這里寫自定義目錄標題
- 所用資料
- 一、從文件中讀取數據
- 1.1 讀取整個文件
- 1.2 文件路徑
- 1.3 逐行讀取
- 1.4 創建一個包含文件各行內容的列表
- 1.5 使用文件的內容
- 1.6 包含一百萬位的大型文件
- 1.7 圓周率值中包含你的生日嗎
- 練習題
- 二、寫入文件
- 2.1 寫入空文件
- 2.2 寫入多行
- 2.3 附加到文件
- 練習題
- 三、異常
- 3.1 ZeroDivisionError異常
- 3.2 使用 try - except 模塊
- 3.3 try - except - else 代碼塊
- 3.4 處理 FileNotFoundError 異常
- 3.5 分析文本的字符
- 3.6 分析多個文件
- 3.7 遇到異常時保持靜默
- 練習題
- 四、存儲數據
- 4.1 使用json.dump( )和json.load( )
- 4.2 保存和讀取用戶生成的數據
所用資料
代碼中所用到的文件可以從下面的網站進行下載:
https://www.ituring.com.cn/book/2784
一、從文件中讀取數據
1.1 讀取整個文件
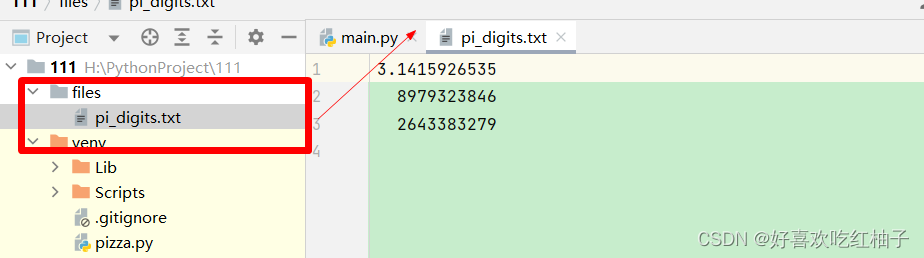
with open('files/pi_digits.txt') as file_object:contents = file_object.read()
print(contents)

- open函數
打開一個文件。接收參數為需要打開的文件名。Python會在當前執行的文件所在目錄下查找指定文件,因此需要把pi_digits.txt文件放在執行文件的同目錄下。
open函數返回一個表示文件的對象,Python將通過as關鍵字該對象賦予file_object。
- with關鍵字
再不需要訪問文件后,Python會將其自動關閉。比直接使用close函數(關閉文件函數)更加安全。
- read函數
讀取文件內容,以字符串形式賦給contents變量。read函數在讀取到文件末尾時會返回一個空字符串,打印出來就是一個空行,可以對contents中使用rstrip函數進行結尾的空行刪除。
with open('pi_digits.txt') as file_object:contents = file_object.read()
print(contents.rstrip())

可以看到空白行被刪除掉了。
1.2 文件路徑
-
相對路徑: 相對于當前運行的程序所在的目錄位置進行查找。如當前運行的程序為python_work,其中有一個名為files的文件夾存儲了file.txt文件,路徑為: files\file.txt,python會自動在python_work中尋找。
-
絕對路徑:計算機中文件存儲的準確位置,如:C:學習\Python從入門到實踐第二版源代碼文件\源代碼文件\chapter_10。因為絕對路徑較長,一般會將該字符串先賦給一個變量file_path,然后傳入Open函數中
注:顯示文件路徑時,Windows系統使用反斜杠(\ )而不是斜杠(/ ),但在代碼中使用斜杠來代表路徑。
1.3 逐行讀取
以每一行的方式讀取文件:使用for循環。
file_path = 'files/pi_digits.txt'
with open(file_path) as file_object:for line in file_object:print(line.rstrip())
使用for循環,讓變量line代表文件中的每一行進行輸出。
1.4 創建一個包含文件各行內容的列表
- readlines函數:從文件中讀取每一行并將其存儲在一個列表中。
- readline函數:從文件中讀取一行,并作為字符串保存。
file_path = 'files/pi_digits.txt'
with open(file_path) as file_object:line = file_object.readline()lines = file_object.readlines()print(line)
print(lines)代碼使用lines接收readlines函數讀到的存儲文件中的每一行內容的列表。
可以看到每一行后面都有一個換行符。

