自己實現?
傳統MD5可通過彩虹表暴力破解,?
加鹽加密算法是一種常用的密碼保護方法,它將一個隨機字符串(鹽)添加到原始密碼中,然后再進行加密處理。
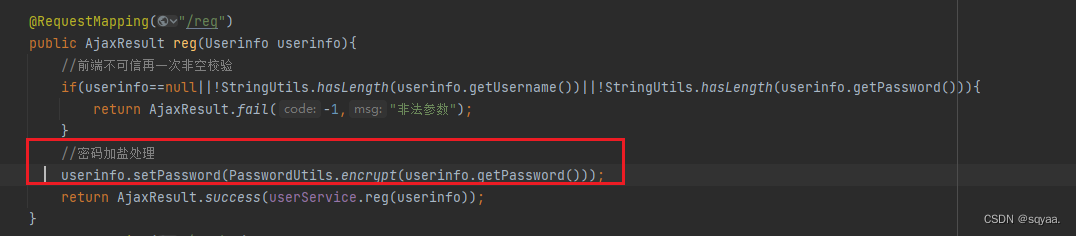
- 1. 每次調用方法產生一個唯一鹽值(UUID )+密碼=最終密碼。
- 解密:需要驗證的密碼(用戶輸入的密碼),最終加密的密碼(存在于數據庫)得到鹽值,鹽值存在最終密碼的某個位置,——>鹽值{32位}$最終密碼{32位};
- ?2. 對組合后的字符串進行多次哈希計算,每次哈希時都使用鹽值和先前的哈希值。哈希計算的次數由工作因子控制。
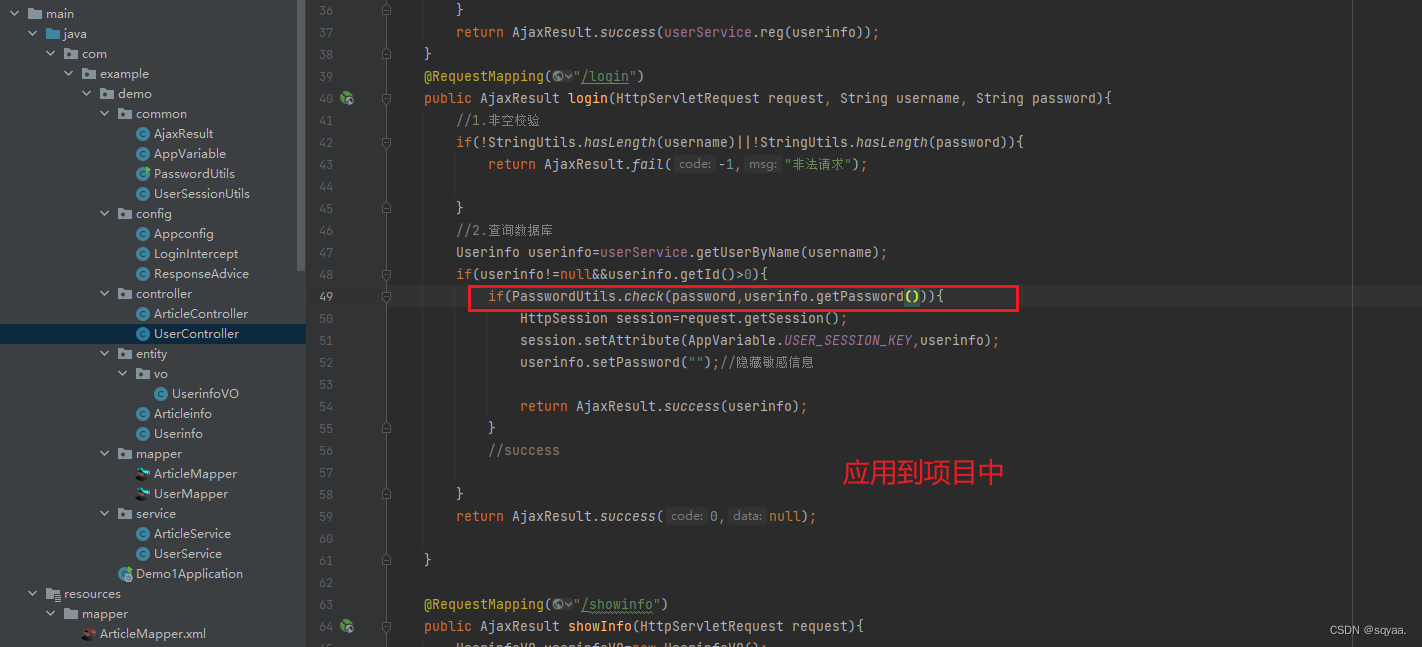
驗證密碼
已有:用戶輸入的明文密碼、此用戶在數據庫存儲的最終密碼=[鹽值$加密后的密碼]
32位32位
1.從最終密碼中得到鹽值
2.將用戶輸入的明文密碼+鹽值進行加密操作=加密后的密碼3.使用鹽值+分隔符+加密后的密碼生成數據庫存儲的密碼
4.對比生成的最終密碼和數據庫最終的密碼是否相等如果相等,那么用戶名和密碼就是對的,反之則是密碼輸入錯誤。?
package com.example.demo.common;import org.springframework.util.DigestUtils;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.UUID;public class PasswordUtils {//1.加鹽生成密碼public static String encrypt(String password){//鹽32位String salt= UUID.randomUUID().toString().replace("-","");String saltPassword = DigestUtils.md5DigestAsHex((salt+password).getBytes());String finalPassword=salt+"$"+saltPassword;return finalPassword;}//2.生成加鹽密碼public static String encrypt(String password,String salt){String saltPassword = DigestUtils.md5DigestAsHex((salt+password).getBytes());String finalPassword=salt+"$"+saltPassword;return finalPassword;}/**驗證密碼** @param :用戶輸入的明文密碼* @param :數據庫保存的最終密碼* @return*/public static boolean check(String inputPassword , String finalPassword){if(StringUtils.hasLength(inputPassword)&&StringUtils.hasLength(finalPassword)&&finalPassword.length()==65){String salt=finalPassword.split("\\$")[0];String confirmPssword=PasswordUtils.encrypt(inputPassword,salt);return confirmPssword.equals(finalPassword);}return false;}public static void main(String[] args) {String password="123456";String finalPassword=encrypt(password);System.out.println(PasswordUtils.encrypt(password));String inputPassword="12345";String inputPassword2="123456";System.out.println("比對結果1:"+ check(inputPassword,finalPassword));System.out.println("比對結果2 :"+ check(inputPassword2,finalPassword));//check(inputPassword2,finalPassword);}
}
 ?
?
?Spring Security
是提供身份驗證和授權的框架?,可用于用戶認證,訪問控制,安全事件和日志記錄等
還有就是Spring Security加鹽
