自我介紹
- 做一個簡單介紹,年近48 ,有20多年IT工作經歷,目前在一家500強做企業架構.因為工作需要,另外也因為興趣涉獵比較廣,為了自己學習建立了三個博客,分別是【全球IT瞭望】,【架構師酒館】和【開發者開聊】.
- 企業架構師需要比較廣泛的知識面,了解一個企業的整體的業務,應用,技術,數據,治理和合規。之前4年主要負責企業整體的技術規劃,標準的建立和項目治理。最近一年主要負責數據,涉及到數據平臺,數據戰略,數據分析,數據建模,數據治理,還涉及到數據主權,隱私保護和數據經濟。 因為需要,最近在學習財務,金融和法律。打算先備考CPA,然后CFA,如果可能可以學習法律,備戰律考。
- 歡迎按學習的同學朋友關注,也歡迎大家交流。微信小號【ca_cea】
在本文中,我將演示如何僅使用Angular Signals和一個小函數來管理應用程序的狀態。
不僅僅是“與主題一起服務”
讓我們從解釋為什么在服務中使用一堆BehaviorSubject對象不足以管理異步事件引起的狀態修改開始。
在下面的代碼中,我們有一個方法saveItems(),它將調用API服務,以異步更新項列表:
saveItems(items: Item[]) {this.apiService.saveItems(items).pipe(takeUntilDestroyed(this.destroyRef)).subscribe((items) => this.items$.next(items));
}
每次我們調用這種方法,都是在冒險。
例如:假設我們有兩個請求,A和B。
請求A在0s 0ms開始,請求B在0s 250ms開始。然而,由于某些問題,API在500ms后對A做出響應,在150ms后對B做出響應。
結果,a在0s 500ms時完成,B在0s 400ms時完成。
這可能會導致保存錯誤的項目集。
它也適用于GET請求——有時,對搜索請求應用什么過濾器非常重要。
我們可以添加一些支票,如下所示:
saveItems(items: Item[]) {if (this.isSaving) {return;}this.isSaving = true;this.apiService.saveItems(items).pipe(finalize(() => this.isSaving = false),takeUntilDestroyed(this.destroyRef)).subscribe((items) => this.items$.next(items));
}
但是,正確的項目集將根本沒有機會保存。
這就是為什么我們的Store需要效果。
使用NgRx ComponentStore,我們可以這樣寫:
readonly saveItems = this.effect<Item[]>(_ => _.pipe(concatMap((items) => this.apiService.saveItems(items)),tapResponse((items)=> this.items$.next(items),(err) => this.notify.error(err)) ));
在這里,您可以確保請求將一個接一個地執行,無論每個請求運行多長時間。
在這里,您可以很容易地為請求排隊選擇一種策略:switchMap()、concatMap(),exhautMap()或mergeMap()。
基于信號的存儲
什么是應用程序狀態?應用程序狀態是定義應用程序外觀和行為的變量集合。
應用程序總是有一些狀態,而“Angular?信號”總是有一個值。這是一個完美的匹配,所以讓我們使用信號來保持應用程序和組件的狀態。
class App {$users = signal<User[]>([]);$loadingUsers = signal<boolean>(false);$darkMode = signal<boolean|undefined>(undefined);
}
這是一個簡單的概念,但有一個問題:任何人都可以寫信給$loadingUsers。讓我們將狀態設為只讀,以避免全局可寫變量可能帶來的無限微調器和其他錯誤:
class App {private readonly state = {$users: signal<User[]>([]),$loadingUsers: signal<boolean>(false),$darkMode: signal<boolean|undefined>(undefined),} as const;readonly $users = this.state.$users.asReadonly();readonly $loadingUsers = this.state.$loadingUsers.asReadonly();readonly $darkMode = this.state.$darkMode.asReadonly();setDarkMode(dark: boolean) {this.state.$darkMode.set(!!dark);}
}
是的,我們寫了更多的行;否則,我們將不得不使用getter和setter,這甚至是更多的行。不,我們不能讓它們都是可寫的,并添加一些評論“不要寫!!”😉
在這個存儲中,我們的只讀信號(包括使用computed()創建的信號)是狀態和選擇器的替代品。
剩下的只有:我們需要效果,改變我們的狀態。
Angular Signals中有一個名為effect()的函數,但它只對信號的變化做出反應,通常我們應該在向API發出一些請求后修改狀態,或者作為對某些異步發出的事件的反應。雖然我們可以使用toSignal()創建額外的字段,然后在Angular的effect()中觀察這些信號,但它仍然不能像我們想要的那樣對異步代碼進行控制(沒有switchMap()、沒有concatMap(),沒有debounceTime()和許多其他東西)。
但是,讓我們使用一個著名的、經過充分測試的函數,使用一個強大的API:ComponentStore.effect(),并使其獨立!