讀取到的lines即可使用for循環進行每一行內容的讀取。
1.5 使用文件的內容
將文件讀取到內存中后即可使用數據。
Python中有三個去除頭尾字符、空白符的函數,它們依次為:
- strip: 用來去除頭尾字符、空白符(包括\n、\r、\t、’ ‘,即:換行、回車、制表符、空格)
- lstrip:用來去除開頭字符、空白符(包括\n、\r、\t、’ ‘,即:換行、回車、制表符、空格)
- rstrip:用來去除結尾字符、空白符(包括\n、\r、\t、’ ',即:換行、回車、制表符、空格)
為了把文件中拿到的內容整合成一行沒有中間空白字符的字符串,使用strip函數進行去空白。
去空白函數
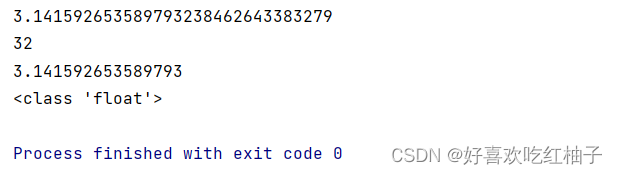
file_path = 'files\pi_digits.txt'with open(file_path) as file_objects:lines = file_objects.readlines()pi_strings = ""
for line in lines:pi_strings += line.strip()print(pi_strings)
print(len(pi_strings))
pi_number = float(pi_strings)
print(pi_number)
print(type(pi_number))
strip函數不僅可以刪除每行后面的空白字符,還可以把每行開頭的空白符也進行刪除。這樣就得到了一個pi_string的字符串。
如果想后續進行數值的計算,需要把字符串轉為數值進行使用,可以使用float函數進行類型轉換。
1.6 包含一百萬位的大型文件
所需文件:
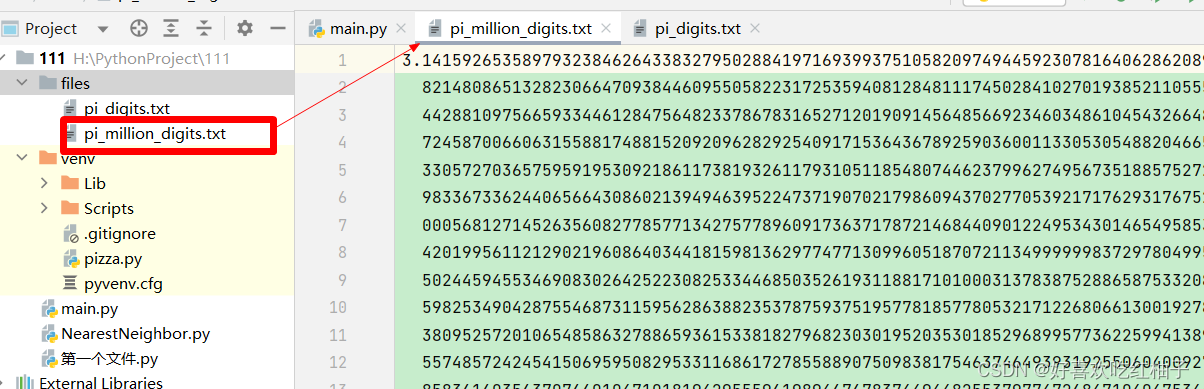
讀取一個精確到小數點后1000000位的圓周率文件。
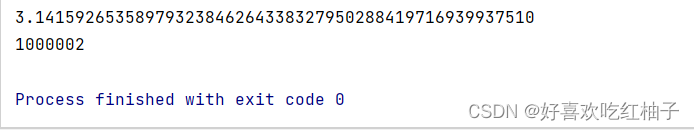
file_path = 'files/pi_million_digits.txt'with open(file_path) as file_objects:lines = file_objects.readlines()pi_string = ""
for line in lines:pi_string += line.strip()print(pi_string[:52])
print(len(pi_string))打印前52位,然后輸出一下字符串的長度,證明確實是有1000002位數。
1.7 圓周率值中包含你的生日嗎
可以查看一下自己的生日是否在圓周率中,如果存在,使用index函數查找到生日字符串在pi字符串中的位置并且輸出。
file_path = 'files/pi_million_digits.txt'with open(file_path) as file_objects:lines = file_objects.readlines()pi_string = ""
for line in lines:pi_string += line.strip()birthday = input("Please enter your birthday, in the form mmdd: ")if birthday in pi_string:print(f"Your birthday appears in the first million digits of pi at the index of {pi_string.index(birthday)}!")
else:print("Sorry~")練習題


