目錄
1.關于unordered系列關聯式容器
2.關于unordered_map
?3.哈希(散列)表的實現
一,直接定址法
二,除留余數法
方法一:閉散列:開放定址法?
方法二:閉散列:哈希桶/拉鏈法
?4.哈希表的封裝
哈希表封裝后
unordered_map簡單封裝
unordered_set簡單封裝
1.關于unordered系列關聯式容器
?unordered_map和unordered_set是最常用的兩個容器,它們的底層結構都是哈希,unordered_map是存儲<key, value>鍵值對的關聯式容器,它允許通過key快速的索引到與其對應的value。??
? 在unordered_map中,鍵值通常用于惟一地標識元素,而映射值是一個對象,其內容與此鍵關聯。鍵和映射值的類型可能不同。在內部,unordered_map沒有對<key, value>按照任何特定的順序排序,為了能在常數范圍內找到key所對應的value,unordered_map將相同哈希值的鍵值對放在相同的桶中。unordered_map容器通過key訪問單個元素要比map快,但它通常在遍歷元素子集的范圍迭代方面效率較低。
? ?unordered_set是一個存儲唯一元素的集合,它的底層結構也是哈希表。它的元素是不可重復的,因此它的查詢速度非常快。
2.關于unordered_map
先來看看庫中的介紹:

對于map,還是以key_value為數據模型的,那么這里的key肯定也是不可以修改的,unodered_map強調的是查找效率,其次對于其迭代器是單向的。
對于它的接口也大差不差,,但是有兩個我們沒見過的,實際上在實現unordered_map中引入了其他參數及接口,如這里的負載因子(load_factor),哈希桶(Buckts).