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId></dependency>?這樣甚至改了頁面
當用這個認證密碼授權成功后才會到我們的登錄頁面
所以我們要排除SpringSecurity自動加載
?
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = {SecurityAutoConfiguration.class})
package com.example.demo;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.SecurityAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;@SpringBootTest()
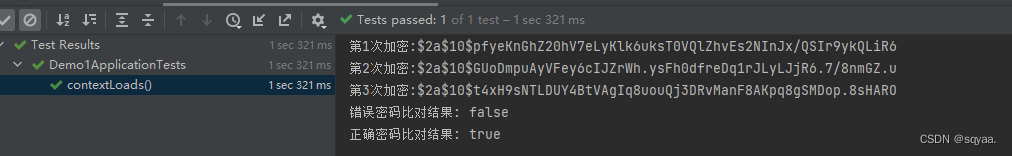
class Demo1ApplicationTests {@Testvoid contextLoads() {BCryptPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder();String password ="123456";// 第一次加密String finalPassword1 = passwordEncoder.encode(password);System.out.println("第1次加密:" + finalPassword1);// 第二次加密String finalPassword2 = passwordEncoder.encode(password);System.out.println("第2次加密:" + finalPassword2);// 第三次加密String finalPassword3 = passwordEncoder.encode(password);System.out.println("第3次加密:" + finalPassword3);// 驗證密碼String inputPassword = "12345";System.out.println("錯誤密碼比對結果: " + (passwordEncoder.matches(inputPassword, finalPassword1)));String inputPassword2 = "123456";System.out.println("正確密碼比對結果: " + (passwordEncoder.matches(inputPassword2, finalPassword1)));}}
?
java nio中一種基于MappedByteBuffer操作大文件
在Java中,處理大文件時常用的有基于`MappedByteBuffer`的NIO(New I/O)和基于`BufferedInputStream`、`BufferedOutputStream`等帶緩沖的傳統IO流。下面是它們之間的一些區別和相對優勢:
1. 內存映射文件(MappedByteBuffer):
? ?- **優勢**:
? ? ?- 避免了數據在Java堆內存和本地內存的多次拷貝,提高了IO操作的效率。
? ? ?- 可以利用操作系統的虛擬內存機制,對文件進行部分映射,實現了按需加載,對于大文件的處理性能更好。
? ? ?- 適合隨機訪問,可以直接在內存中修改文件內容,不需要通過讀取和寫入的方式。
? ?- **劣勢**:
? ? ?- 需要謹慎管理內存映射,避免內存泄漏和資源未釋放的問題。
? ? ?- 對于頻繁讀寫的大文件,可能會導致內存占用過高。2. 緩沖流(BufferedInputStream、BufferedOutputStream):
? ?- **優勢**:
? ? ?- 通過緩沖區減少了對底層IO系統調用的次數,提高了IO操作效率。
? ? ?- 可以適應各種大小的文件讀寫,并且易于使用。
? ? ?- 適合順序讀寫,對于較小的文件處理效率較高。
? ?- **劣勢**:
? ? ?- 在處理大文件時,需要在Java和操作系統之間來回拷貝數據,可能會導致性能瓶頸。
? ? ?- 不支持直接在內存中修改文件內容,需要通過讀取和寫入的方式來進行操作。綜上所述,對于大文件的處理,基于`MappedByteBuffer`的NIO操作相對于傳統的緩沖流操作具有更高的性能和更少的內存開銷,特別是在需要隨機訪問大文件內容時,`MappedByteBuffer`更為適用。但需要注意合理管理內存映射,避免潛在的風險。而基于緩沖流的傳統IO操作適用于各種大小的文件處理,易于使用,但在處理大文件時可能會存在性能瓶頸。
?


 python門面模式)

)









)

:建模基礎)

)