createEffect()
使用此鏈接,您可以獲得修改后的函數的代碼。它很短,但如果你不能理解它是如何在引擎蓋下工作的,請不要擔心(這需要一些時間):你可以在這里閱讀關于如何使用原始effect()方法的文檔:NgRx Docs,并以同樣的方式使用createEffect()。
如果不鍵入注釋,它非常小:
function createEffect(generator) {const destroyRef = inject(DestroyRef);const origin$ = new Subject();generator(origin$).pipe(retry(),takeUntilDestroyed(destroyRef)).subscribe();return ((observableOrValue) => {const observable$ = isObservable(observableOrValue)? observableOrValue.pipe(retry()): of(observableOrValue);return observable$.pipe(takeUntilDestroyed(destroyRef)).subscribe((value) => {origin$.next(value);});});
}
它被命名為createEffect(),以不干擾Angular的effect()函數。
修改:
createEffect()?is a standalone function. Under the hood, it subscribes to an observable, and because of that?createEffect()?can only be called in an injection context. That’s exactly how we were using the original?effect()?method;createEffect()?function will resubscribe on errors, which means that it will not break if you forget to add?catchError()?to your API request.
當然,您可以隨意添加您的修改:)
把這個函數放在項目的某個地方,現在就可以管理應用程序狀態,而不需要任何額外的庫:Angular Signals+createEffect()。
Store類型
有三種類型的Store:
- 全局存儲(應用程序級)--應用程序中的每個組件和服務都可以訪問;
- 功能存儲(“功能”級別)——某些特定功能的后代可以訪問;
- 本地存儲(也稱為“組件存儲”)--不共享,每個組件都會創建一個新實例,當組件被銷毀時,該實例將被銷毀。
我編寫了一個示例應用程序,向您展示如何使用Angular Signals和createEffect()實現每種類型的存儲。我將使用該應用程序中的存儲和組件(不帶模板),讓您看到本文中的代碼示例。你可以在這里找到這個應用程序的全部代碼:GitHub鏈接。
Global Store
@Injectable({ providedIn: 'root' })
export class AppStore {private readonly state = {$planes: signal<Item[]>([]),$ships: signal<Item[]>([]),$loadingPlanes: signal<boolean>(false),$loadingShips: signal<boolean>(false),} as const;public readonly $planes = this.state.$planes.asReadonly();public readonly $ships = this.state.$ships.asReadonly();public readonly $loadingPlanes = this.state.$loadingPlanes.asReadonly();public readonly $loadingShips = this.state.$loadingShips.asReadonly();public readonly $loading = computed(() => this.$loadingPlanes() || this.$loadingShips());constructor() {this.generateAll();}generateAll() {this.generatePlanes();this.generateShips();}private generatePlanes = createEffect(_ => _.pipe(concatMap(() => {this.state.$loadingPlanes.set(true);return timer(3000).pipe(finalize(() => this.state.$loadingPlanes.set(false)),tap(() => this.state.$planes.set(getRandomItems())))})));private generateShips = createEffect(_ => _.pipe(exhaustMap(() => {this.state.$loadingShips.set(true);return timer(3000).pipe(finalize(() => this.state.$loadingShips.set(false)),tap(() => this.state.$ships.set(getRandomItems())))})));
