數據的處理流程可以看一張圖來幫助理解
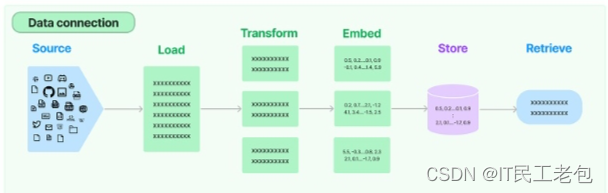
數據來源可以是網絡,可以是郵件,可以是本地文件
經過 Document Loaders 加載,再在 Transform 階段對文檔進行 split, filter, translate, extract metadata 等操作,之后在?Embed 階段進行向量化,存儲在向量數據庫中后期用于檢索。
加載文檔
準備工作:
安裝依賴庫:pip install pypdf
加載本地文檔
from langchain_community.document_loaders import PyPDFLoaderloader = PyPDFLoader("./data/spyl.pdf") # pdf 是從網上下載的,放在了 ./data 目錄下
pages = loader.load_and_split()print(pages[0].page_content)輸出:

加載 web 網頁:
from langchain_community.document_loaders import WebBaseLoaderloader = WebBaseLoader("https://docs.smith.langchain.com/user_guide") # LangSmith 的官方介紹
pages = loader.load_and_split()
print(pages[2].page_content)輸出:
文檔處理器
1. TextSplitter
安裝依賴庫:pip install?--upgrade langchain-text-splitters
接下來我們將前面的文檔進一步切分處理
from langchain_text_splitters import RecursiveCharacterTextSplittertext_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=300,chunk_overlap=50,length_function=len,add_start_index=True
)paragraphs = text_splitter.create_documents([p.page_content for p in pages])
for para in paragraphs:print(para.page_content)print("=====================")輸出:
每個 chunk 300 個 token,重疊最多 50 個 token
注意:L昂Chain 的 PDFLoader 和 TextSplitter 實現都比較粗糙,實際生產不建議使用
向量數據庫與向量檢索
文檔已經加載到內存中,接下來就需要將文檔向量化,然后灌入向量數據庫
from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain_community.vectorstores import FAISS# 灌庫
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings(model="text-embedding-ada-002")
db = FAISS.from_documents(paragraphs, embeddings)# 檢索 top-5 結果
retriever = db.as_retriever(search_kwargs={"k": 5})docs = retriever.invoke("白酒最近的產量")for doc in docs:print(doc.page_content)print("+++++++++++++++++++++")輸出:

根據檢索結果,檢索成功匹配到了最相關的信息
小結:
- 文檔處理部分 LangChain 實現較為粗糙,實際生產中不建議使用
- 與向量數據庫的鏈接部分本質是接口封裝,向量數據庫需要自己選型
記憶封裝
先來看幾個簡單的例子:
對話上下文:ConversationBufferMemory
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory, ConversationBufferWindowMemoryhistory = ConversationBufferMemory()
history.save_context({"input": "你好啊"}, {"output": "你也好啊"})print(history.load_memory_variables({}))history.save_context({"input": "你再好啊"}, {"output": "你又好啊"})print(history.load_memory_variables({})){'history': 'Human: 你好啊\nAI: 你也好啊'}
{'history': 'Human: 你好啊\nAI: 你也好啊\nHuman: 你再好啊\nAI: 你又好啊'}
只保留一個窗口的上下文:ConversationBufferWindowMemory
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferWindowMemorywindow = ConversationBufferWindowMemory(k=2)
window.save_context({"input":"第一輪問"}, {"output":"第一輪答"})
window.save_context({"input":"第二輪問"}, {"output":"第二輪答"})
window.save_context({"input":"第三輪問"}, {"output":"第三輪答"})print(window.load_memory_variables({})){'history': 'Human: 第二輪問\nAI: 第二輪答\nHuman: 第三輪問\nAI: 第三輪答'}
限制上下文長度:ConversationTokenBufferMemory
from langchain.memory import ConversationTokenBufferMemory
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAIllm = ChatOpenAI()
memory = ConversationTokenBufferMemory(max_token_limit=200,llm=llm
)
memory.save_context({"input":"你好"}, {"output":"你好,我是你的AI助手。"})
memory.save_context({"input":"你會干什么?"}, {"output":"我上知天文下知地理,什么都會。"})
print(memory.load_memory_variables({})){'history': 'Human: 你會干什么?\nAI: 我上知天文下知地理,什么都會。'}
應用場景:
我們通過一個簡單的示例來展示 memory 的作用,這里設置 verbose=True ,這樣我們就可以看到 prompt 的生成。
from langchain.chains import ConversationChainconversation_with_summary = ConversationChain(llm=llm,# We set a very low max_token_limit for the purposes of testing.memory=memory,verbose=True,
)
conversation_with_summary.predict(input="今天天氣真不錯!")> Entering new ConversationChain chain... Prompt after formatting: The following is a friendly conversation between a human and an AI. The AI is talkative and provides lots of specific details from its context. If the AI does not know the answer to a question, it truthfully says it does not know.Current conversation: Human: 你好 AI: 你好,我是你的AI助手。 Human: 你會干什么? AI: 我上知天文下知地理,什么都會。 Human: 今天天氣真不錯! AI: 是的,今天天氣晴朗,氣溫適宜,適合出門活動。您有什么計劃嗎? Human: 今天天氣真不錯! AI:> Finished chain.[13]:
'是的,今天天氣確實很好,陽光明媚,適合戶外活動。您想去哪里呢?'
