
資源共享的方式
- Exclusive(獨占,只有一個線程能執行,如ReentrantLock)
- Share(共享,多個線程可以同時執行,如Semaphore/CountDownLatch)
同步隊列
AQS依靠同步隊列(一個FIFO的雙向隊列)來完成同步狀態的管理。當當前線程獲取狀態失敗后,同步器會將當前線程以及等待信息構造成一個節點(Node),并嘗試將他加入到同步隊列。Head節點不保存等待的線程信息,僅通過next指向隊列中第一個保存等待線程信息的Node。
?
雙向同步隊列
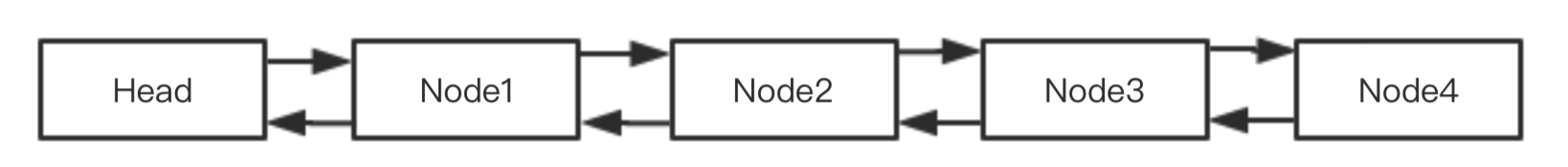
Node類
源碼(中字注釋)
?
static final class Node {/** 代表共享模式 */static final Node SHARED = new Node();/** 代表獨占模式 */static final Node EXCLUSIVE = null;/** 以下四個狀態解釋見下文等待狀態 */static final int CANCELLED = 1;static final int SIGNAL = -1;static final int CONDITION = -2;static final int PROPAGATE = -3;/** 標識等待狀態,通過CAS操作更新,原子操作不會被打斷*/volatile int waitStatus;/** 當前節點的前置節點 */volatile Node prev;/** 當前節點的后置節點 */volatile Node next;/** 該節點關聯的線程(未能獲取鎖,進入等待的線程) */volatile Thread thread;/** 指向下一個在某個條件上等待的節點,或者指向 SHARE 節點,表明當前處于共享模式*/Node nextWaiter;/*** 判斷是否處于共享模式*/final boolean isShared() {return nextWaiter == SHARED;}/** * 返回當前節點的前置節點 * 會做對前置節點空值判斷 */final Node predecessor() throws NullPointerException {Node p = prev;if (p == null)throw new NullPointerException();elsereturn p;}Node() { // Used to establish initial head or SHARED marker}Node(Thread thread, Node mode) { // Used by addWaiterthis.nextWaiter = mode;this.thread = thread;}Node(Thread thread, int waitStatus) { // Used by Conditionthis.waitStatus = waitStatus;this.thread = thread;}
}
等待狀態:
等待狀態的修改是CAS原子操作
- CANCELED: 1,因為等待超時 (timeout)或者中斷(interrupt),節點會被置為取消狀態。處于取消狀態的節點不會再去競爭鎖,也就是說不會再被阻塞。節點會一直保持取消狀態,而不會轉換為其他狀態。處于 CANCELED 的節點會被移出隊列,被 GC 回收。
- SIGNAL: -1,表明當前的后繼結點正在或者將要被阻塞(通過使用 LockSupport.pack 方法),因此當前的節點被釋放(release)或者被取消時(cancel)時,要喚醒它的后繼結點(通過 LockSupport.unpark 方法)。
- CONDITION: -2,表明當前節點在條件隊列中,因為等待某個條件而被阻塞。
- PROPAGATE: -3,在共享模式下,可以認為資源有多個,因此當前線程被喚醒之后,可能還有剩余的資源可以喚醒其他線程。該狀態用來表明后續節點會傳播喚醒的操作。需要注意的是只有頭節點才可以設置為該狀態(This is set (for head node only) in doReleaseShared to ensure propagation continues, even if other operations have since intervened.)。
- 0:新創建的節點會處于這種狀態
鎖的獲取與釋放:
獲取獨占鎖
?
