#全部是重點知識,必須會。
了解序列和索引|的相關概念
掌握序列的相關操作
掌握列表的相關操作
掌握元組的相關操作
掌握字典的相關操作
掌握集合的相關操作
1,序列和索引
1,序列是一個用于存儲多個值的連續空間,每一個值都對應一個整數的編號,稱為 索引。
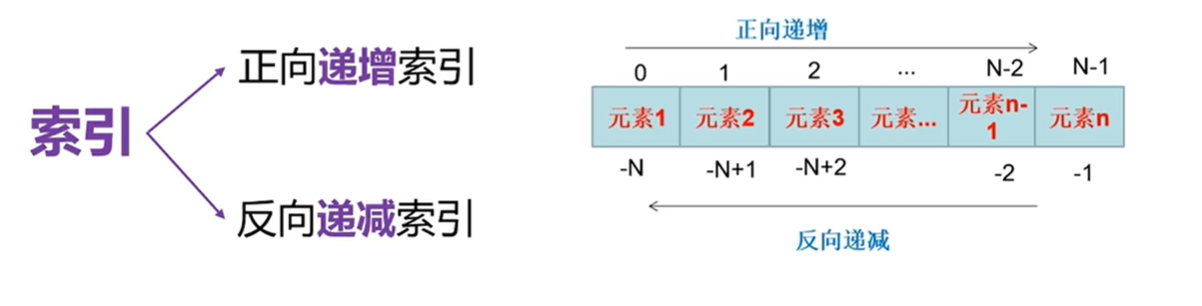
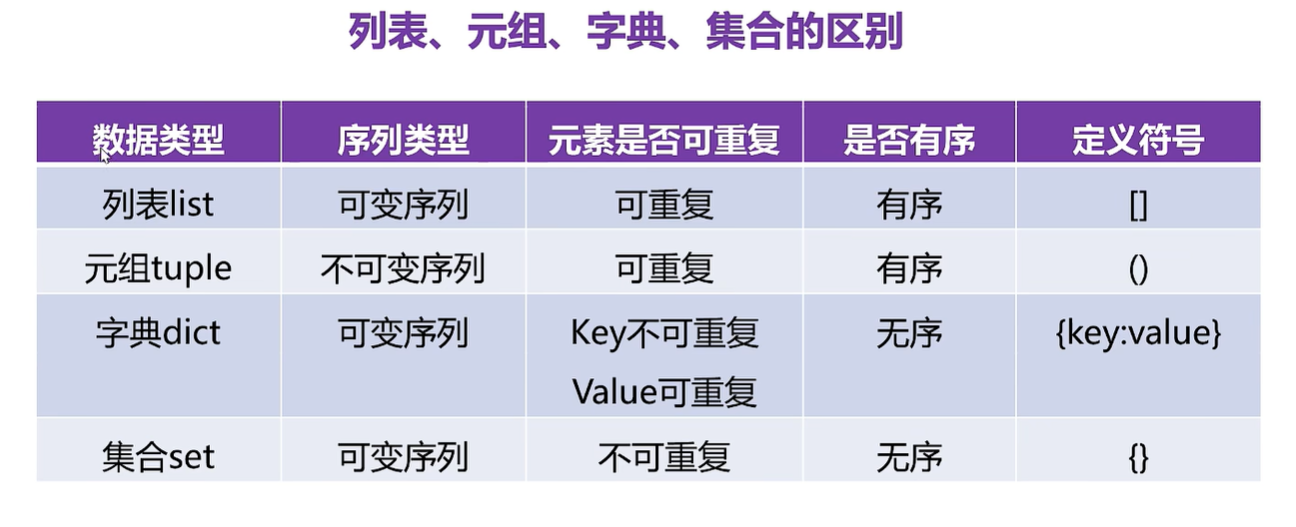
2,屬于序列結構的還有列表,元組,集合和字典。
- 列表和元組稱為有序序列。
- 集合和字典稱為無需序列。
#正向遞增
s='helloworld'
for i in range(0,len(s)):print(i,s[i],end='\t\t') #\t不換行輸出
print('\n--------------')
#反向遞減
for i in range(-10,0):print(i,s[i],end='\t\t') #\t不換行輸出
切片
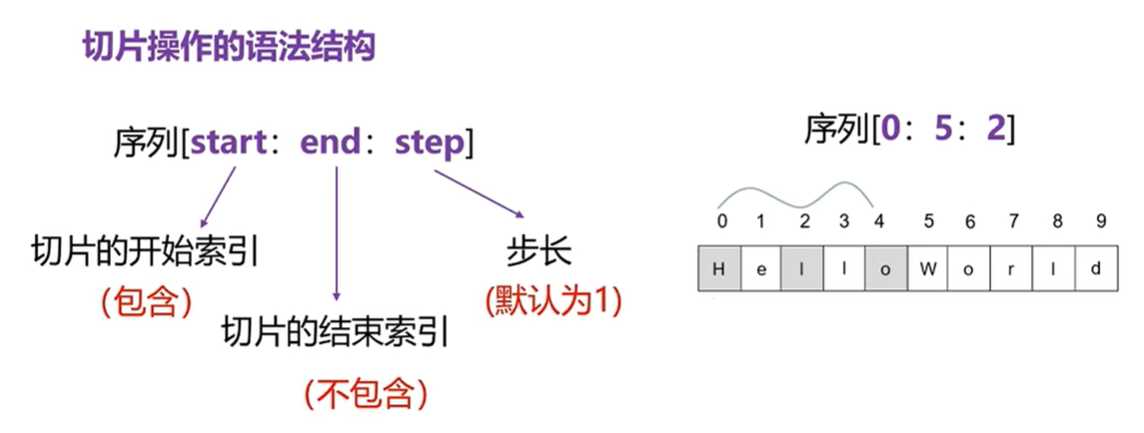
- 省略1。默認從0開始。
- 省略1,2
- 省略1,3
- 省略2。默最后一個元素包含最后一個。
- 省略2,3
- 省略3。默認步長為1.
- 省略1,2,3
s='helloworld'
#切片操作
s1=s[0:5:2]
print(s1)
#如果省略start,默認從0開始。
print(s[:5:2])#省略start和end
print(s[::2])
#step為-1 逆序序列***
print(s[::-1])
print(s[-1:-11:-1])#省略start和step。
print(s[:5:])#省略end,默認到序列的最后一個元素(包含最后一個元素)
print(s[0::1])#省略end和step,
print(s[5::])
print(s[5:])#全省略就都打印
print(s[::])#更改step
print(s[0:5:2])
序列
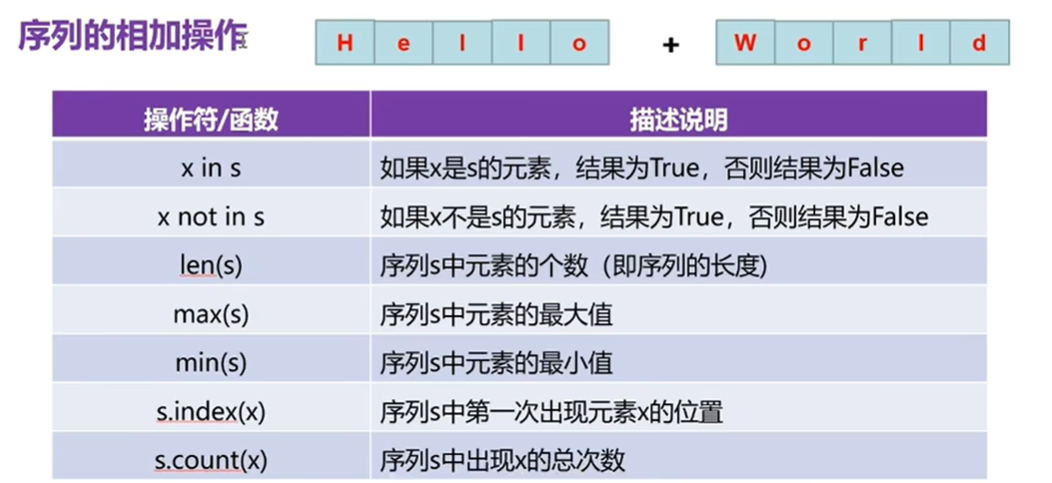
#序列的相加