file_path = 'files/learning_python.txt'with open(file_path) as file_objects:contents = file_objects.read()
print(contents)with open(file_path) as file_objects:for line in file_objects:print(line.rstrip())with open(file_path) as file_objects:lines = file_objects.readlines()
print(lines)
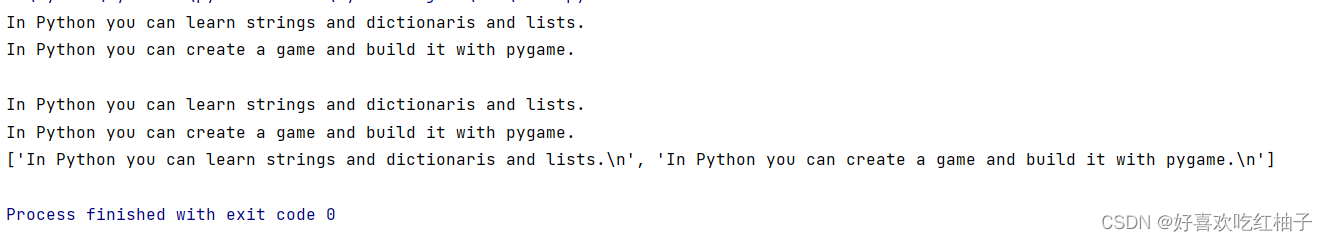
file_path = 'files/learning_python.txt'with open(file_path) as f:lines = f.readlines()for line in lines:print(line.rstrip().replace('Python','c++'))
二、寫入文件
2.1 寫入空文件
調用open() 時提供了兩個實參:
- 第一個實參:要打開的文件的名稱。
- 第二個實參(‘w’ ):告訴Python要以寫入模式打開這個文件。
打開文件時,可指定讀取模式 (‘r’ )、寫入模式 (‘w’ )、附加模式 (‘a’ )或讀寫模式 (‘r+’ )。如果省略了模式實參,Python將以默認的只讀模式打開文件。
如果要寫入的文件不存在,函數open() 將自動創建它。
然而,以寫入模式(‘w’)打開文件時千萬要小心,因為如果指定的文件已經存在,Python將在返回文件對象前清空該文件的內容。
Python只能將字符串寫入文本文件。 要將數值數據存儲到文本文件中,必須先使用函數str() 將其轉換為字符串格式。
filename = 'programming.txt'with open(filename,'w') as f:f.write('I love programming!')
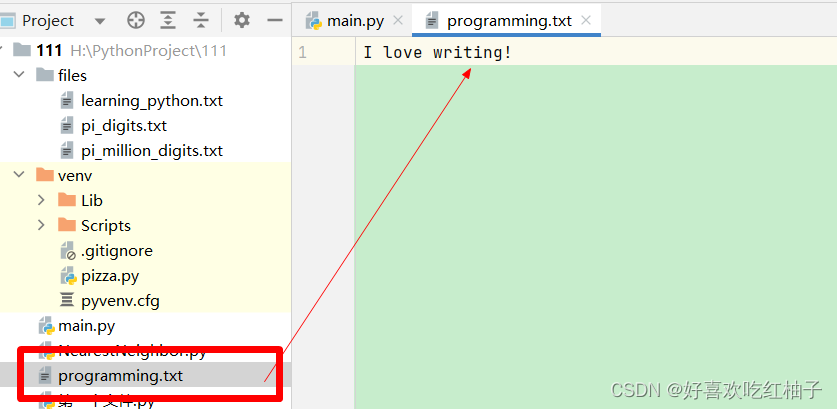
2.2 寫入多行
在writer函數中添加換行符。
filename = 'programming.txt'with open(filename,'w') as f:f.write('I love writing!\n')f.write('I love programming!\n')
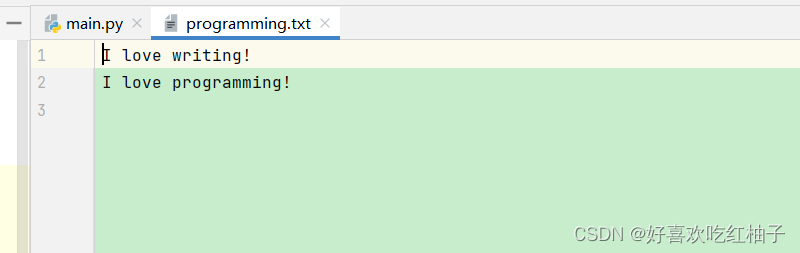
2.3 附加到文件
如果不想覆蓋掉之前的內容,而是想給文件添加內容的話,可以以附加模式(a) 打開文件。
以附加模式打開文件時,Python不會在返回文件對象前清空文件的內容,而是將寫入文件的行添加到文件末尾。
如果指定的文件不存在,Python將為你創建一個空文件。
filename = 'programming.txt'with open(filename,'a') as f:f.write('I love painting!\n')f.write('I love swimming!\n')with open(filename) as f:lines = f.read()
print(lines)
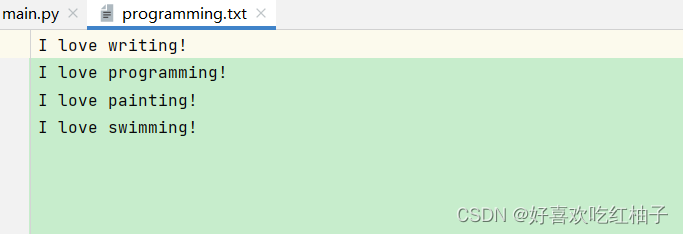
練習題

