1、簡介
ArrayList是Java集合框架中的一個重要的類,它繼承于AbstractList,實現了List接口,是一個長度可變的集合,提供了增刪改查的功能。集合中允許null的存在。ArrayList類還是實現了RandomAccess接口,可以對元素進行快速訪問。實現了Serializable接口,說明ArrayList可以被序列化,還有Cloneable接口,可以被復制。和Vector不同的是,ArrayList不是線程安全的。
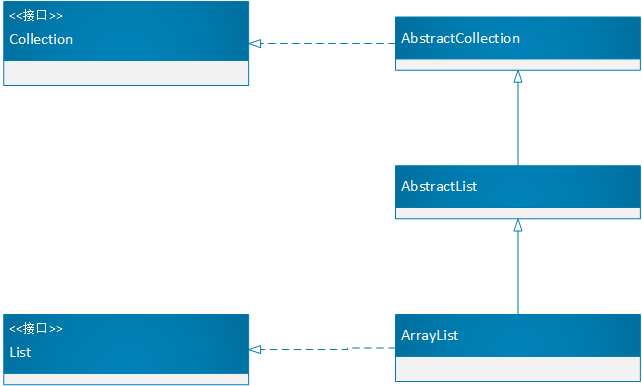
下圖是ArrayList的結構層次:
2、主要方法詳解
ArrayList底層使用的是Java數組來存儲集合中的內容,這個數組是Object類型的:
transient Object[] elementData;同時,elementData的訪問級別為包內私有,是為了使內部類能夠訪問到其中的元素。
使用int類型的size表示數組中元素的個數:
private int size;為了對應不同的構造函數,ArrayList使用了不同的數組:
/*** Shared empty array instance used for empty instances.*/private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};/*** Shared empty array instance used for default sized empty instances. We* distinguish this from EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA to know how much to inflate when* first element is added.*/private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};代碼中有個常量,表示數組的默認容量,大小為10:
/*** Default initial capacity.*/private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;常量EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA和DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA是為了初始化elementData的。如果為無參構造函數,使用DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;如果為含參構造函數,使用EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA:
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {if (initialCapacity > 0) {this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;} else {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+initialCapacity);}}/*** Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.*/public ArrayList() {this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;}使用上述構造函數,elementData中沒有元素,size為0,不過elementData的長度有可能不同。
ArrayList還提供了使用集合構造的構造函數:
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {elementData = c.toArray();if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) {// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);} else {// replace with empty array.this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;}}
(2)trimToSize()
由于表示集合中元素個數的size和表示集合容量的elementData.length可能不同,在不太需要增加集合元素的情況下容量有浪費,可以使用trimToSize方法減小elementData的大小。代碼如下:
public void trimToSize() {modCount++;if (size < elementData.length) {elementData = (size == 0)? EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA: Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);}}(3)ensureCapacity(int minCapacity)
這個方法可以用來保證數組能夠包含給定參數個元素,也就是說如果需要的話可以擴大數組的容量。主要代碼:
public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {int minExpand = (elementData != DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA)// any size if not default element table? 0// larger than default for default empty table. It's already// supposed to be at default size.: DEFAULT_CAPACITY;if (minCapacity > minExpand) {ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);}} private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);}ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);} private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {modCount++;// overflow-conscious codeif (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)grow(minCapacity);} private void grow(int minCapacity) {// overflow-conscious codeint oldCapacity = elementData.length;int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)newCapacity = minCapacity;if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);} private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {if (minCapacity < 0) // overflowthrow new OutOfMemoryError();return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?Integer.MAX_VALUE :MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;}(4)size()
函數返回集合中元素的數量:
public int size() {return size;}函數返回集合是否為空,檢查size是否為0,即使容量不為0(沒有元素):
public boolean isEmpty() {return size == 0;}檢查集合中是否包含給定的元素:
public boolean contains(Object o) {return indexOf(o) >= 0;}使用indexOf方法,如果返回值非負,表示集合中函數這個元素。
(7)indexOf(Object o)
函數返回集合中給定元素的第一次出現的位置,如果沒有就返回-1:
public int indexOf(Object o) {if (o == null) {for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)if (elementData[i]==null)return i;} else {for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)if (o.equals(elementData[i]))return i;}return -1;}首先檢查o是否為null,如果為null,就返回集合中第一個null元素的位置;如果不為null,就是用equals函數進行相等性檢查。之所以這樣,是因為如果直接對null調用equals方法,會拋出空指針異常。同時也不能循環遍歷數組中的元素調用equals方法檢查是否相等,因為ArrayList集合中允許有null元素的存在。
(8)lastIndexOf(Object o)
函數返回給定元素最后一次出現的位置,如果沒有就返回-1:
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {if (o == null) {for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--)if (elementData[i]==null)return i;} else {for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--)if (o.equals(elementData[i]))return i;}return -1;}原理和indexOf一樣,不過對集合元素遍歷的時候是倒序遍歷的。
(9)clone()
復制集合:
public Object clone() {try {ArrayList<?> v = (ArrayList<?>) super.clone();v.elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);v.modCount = 0;return v;} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {// this shouldn't happen, since we are Cloneablethrow new InternalError(e);}}本質上就是使用Arrays類進行元素的復制。
(10)toArray()
將集合轉化為數組:
public Object[] toArray() {return Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);}(11)toArray(T[] a)
轉化為數組,和上一個不同的是,上一個返回的數組是Object[]類型的,這個函數返回的數組類型根據參數確定:
