上一篇Spring源碼八:容器擴展一,我們看到ApplicationContext容器通過refresh方法中的prepareBeanFactory方法對BeanFactory擴展的一些功能點,包括對SPEL語句的支持、添加屬性編輯器的注冊器擴展解決Bean屬性只能定義基礎變量的問題、以及一些對Aware接口的實現。
這一篇,我們回到refresh方法中,接著往下看:
{synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {// Prepare this context for refreshing. 1、初始化上下文信息,替換占位符、必要參數的校驗prepareRefresh();// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. 2、解析類Xml、初始化BeanFactoryConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // 這一步主要是對初級容器的基礎設計// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. 3、準備BeanFactory內容:prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); // 對beanFactory容器的功能的擴展:try {// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. 4、擴展點加一:空實現,主要用于處理特殊Bean的后置處理器//!!!!!!!!!!!! 這里 這里 今天看這里 !!!!!!!!!!!//postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. 5、spring bean容器的后置處理器invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);//!!!!!!!!!!!! 這里 這里 今天看這里 !!!!!!!!!!!//// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. 6、注冊bean的后置處理器registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);// Initialize message source for this context. 7、初始化消息源initMessageSource();// Initialize event multicaster for this context. 8、初始化事件廣播器initApplicationEventMulticaster();// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. 9、擴展點加一:空實現;主要是在實例化之前做些bean初始化擴展onRefresh();// Check for listener beans and register them. 10、初始化監聽器registerListeners();// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. 