獲取獨占鎖

- acquire方法
?
public final void acquire(int arg) {// 首先嘗試獲取鎖,如果獲取失敗,會先調用 addWaiter 方法創建節點并追加到隊列尾部// 然后調用 acquireQueued 阻塞或者循環嘗試獲取鎖if (!tryAcquire(arg) && acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg)){// 在 acquireQueued 中,如果線程是因為中斷而退出的阻塞狀態會返回 true// 這里的 selfInterrupt 主要是為了恢復線程的中斷狀態selfInterrupt();}
}
釋放獨占鎖
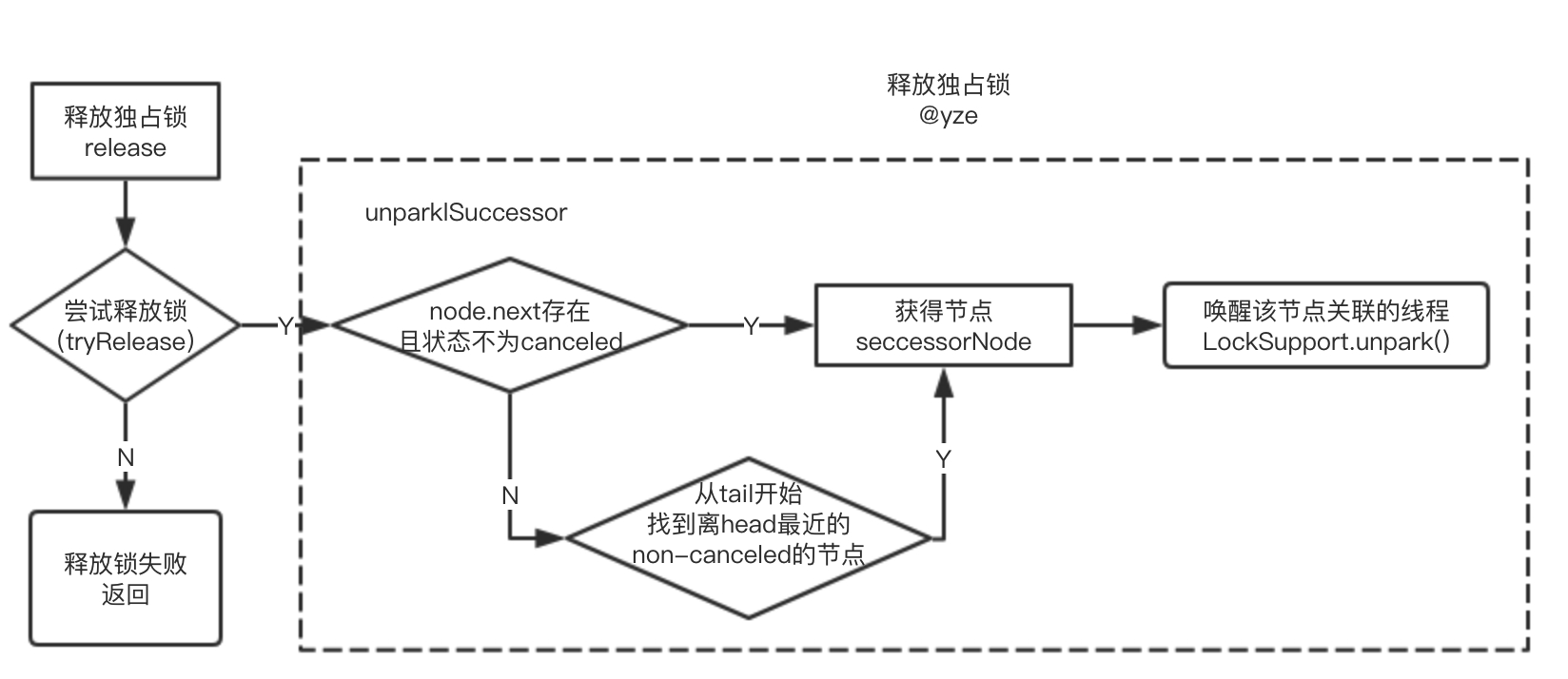
?
釋放獨占鎖
? 在獨占模式中,鎖的釋放由于沒有其他線程競爭,相對簡單。鎖釋放失敗的原因是由于該線程本身不擁有鎖,而非多線程競爭。鎖釋放成功后會檢查后置節點的狀態,找到合適的節點,調用unparkSuccessor方法喚醒該節點所關聯的線程。
- release方法
?
