For a positive integer?n?let's define a function?f:
f(n)?=??-?1?+?2?-?3?+?..?+?(?-?1)nn
Your task is to calculate?f(n)?for a given integer?n.
The single line contains the positive integer?n?(1?≤?n?≤?1015).
Print?f(n)?in a single line.
4
2
5
-3
f(4)?=??-?1?+?2?-?3?+?4?=?2
f(5)?=??-?1?+?2?-?3?+?4?-?5?=??-?3
簡單公式:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>using namespace std;typedef long long int LL;LL n;int main()
{cin>>n;if(n%2==0){LL t=n/2;cout<<t<<endl;}else{LL t=(n-1)/2;cout<<t-n<<endl;}return 0;
}Let's define logical?OR?as an operation on two logical values (i. e. values that belong to the set?{0,?1}) that is equal to?1?if either or both of the logical values is set to?1, otherwise it is?0. We can define logical?OR?of three or more logical values in the same manner:
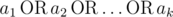 ?where?
?where?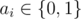 ?is equal to?1?if some?ai?=?1, otherwise it is equal to?0.
?is equal to?1?if some?ai?=?1, otherwise it is equal to?0.
Nam has a matrix?A?consisting of?m?rows and?n?columns. The rows are numbered from?1?to?m, columns are numbered from?1?to?n. Element at row?i(1?≤?i?≤?m) and column?j?(1?≤?j?≤?n) is denoted as?Aij. All elements of?A?are either 0 or 1. From matrix?A, Nam creates another matrix?B?of the same size using formula:
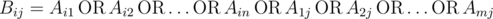 .
.
(Bij?is?OR?of all elements in row?i?and column?j?of matrix?A)
Nam gives you matrix?B?and challenges you to guess matrix?A. Although Nam is smart, he could probably make a mistake while calculating matrix?B, since size of?A?can be large.
The first line contains two integer?m?and?n?(1?≤?m,?n?≤?100), number of rows and number of columns of matrices respectively.
The next?m?lines each contain?n?integers separated by spaces describing rows of matrix?B?(each element of?B?is either?0?or?1).
In the first line, print "NO" if Nam has made a mistake when calculating?B, otherwise print "YES". If the first line is "YES", then also print?m?rows consisting of?n?integers representing matrix?A?that can produce given matrix?B. If there are several solutions print any one.
2 2 1 0 0 0
NO
2 3 1 1 1 1 1 1
YES 1 1 1 1 1 1
2 3 0 1 0 1 1 1
YES 0 0 0 0 1 0
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>using namespace std;int n,m;int B[220][220];
int A[220][220];
bool vis[220][220];bool check(int x,int y)
{bool flag=true;for(int i=0;i<m&&flag;i++){if(vis[x][i]==false&&B[x][i]==0) flag=false;}for(int i=0;i<n&&flag;i++){if(vis[i][y]==false&&B[i][y]==0) flag=false;}return flag;
}void CL(int x,int y)
{for(int i=0;i<m;i++)vis[x][i]=true;for(int i=0;i<n;i++)vis[i][y]=true;
}int main()
{cin>>n>>m;for(int i=0;i<n;i++)for(int j=0;j<m;j++)cin>>B[i][j];for(int i=0;i<n;i++){for(int j=0;j<m;j++){if(check(i,j))///ONE{A[i][j]=1;CL(i,j);}}}bool flag=true;for(int i=0;i<n&&flag;i++)for(int j=0;j<m&&flag;j++)if(B[i][j]==1&&vis[i][j]==0) flag=false;if(flag){puts("YES");for(int i=0;i<n;i++){for(int j=0;j<m;j++)cout<<A[i][j]<<" ";cout<<endl;}}else puts("NO");return 0;
}Nam is playing with a string on his computer. The string consists of?n?lowercase English letters. It is meaningless, so Nam decided to make the string more beautiful, that is to make it be a palindrome by using 4 arrow keys: left, right, up, down.