11、實例化:非蘭加載BeanfinishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);// Last step: publish corresponding event. 12、發布相應的事件通知finishRefresh();}catch (BeansException ex) {if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);}// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.destroyBeans();// Reset 'active' flag.cancelRefresh(ex);// Propagate exception to caller.throw ex;}finally {// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...resetCommonCaches();}}}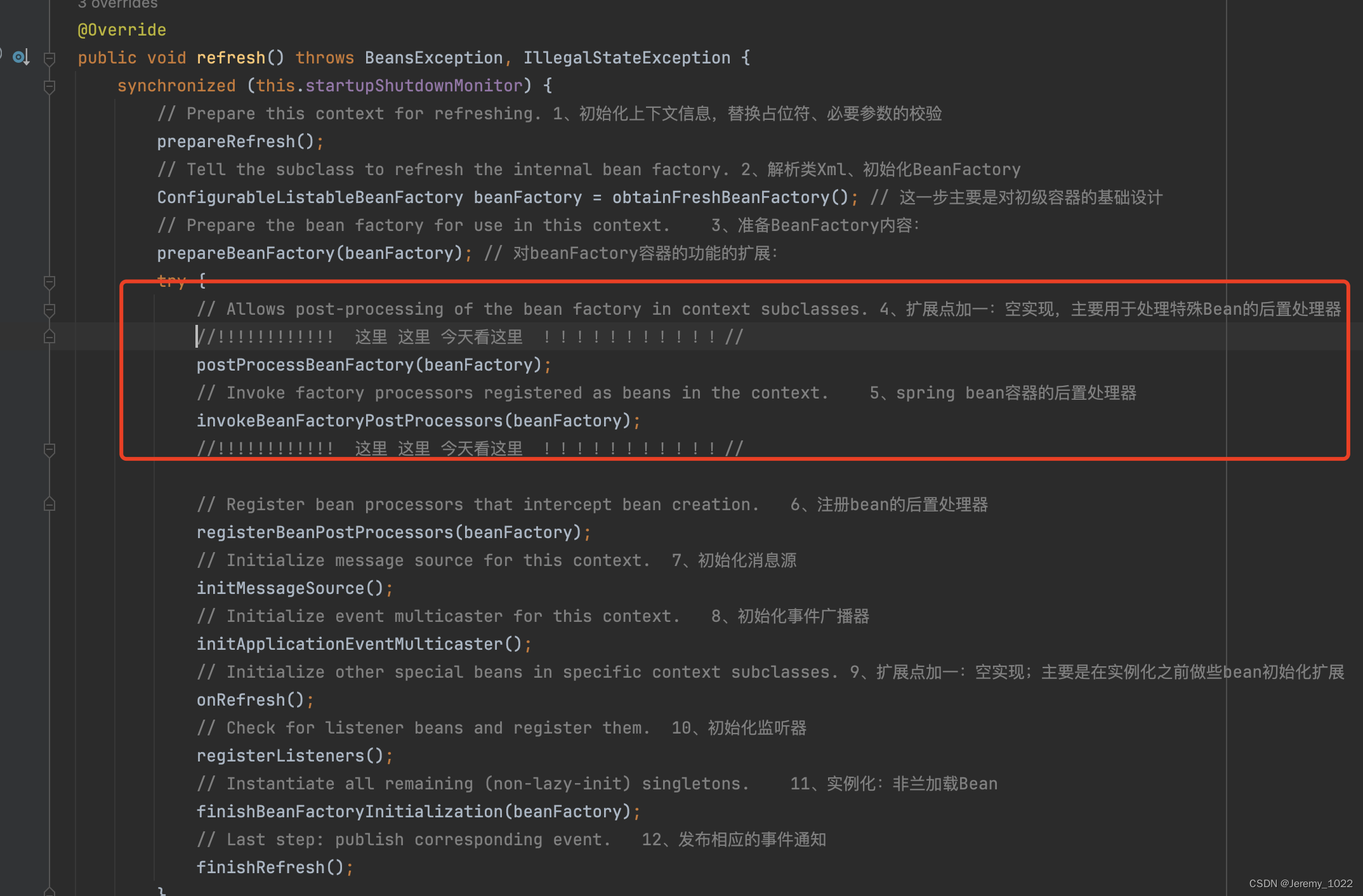
工廠后置處理方法:postProcessBeanFactory
上一篇我們看到了方法prepareBeanFactory方法,我們接著這個方法往下可以看到postProcessBeanFactory,進入該方法如下:
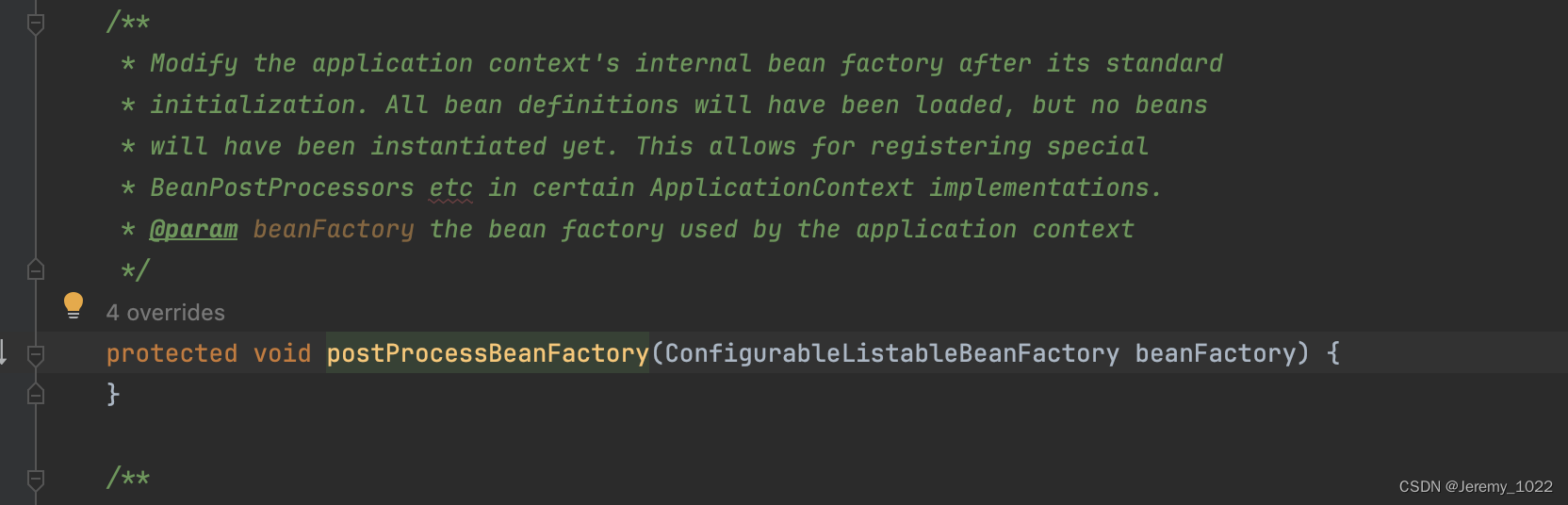
沒錯,又是一個空實現,看到這里我的風格都會說:擴展點加一;postProcessBeanFactory方法使用保護修飾且留給子類自己去具體實現。結合注釋我們可以簡單猜測一下,該方法是Spring暴露給子類去修改初級容器BeanFactory的。
那到底是什么時候可以允許子類對BeanFactory容器進行修改呢?通過方法在refresh方法的位置在prepareBeanFactory方法之后,說明是在BeanDefiniton都已經注冊到BeanFactory以后,但是還未進行實例化的時候進行修改。
我們在前面8篇內容,一點點撥開Spring的方法,到這里其實我們的進程,僅僅進行到將xml文件中的Bean標簽內容解析成BeanDefinition對象然后注入到Spring的BeanFactory容器里而已,這個和我們真正意義上的Bean還有一段距離呢。BeanDefintiion從名字上來看是Bean的定義,解釋下應該算是Bean屬性信息的初始化。
而我們在Java代碼里面使用的Bean的實例化對象,需要利用我們BeanDefinition定義的屬性信息去創建我們的實例化對象。在Spring中最常見的一個場景就是我們通過Spring容器getBean方法獲取一個實例。這個過程我們經常稱之為bean的實例化。
所以方法postBeanFactory在Bean初始化以后實例化之前為我們提供了一個可以修改BeanDefinition的機會,我們可以通過實現postBeanFactory方法去修改beanFactory的參數。
重寫postProcessBeanFactory示例