print('*'*10)
print('hello'+'world')
#x in s的使用
s='helloworld'
print('l是在s中存在嗎?',('l' in s))
print('k是在s中存在嗎?',('k' in s))
#x not in s的使用
print('l是在s中存在嗎?',('l'not in s))
print('l是在s中存在嗎?',('k'not in s))
#內置函數
print(len(s))#len:列出元素的個數
print(max(s))#按照ACSII碼計算
print(min(s))
#序列的相關方法
print('s.index',s.index('o'))
print('s.index',s.index('l'))
print('s.count',s.index('l'))
2,列表
- 是指一系列的按特定順序排列的元素組成。
- 是Python中內置的可變序列
- 在Python中使用[]定義列表,元素與元素之間使用英文的逗號分隔
- 列表中的元素可以是任意的數據類型
- 字符串是不可變序列。
#(1)用 []直接創建列表
#語法:
列表名=[element1,element2...]#(2)用內置函數list()創建列表
#語法:
列表名=list(序列)#列表的刪除
#語法:
del 列表名
#直接使用[]創建列表
lst=['python','hello',888,3.14]
print(lst)#內置函數list()創建列表
lst2=list('pythonpyhton')
lst3=list(range(1,10,2))
print(lst2)
print(lst3)#列表是序列中的一種,對序列的操作,運算符,函數均可以使用
print(lst3+lst2)
print(lst3*3)
print(max(lst3))
print(min(lst3))
print(len(lst))print(lst2.index('y'))
print(lst2.count('o'))#列表的刪除
lst4=[10,20,30]
del lst4
enum函數