There is a cursor pointing at some symbol of the string. Suppose that cursor is at position?i?(1?≤?i?≤?n, the string uses 1-based indexing) now. Left and right arrow keys are used to move cursor around the string. The string is cyclic, that means that when Nam presses left arrow key, the cursor will move to position?i?-?1?if?i?>?1?or to the end of the string (i. e. position?n) otherwise. The same holds when he presses the right arrow key (if?i?=?n, the cursor appears at the beginning of the string).
When Nam presses up arrow key, the letter which the text cursor is pointing to will change to the next letter in English alphabet (assuming that alphabet is also cyclic, i. e. after 'z' follows 'a'). The same holds when he presses the down arrow key.
Initially, the text cursor is at position?p.
Because Nam has a lot homework to do, he wants to complete this as fast as possible. Can you help him by calculating the minimum number of arrow keys presses to make the string to be a palindrome?
The first line contains two space-separated integers?n?(1?≤?n?≤?105) and?p?(1?≤?p?≤?n), the length of Nam's string and the initial position of the text cursor.
The next line contains?n?lowercase characters of Nam's string.
Print the minimum number of presses needed to change string into a palindrome.
8 3 aeabcaez
6
A string is a palindrome if it reads the same forward or reversed.
In the sample test, initial Nam's string is:?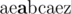 ?(cursor position is shown bold).
?(cursor position is shown bold).
In optimal solution, Nam may do?6?following steps:
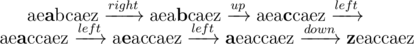
The result,?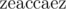 , is now a palindrome.
, is now a palindrome.
由于沒有刪除操作,最后的回文串是什么樣已經是確定的了, A-->A' ?或 A'--->A 或到A和A'的中間值上下移動的次數是一樣的,所以沒有必要跨越中點
僅僅要計算出在一邊的左右移動次數就能夠了....
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>using namespace std;const int maxn=200100;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;char str[maxn];
char rstr[maxn];
int n,p;int change[maxn][2];void getC()
{for(int i=0;i<n;i++){/// 0: A --> A'change[i][0]=max(str[i],rstr[i])-min(str[i],rstr[i]);change[i][0]=min(change[i][0],min(str[i],rstr[i])+26-max(str[i],rstr[i]));/// 1: A --> m <-- A'change[i][1]=change[i][0];}
}int main()
{cin>>n>>p;p--;cin>>str;int tt=n/2;if(n%2==0) tt--;if(p>tt){reverse(str,str+n);p=n-1-p;}memcpy(rstr,str,sizeof(str));reverse(rstr,rstr+n);getC();int temp=0;///改變字符的花費for(int i=0;i<=tt;i++){temp+=change[i][0];}///移動的花費///須要改變的左右邊界int R=-1;for(int i=tt;i>=0;i--){if(change[i][0]!=0){R=i; break;}}int L=-1;for(int i=0;i<=tt;i++){if(change[i][0]!=0){L=i; break;}}if(L==-1||R==-1){puts("0");}else if(L==R){cout<<abs(p-L)+temp<<endl;}else{/// L <----> Rif(p>=L&&p<=R){int t=min(abs(R-p),abs(L-p));cout<<R-L+t+temp<<endl;}else if(p<L){cout<<abs(R-p)+temp<<endl;}else if(p>R){cout<<abs(L-p)+temp<<endl;}}return 0;
}
As you know, an undirected connected graph with?n?nodes and?n?-?1?edges is called a?tree. You are given an integer?d?and a tree consisting of?nnodes. Each node?i?has a value?ai?associated with it.
We call a set?S?of tree nodes?valid?if following conditions are satisfied:
- S?is non-empty.
- S?is connected. In other words, if nodes?u?and?v?are in?S, then all nodes lying on the simple path between?u?and?v?should also be presented in?S.
-
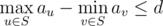 .
