new和delete操作自定義類型class Stack { public:Stack(int capacity = 3):_top(0), _capacity(capacity){cout << "Stack(int capacity = 3)" << endl;_a = new int[capacity];}~Stack(){cout << "~Stack()" << endl;delete _a;_top = _capacity = 0;} private:int* _a;int _top;int _capacity; };int main() {Stack* s1 = new Stack;delete s1;return 0; }
new:開對象空間+調用構造函數delete:調用析構函數+釋放對象空間
一、operator new與operator delete函數
1.1
operator new與operator delete是系統提供的全局函數,new通過調用operator new申請空間,delete通過調用operator delete釋放空間。

int main() {Stack* s1 = (Stack*)operator new(sizeof(Stack));operator delete(s1);return 0; }
實際上,operator new通過malloc申請空間,operator delete通過free釋放空間。
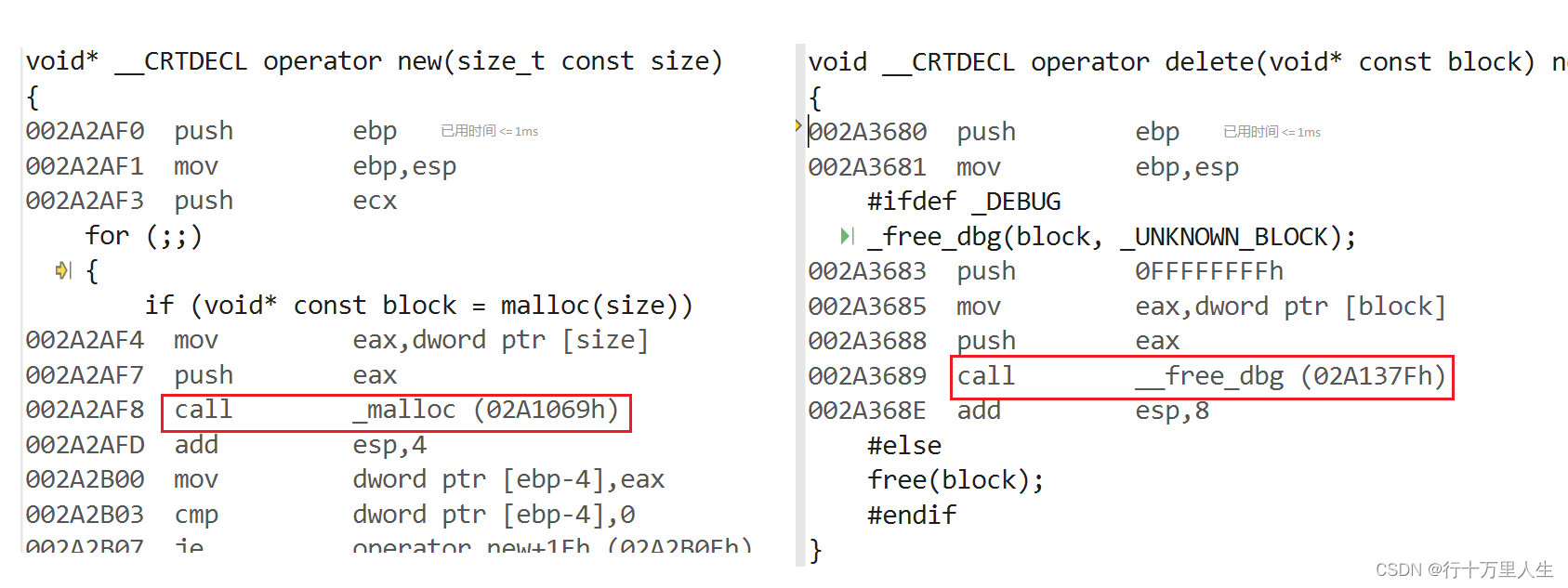
二、new和delete實現原理
2.1 內置類型
申請內置類型空間時,new/delete與malloc/free基本類似。
new/delete申請和釋放的是單個元素的空間,new[]/delete[]申請和釋放的是連續空間。new申請失敗會拋異常,malloc則返回NULL。
2.2 自定義類型
T為某一種類
new T:1. 調用operator new函數申請空間 2. 在已申請空間上調用構造函數,完成對象的構造。delete:1. 調用析構函數,完成對象資源清理 2. 調用operator delete釋放空間。new T[N]:1. 調用operator new[]2. 在operator new[]過程中,實際調用operator new完成對 N 個對象空間的申請 3. 在申請的空間上執行 N 次構造delete[]:1. 在申請空間上完成 N 次析構 2. 調用operator delete[]3. 實際調用operator delete釋放空間。
三、定位new表達式
3.1 概念
定位new表達式,指在已分配的內存空間上調用構造函數初始化對象。
格式: new(地址)type(已有默認構造可以不傳參)或 new(地址)type(初始化列表)
int main()
{Stack* s1 = (Stack*)operator new(sizeof(Stack));new(s1)Stack(2);// new(地址)type(初始化列表)delete s1;return 0;
}
四、總結malloc/free和new/delete的區別
共同點:
都是從堆上申請空間,且需要用戶手動釋放。
4.1 用法上
malloc/free是函數,new/delete是操作符。malloc申請的空間無法初始化,new可以初始化。malloc申請空間時需要手動計算大小并傳遞;new只需要+申請空間的類型即可,多個對象,在[]中指明個數。malloc的返回值類型是void*,需要強制轉換,new不需要。malloc申請空間失敗返回NULL,需要 ”判空 “;new需要捕獲異常。
4.2 原理上
- 申請自定義類型空間時,
malloc/free不會調用構造函數和析構函數;new/delete可以。

)




)
)


陰影遮罩)





)



: Index is supposed to be a vector)