package org.springframework;import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;/*** @author Jeremy* @version 1.0* @description: 自定義容器* @date 2024/7/1 20:17*/
public class MyselfClassPathXmlApplicationContext extends ClassPathXmlApplicationContext {/*** Create a new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext, loading the definitions* from the given XML file and automatically refreshing the context.* @param configLocations resource location* @throws BeansException if context creation failed*/public MyselfClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String... configLocations) throws BeansException {super(configLocations);}/**** Spring refresh 方法第擴展點加一:refresh方法中的prepareRefresh();* 重寫initPropertySources 設置環境變量和設置requiredProperties**/@Overrideprotected void initPropertySources() {System.out.println("自定義 initPropertySources");getEnvironment().getSystemProperties().put("systemOS", "mac");getEnvironment().setRequiredProperties("systemOS");}/**** Spring refresh 方法第擴展點加一:refresh方法中的postProcessBeanFactory();* 重寫該方法,修改基礎容器BeanFactory內容* @param beanFactory**/@Overrideprotected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {System.out.println("自定義 postProcessBeanFactory");// 獲取容器中的對象BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition("jsUser");beanDefinition.getScope();// 修改屬性beanDefinition.setScope(BeanDefinition.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE);}
}
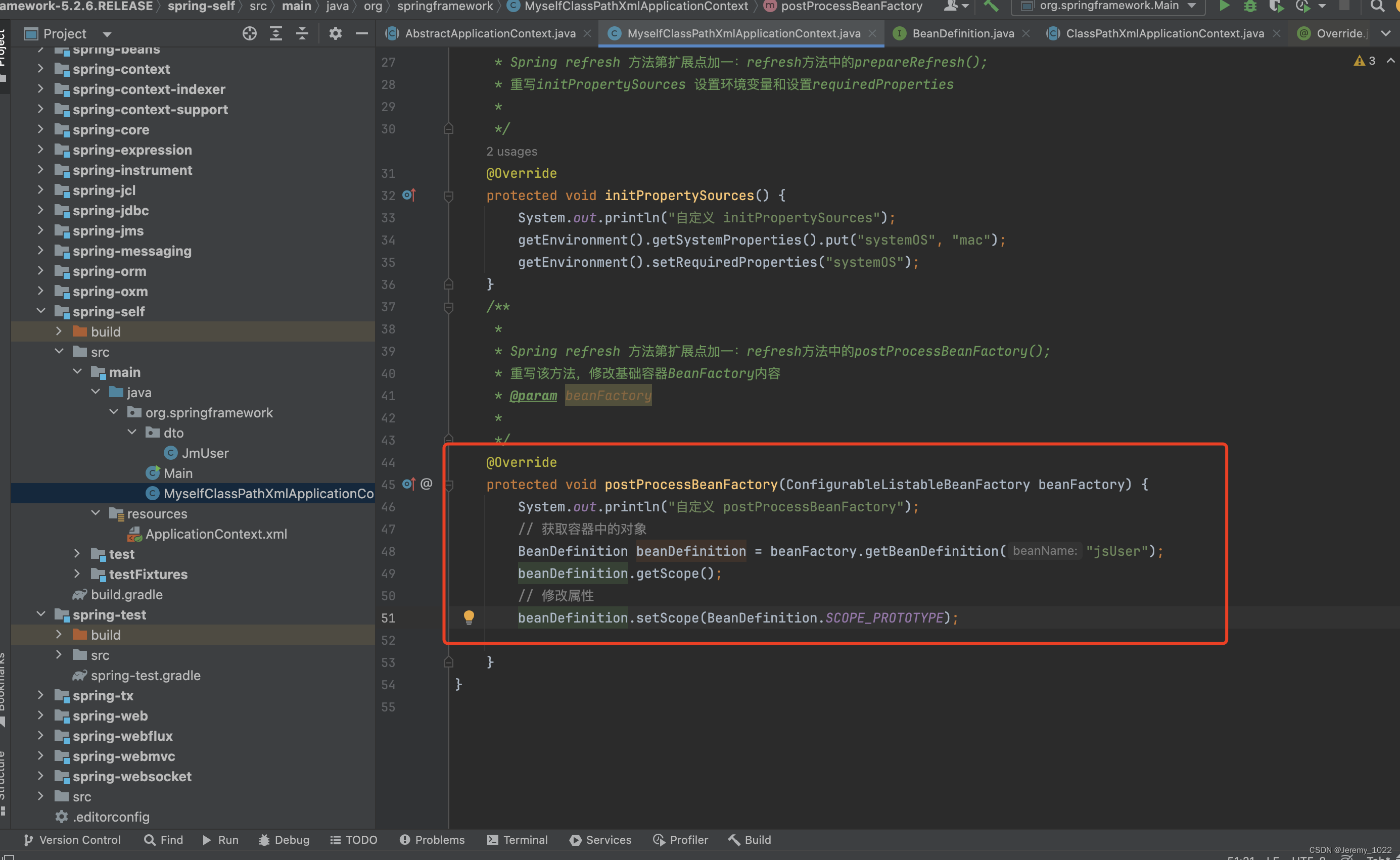
