一、String對象
String對象和python中的字符串一樣,也有很多方法,這些方法大概分為以下種類:
1、索引和查找
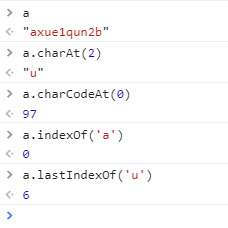
1、charAt()? ?返回指定位置的字符。
2、charCodeAt()?返回指定位置的字符的 Unicode 編碼。這個返回值是 0 - 65535 之間的整數。
3、indexOf()??檢索字符串。
4、lastIndexOf() 方法可返回一個指定的字符串值最后出現的位置,在一個字符串中的指定位置從后向前搜索
?
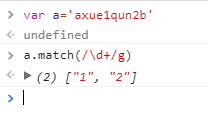
5、match()??在字符串內檢索指定的值,或找到一個或多個正則表達式的匹配。
match支持正則表達式進行匹配,注意:和sed一樣,/g,代表全部查找,不加/g的話,只會返回匹配到的第一個元素。

?
6、search()??檢索字符串中指定的子字符串,或檢索與正則表達式相匹配的子字符串。
語法:stringObject.search(regexp)
返回值:返回首次匹配后的索引,如果沒有匹配到內容,則返回-1。
注意:
- search() 方法不執行全局匹配,它將忽略標志 g。它同時忽略 regexp 的 lastIndex 屬性,并且總是從字符串的開始進行檢索,這意味著它總是返回 stringObject 的第一個匹配的位置。
- 要執行忽略大小寫的檢索,請追加標志 i。

?
?
7、slice() 切片,返回指定索引值之間的子字符串,和python一樣,半封閉取值【)

?
8、split()? 分隔字符串,按照指定子字符串進行分隔,返回array

?
9、substr()? ?返回從指定索引開始的子字符串。參數為index,索引從0開始
參數:stringObject.substr(start,length)
start:起始位置
lenght:字符串個數,默認是到結尾的字符。

?
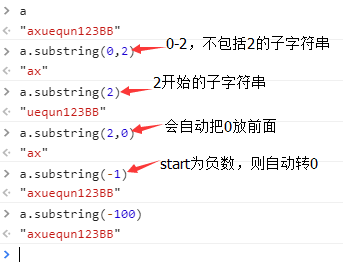
10、substring(start,stop)? 獲取子字符串,參數為start,stop,注意:是通過索引號提取子字符串。遵循半開半閉合原則:【)
substring(start,stop)
參數:起始位置,結束為止
substring類似python中的切片:例如[2,4]表示提取索引號為2、3的子字符串,[2:]表示提取2以后的子字符串。
?
?
2、樣式
樣式主要是對字符串添加對應的樣式,實際上就是添加HTML標簽。
1、anchor()??創建 HTML 錨。
2、big()? 字體加大
3、small() 字體變小
4、blink()?顯示閃動字符串。
5、bold()??使用粗體顯示字符串。
6、fixed()?以打字機文本顯示字符串。
7、fontcolor()?使用指定的顏色來顯示字符串。
8、fontsize()??使用指定的尺寸來顯示字符串。
9、italics() 方法用于把字符串顯示為斜體。
10、link() 方法用于把字符串顯示為超鏈接。
11、strike() 刪除線
12、Lowercase() 小寫
13、Uppercase() 大寫
14、sub() 下標
15、sup() 上標
?例子:
<html>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
var txt="Hello World!"
document.write("<p>Big: " + txt.big() + "</p>")
document.write("<p>Small: " + txt.small() + "</p>")
document.write("<p>Bold: " + txt.bold() + "</p>")
document.write("<p>Italic: " + txt.italics() + "</p>")
document.write("<p>Blink: " + txt.blink() + " (does not work in IE)</p>")
document.write("<p>Fixed: " + txt.fixed() + "</p>")
document.write("<p>Strike: " + txt.strike() + "</p>")
document.write("<p>Fontcolor: " + txt.fontcolor("Red") + "</p>")
document.write("<p>Fontsize: " + txt.fontsize(16) + "</p>")
document.write("<p>Lowercase: " + txt.toLowerCase() + "</p>")
document.write("<p>Uppercase: " + txt.toUpperCase() + "</p>")
document.write("<p>Subscript: " + txt.sub() + "</p>")
document.write("<p>Superscript: " + txt.sup() + "</p>")
document.write("<p>Link: " + txt.link("http://www.cnblogs.com/skyflask") + "</p>")
</script>
</body>
</html>
結果為:
Big:?Hello World!
Small:?Hello World!
Bold:?Hello World!
Italic:?Hello World!
Blink:?Hello World!?(does not work in IE)
Fixed:?Hello World!
Strike:?Hello World!
Fontcolor:?Hello World!
Fontsize:?Hello World!
Lowercase: hello world!
Uppercase: HELLO WORLD!
Subscript:?Hello World!
Superscript:?Hello World!
Link:?Hello World!
?
3、轉換
1、concat()? ?連接字符串。

?
2、formCharCode()? 從字符編碼創建一個字符串。

?
3、toLocaleLowerCase() 按照本地方式轉換為小寫,只有幾種語言(如土耳其語)具有地方特有的大小寫映射,所有該方法的返回值通常與 toLowerCase() 一樣。
4、toLocaleUpperCase() 按照本地方式轉換為大寫 ,只有幾種語言(如土耳其語)具有地方特有的大小寫映射,所有該方法的返回值通常與 toLowerCase() 一樣。
5、toLowerCase()? 轉換為小寫
6、toUpperCase() 轉換為大寫

?
7、toString()? ?返回字符串
?
?
4、替換
1、replace()
語法:stringObject.replace(regexp/substr,replacement)
substr/regexp:符合正則表達的字符串
replacement:替換的子字符串

?
?
5、比較
1、string1.fromCharCode(string2)用本地特定的順序來比較兩個字符串。
?
?未完,以下內容待續。。。
三、Date對象
四、Number對象
五、Function對象
六、RexExp對象















)