?3.哈希(散列)表的實現
一,直接定址法

?數據集中的時候我們開辟空間就小,但太分散時,如2作為key值插入位置2,95作為key插入位置95,9999插入位置9999.那對于空間無疑是巨大的浪費,那該怎么辦呢?
二,除留余數法
有人就提出太大,那就對這個數取模,讓它處在在一個合適的位置,比如上面7個數據,size為7,那就對每個數據模7,使它在這里個范圍之內。
但是會出現新的問題,可能有數據會沖突,她兩模完值是一樣的,但對應的value是不一樣的,這種問題被叫做哈希碰撞/哈希沖突,那么如何解決哈希碰撞呢?這時候有兩種法案可以解決:
方法一:閉散列:開放定址法?
本質上就是如果新插入的數據的位置已經有數據了(value不一樣),那就在這個開放的空間中,重新找一個空位置。這里也會有兩種查找新位置的方法--1.線性探測(一個個往后找)2.二次探測(以2次方遞增查找)。
如果沖突,我們就往后找沒有被占的位置。可是當我們的后面空間快要滿員時,此時再往后找新的位置,就可能位置存在不夠的情況,那么在實際上,插入數據的個數在空間達到70%等的時候就需要擴容了,這里我么就引入了一個參數-負載因子(存儲關鍵字的個數/空間大小)來空間空間大小。
為什么會有兩種探測或者其他方式來尋找都是避免多次沖突,比如對于線性探測,重新找位置的話,如果有一部分數據是連續的,一個位置被提前占了,那么就會引起一片的哈希沖突,面對這個問題因此有了的探測二次探測。
那么我們就先來實現一下哈希表:
對于這里的負載因子,即不能太大,也不能太小,太大,容易發生沖突,太小,空間浪費太多。
這里我們一般使用0.7較為合適。
namespace myspace
{using namespace std;//如何去插入首先就需要對插入的每個位置做標記,該位置下可能存在三種狀態,已經有數據,為空,之前有現在刪除了enum State{EXIST,EMPTY,DELETE};//存放哈希表的數據的類型template<class K,class V>struct HashData{pair<K, V> _kv;State _sta=EMPTY;};//類型轉換,計算出key的大小,來確定平衡因子template<class K>struct HahFunc{size_t operator()(const K&k){return size_t(k);}};template<>struct HahFunc<string>{//如果是字符串,我們用所有字符的ascll的和表示key//但是字符串之和也是有很大可能重合,很多人通過在數學方面的研究出了一些解決辦法//這里最好的方式是采用的BKDR方法,給每個字符乘以31,131....這樣的數 之后的和大概率不會重復size_t operator()(const string& k){size_t sum = 0;for (int i = 0; i < k.size(); i++){sum = sum * 31;sum=sum+k[i];}return sum;}};
template<class K, class V,class Hash=HahFunc<V>>class HashTable
{
public:HashTable(){//初始化空間為tables.resize(10);}bool insert( const pair<K,V>& kv){if (find(kv.first) != NULL){return false;}//負載因子決定是否擴容if (_n * 10 / tables.size() == 7){//擴容//注意這里的擴容不能直接擴容,因為擴容之后size發生改變,對應的位置發生改變,因此需要重新開辟空間//在一個個重新(映射)插入,之后釋放舊空間size_t newsize = tables.size() * 2;//擴二倍HashTable<K, V> newHaTa;newHaTa.tables.resize(newsize);//新表for (int i = 0; i < tables.size(); i++){newHaTa.insert(tables[i]._kv);//重新走一遍映射再插入其中}//現在的需要的哈希表是新的,交換過來tables.swap(newHaTa.tables);}//通過取模size使得對應的位置在該size內Hash hf;size_t hashi = hf(kv.first % tables.size()) ;while (tables[hashi]._sta == EXIST){//先確定好位置hashi++;hashi %= tables.size();}//再插入tables[hashi]._kv = kv;tables[hashi]._sta = EXIST;_n++;return true;}HashData<K,V>* find(const K &key){Hash hf;size_t hashi = hf(key % tables.size());while (tables[hashi]._sta!=EMPTY ){if (tables[hashi]._sta==EXIST&&tables[hashi]._kv.first == key){return &tables[hashi];}hashi++;hashi %= tables.size();}return NULL;}//偽刪除bool erase(const K&key){HashData<K, V> tmp = find(key);if (tmp){tmp._sta == DELETE;_n--;return true;}else{return false;}}void Printf(){for (int i = 0; i < tables.size(); i++){if (tables[i]._sta == EXIST){cout<< i<<" " << tables[i]._sta << "->" << tables[i]._kv.first << endl;}else if (tables[i]._sta == DELETE){cout << i <<" " << "DELETE" << tables[i]._kv.first << endl;}else if (tables[i]._sta == EMPTY){cout << i <<" " << "EMPTY" << tables[i]._kv.first << endl;}}}private:vector<HashData<K,V>> tables;size_t _n;//插入的關鍵字的個數
};
}方法二:閉散列:哈希桶/拉鏈法
不同于上述的除留余數法,在實際的應用當中,而是引用哈希桶的方法,所謂的哈希桶,就是將哈希沖突的值放一起內部處理,此時整體結構就是vecor<list>型的結構。
? ? ?每一個key對應有一個桶,相同也沒事,放在一起內部解決。
我來們可以將上面的掛著的鏈表理解為桶,里面存放著相同key的值,但是當存放的值太多,遍歷桶里的值時間復雜度就是O(N),效率太低,因此當長度達到某個界限時,就會換成紅黑樹來存放,提高查找效率。
在結構上,vector中的list,我們為了實現迭代器,我們自己寫單鏈表,里面存放Node*,再插入時,我們采用頭插的方式,如下圖假設1,11,111他們的key值一樣。
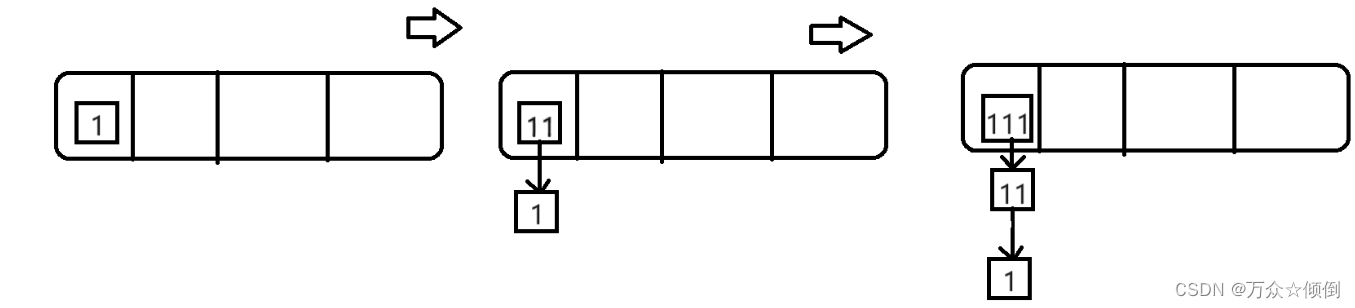
由于key類型不一定是整形,也有可能是其他類型,對于字符換類型,我們選他們的ascll碼之和,再稱31,用仿函數轉化為size_t,以此來表示位置。