}
要創建全局存儲,請添加以下裝飾器:@Injectable({ providedIn: ‘root’ })
在這里,你可以看到,每次你點擊紫色的大按鈕“Reload”,“飛機”和“飛船”這兩個列表都會被重新加載。不同之處在于,“平面”將被連續加載,與您單擊按鈕的次數一樣多。“Ships”將只加載一次,所有連續的點擊都將被忽略,直到上一次請求完成。
字段$loading被稱為“派生的”——它的值是使用compute()從其他信號的值中創建的。它是角信號中最強大的部分。與基于可觀察的存儲中的派生選擇器相比,computed()具有一些優勢:
- 動態依賴項跟蹤:在上面的代碼中,當$loadingPlanes()返回true時,$loadingShips()將從依賴項列表中刪除。對于非平凡的派生字段,它可能會節省內存;
- 無毛刺,無脫落;
- 懶惰的計算:派生值不會在它所依賴的信號的每次變化時重新計算,而是只有在讀取該值時(或者如果生成的信號在effect()函數內部或在模板中使用)。
還有一個缺點:你無法控制依賴關系,它們都是自動跟蹤的。
Feature Store
@Injectable()
export class PlanesStore {private readonly appStore = inject(AppStore);private readonly state = {$page: signal<number>(0),$pageSize: signal<number>(10),$displayDescriptions: signal<boolean>(false),} as const;public readonly $items = this.appStore.$planes;public readonly $loading = this.appStore.$loadingPlanes;public readonly $page = this.state.$page.asReadonly();public readonly $pageSize = this.state.$pageSize.asReadonly();public readonly $displayDescriptions = this.state.$displayDescriptions.asReadonly();public readonly paginated = createEffect<PageEvent>(_ => _.pipe(debounceTime(200),tap((event) => {this.state.$page.set(event.pageIndex);this.state.$pageSize.set(event.pageSize);})));setDisplayDescriptions(display: boolean) {this.state.$displayDescriptions.set(display);}
}
該功能的根組件(或路由)應“提供”此存儲:
@Component({// ...providers: [PlanesStore]
})
export class PlanesComponent { ... }
不要將此存儲添加到子代組件的提供程序中,否則,它們將創建自己的本地功能存儲實例,這將導致令人不快的錯誤。
Local Store
@Injectable()
export class ItemsListStore {public readonly $allItems = signal<Item[]>([]);public readonly $page = signal<number>(0);public readonly $pageSize = signal<number>(10);public readonly $items: Signal<Item[]> = computed(() => {const pageSize = this.$pageSize();const offset = this.$page() * pageSize;return this.$allItems().slice(offset, offset + pageSize);});public readonly $total: Signal<number> = computed(() => this.$allItems().length);public readonly $selectedItem = signal<Item | undefined>(undefined);public readonly setSelected = createEffect<{item: Item,selected: boolean}>(_ => _.pipe(tap(({ item, selected }) => {if (selected) {this.$selectedItem.set(item);} else {if (this.$selectedItem() === item) {this.$selectedItem.set(undefined);}}})));
}
與功能存儲非常相似,組件應該為自己提供此存儲:
@Component({selector: 'items-list',// ...providers: [ItemsListStore]
})
export class ItemsListComponent { ... }
Component as a Store
如果我們的組件沒有那么大,我們確信它不會那么大,而且我們只是不想為這個小組件創建一個存儲區,該怎么辦?
我有一個組件的例子,是這樣寫的:
@Component({selector: 'list-progress',// ...
