【LetMeFly】1631.最小體力消耗路徑:廣度優先搜索BFS
力扣題目鏈接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-with-minimum-effort/
你準備參加一場遠足活動。給你一個二維?rows x columns?的地圖?heights?,其中?heights[row][col]?表示格子?(row, col)?的高度。一開始你在最左上角的格子?(0, 0)?,且你希望去最右下角的格子?(rows-1, columns-1)?(注意下標從 0 開始編號)。你每次可以往 上,下,左,右?四個方向之一移動,你想要找到耗費 體力 最小的一條路徑。
一條路徑耗費的 體力值?是路徑上相鄰格子之間 高度差絕對值?的 最大值?決定的。
請你返回從左上角走到右下角的最小?體力消耗值?。
?
示例 1:
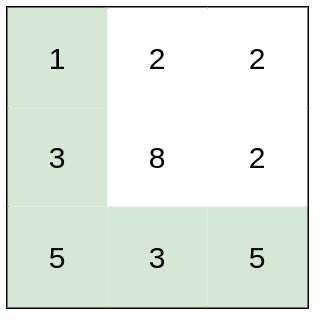
輸入:heights = [[1,2,2],[3,8,2],[5,3,5]] 輸出:2 解釋:路徑 [1,3,5,3,5] 連續格子的差值絕對值最大為 2 。 這條路徑比路徑 [1,2,2,2,5] 更優,因為另一條路徑差值最大值為 3 。
示例 2:

輸入:heights = [[1,2,3],[3,8,4],[5,3,5]] 輸出:1 解釋:路徑 [1,2,3,4,5] 的相鄰格子差值絕對值最大為 1 ,比路徑 [1,3,5,3,5] 更優。
示例 3:
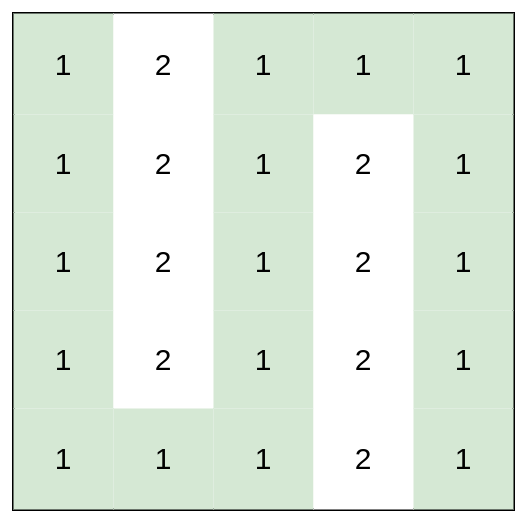
輸入:heights = [[1,2,1,1,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,1,1,2,1]] 輸出:0 解釋:上圖所示路徑不需要消耗任何體力。
?
提示:
rows == heights.lengthcolumns == heights[i].length1 <= rows, columns <= 1001 <= heights[i][j] <= 106
方法一:廣度優先搜索BFS
首先我們可以構造一個圖,圖中頂點是矩陣中的點,圖中的邊是矩陣中相鄰點的絕對值之差。
這樣,我們只需要從起點0開始,使用一個優先隊列進行廣度優先搜索。每次找出未遍歷的點中與已遍歷的點中絕對值之差最小的點。入隊時將“點的位置”和“從起點到該點的最大絕對值之差”入隊。
最終返回最后一個位置距離起點的最大絕對值之差即為答案。
- 時間復雜度 O ( n m log ? n m ) O(nm\log nm) O(nmlognm),其中 s i z e ( g r a p h ) = n × m size(graph)=n\times m size(graph)=n×m
- 空間復雜度 O ( n m ) O(nm) O(nm)
AC代碼
C++
const int directions[4][2] = {{0, -1}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {1, 0}};class Solution {
public:int minimumEffortPath(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {int n = heights.size(), m = heights[0].size();vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> graph(n * m); // graph[i]: [[j, 5], [k, 3]]for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {for (int d = 0; d < 4; d++) {int ti = i + directions[d][0], tj = j + directions[d][1];if (ti < 0 || ti >= n || tj < 0 || tj >= m) {continue;}int diff = abs(heights[i][j] - heights[ti][tj]);int x = i * m + j, y = ti * m + tj;graph[x].push_back({y, diff});}}}auto cmp = [](const pair<int, int>& a, const pair<int, int>& b) {return a.second > b.second;};priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, decltype(cmp)> pq(cmp);pq.push({0, 0});vector<int> ans(n * m, 1e9); // 從0到i的最大絕對值之差ans[0] = 0;while (pq.size()) {auto [index, diff] = pq.top();pq.pop();for (auto [toIndex, toDiff] : graph[index]) {int nextDiff = max(diff, toDiff);if (ans[toIndex] > nextDiff) {ans[toIndex] = nextDiff;pq.push({toIndex, nextDiff});}}}return ans.back();}
};
Python
# from typing import List
# import heapqdirections = [[-1, 0], [1, 0], [0, -1], [0, 1]]class Solution:def minimumEffortPath(self, heights: List[List[int]]) -> int:n, m = len(heights), len(heights[0])graph = [[] for _ in range(n * m)]for i in range(n):for j in range(m):for di, dj in directions:ti, tj = i + di, j + djif ti < 0 or ti >= n or tj < 0 or tj >= m:continuegraph[i * m + j].append((ti * m + tj, abs(heights[ti][tj] - heights[i][j])))pq = [(0, 0)]ans = [1000000000] * (n * m)ans[0] = 0while pq:thisDiff, thisNode = heapq.heappop(pq)for toNode, toDiff in graph[thisNode]:newDiff = max(thisDiff, toDiff)if ans[toNode] > newDiff:ans[toNode] = newDiffheapq.heappush(pq, (newDiff, toNode))# print(thisNode, toNode, newDiff)return ans[-1]
同步發文于CSDN,原創不易,轉載經作者同意后請附上原文鏈接哦~
Tisfy:https://letmefly.blog.csdn.net/article/details/134934684




)






)



算法 挖掘機技術哪家強 選擇排序 貪心算法)