namespace Hash_Bucket
{using namespace std;template<class K>struct HahFunc{size_t operator()(const K& k){return size_t(k);}};template<>struct HahFunc<string>{//如果是字符串,我們用所有字符的ascll的和表示key//但是字符串之和也是有很大可能重合,很多人通過在數學方面的研究出了一些解決辦法//這里最好的方式是采用的BKDR方法,給每個字符乘以31,131....這樣的數 之后的和大概率不會重復size_t operator()(const string& k){size_t sum = 0;for (int i = 0; i < k.size(); i++){sum = sum * 31;sum = sum + k[i];}return sum;}};template<class K, class V > struct HashNode{pair<K, V> _kv;HashNode* next;HashNode(const pair<K, V>& kv):_kv (kv),next(nullptr){}};template<class K, class V,class Hash= HahFunc<K>>class HashTable{public:typedef HashNode<K, V> Node;HashTable(){_table.resize(10);}~HashTable(){//循環遍歷釋放桶的每一個節點for (int i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++){Node* cur = _table[i];while (cur){Node* next = cur->next;delete cur;cur = next;}_table[i] = nullptr;}}bool insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){Hash hf;if (find(kv.first)){//不插入相同的值return false;}//對于哈希桶,如果滿了就要擴容,也就是負載因子為1if (_n == _table.size()){//第一種擴容方式,我們延續上面的擴容方式//size_t newsize = _table.size() * 2;//擴二倍//HashTable<K, V> newHaTa;//newHaTa.tables.resize(newsize);//新表//for (int i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++)//{// Node* cur = _table[i];// while (cur)// {//newHaTa.insert(cur->kv);//重新走一遍映射再插入其中// }// //}現在的需要的哈希表是新的,交換過來//_table.swap(newHaTa.tables);//沒必要用上述方式,我們直接重新弄個表,把節點挪動下來vector<Node*> newtable;newtable.resize(2 * _table.size());for (int i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++){Node* cur = _table[i];while (cur){Node* Next = cur->next;//重新映射到新表當中size_t hashi = hf(kv.first) % newtable.size();//頭插cur->next = newtable[i];//表中的新頭newtable[i] = cur;cur = Next;//遍歷下一個}//舊表置空_table[i] == nullptr;}//交換舊表與新表_table.swap(newtable);}//還是先通過取模節省空間size_t hashi = hf(kv.first) % _table.size();//頭插Node* newnode = new Node(kv);newnode->next = _table[hashi];_table[hashi] = newnode;++_n;return true;}Node* find( const K&key){Hash hf;size_t hashi = hf( key) % _table.size();Node* cur = _table[hashi];while (cur){if (cur->_kv.first == key){return cur;}cur = cur->next;}return NULL;}bool erase(const K* key){Hash hf;size_t hashi = hf(key )% _table.size();Node* cur = _table[hashi];Node* prev = nullptr;while (cur){if (cur->_kv.first == key){//找到并刪除//頭刪if (prev == nullptr){_table[hashi] = cur->next;//如果頭被斷開為空,cur的下一個就是新頭節點}else{prev->next = cur->next;//和相對的頭節點斷開關系}delete cur;return true;}prev = cur;//上一個節點,相對下一節點的頭節點cur = cur->next;//下一個節點}return false;}//那么實際上我們來看桶的大小其實并不會很大void Some(){size_t bucketSize = 0;size_t maxBucketLen = 0;size_t sum = 0;double averageBucketLen = 0;for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++){Node* cur = _tables[i];if (cur){++bucketSize;}size_t bucketLen = 0;while (cur){++bucketLen;cur = cur->_next;}sum += bucketLen;if (bucketLen > maxBucketLen){maxBucketLen = bucketLen;}}averageBucketLen = (double)sum / (double)bucketSize;printf("all bucketSize:%d\n", _tables.size());printf("bucketSize:%d\n", bucketSize);printf("maxBucketLen:%d\n", maxBucketLen);printf("averageBucketLen:%lf\n\n", averageBucketLen);}void Print(){for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++){Node* cur = _table[i];while (cur){if (cur){cout << cur->_kv.first << cur->_kv.second << endl;} cur = cur->next;}}cout << endl;}private:vector<Node*> _table;//這里存放節點指針,目的是為了實現迭代器size_t _n;};可能有些人覺得哈希桶可能太長,效率可能太低 ,但實際上哈希桶并不會太長,通過BKDR,以及負載因子的控制,不會有太多相同的key值。因此哈希桶實現的哈希表效率與上述基本不差。4.
