簡述
numpy.unique:用于去除數組中重復元素,并從小到大排序(找到唯一元素并排序)。
def unique(ar, return_index=False, return_inverse=False,return_counts=False, axis=None):
ar: 這是輸入的數組或類數組對象。return_index: 如果設置為True,函數會同時返回唯一元素的索引數組,這些索引對應于原始數組中的位置。return_inverse: 如果設置為True,函數會返回一個數組,其中包含輸入數組中的元素在處理后的唯一數組中的索引。這可以用于重構原始數組。return_counts: 如果設置為True,函數將返回一個數組,其中包含輸入數組中每個唯一元素的出現次數。axis: 用于指定在哪個軸上執行操作。如果是None,則表示在整個數組上執行操作。函數返回一個包含唯一元素的排序數組。根據參數的設置,它可能還返回與唯一元素相關聯的索引數組、原始數組元素在唯一數組中的索引數組,以及每個唯一元素的出現次數。
以下是一個簡單的例子:
import numpy as nparr = np.array([2, 1, 6, 6, 4, 8, 5, 5, 6,7])unique_values = np.unique(arr)
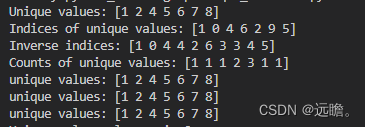
print("Unique values:", unique_values)# 返回唯一元素的索引數組
unique_indices = np.unique(arr, return_index=True)[1]
print("Indices of unique values:", unique_indices)# 返回輸入數組中的元素在唯一數組中的索引數組
inverse_indices = np.unique(arr, return_inverse=True)[1]
print("Inverse indices:", inverse_indices)# 返回每個唯一元素的出現次數
unique_counts = np.unique(arr, return_counts=True)[1]
print("Counts of unique values:", unique_counts)# 以上如果索引是[0],則返回的是處理過后的數組print("unique values:", np.unique(arr, return_index=True)[0])
print("unique values:", np.unique(arr, return_inverse=True)[0])
print("unique values:", np.unique(arr, return_counts=True)[0])輸出
最后參數axis的含義
在 numpy.unique 函數中,axis 參數用于指定在哪個軸上執行操作,但在默認情況下,該參數通常是 None,表示在整個數組上執行操作。在很多情況下,我們不需要設置 axis 參數,因為默認值已經能夠滿足大多數需求。
如果你的輸入數組是多維的,而且你想在特定軸上找到唯一元素,那么你可以指定 axis 參數。
arr_2d = np.array([[1, 2, 3,2],[4, 2, 6,5],[1, 2, 3,1],[1, 2, 3,1]])# 在軸 0 上找到唯一元素
unique_values_axis_0 = np.unique(arr_2d, axis=0,return_index=True)[1]
print("Unique values along axis 0:\n", unique_values_axis_0)# 在軸 1 上找到唯一元素
unique_values_axis_1 = np.unique(arr_2d, axis=1,return_index=True)[1]
print("Unique values along axis 1:\n", unique_values_axis_1)
輸出
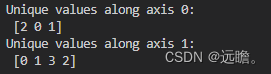
也就是如果選定axis=0,就是從第一個維度arr_2d[i] 中挑選其中最小值,并排序,最小值的排序方式是遍歷 arr_2d[i]的每個值,先排第一個數字,再排第二個數字,以此類推。
選定axis=1,就是在第一個維度的第一個向量找到第二維的排序方式,也就是按照arr_2d[0][i]排序,得到的索引,用于其他的維度 arr_2d[i]。


 - 簡介及Cargo使用)


Mysql中事務的概念,什么是事務,如何使用事務,以及事務的隔離級別,什么是臟讀、幻讀,代碼演示)

)




)