})
export class ListProgressComponent {protected readonly $total = signal<number>(0);protected readonly $page = signal<number>(0);protected readonly $pageSize = signal<number>(10);protected readonly $progress: Signal<number> = computed(() => {if (this.$pageSize() < 1 && this.$total() < 1) {return 0;}return 100 * (this.$page() / (this.$total() / this.$pageSize()));});@Input({ required: true })set total(total: number) {this.$total.set(total);}@Input() set page(page: number) {this.$page.set(page);}@Input() set pageSize(pageSize: number) {this.$pageSize.set(pageSize);}@Input() disabled: boolean = false;
}
在Angular的版本17中,將引入input()函數來創建作為信號的輸入,從而使此代碼變得更短。
此示例應用程序部署在此處:?GitHub Pages link.
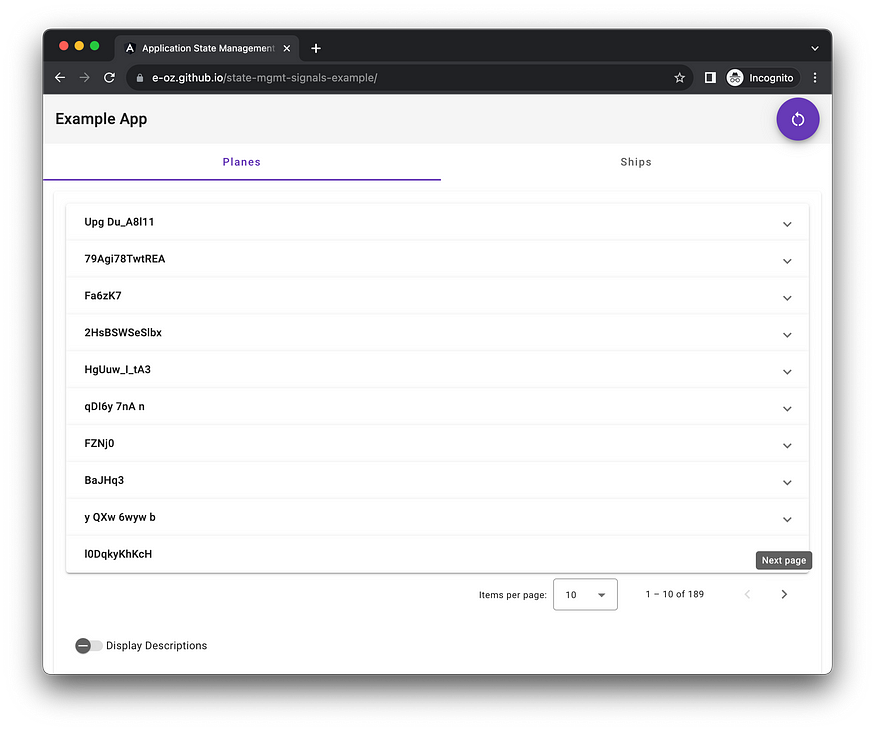
您可以使用它來查看不同列表的狀態是如何獨立的,功能狀態如何在功能的組件之間共享,以及所有組件如何使用應用程序全局狀態中的列表。
在代碼中,您可以找到對事件的反應、異步狀態修改的排隊、派生(計算)狀態字段和其他詳細信息的示例。
我知道我們可以改進代碼,讓事情變得更好——但這不是這個示例應用程序的重點。這里的所有代碼只有一個目的:說明本文并解釋事情是如何工作的。
我已經演示了如何在沒有第三方庫的情況下管理Angular應用程序狀態,只使用Angular Signals和一個附加函數。
感謝您的閱讀!
文章鏈接:
【Angular 開發】Angular 信號的應用狀態管理 | 程序員云開發,云時代的程序員.
歡迎收藏??【全球IT瞭望】,【架構師酒館】和【開發者開聊】.



)




)





![[JVM 基礎 - Java 類加載機制]](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[JVM 基礎 - Java 類加載機制])

——循環語句)