10-3
filename = 'guests.txt'
name = input('enter the name: ')
with open(filename,'w') as f:f.write(name.title())
10-4
filename = 'guest_book.txt'
with open (filename,'a') as f:while True:name = input("Enter the name: ")if name == 'q':breakprint(f"Hi, {name.title()} !")f.write(f"{name.title()}\n")

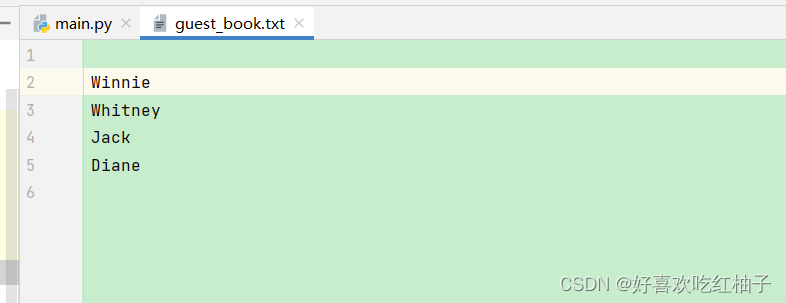
10-5
filename = 'reason.txt'
with open(filename,'a') as f:while True:reason = input('Enter the reason why you like programming')if reason=='quit':breakf.write(f"{reason}\n")
三、異常
異常:一個特殊對象,管理程序執行期間發生的錯誤。
每當發生讓Python不知所措的錯誤時,它都會創建一個異常對象。如果你編寫了處理該異常的代碼,程序將繼續運行;如果未對異常進行處理,程序將停止并顯示traceback,其中包含有關異常的報告。
異常是使用try-except 代碼塊處理的。
try-except 代碼塊讓Python執行指定的操作,同時告訴Python發生異常時怎么辦。使用try-except 代碼塊時,即便出現異常,程序也將繼續運行:顯示你編寫的友好的錯誤消息,而不是令用戶迷惑的traceback。
3.1 ZeroDivisionError異常
ZeroDivisionError異常:被除數不能為0的異常。
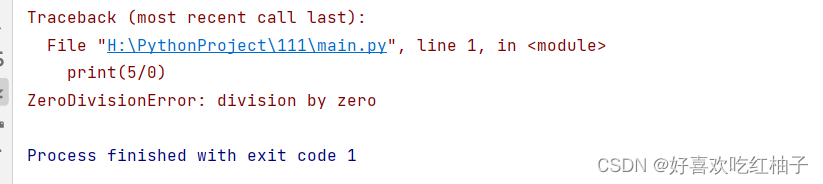
3.2 使用 try - except 模塊
當認為可能會發生錯誤時,可編寫一個try-except 代碼塊來處理可能引發的異常。
- try下寫讓Python嘗試運行一些代碼,
- except下寫如果這些代碼引發了指定的異常該怎么辦。
try:print(5/0)
except ZeroDivisionError:print("You can't divide by zero! ")
將導致錯誤的代碼行 print(5/0) 放在一個try 代碼塊中。如果try 代碼塊中的代碼運行起來沒有問題,Python將跳過except 代碼塊;如果try 代碼塊中的代碼導致了錯誤,Python將查找與之匹配的except 代碼塊并運行其中的代碼。
在本例中,try 代碼塊中的代碼引發了ZeroDivisionError 異常,因此Python查找指出了該怎么辦的except 代碼塊,并運行其中的代碼。這樣,用戶看到的是一條友好的錯誤消息,而不是traceback。
3.3 try - except - else 代碼塊
使用try-except進行異常處理,而依賴try代碼塊成功執行的代碼都應放到else代碼塊中。
while True:n1 = input("First number: ")if n1 == 'q':breakn2 = input('Second number: ')if n2 == 'q':breaktry:result = int(n1)/int(n2)except ZeroDivisionError:print("You can't divide by 0!")else:print(result)
3.4 處理 FileNotFoundError 異常
FileNotFoundError 異常:找不到文件
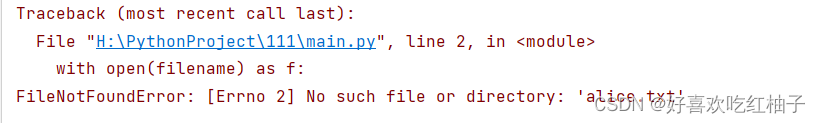
filename = 'alice.txt'try:with open(filename) as f:contents = f.read()except FileNotFoundError:print(f"{filename} doesn't exit!")
3.5 分析文本的字符
統計alice.txt文件中所有的英文單詞數量。
- split()函數:為一個字符串中的英文單詞創建一個單詞列表
- encoding = ‘utf-8’:當系統默認編碼和讀取文件使用的編碼不一致時使用。
filename = 'alice.txt'try:with open(filename,encoding = 'utf-8') as f:contents = f.read()except FileNotFoundError:print(f"{filename} doesn't exit!")else:words = contents.split()num_word = len(words)print(f"The file {filename} has about {num_word} words.")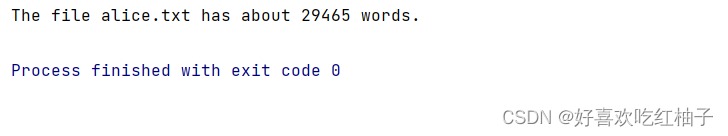
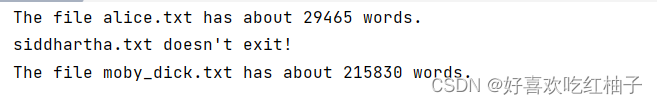
3.6 分析多個文件
filenames = [‘alice.txt’,‘siddhartha.txt’,‘mobd_dick.txt’]
其中siddhartha.txt文件不存在。使用for循環對文件列表中的文件一次讀取并且分析。
def count_words(filename):try:with open(filename, encoding='utf-8') as f:contents = f.read()except FileNotFoundError:print(f"{filename} doesn't exit!")else:words = contents.split()num_word = len(words)print(f"The file {filename} has about {num_word} words.")filenames = ['alice.txt','siddhartha.txt','moby_dick.txt']
for filename in filenames:count_words(filename)
3.7 遇到異常時保持靜默
如果想要發生異常時程序什么也不說,像什么都沒有發生過一樣繼續執行,那就在except模塊下使用pass語句。
def count_words(filename):try:with open(filename, encoding='utf-8') as f:contents = f.read()except FileNotFoundError:passelse:words = contents.split()num_word = len(words)print(f"The file {filename} has about {num_word} words.")filenames = ['alice.txt','siddhartha.txt','moby_dick.txt']
for filename in filenames:count_words(filename)

