@Target
@Target說明了Annotation所修飾的對象范圍:Annotation可被用于 packages、types(類、接口、枚舉、Annotation類型)、類型成員(方法、構造方法、成員變量、枚舉值)、方法參數和本地變量(如循環變量、catch參數)。在Annotation類型的聲明中使用了target可更加明晰其修飾的目標。
作用:用于描述注解的使用范圍(即:被描述的注解可以用在什么地方)

取值(ElementType)有
public enum ElementType {/**用于描述類、接口(包括注解類型) 或enum聲明 Class, interface (including annotation type), or enum declaration */TYPE,/** 用于描述域 Field declaration (includes enum constants) */FIELD,/**用于描述方法 Method declaration */METHOD,/**用于描述參數 Formal parameter declaration */PARAMETER,/**用于描述構造器 Constructor declaration */CONSTRUCTOR,/**用于描述局部變量 Local variable declaration */LOCAL_VARIABLE,/** Annotation type declaration */ANNOTATION_TYPE,/**用于描述包 Package declaration */PACKAGE,/*** 用來標注類型參數 Type parameter declaration* @since 1.8*/TYPE_PARAMETER,/***能標注任何類型名稱 Use of a type* @since 1.8*/TYPE_USE
ElementType.TYPE_PARAMETER(Type parameter declaration) 用來標注類型參數, 栗子如下:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE_PARAMETER)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface TypeParameterAnnotation {}// 如下是該注解的使用例子
public class TypeParameterClass<@TypeParameterAnnotation T> {public <@TypeParameterAnnotation U> T foo(T t) {return null;}
}
ElementType.TYPE_USE(Use of a type) 能標注任何類型名稱,包括上面這個(ElementType.TYPE_PARAMETER的),栗子如下:
public class TestTypeUse {@Target(ElementType.TYPE_USE)@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)public @interface TypeUseAnnotation {}public static @TypeUseAnnotation class TypeUseClass<@TypeUseAnnotation T> extends @TypeUseAnnotation Object {public void foo(@TypeUseAnnotation T t) throws @TypeUseAnnotation Exception {}}// 如下注解的使用都是合法的@SuppressWarnings({ "rawtypes", "unused", "resource" })public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {TypeUseClass<@TypeUseAnnotation String> typeUseClass = new @TypeUseAnnotation TypeUseClass<>();typeUseClass.foo("");List<@TypeUseAnnotation Comparable> list1 = new ArrayList<>();List<? extends Comparable> list2 = new ArrayList<@TypeUseAnnotation Comparable>();@TypeUseAnnotation String text = (@TypeUseAnnotation String)new Object();java.util. @TypeUseAnnotation Scanner console = new java.util.@TypeUseAnnotation Scanner(System.in);}
}
@Retention
元注解的作用就是負責注解其他注解。Java5.0定義了4個標準的meta-annotation類型,它們被用來提供對其它 annotation類型作說明。Java5.0定義的元注解:
1.@Target,
2.@Retention,
3.@Documented,
4.@Inherited
這些類型和它們所支持的類在java.lang.annotation包中可以找到。下面我們看一下每個元注解的作用和相應分參數的使用說明。
@Target:
@Target說明了Annotation所修飾的對象范圍:Annotation可被用于 packages、types(類、接口、枚舉、Annotation類型)、類型成員(方法、構造方法、成員變量、枚舉值)、方法參數和本地變量(如循環變量、catch參數)。在Annotation類型的聲明中使用了target可更加明晰其修飾的目標。
作用:用于描述注解的使用范圍(即:被描述的注解可以用在什么地方)
取值(ElementType)有:
1.CONSTRUCTOR:用于描述構造器
2.FIELD:用于描述域
3.LOCAL_VARIABLE:用于描述局部變量
4.METHOD:用于描述方法
5.PACKAGE:用于描述包
6.PARAMETER:用于描述參數
7.TYPE:用于描述類、接口(包括注解類型) 或enum聲明
使用實例:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface Table {
/**
* 數據表名稱注解,默認值為類名稱
* @return
*/
public String tableName() default “className”;
}
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
public @interface NoDBColumn {
}
注解Table 可以用于注解類、接口(包括注解類型) 或enum聲明,而注解NoDBColumn僅可用于注解類的成員變量。
@Retention:
@Retention定義了該Annotation被保留的時間長短:某些Annotation僅出現在源代碼中,而被編譯器丟棄;而另一些卻被編譯在class文件中;編譯在class文件中的Annotation可能會被虛擬機忽略,而另一些在class被裝載時將被讀取(請注意并不影響class的執行,因為Annotation與class在使用上是被分離的)。使用這個meta-Annotation可以對 Annotation的“生命周期”限制。
作用:表示需要在什么級別保存該注釋信息,用于描述注解的生命周期(即:被描述的注解在什么范圍內有效)
取值(RetentionPoicy)有:
1.SOURCE:在源文件中有效(即源文件保留)
2.CLASS:在class文件中有效(即class保留)
3.RUNTIME:在運行時有效(即運行時保留)
Retention meta-annotation類型有唯一的value作為成員,它的取值來自java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy的枚舉類型值。具體實例如下:
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Column {public String name() default "fieldName";public String setFuncName() default "setField";public String getFuncName() default "getField"; public boolean defaultDBValue() default false;
}
Column注解的的RetentionPolicy的屬性值是RUTIME,這樣注解處理器可以通過反射,獲取到該注解的屬性值,從而去做一些運行時的邏輯處理
@Documented:
@Documented用于描述其它類型的annotation應該被作為被標注的程序成員的公共API,因此可以被例如javadoc此類的工具文檔化。Documented是一個標記注解,沒有成員。
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Column {public String name() default "fieldName";public String setFuncName() default "setField";public String getFuncName() default "getField"; public boolean defaultDBValue() default false;
}
@Inherited:
@Inherited 元注解是一個標記注解,@Inherited闡述了某個被標注的類型是被繼承的。如果一個使用了@Inherited修飾的annotation類型被用于一個class,則這個annotation將被用于該class的子類。
注意:@Inherited annotation類型是被標注過的class的子類所繼承。類并不從它所實現的接口繼承annotation,方法并不從它所重載的方法繼承annotation。
當@Inherited annotation類型標注的annotation的Retention是RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME,則反射API增強了這種繼承性。如果我們使用java.lang.reflect去查詢一個@Inherited annotation類型的annotation時,反射代碼檢查將展開工作:檢查class和其父類,直到發現指定的annotation類型被發現,或者到達類繼承結構的頂層。
實例代碼:
/*** * @author peida**/
@Inherited
public @interface Greeting {public enum FontColor{ BULE,RED,GREEN};String name();FontColor fontColor() default FontColor.GREEN;
}
自定義注解:
使用@interface自定義注解時,自動繼承了java.lang.annotation.Annotation接口,由編譯程序自動完成其他細節。在定義注解時,不能繼承其他的注解或接口。@interface用來聲明一個注解,其中的每一個方法實際上是聲明了一個配置參數。方法的名稱就是參數的名稱,返回值類型就是參數的類型(返回值類型只能是基本類型、Class、String、enum)。可以通過default來聲明參數的默認值。
定義注解格式:
public @interface 注解名 {定義體}
注解參數的可支持數據類型:
1.所有基本數據類型(int,float,boolean,byte,double,char,long,short)
2.String類型
3.Class類型
4.enum類型
5.Annotation類型
6.以上所有類型的數組
Annotation類型里面的參數該怎么設定:
第一,只能用public或默認(default)這兩個訪問權修飾.例如,String value();這里把方法設為defaul默認類型;
第二,參數成員只能用基本類型byte,short,char,int,long,float,double,boolean八種基本數據類型和 String,Enum,Class,annotations等數據類型,以及這一些類型的數組.例如,String value();這里的參數成員就為String;
第三,如果只有一個參數成員,最好把參數名稱設為"value",后加小括號.例:下面的例子FruitName注解就只有一個參數成員。
簡單的自定義注解和使用注解實例:
package annotation;import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;/*** 水果名稱注解* @author peida**/
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface FruitName {String value() default "";
}
package annotation;import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;/*** 水果顏色注解* @author peida**/
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface FruitColor {/*** 顏色枚舉* @author peida**/public enum Color{ BULE,RED,GREEN};/*** 顏色屬性* @return*/Color fruitColor() default Color.GREEN;}
package annotation;import annotation.FruitColor.Color;public class Apple {@FruitName("Apple")private String appleName;@FruitColor(fruitColor=Color.RED)private String appleColor;public void setAppleColor(String appleColor) {this.appleColor = appleColor;}public String getAppleColor() {return appleColor;}public void setAppleName(String appleName) {this.appleName = appleName;}public String getAppleName() {return appleName;}public void displayName(){System.out.println("水果的名字是:蘋果");}
}
注解元素的默認值:
注解元素必須有確定的值,要么在定義注解的默認值中指定,要么在使用注解時指定,非基本類型的注解元素的值不可為null。因此, 使用空字符串或0作為默認值是一種常用的做法。這個約束使得處理器很難表現一個元素的存在或缺失的狀態,因為每個注解的聲明中,所有元素都存在,并且都具有相應的值,為了繞開這個約束,我們只能定義一些特殊的值,例如空字符串或者負數,一次表示某個元素不存在,在定義注解時,這已經成為一個習慣用法。例如:
package annotation;import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;/*** 水果供應者注解* @author peida**/
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface FruitProvider {/*** 供應商編號* @return*/public int id() default -1;/*** 供應商名稱* @return*/public String name() default "";/*** 供應商地址* @return*/public String address() default "";
}
定義了注解,并在需要的時候給相關類,類屬性加上注解信息,如果沒有響應的注解信息處理流程,注解可以說是沒有實用價值。如何讓注解真真的發揮作用,主要就在于注解處理方法,下一步我們將學習注解信息的獲取和處理!