.
Your task is to count the number of valid sets. Since the result can be very large, you must print its remainder modulo?1000000007?(109?+?7).
The first line contains two space-separated integers?d?(0?≤?d?≤?2000) and?n?(1?≤?n?≤?2000).
The second line contains?n?space-separated positive integers?a1,?a2,?...,?an(1?≤?ai?≤?2000).
Then the next?n?-?1?line each contain pair of integers?u?and?v?(1?≤?u,?v?≤?n) denoting that there is an edge between?u?and?v. It is guaranteed that these edges form a tree.
Print the number of valid sets modulo?1000000007.
1 4 2 1 3 2 1 2 1 3 3 4
8
0 3 1 2 3 1 2 2 3
3
4 8 7 8 7 5 4 6 4 10 1 6 1 2 5 8 1 3 3 5 6 7 3 4
41
In the first sample, there are exactly 8 valid sets:?{1},?{2},?{3},?{4},?{1,?2},?{1,?3},?{3,?4}?and?{1,?3,?4}. Set?{1,?2,?3,?4}?is not valid, because the third condition isn't satisfied. Set?{1,?4}?satisfies the third condition, but conflicts with the second condition.
樹型DP,從每個節點走僅僅擴展和根節點 root ?權值 在 root<=w[v]<=root+D 之內的點, DP[u]= 全部子節點(DP[v]+1)相乘?
假設擴展到某個節點 w[v]==w[root] ? 則標記一下,不要反復走
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>using namespace std;typedef long long int LL;const int maxn=2222;
const LL mod=1000000007;int n,d,root;
LL w[maxn];
vector<int> g[maxn];
bool vis[maxn][maxn];LL dp[maxn];LL dfs(int u,int fa)
{dp[u]=1;for(int i=0,sz=g[u].size();i<sz;i++){int v=g[u][i];if(v==fa) continue;if(!((w[root]<=w[v])&&(w[v]<=w[root]+d))) continue;if(vis[root][v]) continue;if(w[root]==w[v]) vis[root][v]=vis[v][root]=true;int temp=dfs(v,u);dp[u]=(dp[u]+temp*dp[u])%mod;}return dp[u];
}int main()
{cin>>d>>n;for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)cin>>w[i];for(int i=0; i<n-1; i++){int a,b;cin>>a>>b;g[a].push_back(b);g[b].push_back(a);}LL sum=0;for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){root=i;sum=(sum+dfs(i,i))%mod;}cout<<sum<<endl;return 0;
}The next "Data Structures and Algorithms" lesson will be about Longest Increasing Subsequence (LIS for short) of a sequence. For better understanding, Nam decided to learn it a few days before the lesson.
Nam created a sequence?a?consisting of?n?(1?≤?n?≤?105) elements?a1,?a2,?...,?an?(1?≤?ai?≤?105). A subsequence?ai1,?ai2,?...,?aik?where?1?≤?i1?<?i2?<?...?<?ik?≤?n?is called increasing if?ai1?<?ai2?<?ai3?<?...?<?aik. An increasing subsequence is called longest if it has maximum length among all increasing subsequences.
Nam realizes that a sequence may have several longest increasing subsequences. Hence, he divides all indexes?i?(1?≤?i?≤?n), into three groups:
- group of all?i?such that?ai?belongs to no longest increasing subsequences.
- group of all?i?such that?ai?belongs to at least one?but not every?longest increasing subsequence.
- group of all?i?such that?ai?belongs to every longest increasing subsequence.
Since the number of longest increasing subsequences of?a?may be very large, categorizing process is very difficult. Your task is to help him finish this job.
The first line contains the single integer?n?(1?≤?n?≤?105) denoting the number of elements of sequence?a.
The second line contains?n?space-separated integers?a1,?a2,?...,?an?(1?≤?ai?≤?105).
Print a string consisting of?n?characters.?i-th character should be '1', '2' or '3' depending on which group among listed above index?i?belongs to.
