Wei, Ze-Gang, et al. "Comparison of methods for biological sequence clustering."?IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics?(2023).?https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10066180
- 被引次數:1;
- 研究背景:測序技術進步極大促進了基因組學研究。這一巨大進步帶來了大量的測序數據。聚類分析對于研究和探索大規模序列數據具有強大的作用。過去十年中已經開發了許多可用的聚類方法。盡管發表了大量的比較研究,但我們注意到它們有兩個主要局限性:僅比較傳統的基于比對的聚類方法,并且評估指標嚴重依賴于標記的序列數據。
- 研究意義:序列聚類有利于去除數據庫中冗余序列
- 作者信息:

一、傳統序列聚類方法
傳統方法:基于分層策略、需要對序列進行逐對對齊來進行聚類
1. mothur
[42] P. D. Schloss et al., “Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform- independent, community-supported software for describing and compar- ing microbial communities,” Appl. Environ. Microbiol., vol. 75, no. 23,pp. 7537–7541, 2009.
2. ESPRIT
[43] Y. Sun et al., “ESPRIT: Estimating species richness using large collections of 16S rRNA pyrosequences,” Nucleic Acids Res., vol. 37, no. 10, pp. e76–e76, 2009.
3. HPC-CLUST
?[44] M. Rodrigues, J. F., and C. von Mering, “HPC-CLUST: Distributed hierarchical clustering for large sets of nucleotide sequences,” Bioinformatics,vol. 30, no. 2, pp. 287–288, 2013.
4. mcClust
[45] Q. Wang et al., “Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy,” Appl. Environ. Microbiol.,vol. 73, no. 16, pp. 5261–5267, 2007.
二、現代大規模序列聚類方法
1.?CD-HIT:應用貪婪增量策略
巧妙地應用了統計k-mer(固定長度的子序列?k) 過濾以避免不必要的成對序列比對
[46] L. Fu et al., “CD-HIT: Accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data,” Bioinformatics, vol. 28, no. 23, pp. 3150–3152, 2012.
[47] Y. Huang et al., “CD-HIT Suite: A web server for clustering and comparing biological sequences,” Bioinformatics, vol. 26, no. 5, pp. 680–682, 2010.
[48] W. Li and A. Godzik, “Cd-hit: A fast program for clustering and comparing large sets of protein or nucleotide sequences,” Bioinformatics, vol. 22,no. 13, pp. 1658–1659, 2006.
2.?UCLUST :采用?USEARCH 的貪婪搜索算法
應用?k-mer 過濾器來避免不必要的低相似性序列對
[49] R. C. Edgar, “Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST,” Bioinformatics, vol. 26, no. 19, pp. 2460–2461, 2010.
3. VSEARCH:作為 UCLUST 的替代品
VSEARCH 是一款免費的 64 位開源軟件,用于序列聚類。它使用基于?k-mers 的快速啟發式(UCLUST 中應用的類似策略)來有效檢測相似序列。 VSEARCH 實現了 UCLUST 中用于分析生物序列的大部分功能,例如序列排序和去重復。因此,評估VSEARCH和UCLUST在序列聚類方面的性能非常有意義。
[50] T. Rognes et al., “VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics,” PeerJ, vol. 4, 2016, Art. no. e2584.
4.?DBH:基于de Bruijn (DB) graph
克服傳統啟發式聚類算法中關鍵問題——種子選擇的敏感性,并減少大規模 16S rRNA 序列的計算負擔,我們開發了一種基于啟發式聚類方法
[51] Z. - G. Wei and S. - W. Zhang, “DBH: A de Bruijn graph-based heuristic
method for clustering large-scale 16S rRNA sequences into OTUs,” J. Theor. Biol., vol. 425, pp. 80–87, 2017.
5.?edClust:基于Edlib library
對相似序列進行分組,由 C/C++ 編程,可實現高速精確的半全局成對序列比對。 edClust 也是一種啟發式方法,遵循 CD-HIT 的貪婪增量方法。應用了Edlib中實現的半全局序列比對來計算相似度對于帶有種子的每個查詢序列。
[52] M. Cao et al., “EdClust: A heuristic sequence clustering method with higher sensitivity,” J. Bioinf. Comput. Biol., vol. 20, 2021, Art. no. 2150036.
[53] M. ?o?ic ? and M. ?ikic ?, “Edlib: A C/C++ library for fast, exact sequence alignment using edit distance,” Bioinformatics, vol. 33, no. 9, pp. 1394–1395, 2017.
在預過濾過程中,CD-HIT、UCLUST、VSEARCH、DBH 和 edClust 僅計算序列之間相同k-mers 的數量。因為這個數字隨著比較序列的相似性降低而迅速下降,所以大多數上述方法將在低聚類閾值(特別是低于 50%)下形成包含非同源序列的損壞簇的很大一部分。
6.?kClust
為了提高低聚類閾值下的聚類敏感性,開發了 kClust,可以通過查找相似的?k-mers 以實現高靈敏度。
[54] M. Hauser, C. E. Mayer, and J. S?ding, “kClust: Fast and sensitive clustering of large protein sequence databases,” BMC Bioinf., vol. 14, no. 1, 2013, Art. no. 248.