列表的遍歷操作有三種:
- for循環
- for循環+索引
- enumerate
lst=['hello','linux','python','world']
#使用遍歷循環for遍歷列表元素
for item in lst:print(item)#使用for循環,range函數,len函數,根據索引遍歷
for i in range(0,len(lst)):print(i,'--->',lst[i])#enumerate函數
for index,item in enumerate(lst):print(index,item)
print('\n----------')
#手動修改序列號的起始值
for index,item in enumerate(lst,start=1):print(index,item)
列表類型
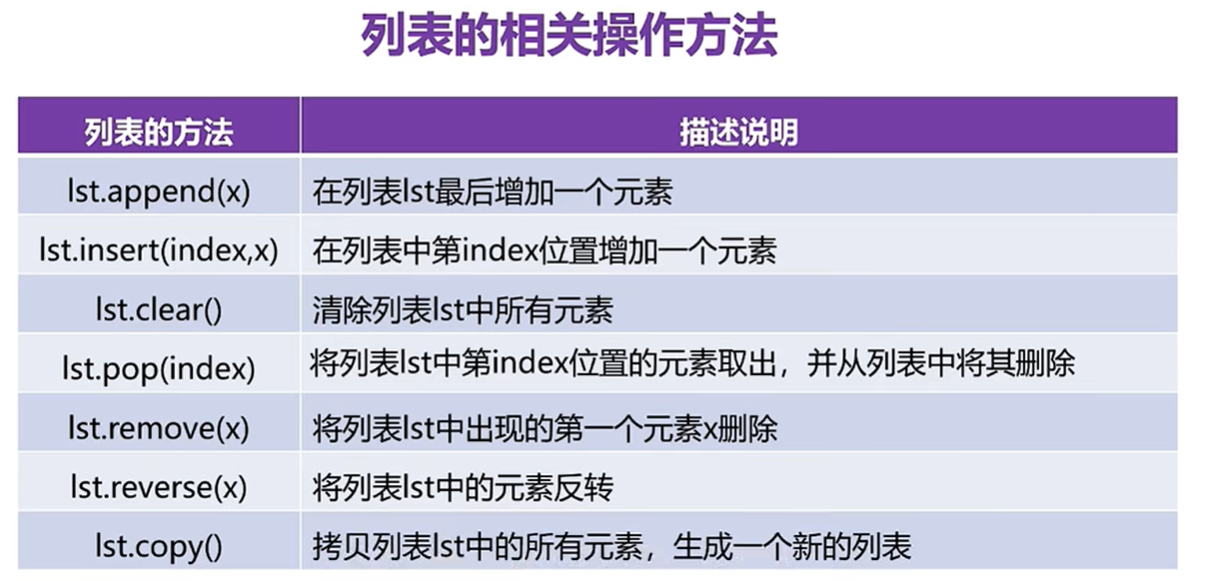
lst=['hello','linux','python','world']
print('原列表',lst,id(lst))
lst.append(100)
print('附加后',lst,id(lst))
lst.insert(2,'mysql')
print('指定增加',lst,id(lst))
lst.pop(1) #這個1是索引
print('先取后刪',lst,id(lst))
# lst.remove('linux')
# print('指定刪除',lst,id(lst))
lst.reverse()