如上述方法,我們重寫了postProcessorBeanFactory方法,通過beanFactory參數獲取Bean Definition對象,然后修改BeanDefinition屬性值。當讓我還可以修改BeanFactory的其他屬性,因為這個參數是將整個BeanDefinition委托給我們自己定義的。
package org.springframework;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.dto.JmUser;/*** @author Jeremy* @version 1.0* @description: TODO* @date 2024/6/30 02:58*/
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {ApplicationContext context = new MyselfClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");JmUser jmUser = (JmUser)context.getBean("jmUser");System.out.println(jmUser.getName());System.out.println(jmUser.getAge());}
}
運行上述代碼,可以看到結果如上圖所示,Spring的postProcessorBeanFactory有回調我自定義的方法。正因為Spring在這立留了鉤子函數,所以很多框架可以通過這個方法或有類似功能的擴展點來操作整個beanFactory容器,從而可以自定義自己的框架使之擁有更加豐富與個性化的功能。后面會單獨留一篇用來說Spring的擴展點,接口SpringCloud相關組件來來看看。
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors
看到這里其實今天的核心內容已經結束了,但是我們在文章開始的時候給大家圈里了兩個方法,這里我們在提一下和上述方法功能上一致的一個類。
/*** 實例化并調用所有已經注冊BeanFactoryPostProcessor* Instantiate and invoke all registered BeanFactoryPostProcessor beans,* respecting explicit order if given.* <p>Must be called before singleton instantiation.*/protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {//PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found in the meantime// (e.g. through an @Bean method registered by ConfigurationClassPostProcessor)if (beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));}}/*** Return the list of BeanFactoryPostProcessors that will get applied* to the internal BeanFactory.*/public List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> getBeanFactoryPostProcessors() {return this.beanFactoryPostProcessors;}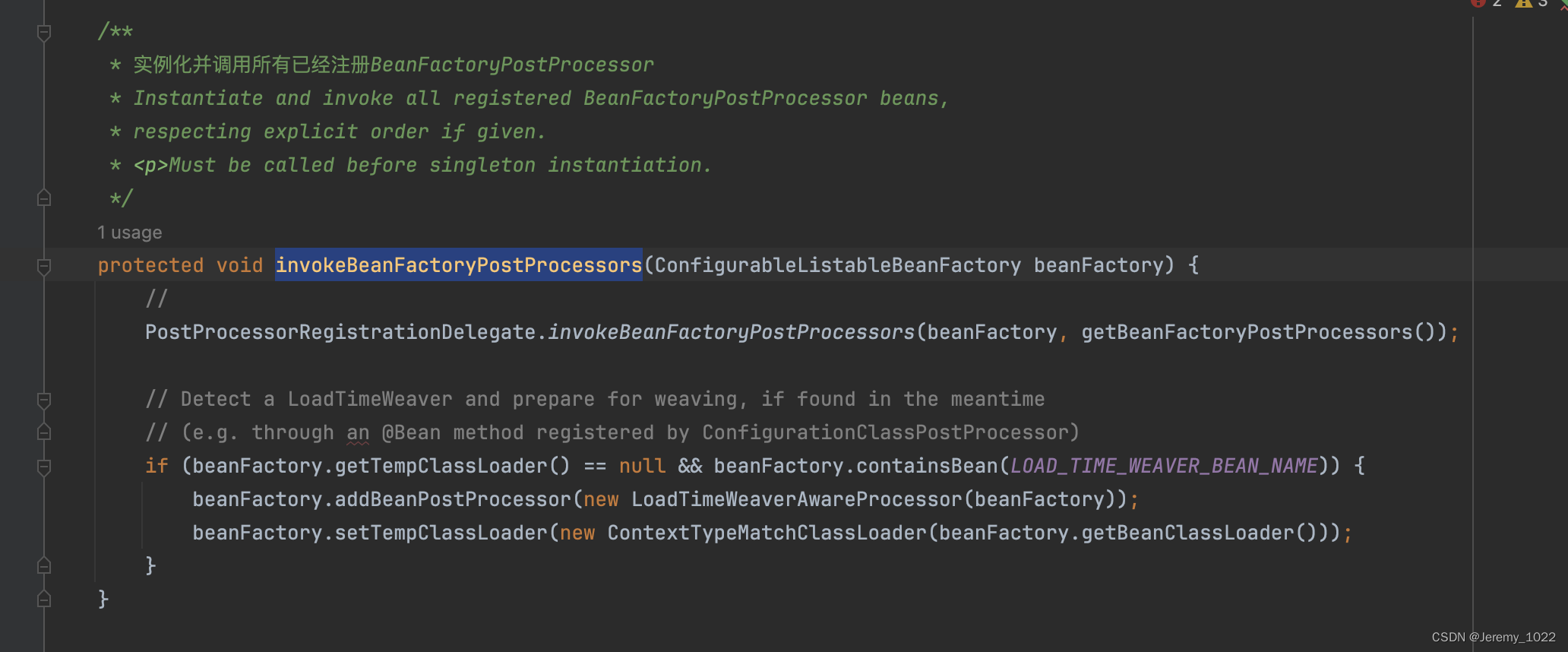