練習題


10-6
try:n1 = int(input("the first number is :"))n2 = int(input("The second number is :"))
except ValueError:print("Please enter number not text!")
else:print(n1+n2)
10-7
while True:try:n1 = int(input("the first number is :"))n2 = int(input("The second number is :"))except ValueError:print("Please enter number not text!")else:print(n1+n2)10-8
四、存儲數據
JSON格式:存儲數據結構,最初是為JavaScript開發,但隨后成了一種常見格式,被包括Python在內的眾多語言采用。
模塊json 讓你能夠將簡單的Python數據結構轉儲到文件中,并在程序再次運行時加載該文件中的數據。
還可以使用json 在Python程序之間分享數據。
更重要的是,JSON數據格式并非Python專用的,JSON格式存儲的數據可以與使用其他編程語言共享。
4.1 使用json.dump( )和json.load( )
-
函數json.dump() : 把數據存儲在文件中。接受兩個實參,要存儲的數據,以及可用于存儲數據的文件對象。
-
json.load() : 把數據讀取到內存中。
import json
numbers = [2,3,4,5,7.11,13]
filename = 'numbers.json'
with open(filename,'w') as f:json.dump(numbers,f)首先import json模塊,然后使用json.dump把數字列表存儲進number.json文件中。
使用json.load(f)把numbers.json文件中的數據結構存進內存中,然后打印輸出。
import json
filename = 'numbers.json'
with open(filename) as f:numbers = json.load(f)
print(numbers)
帶有依賴的可以直接執行的一個 jar 包)











)