二、注解的使用:
第一步:新建一個annotation,名字為:MyAnnotation.java。
package com.dragon.test.annotation;import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;/*** Created by gmq on 2015/9/10.*/
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyAnnotation
{String hello () default "hello";String world();
}
第二步:建立一個MyTest.java 來使用上面的annotation。
package com.dragon.test.annotation;/*** Created by gmq on 2015/9/10.*/
public class MyTest
{@MyAnnotation(hello = "Hello,Beijing",world = "Hello,world")public void output() {System.out.println("method output is running ");}
}
第三步:用反射機制來調用注解中的內容
package com.dragon.test.annotation;import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;/*** 用反射機制來調用注解中的內容* Created by gmq on 2015/9/10.*/
public class MyReflection
{public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{// 獲得要調用的類Class<MyTest> myTestClass = MyTest.class;// 獲得要調用的方法,output是要調用的方法名字,new Class[]{}為所需要的參數。空則不是這種Method method = myTestClass.getMethod("output", new Class[]{});// 是否有類型為MyAnnotation的注解if (method.isAnnotationPresent(MyAnnotation.class)){// 獲得注解MyAnnotation annotation = method.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);// 調用注解的內容System.out.println(annotation.hello());System.out.println(annotation.world());}System.out.println("----------------------------------");// 獲得所有注解。必須是runtime類型的Annotation[] annotations = method.getAnnotations();for (Annotation annotation : annotations){// 遍歷所有注解的名字System.out.println(annotation.annotationType().getName());}}
}
輸出:
Hello,Beijing
Hello,world
@Documented
Documented注解表明這個注釋是由 javadoc記錄的,在默認情況下也有類似的記錄工具。 如果一個類型聲明被注釋了文檔化,它的注釋成為公共API的一部分。
@Component
@Component and @Bean do two quite different things, and shouldn’t be confused.
@Component (and @Service and @Repository) are used to auto-detect and auto-configure beans using classpath scanning. There’s an implicit one-to-one mapping between the annotated class and the bean (i.e. one bean per class). Control of wiring is quite limited with this approach, since it’s purely declarative.
@Bean is used to explicitly declare a single bean, rather than letting Spring do it automatically as above. It decouples the declaration of the bean from the class definition, and lets you create and configure beans exactly how you choose.
看了一些文章,這兩個注解可以互換使用,但還有一些使用目的進行區別的。
@Component被用在要被自動掃描和裝配的類上。
@Bean主要被用在方法上,來顯式聲明要用生成的類。
現在項目上,本工程中的類,一般都使用@Component來生成bean。在把通過web service取得的類,生成Bean時,使用@Bean和getter方法來生成bean。
@Conditional
Conditional 是由 SpringFramework 提供的一個注解,位于 org.springframework.context.annotation 包內,定義如下。
package org.springframework.context.annotation;import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
public @interface Conditional {Class<? extends Condition>[] value();}
Conditional 注解類里只有一個 value 屬性,需傳入一個 Condition 類型的數組,我們先來看看這個 Condition 接口長什么樣。
package org.springframework.context.annotation;import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotatedTypeMetadata;
public interface Condition {boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata);}
其中,matches() 方法傳入的參數 ConditionContext 是專門為 Condition 而設計的一個接口類,可以從中獲取到Spring容器的以下對象信息。
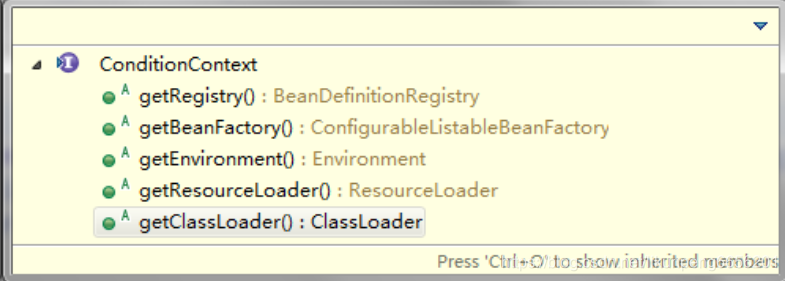
當一個 Bean 被 Conditional 注解修飾時,Spring容器會對數組中所有 Condition 接口的 matches() 方法進行判斷,只有當其中所有 Condition 接口的 matches()方法都為 ture 時,才會創建 Bean 。
自定義Conditional
接下來,我們將以一個國際化 I18n Bean 動態創建為例(根據配置中的 i18n.lang 屬性值來動態地創建國際化 I18n Bean),對如何使用 Conditional 注解進行簡單舉例:
當 i18n.lang=zh_CN 就創建中文 I18nChs Bean,
當 i18n.lang=en_US 就創建英文 I18nEng Bean。
創建好的兩個 Condition 實現類 I18nChsCondition 和 I18nEngCondition 代碼如下。