conversation_with_summary.predict(input="我喜歡跑步,喜歡放風箏")> Entering new ConversationChain chain... Prompt after formatting: The following is a friendly conversation between a human and an AI. The AI is talkative and provides lots of specific details from its context. If the AI does not know the answer to a question, it truthfully says it does not know.Current conversation: Human: 你好 AI: 你好,我是你的AI助手。 Human: 你會干什么? AI: 我上知天文下知地理,什么都會。 Human: 今天天氣真不錯! AI: 是的,今天天氣晴朗,氣溫適宜,適合出門活動。您有什么計劃嗎? Human: 今天天氣真不錯! AI: 是的,今天天氣確實很好,陽光明媚,適合戶外活動。您想去哪里呢? Human: 我喜歡跑步,喜歡放風箏 AI:> Finished chain.[14]:
'那真是個好主意!跑步和放風箏都是很棒的戶外活動。您喜歡在什么樣的地方跑步呢?有沒有特別喜歡去的公園或者跑步道?'
conversation_with_summary.predict(input="獲取爬山也不錯,不如去爬一次黃山吧")> Entering new ConversationChain chain... Prompt after formatting: The following is a friendly conversation between a human and an AI. The AI is talkative and provides lots of specific details from its context. If the AI does not know the answer to a question, it truthfully says it does not know.Current conversation: AI: 是的,今天天氣晴朗,氣溫適宜,適合出門活動。您有什么計劃嗎? Human: 今天天氣真不錯! AI: 是的,今天天氣確實很好,陽光明媚,適合戶外活動。您想去哪里呢? Human: 我喜歡跑步,喜歡放風箏 AI: 那真是個好主意!跑步和放風箏都是很棒的戶外活動。您喜歡在什么樣的地方跑步呢?有沒有特別喜歡去的公園或者跑步道? Human: 獲取爬山也不錯,不如去爬一次黃山吧 AI:> Finished chain.[15]:
'黃山是一個非常著名的旅游勝地,有著壯麗的風景和豐富的自然資源。黃山位于安徽省,被譽為中國的五大名山之一。登上黃山,您可以欣賞到奇松怪石、云海日出等壯麗景觀。不過需要注意的是,黃山地勢險峻,需要一定的體力和意志力來完成登山之旅。希望您在黃山能夠享受到美妙的風景和登山的樂趣!您需要我為您提供黃山的相關信息嗎?'
conversation_with_summary.predict(input="我喜歡什么運動?")> Entering new ConversationChain chain... Prompt after formatting: The following is a friendly conversation between a human and an AI. The AI is talkative and provides lots of specific details from its context. If the AI does not know the answer to a question, it truthfully says it does not know.Current conversation: AI: 黃山是一個非常著名的旅游勝地,有著壯麗的風景和豐富的自然資源。黃山位于安徽省,被譽為中國的五大名山之一。登上黃山,您可以欣賞到奇松怪石、云海日出等壯麗景觀。不過需要注意的是,黃山地勢險峻,需要一定的體力和意志力來完成登山之旅。希望您在黃山能夠享受到美妙的風景和登山的樂趣!您需要我為您提供黃山的相關信息嗎? Human: 我喜歡什么運動? AI:> Finished chain.[16]:
'很抱歉,我不知道您喜歡什么運動。您可以告訴我您感興趣的領域,我會盡力為您提供相關信息。比如,如果您喜歡戶外活動,我可以為您介紹一些常見的戶外運動項目。如果您喜歡健身運動,我也可以為您提供一些健身的建議和指導。請告訴我您的興趣方向,我會盡力幫助您。'
從上面的實驗結果看,前面的對話長度 token 沒到 200 的時候,AI 能根據前面的對話來回答你的問題,但是當超過 200 之后,前面的信息就丟了,相當于遺忘了。
ConversationSummaryMemory
如果對話歷史如果很長,可以通過摘要記憶對信息進行濃縮
from langchain.memory import ConversationSummaryMemory, ChatMessageHistory
from langchain_openai import OpenAImemory = ConversationSummaryMemory(llm=OpenAI(temperature=0))
memory.save_context({"input": "你好"}, {"output": "你好,有什么需要幫助?"})
memory.load_memory_variables({})
{'history': '\nThe human greets the AI in Chinese. The AI responds in Chinese and asks if there is anything it can help with.'}
通過已經存在的messages或者摘要初始化
history = ChatMessageHistory()
history.add_user_message("hi")
history.add_ai_message("hi there!")memory = ConversationSummaryMemory.from_messages(llm=OpenAI(temperature=0),chat_memory=history,return_messages=True
)memory.buffer輸出:'\nThe human greets the AI, to which the AI responds with a friendly greeting.'通過之前的摘要進行初始化來加快初始化速度
memory = ConversationSummaryMemory(llm=OpenAI(temperature=0),buffer="The human asks what the AI thinks of artificial intelligence. The AI thinks artificial intelligence is a force for good because it will help humans reach their full potential.",chat_memory=history,return_messages=True
)在 chain 使用
from langchain_openai import OpenAI
from langchain.chains import ConversationChain
llm = OpenAI(temperature=0)
conversation_with_summary = ConversationChain(llm=llm,memory=ConversationSummaryMemory(llm=OpenAI()),verbose=True
)
conversation_with_summary.predict(input="Hi, what's up?")輸出:
? ? > Entering new ConversationChain chain...