?4.哈希表的封裝
對于哈希表的封裝,和封裝紅黑樹一樣,我們可以封裝出unordered_map與unordered_map。
首先就是統一哈希表的模板參數,直接傳pair,哈希表中用T表示,通過仿函數傳T張key的類型,
?之后就是實現迭代器,迭代器與哈希表兩者相互依賴,需要提前聲明,以及再哈希表中聲明友元迭代器方便我們使用,在之后為了實現const迭代器,在傳入參數Ref,Ptr作為T&,T*.
對于迭代器的封裝,這里我們需要三個參數,分別是哈希表(也可用vector),結點指針,以及下標位置hashi,通過遍歷判斷實現前置++。
哈希表封裝后
namespace Hash_Bucket
{using namespace std;template<class K>struct HahFunc{size_t operator()(const K& k){return size_t(k);}};template<>struct HahFunc<string>{//如果是字符串,我們用所有字符的ascll的和表示key//但是字符串之和也是有很大可能重合,很多人通過在數學方面的研究出了一些解決辦法//這里最好的方式是采用的BKDR方法,給每個字符乘以31,131....這樣的數 之后的和大概率不會重復size_t operator()(const string& k){size_t sum = 0;for (int i = 0; i < k.size(); i++){sum = sum * 31;sum = sum + k[i];}return sum;}};template<class T > struct HashNode{T _data;HashNode* next;HashNode(const T& data):_data (data),next(nullptr){}};//迭代器//由于迭代器與哈希表存在雙向依賴//我們在這里給上前置聲明template<class K, class T, class keyofT, class Hash>class HashTable;template<class K, class T, class Ref, class Ptr, class keyofT, class Hash>struct HTiterator{typedef HashNode< T > Node;HTiterator(Node*node, HashTable< K, T, keyofT, Hash>* _tab,size_t _hashi):_node(node), tab(_tab),hashi(_hashi){}//這里除了傳一個指針,還需要數組或整個表Node* _node;const HashTable< K, T, keyofT, Hash>* tab;size_t hashi;typedef HTiterator< K, T, Ref,Ptr,keyofT, Hash > self;//后置加加self &operator++(){if (_node->next){//繼續走這個桶_node = _node->next;}else{//下一個桶,找下一個桶++hashi;//新的桶while (hashi < tab->_table.size()){if (tab->_table[hashi]){//如果不為空,我的節點就是這個新節點_node = tab->_table[hashi];break;}else {++hashi;}}if (hashi == tab->_table.size()){_node = nullptr;}}return *this;}Ptr operator->(){return &(_node->data);}Ref operator*(){return (_node->_data);}bool operator!=(const self &tmp){return _node != tmp._node;}};template<class K,class T,class keyofT,class Hash= HahFunc<K>>class HashTable{public://聲明友元template<class K, class T,class Ref,class Ptr, class keyofT, class Hash >friend struct HTiterator;typedef HTiterator< K, T,T&,T*, keyofT, Hash > iterator;typedef HTiterator< K, T, const T&, const T*, keyofT, Hash > const_iterator;iterator begin(){for (int i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++){if (_table[i]){return iterator(_table[i],this,i);}}return end();}iterator end(){return iterator(nullptr, this,-1);}const_iterator begin()const{for (int i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++){if (_table[i]){return const_iterator(_table[i], this, i);}}return end();}const_iterator end()const{return const_iterator(nullptr, this, -1);}typedef HashNode<T> Node;HashTable(){_table.resize(10);}~HashTable(){//循環遍歷釋放桶的每一個節點for (int i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++){Node* cur = _table[i];while (cur){Node* next = cur->next;delete cur;cur = next;}_table[i] = nullptr;}}Hash hf;keyofT kot;bool insert(const T& data){if (find(kot(data))){return false;}//對于哈希桶,如果滿了就要擴容,也就是負載因子為1if (_n == _table.size()){vector<Node*> newtable;newtable.resize(2 * _table.size());for (int i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++){Node* cur = _table[i];while (cur){Node* Next = cur->next;//重新映射到新表當中size_t hashi = hf(kot(data)) % newtable.size();//頭插cur->next = newtable[i];//表中的新頭newtable[i] = cur;cur = Next;//遍歷下一個}//舊表置空_table[i] == nullptr;}//交換舊表與新表_table.swap(newtable);}//還是先通過取模節省空間size_t hashi = hf(kot(data)) % _table.size();//頭插Node* newnode = new Node(data);newnode->next = _table[hashi];_table[hashi] = newnode;++_n;return true;}Node* find( const K&key){Hash hf;size_t hashi = hf( key) % _table.size();Node* cur = _table[hashi];while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) == key){return cur;}cur = cur->next;}return NULL;}bool erase(const K* key){Hash hf;size_t hashi = hf(key )% _table.size();Node* cur = _table[hashi];Node* prev = nullptr;while (cur){if (kot(cur->data) == key){//找到并刪除//頭刪if (prev == nullptr){_table[hashi] = cur->next;//如果頭被斷開為空,cur的下一個就是新頭節點}else{prev->next = cur->next;//和相對的頭節點斷開關系}delete cur;return true;}prev = cur;//上一個節點,相對下一節點的頭節點cur = cur->next;//下一個節點}return false;}//那么實際上我們來看桶的大小其實并不會很大void Some(){size_t bucketSize = 0;size_t maxBucketLen = 0;size_t sum = 0;double averageBucketLen = 0;for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++){Node* cur = _table[i];if (cur){++bucketSize;}size_t bucketLen = 0;while (cur){++bucketLen;cur = cur->_next;}sum += bucketLen;if (bucketLen > maxBucketLen){maxBucketLen = bucketLen;}}averageBucketLen = (double)sum / (double)bucketSize;printf("all bucketSize:%d\n", _table.size());printf("bucketSize:%d\n", bucketSize);printf("maxBucketLen:%d\n", maxBucketLen);printf("averageBucketLen:%lf\n\n", averageBucketLen);}void Print(){for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++){Node* cur = _table[i];while (cur){if (cur){cout << kot(cur->data) << kot(cur->data) << endl;} cur = cur->next;}}cout << endl;}private:vector<Node*> _table;//這里存放節點指針,目的是為了實現迭代器size_t _n;};};unordered_map簡單封裝
namespace myspace1
{using namespace std;template<class K, class V>class unordered_map{struct mapkeyofT{const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& data){return data.first;}};public:typedef typename Hash_Bucket::HashTable< K, pair<K, V>, mapkeyofT >::iterator iterator;iterator begin(){return table.begin();}iterator end(){return table.end();}bool insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){return table.insert(kv);}private:Hash_Bucket::HashTable<K, pair<K, V>, mapkeyofT> table;};void test(){unordered_map<std::string, std::string> dictionary;dictionary.insert(std::make_pair<std::string, std::string>("蘋果", "兩個"));dictionary.insert(std::make_pair<std::string, std::string>("梨子", "兩個"));dictionary.insert(std::make_pair<std::string, std::string>("香蕉", "兩個"));unordered_map<std::string, std::string>::iterator it = dictionary.begin();while (it != dictionary.end()){cout << (*it).first<< (*it).second<<" ";++it;}}
};unordered_set簡單封裝
namespace myspace2
{template<class K>class unodered_set{struct setkeyofT{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};public:typedef typename Hash_Bucket::HashTable< K,K>, setkeyofT >::iterator iterator;iterator begin(){return table.begin();}iterator end(){return table.end();}bool insert(const K& key){return table.insert(key);}private:Hash_Bucket::HashTable<K, K, setkeyofT> table;};
};

)





-墨者-url信息)

(二))

 C++程序LNK2005錯誤,提示“error LNK2005: _XXX已經在xxx.obj中定義”解決方案)


,解開JVM神秘的面紗)



)