public class I18nChsCondition extends SpringBootCondition {@Overridepublic ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {String lang = context.getEnvironment().getProperty("i18n.lang");ConditionOutcome outCome = new ConditionOutcome("zh_CN".equals(lang), "i18n.lang=" + lang);return outCome;}
}
public class I18nEngCondition extends SpringBootCondition {@Overridepublic ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {String lang = context.getEnvironment().getProperty("i18n.lang");ConditionOutcome outCome = new ConditionOutcome("en_US".equals(lang), "i18n.lang=" + lang);return outCome;}}
I18n 接口定義如下。
public interface I18n {// 獲取 name 屬性的值String i18n(String name);}
I18n 接口的兩個實現類 I18nChs 和 I18nEng 定義如下。
@Component
@Conditional(I18nChsCondition.class)
public class I18nChsImpl implements I18n {Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>() {private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;{put("lang", "中文");}};@Overridepublic String i18n(String name) {return map.get(name);}
}
@Component
@Conditional(I18nEngCondition.class)
public class I18nEngImpl implements I18n {Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>() {private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;{put("lang", "English");}};@Overridepublic String i18n(String name) {return map.get(name);}}
在啟動類中添加測試代碼代碼如下。
@SpringBootApplication
public class App
{public static void main( String[] args ){ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);I18n i18n = context.getBean(I18n.class);System.out.println(i18n.getClass().getName());System.out.println(i18n.i18n("lang"));context.close();}
}
配置 application.properties 內容如下:
# language : zh_CN/Chinese,en_US/America
i18n.lang=zh_CN
運行程序,打印結果:
com.pengjunlee.condition.I18nChsImpl
中文
配置 application.properties 內容如下:
# language : zh_CN/Chinese,en_US/America
i18n.lang=en_US
再次運行程序,打印結果:
com.pengjunlee.condition.I18nEngImpl
English
為了書寫和調用方便,我們還可以把上面的條件定義成注解,以 I18nChsCondition 為例,定義代碼如下。
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Conditional(I18nChsCondition.class)
public @interface I18nChs {}
將 I18nChs 注解添加到 I18nChsImpl 上。
@Component
@I18nEng
public class I18nChsImpl implements I18n {//內容同上,此處省略}
SpringBoot 擴展注解
從上面的示例不難看出,如果要使用我們自定義條件類實現起來還是有點小麻煩的,不過比較慶幸的是, SpringBoot 在 Conditional 注解的基礎上已經提前為我們定義好了一系列功能豐富的注解,我們可以直接使用。

接下來我們使用 ConditionalOnProperty 注解來實現上面的國際化示例。
僅需修改 I18nChsImpl 和 I18nEngImpl 兩個實現組件類,其他代碼不變,程序執行結果與之前相同。
@Component
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "i18n.lang", havingValue = "zh_CN", matchIfMissing = true)
public class I18nChsImpl implements I18n {//內容同上,此處省略}
@Component
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "i18n.lang", havingValue = "en_US", matchIfMissing = false)
public class I18nEngImpl implements I18n {//內容同上,此處省略}
![[pytorch、學習] - 5.1 二維卷積層](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[pytorch、學習] - 5.1 二維卷積層)
![[51CTO]給您介紹Windows10各大版本之間區別](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[51CTO]給您介紹Windows10各大版本之間區別)
-NSData轉換成int)
)
![[pytorch、學習] - 5.2 填充和步幅](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[pytorch、學習] - 5.2 填充和步幅)



![[pytorch、學習] - 5.3 多輸入通道和多輸出通道](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[pytorch、學習] - 5.3 多輸入通道和多輸出通道)


![[pytorch、學習] - 5.4 池化層](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[pytorch、學習] - 5.4 池化層)


![[pytorch、學習] - 5.5 卷積神經網絡(LeNet)](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[pytorch、學習] - 5.5 卷積神經網絡(LeNet))


![[pytorch、學習] - 5.6 深度卷積神經網絡(AlexNet)](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[pytorch、學習] - 5.6 深度卷積神經網絡(AlexNet))