在上述代碼里的注釋里面,已經解釋了這個代碼的功能是為了實例化并調用所有已經注冊的BeanFactoryPostProcessor。所以能知道我這個放的核心其實是BeanFactoryPostProcessor,進入BeanFactoryPostProcessor類看下:
/** Copyright 2002-2019 the original author or authors.** Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.* You may obtain a copy of the License at** https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0** Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and* limitations under the License.*/package org.springframework.beans.factory.config;import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;/*** Factory hook that allows for custom modification of an application context's* bean definitions, adapting the bean property values of the context's underlying* bean factory.** <p>Useful for custom config files targeted at system administrators that* override bean properties configured in the application context. See* {@link PropertyResourceConfigurer} and its concrete implementations for* out-of-the-box solutions that address such configuration needs.** <p>A {@code BeanFactoryPostProcessor} may interact with and modify bean* definitions, but never bean instances. Doing so may cause premature bean* instantiation, violating the container and causing unintended side-effects.* If bean instance interaction is required, consider implementing* {@link BeanPostProcessor} instead.** <h3>Registration</h3>* <p>An {@code ApplicationContext} auto-detects {@code BeanFactoryPostProcessor}* beans in its bean definitions and applies them before any other beans get created.* A {@code BeanFactoryPostProcessor} may also be registered programmatically* with a {@code ConfigurableApplicationContext}.** <h3>Ordering</h3>* <p>{@code BeanFactoryPostProcessor} beans that are autodetected in an* {@code ApplicationContext} will be ordered according to* {@link org.springframework.core.PriorityOrdered} and* {@link org.springframework.core.Ordered} semantics. In contrast,* {@code BeanFactoryPostProcessor} beans that are registered programmatically* with a {@code ConfigurableApplicationContext} will be applied in the order of* registration; any ordering semantics expressed through implementing the* {@code PriorityOrdered} or {@code Ordered} interface will be ignored for* programmatically registered post-processors. Furthermore, the* {@link org.springframework.core.annotation.Order @Order} annotation is not* taken into account for {@code BeanFactoryPostProcessor} beans.** @author Juergen Hoeller* @author Sam Brannen* @since 06.07.2003* @see BeanPostProcessor* @see PropertyResourceConfigurer*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface BeanFactoryPostProcessor {/*** Modify the application context's internal bean factory after its standard* initialization. All bean definitions will have been loaded, but no beans* will have been instantiated yet. This allows for overriding or adding* properties even to eager-initializing beans.