print('反轉后',lst,id(lst))
# lst.clear()
# print('全清后',lst,id(lst))
new_lst=lst.copy() #會產生新列表對象
print(lst,id(lst))
print(new_lst,id(new_lst))#list的修改操作
lst[1]='mysql'
print(lst)
列表排序
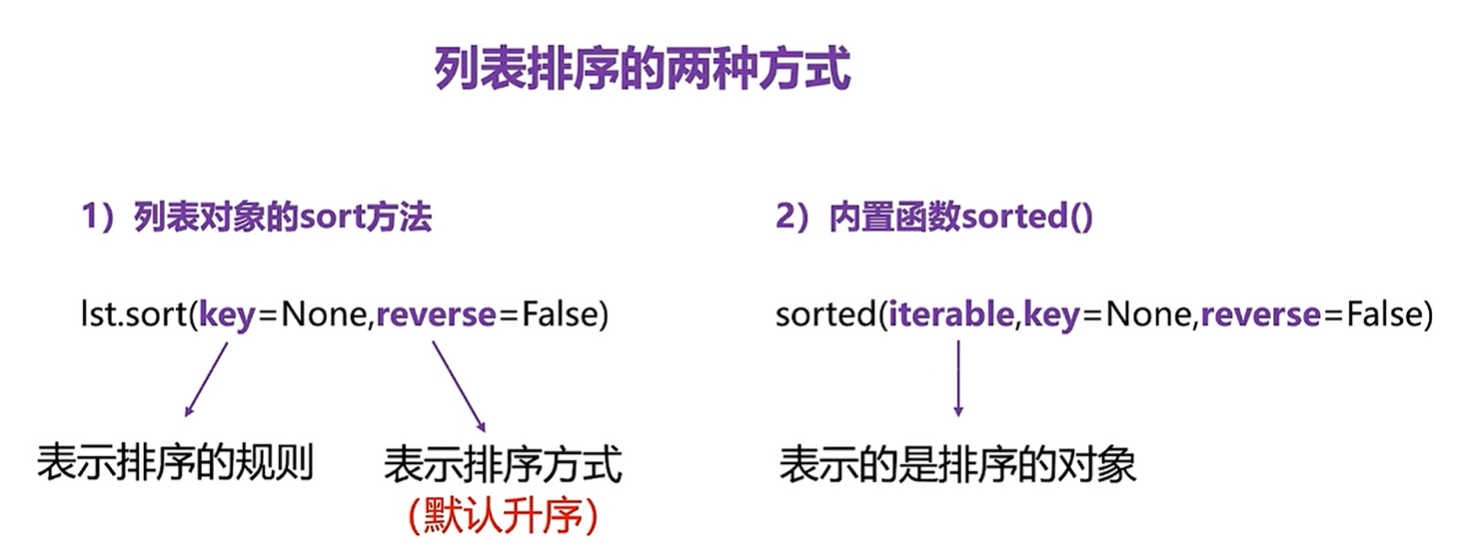
lst=[1,5,8,10,6,88,3.14]
print('原列表',lst)
lst.sort()
print('升序',lst)
lst.sort(reverse=True)
print('降序',lst)
print('-'*30)
lst2=['a','d','c','B']
print('原列表',lst2)
#忽略大小寫。升序排序,先排大寫,再排消寫。降序反之
lst2.sort(key=str.lower)
print('升序',lst2)
print('-'*30)
#sorted內置函數會產生新列表對象
lst=[1,5,8,10,6,88,3.14]
print('原列表',lst)
#sorted內置函數會產生新列表對象
asc_lst=sorted(lst)
print('升序',asc_lst)
desc_lst=sorted(lst,reverse=True)
print('降序',desc_lst)
列表生成式