根據上面的描述,我們可以總結出CD-HIT、UCLUST、VSEARCH、DBH、edClust、kClust和MMseqs2將貪婪增量策略應用于聚類序列,計算復雜度約為O(KN),其中?N?和?K?分別是序列數和簇數。對于數億個序列,K?通常與?N?具有相似的順序,導致計算復雜度幾乎以?N?的二次方增加。
7.?Linclust: 線性時間 O(N)
對大蛋白進行聚類
[57] M. Steinegger and J. S?ding, “Clustering huge protein sequence sets in linear time,” Nature Commun., vol. 9, no. 1, 2018, Art. no. 2542.
8.?MMseq2
[55] M. Hauser, M. Steinegger, and J. S?ding, “MMseqs software suite for fast and deep clustering and searching of large protein sequence sets,” Bioinformatics, vol. 32, no. 9, pp. 1323–1330, 2016.
[56] M. Steinegger and J. S?ding, “MMseqs2 enables sensitive protein sequence searching for the analysis of massive data sets,” Nature Biotechnol.,vol. 35, no. 11, pp. 1026–1028, 2017.
9.?MeShClust:均值平移算法
對DNA序列進行聚類
[58] B. T. James, B. B. Luczak, and H. Z. Girgis, “MeShClust: An intelligent tool for clustering DNA sequences,” Nucleic Acids Res., vol. 46, no. 14, pp. e83–e83, 2018.
三、4個?Benchmark datasets
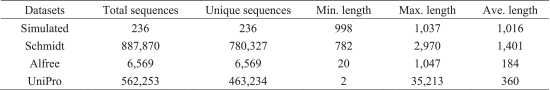
1. 模擬數據集
模擬數據集由 James 等人[58]生成,包含 236 個序列,10 個簇,每個簇由約 23 個序列組成。 所有序列的平均長度約為1000 bp。
[58] B. T. James, B. B. Luczak, and H. Z. Girgis, “MeShClust: An intelligent tool for clustering DNA sequences,” Nucleic Acids Res., vol. 46, no. 14, pp. e83–e83, 2018.
2. Schmidt數據集
Schmidt數據集是Schmidt等人[44]構建的一個綜合性的全球16S rRNA基因序列數據集(http://meringlab.org/suppdata/2014-otu_robustness/)。 該數據集幾乎覆蓋了細菌16S rRNA基因的整個區域,包含從NCBI GenBank收集的887870個序列,平均長度約為1401 bp。
[44] M. Rodrigues, J. F., and C. von Mering, “HPC-CLUST: Distributed hierarchical clustering for large sets of nucleotide sequences,” Bioinformatics,vol. 30, no. 2, pp. 287–288, 2013.
3. Alfree 數據集
Alfree 基準數據集 [39] 是基于 ASTRAL v2.06 數據集 [65] 構建的,該數據集包含 6569 個蛋白質序列,分為 513 個家族組。 該組中的序列范圍在 20 到 1047 之間,平均長度為 184 個氨基酸。 Alfree數據集和類標簽可以從網站鏈接免費下載:http://150.254.123.165/alfree//download/data/。
[39] A. Zielezinski et al., “Alignment-free sequence comparison: Benefits, applications, and tools,” Genome Biol., vol. 18, no. 1, 2017, Art. no. 186.
[65] N. K. Fox, S. E. Brenner, and J. -M. Chandonia, “SCOPe: Structural classification of proteins—Extended, integrating SCOP and ASTRAL data and classification of new structures,” Nucleic Acids Res., vol. 42, no. D1,pp. D304–D309, 2014.
4. UniProt 序列數據集
UniProt 序列數據集 [64] 是一個精心策劃的蛋白質序列數據庫,致力于提供高水平的注釋、最小程度的冗余以及與其他數據庫的高水平集成。 UniProt 數據庫包含~562 K 蛋白質序列,平均序列長度為~359 aa。?
[64] B. E. Suzek et al., “UniRef: Comprehensive and non-redundant UniProt reference clusters,” Bioinformatics, vol. 23, no. 10, pp. 1282–1288, 2007.
四、聚類評估指標
?NMI(歸一化互信息)指標 [43]
[43] Y. Sun et al., “ESPRIT: Estimating species richness using large collections of 16S rRNA pyrosequences,” Nucleic Acids Res., vol. 37, no. 10, pp. e76–e76, 2009.
其它評估指標:cluster number, seed sensitivity (SS), clustered fraction (CF) and the wrong clustered fraction (WCF) of one seed sequence --->?have been applied in previous study 【52】
[52] M. Cao et al., “EdClust: A heuristic sequence clustering method with higher sensitivity,” J. Bioinf. Comput. Biol., vol. 20, 2021, Art. no. 2150036.















)
的使用及練習)
)