* @param beanFactory the bean factory used by the application context* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors*/void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;}
看到這個接口只有一個方法且名稱也叫postProcessBeanFactory,在看代碼的上面的這是與參數和我們refresh中一樣,說明我們也可以通過實現Bean FactoryPostProcessor接口的形式來修改我們的BeanFactory對象。如下所示:
自定義BeanFactoryPostProcessor
package org.springframework;import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;/*** 自定義Bean的后置處理器*/
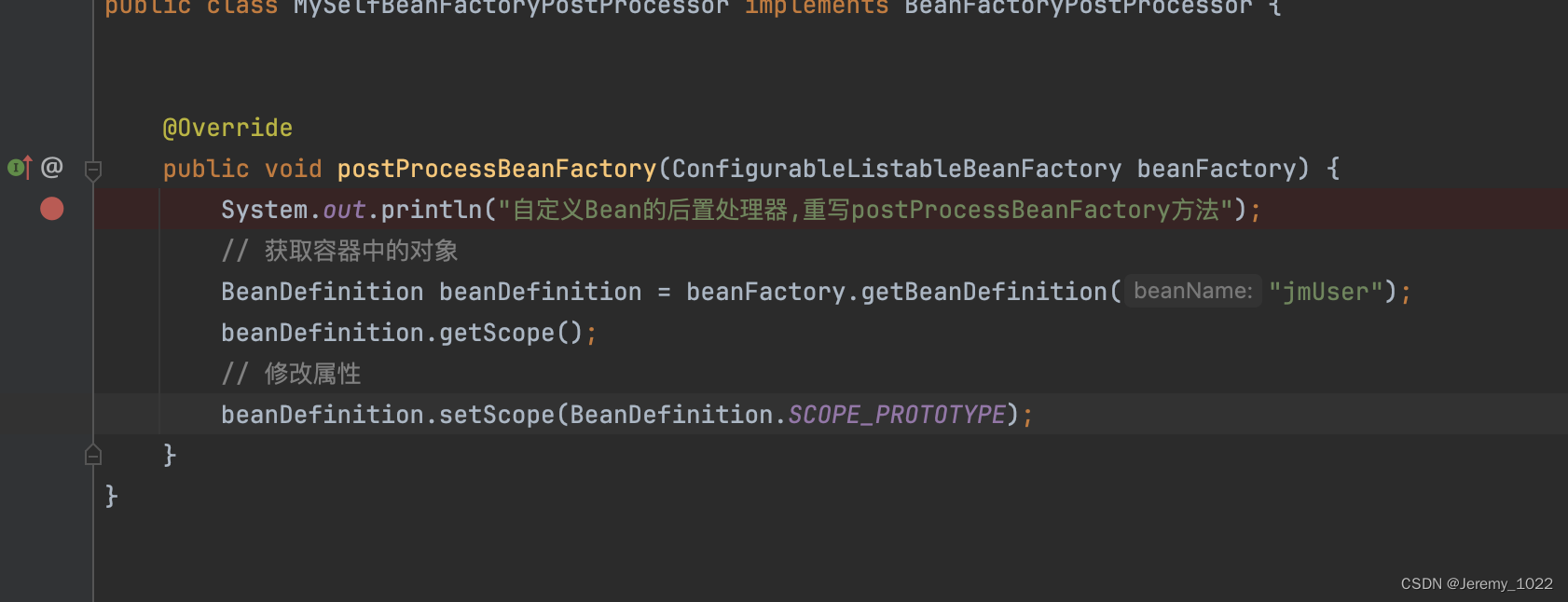
public class MySelfBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {@Overridepublic void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {System.out.println("自定義Bean的后置處理器,重寫postProcessBeanFactory方法");// 獲取容器中的對象BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition("jmUser");beanDefinition.getScope();// 修改屬性beanDefinition.setScope(BeanDefinition.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE);}
}
Spring已經提供了空實現的postProcessorBeanFactory方法,為啥還要單獨搞一個接口來定一個這個方法呢?
Spring提供BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口,而不是在refresh方法中直接進行beanFactory修改,主要是為了提高代碼的解耦性、可維護性和擴展性。通過將不同的修改操作分散到不同的實現類中,每個類都只關注特定的任務,這樣不僅符合單一職責原則,還使得整個框架更加靈活和易于擴展。這種設計理念是
Spring成功的重要原因之一。
整體小結



















函數詳解:能給萬物排序的神奇函數)