1 4
3
4 1 3 2 5
3223
4 1 5 2 3
3133
In the second sample, sequence?a?consists of 4 elements:?{a1,?a2,?a3,?a4}?=?{1,?3,?2,?5}. Sequence?a?has exactly 2 longest increasing subsequences of length 3, they are?{a1,?a2,?a4}?=?{1,?3,?5}?and?{a1,?a3,?a4}?=?{1,?2,?5}.
In the third sample, sequence?a?consists of 4 elements:?{a1,?a2,?a3,?a4}?=?{1,?5,?2,?3}. Sequence?a?have exactly 1 longest increasing subsequence of length 3, that is?{a1,?a3,?a4}?=?{1,?2,?3}.
Solution 2:
// Some notation is re-defined.
-
Let?F1i?be the length of LIS ending exactly at?ai?of sequence?{a1,?a2,?...,?ai}.
-
Let?F2i?be the length of LIS beginning exactly at?ai?of sequence?{ai,?ai?+?1,?...,?an}.
-
l?= length of LIS of?{a1,?a2,?...,?an}?=?max{F1i}?=?max{F2j}.
-
Let?Fi?be the length of LIS of sequence?{a1,?a2,?...,?ai?-?1,?ai?+?1,?...,?an} (i.e the length of LIS of initial sequence?a?after removing element?ai).
-
Index?i?must in group:
1) if?F1i?+?F2i?-?1?<?l, otherwise:
2) if?Fi?=?l
3) if?Fi?=?l?-?1
-
How to caculate?Fi? We have:?Fi?=?max{F1u?+?F2v}?among?1?≤?u?<?i?<?v?≤?n?such that?au?<?av. From this formula, we can use Segment tree to calculate?Fi. Due to limitation of my English, it is really hard to write exactly how. I will post my code soon.
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <map>using namespace std;const int maxn=100100;int n,a[maxn],b[maxn];
int f1[maxn],f2[maxn];
int v1[maxn],n1,v2[maxn],n2;
set<int> st;
map<pair<int,int>,int> mp;int r[maxn],rn;
int ans[maxn];int main()
{scanf("%d",&n);for(int i=0;i<n;i++){scanf("%d",a+i);r[rn++]=a[i];}sort(r,r+rn);rn=unique(r,r+rn)-r;///.....rhash.....for(int i=0;i<n;i++){int id=lower_bound(r,r+rn,a[i])-r;id=rn-1-id;b[n-1-i]=r[id];}int LIS=1;for(int i=0;i<n;i++){if(i==0){v1[n1++]=a[i];v2[n2++]=b[i];f1[0]=f2[0]=1;}else{int p1=lower_bound(v1,v1+n1,a[i])-v1;v1[p1]=a[i];if(p1==n1) n1++;f1[i]=p1+1;LIS=max(LIS,f1[i]);int p2=lower_bound(v2,v2+n2,b[i])-v2;v2[p2]=b[i];if(p2==n2) n2++;f2[i]=p2+1;}}for(int i=0;i<n;i++){int x=i,y=n-1-i;if(f1[x]+f2[y]-1<LIS)ans[i]=1;else if(f1[x]+f2[y]-1==LIS){ans[i]=4;mp[make_pair(f1[x],f2[y])]++;}}for(int i=0;i<n;i++){if(ans[i]==4){int x=i,y=n-1-i;if(mp[make_pair(f1[x],f2[y])]==1) ans[i]=3;else ans[i]=2;}printf("%d",ans[i]);if(i==n-1) putchar('\n');}return 0;
}


![[LeetCode]Maximum Depth of Binary Tree](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[LeetCode]Maximum Depth of Binary Tree)
![BZOJ2435 [Noi2011]道路修建](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/BZOJ2435 [Noi2011]道路修建)














傳遞)