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {if (a.length < size)// Make a new array of a's runtime type, but my contents:return (T[]) Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, a.getClass());System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, a, 0, size);if (a.length > size)a[size] = null;return a;}返回指定位置的元素,這里用到了一個私有函數:
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")E elementData(int index) {return (E) elementData[index];} private void rangeCheck(int index) {if (index >= size)throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));} public E get(int index) {rangeCheck(index);return elementData(index);}設置給定位置的元素為給定的元素,然后返回原來的元素:
public E set(int index, E element) {rangeCheck(index);E oldValue = elementData(index);elementData[index] = element;return oldValue;}(14)add(E e)
添加元素:
public boolean add(E e) {ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!elementData[size++] = e;return true;}(15)add(int index,E element)
在指定位置添加元素:
public void add(int index, E element) {rangeCheckForAdd(index);ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,size - index);elementData[index] = element;size++;}刪除指定位置的元素,然后返回這個元素:
public E remove(int index) {rangeCheck(index);modCount++;E oldValue = elementData(index);int numMoved = size - index - 1;if (numMoved > 0)System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,numMoved);elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its workreturn oldValue;}刪除指定的元素,如果集合中有,則刪除第一次出現的并返回true;如果沒有,集合不變并返回false:
public boolean remove(Object o) {if (o == null) {for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)if (elementData[index] == null) {fastRemove(index);return true;}} else {for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {fastRemove(index);return true;}}return false;} private void fastRemove(int index) {modCount++;int numMoved = size - index - 1;if (numMoved > 0)System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,numMoved);elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work}清空集合,將所有元素設為null,并把size設為0:
public void clear() {modCount++;// clear to let GC do its workfor (int i = 0; i < size; i++)elementData[i] = null;size = 0;}添加給定集合中的所有元素到集合中,從末尾開始添加:
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {Object[] a = c.toArray();int numNew = a.length;ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCountSystem.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew);size += numNew;return numNew != 0;}(20)add(int index,Collection<? extends E> c)
在指定位置開始添加指定集合中的所有元素:
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {rangeCheckForAdd(index);Object[] a = c.toArray();int numNew = a.length;ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCountint numMoved = size - index;if (numMoved > 0)System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew,numMoved);System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew);size += numNew;return numNew != 0;}(21)removeRange(int fromIndex,int toIndex)
刪除給定范圍內的所有元素:
protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {modCount++;int numMoved = size - toIndex;System.arraycopy(elementData, toIndex, elementData, fromIndex,numMoved);// clear to let GC do its workint newSize = size - (toIndex-fromIndex);for (int i = newSize; i < size; i++) {elementData[i] = null;}size = newSize;}這兩個函數都給一個集合參數c,removeAll刪除集合中所有在集合c中出現過的元素;retainAll保留所有在集合c中出現的元素。兩個函數都調用私有函數batchRemove():
public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {Objects.requireNonNull(c);return batchRemove(c, false);}public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) {Objects.requireNonNull(c);return batchRemove(c, true);} private boolean batchRemove(Collection<?> c, boolean complement) {final Object[] elementData = this.elementData;int r = 0, w = 0;boolean modified = false;try {for (; r < size; r++)if (c.contains(elementData[r]) == complement)elementData[w++] = elementData[r];} finally {// Preserve behavioral compatibility with AbstractCollection,// even if c.contains() throws.if (r != size) {System.arraycopy(elementData, r,elementData, w,size - r);w += size - r;}if (w != size) {// clear to let GC do its workfor (int i = w; i < size; i++)elementData[i] = null;modCount += size - w;size = w;modified = true;}}return modified;}(23)ListIterator<E> listIterator()和ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index)
這兩個函數返回在集合上的一個迭代器,不同是第一個是關于所有元素的,第二個是從指定位置開始的。這里ArrayList使用了內部類ListItr,
public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) {if (index < 0 || index > size)throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index);return new ListItr(index);}public ListIterator<E> listIterator() {return new ListItr(0);}(24)Iterator<E> iterator()
也返回一個迭代器,使用了內部類Itr,繼承于ListItr:
public Iterator<E> iterator() {return new Itr();}返回一個從fromIndex到toIndex的子集合:
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size);return new SubList(this, 0, fromIndex, toIndex);}3、例子
三種遍歷方式:
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>Integer[] nums={2,1,3,6,0,4,5,8,7,9};List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>list=Arrays.asList(nums);//使用RandomAccess方式:System.out.println("#1:");for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){System.out.print((int)list.get(i));}//使用foreach:System.out.println("\n#2:");for (Integer integer : list) {System.out.print(integer);}//使用Iterator:System.out.println("\n#3:");Iterator<Integer> it=list.iterator();while(it.hasNext()){System.out.print((int)it.next());}#1:
2136045879
#2:
2136045879
#3:
2136045879







)




)
)
)
)