public final boolean release(int arg) {if (tryRelease(arg)) {Node h = head;// waitStatus 為 0,證明是初始化的空隊列或者后繼結點已經被喚醒了if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)unparkSuccessor(h);return true;}return false;
}
獲取共享鎖
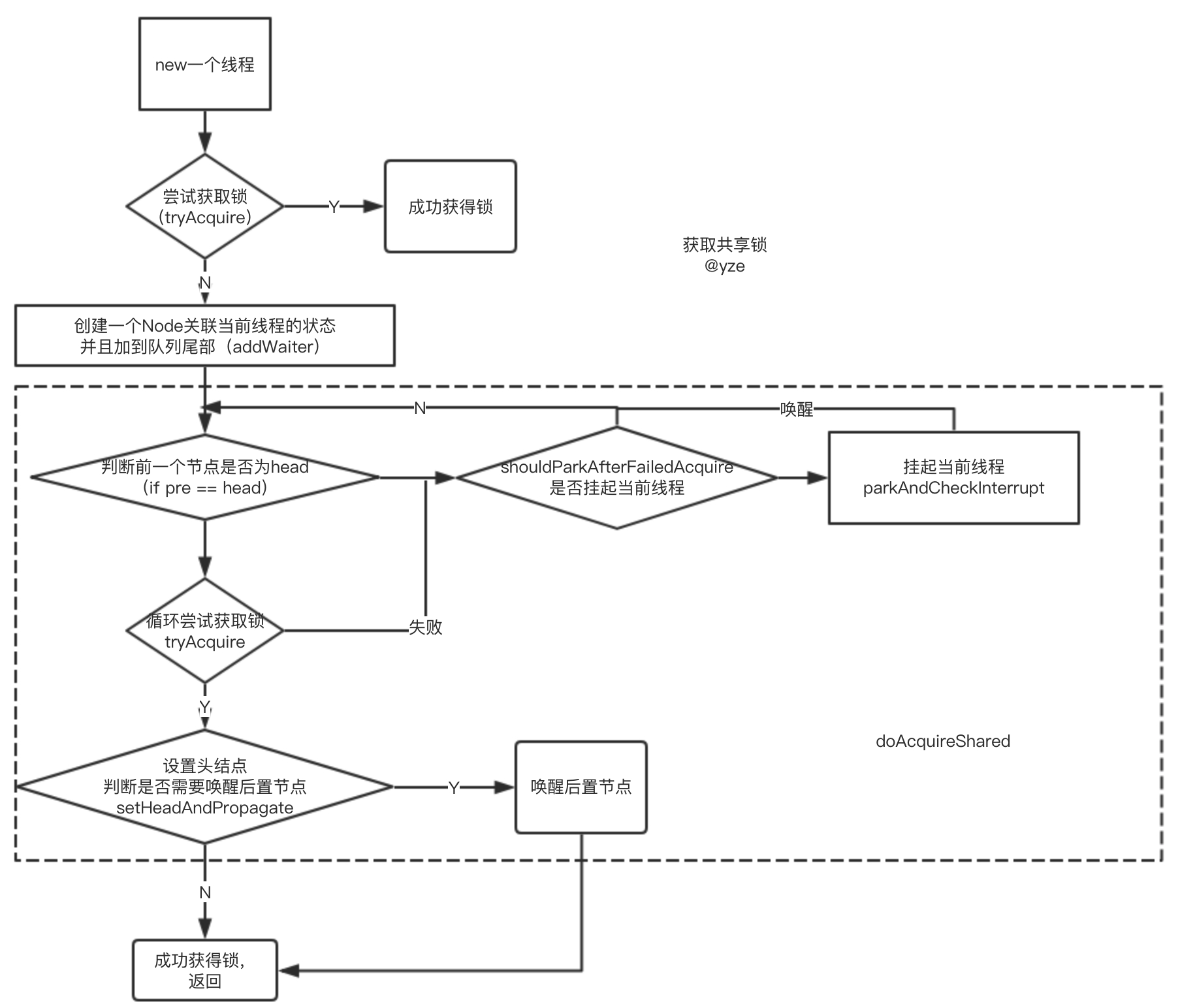
?
獲取共享鎖
-
acquireShared方法
通過該方法可以申請鎖
?
public final void acquireShared(int arg) {// 如果返回結果小于0,證明沒有獲取到共享資源if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)doAcquireShared(arg);
}
- doAcquireShared
?
private void doAcquireShared(int arg) {final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);boolean failed = true;try {boolean interrupted = false;for (;;) {final Node p = node.predecessor();if (p == head) {int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);if (r >= 0) {setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);p.next = null; // help GCif (interrupted)selfInterrupt();failed = false;return;}}if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&parkAndCheckInterrupt())interrupted = true;}} finally {if (failed)cancelAcquire(node);}
}
釋放共享鎖
作者:RealityVibe
鏈接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/2a48778871a9
來源:簡書
著作權歸作者所有。商業轉載請聯系作者獲得授權,非商業轉載請注明出處。



