? ? Prompt after formatting:
? ? The following is a friendly conversation between a human and an AI. The AI is talkative and provides lots of specific details from its context. If the AI does not know the answer to a question, it truthfully says it does not know.? ? Current conversation:
? ? Human: Hi, what's up?
? ? AI:? ? > Finished chain.
? ? " Hi there! I'm doing great. I'm currently helping a customer with a technical issue. How about you?"
向量數據庫支持的VectorStoreRetrieverMemory?
當想引用對話中之前提到過的一些信息,這個 memory 會比較有用
初始化向量數據庫:
這一步會因使用的向量數據庫不同而有所區別,具體細節可以看向量數據庫的文檔
import faiss
from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain_community.docstore import InMemoryDocstore
from langchain_community.vectorstores import FAISSembedding_size = 1536
index = faiss.IndexFlatL2(embedding_size)
embedding = OpenAIEmbeddings()
vectorstore = FAISS(embedding, index, InMemoryDocstore({}), {})創建 VectorStoreRetrieverMemory
from langchain.memory import VectorStoreRetrieverMemoryretriever = vectorstore.as_retriever(search_kwargs={"k":2}) # 實際使用時 k 值會設置得比較高
memory = VectorStoreRetrieverMemory(retriever=retriever)# When added to an agent, the memory object can save pertinent information from conversations or used tools
memory.save_context({"input": "我喜歡披薩"}, {"output": "哦,那太好了"})
memory.save_context({"input": "我喜歡足球"}, {"output": "..."})
memory.save_context({"input": "我不喜歡梅西"}, {"output": "ok"}) #
print(memory.load_memory_variables({"prompt": "我該看什么體育節目?"})["history"])輸出:
input: 我喜歡足球 output: ... input: 我不喜歡梅西 output: ok
在 chain 中使用
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplatellm = OpenAI(temperature=0) # Can be any valid LLM
_DEFAULT_TEMPLATE = """The following is a friendly conversation between a human and an AI. The AI is talkative and provides lots of specific details from its context. If the AI does not know the answer to a question, it truthfully says it does not know.Relevant pieces of previous conversation:
{history}(You do not need to use these pieces of information if not relevant)Current conversation:
Human: {input}
AI:"""
PROMPT = PromptTemplate(input_variables=["history", "input"], template=_DEFAULT_TEMPLATE
)
conversation_with_summary = ConversationChain(llm=llm,prompt=PROMPT,memory=memory,verbose=True
)
conversation_with_summary.predict(input="你好,我是 Gem")輸出:
> Entering new ConversationChain chain... Prompt after formatting: The following is a friendly conversation between a human and an AI. The AI is talkative and provides lots of specific details from its context. If the AI does not know the answer to a question, it truthfully says it does not know.Relevant pieces of previous conversation: input: 我不喜歡梅西 output: ok input: 我喜歡披薩 output: 哦,那太好了(You do not need to use these pieces of information if not relevant)Current conversation: Human: 你好,我是 Gem AI:> Finished chain.[79]:
' 你好,Gem!我是你的AI助手。我可以回答你關于任何事情的問題。你有什么想知道的嗎?'
conversation_with_summary.predict(input="我喜歡什么?")輸出:
> Entering new ConversationChain chain... Prompt after formatting: The following is a friendly conversation between a human and an AI. The AI is talkative and provides lots of specific details from its context. If the AI does not know the answer to a question, it truthfully says it does not know.Relevant pieces of previous conversation: input: 我喜歡披薩 output: 哦,那太好了 input: 我喜歡足球 output: ...(You do not need to use these pieces of information if not relevant)Current conversation: Human: 我喜歡什么? AI:> Finished chain.[80]:
' 你喜歡什么?我不太清楚,因為我是一個人工智能,我沒有自己的喜好。但是我可以告訴你一些我所知道的事情。比如,我知道你喜歡披薩和足球。你還喜歡什么?'
小結:
- LangChain 的 Memory 管理機制屬于可用的部分,尤其是簡單情況如按輪數或按 Token 數管理;
- 對于復雜情況,它不一定是最優的實現,例如檢索向量庫方式,建議根據實際情況和效果評估;
- 但是它對內存的各種維護方法的思路在實際生產中可以借鑒。










與usememo())