import random #隨機導入數字
lst=[item for item in range(1,11)]
print(lst)lst=[item*item for item in range(1,11)]
print(lst)#random.randint()的用法:用于生成一個指定范圍內的隨機整數
lst=[random.randint(1,100) for item in range(10)]
print(lst)#從列表中選擇符合條件的元素組成新的列表
lst=[i for i in range(10) if i%2==0]
print(lst)

#創建二維列表
lst=[['城市','環比','同比'],['北京',100,101],['上海',102,103],['深圳',104,105]
]
print(lst)
#遍歷二維列表使用雙層for循環
for row in lst: #行for item in row: #列print(item,end='\t')print()
#列表生成式生成一個4行5列的二維列表
lst2=[[j for j in range(5)] for i in range(4)]
print(lst2)
3,元組
- 是內置的不可變序列
- 是python中使用()定義元組,element直接用英文的逗號隔開
- 元組中只有一個元素的時候,逗號也不能省略

#使用小括號創建元組
t=('hello',[10,20,30],'python','linux',50)
print(t)#使用內置函數tuple創建元組
t=tuple('helloworld')
print(t)t=tuple([10,20,30])
print(t)#在序列中的應用
print('2在tuple中是否存在:',(10 in t))
print('2在tuple中是否存在:',(10 not in t))
print('min:',min(t))
print('max:',max(t))
print('t.index:',t.index(10))
print('t.count:',t.count(10))#如果元組只有一個element
x=(1)
print(x,type(x))
y=(1,)
print(y,type(y))#tuple的刪除
# del x
# print(x)
遍歷
t=('python','hello','world')
#根據索引訪問元組
print(t[1])#元組切片操作
t2=t[:3:2]
print(t2)#(1)元組的遍歷
for item in t:print(item)#(2)使用for+range+len
for i in range(len(t)):print(i,t[i])#使用enumerate
for index,item in enumerate(t):print(index,'--->',item)tuple
#元組也有生成式,只不過元組的生成式是一個生成器對象,需要轉換成tuple或list才能查看。
t=(i for i in range(1,4))
print(t)
# t=tuple(t)
# print(t)
# #遍歷1
# for item in t:
# print(item)
#遍歷2
print(t.__next__())
print(t.__next__())
print(t.__next__())
#都取完了,如果再打印就為空
t=tuple(t)
print(t)
4,字典
字典類型是根據一個信息查找另一個信息的方式構成了"鍵值對”,它表示索引|用的鍵和對應的值構成的成對關系。
字典為可變數據類型。其中鍵是不可變序列。字符串,整數,浮點,元組可以作為字典中的鍵,但是列表不行。
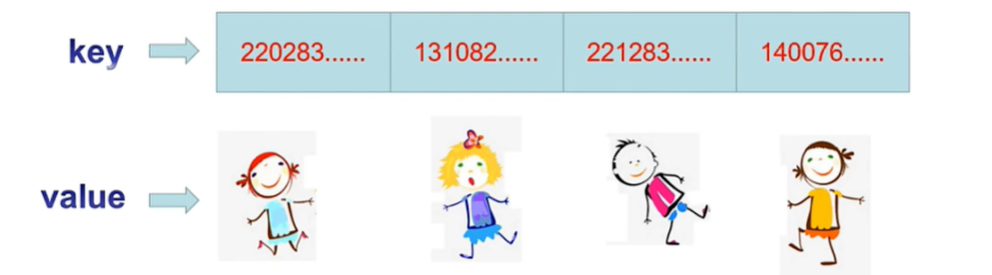
字典類型

#(1)創建字典
d={10:'cat',20:'dog',30:'pet',20:'zoo'}
print(d) #key相同時,value值進行了覆蓋#(2)zip函數
lst1=[10,20,30]
lst2=['ls','cd','pwd','cs']
zipobj=zip(lst1,lst2)
print(zipobj) #<zip object at 0x019AC1C8>
#print(list(zipobj)) #[(10, 'ls'), (20, 'cd'), (30, 'pwd')]
d=dict(zipobj)
print(d) #{10: 'ls', 20: 'cd', 30: 'pwd'}#使用參數創建dict
d=dict(cd=1,ls=2)
print(d) #左側為key,右側為valuet=(10, 20,30)
print({t:10}) # t是key, 10是value , 元組是可以作為字典中的key#字典屬于序列
print('max:',max(d))
print('min:',max(d))
print('len:',len(d)) #看的是元素的個數#刪除
del d

取值與遍歷

d={'hello':10,'world':20,'python':30}
#訪問字典中的元素
#(1)使用d[key]
print(d['python'])
#(2)d.get(key)
print(d.get('hello'))#二者之間是有區別的,如果key不存在,d[key]報錯d.get(key)可以指定默認值
print(d.get('java','不存在'))#dict遍歷
for item in d.items():print(item) #key=value組成的一個元素
#在使用for遍歷時,分別獲取key,value
for key,value in d.items():print(key,value)
相關操作

d={'hello':10,'world':20,'python':30}
print(d)
#添加
d['linux']=40
print(d)#獲取dict中所有的key
key=d.keys()
print(key)
print(list(key))
print(tuple(key))#獲取字典中所有的value
values=d.values()
print(values)
print(list(values))
print(tuple(values))#如何將字典中的數據轉側灰姑娘鍵值對的形式,以元組的形式展示
lst=list(d.items())
print(lst)
空字典,空元組,空列表為False
字典生成式

import random
d={item:random.randint(1,100) for item in range(4)}
print(d)#創建兩個列表
lst1=[1001,1002,1003]
lst2=['hello','world','python']
d={key:value for key,value in zip(lst1,lst2)}
print(d)
5,集合
- Python中的集合與數學中集合的概念一致
- Python中的集合是一個無序的不重復元素序列
- 集合中只能存儲不可變數據類型
- 在Python中集合使用{}定義
- 與列表、字典一樣,是Python中的可變數據類型
集合類型

#{}直接創建集合
s={10,20,30}
print(s)#使用set()創建集合
s=set() #創建空集合
print(s)s={}#創建的是字典
print(s,type(s))s=set('helloworld')
print(s)s2=set([10,20,30])
print(s2)s3=set(range(1,10))
print(s3)
#集合屬于序列的一種,可以用序列測試
#max,min,len,in ,not in#刪除
del s3
操作符
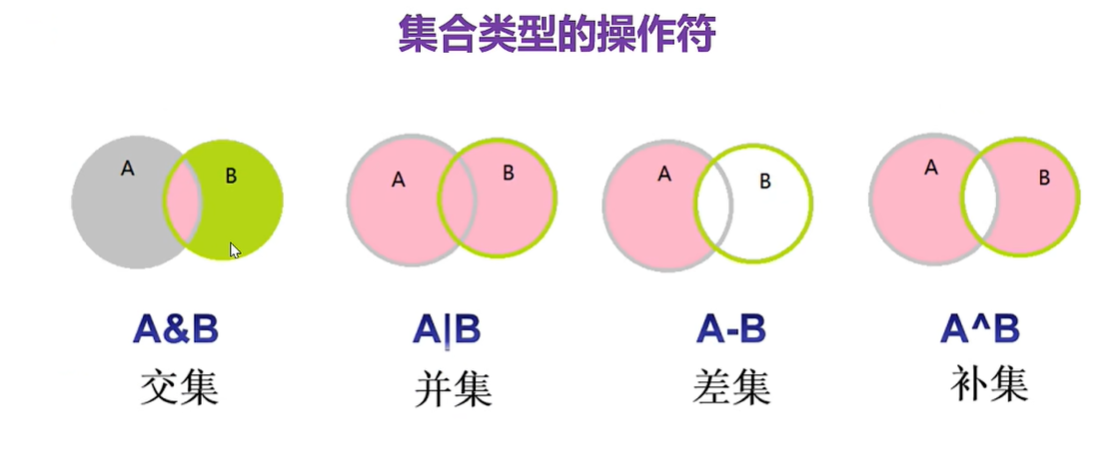
A={10, 20,30, 40, 50}
B={30, 50,88, 76, 20}
print(A&B)
相關操作

A={10, 20,30, 40, 50}
#A.add(100)
#A.remove()
# A.clesr
# print(A)#集合遍歷
for item in A:print(item)for index,item in enumerate(A):print(index,'-->',item)pass#生成式
s={i for i in range(1,10)}
print(s)s={i for i in range(1,10) if i%2==1}
print(s)
6,練習題




![[面試愛問] https 的s是什么意思,有什么作用?](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[面試愛問] https 的s是什么意思,有什么作用?)
)



)






)
)


之C++11新特性)

