目錄
- 1. 特征分析
- 1.1 數據集導入
- 1.2 統計缺失值
- 1.3 可視化缺失值
- 1.4 缺失值相關性分析
- 1.5 訓練集和測試集缺失數據對比
- 1.6 統計特征的數據類型
- 1.7 數值型特征分布直方圖
- 1.8 數值型特征與房價的線性關系
- 1.9 非數值型特征的分布直方圖
- 1.10 非數值型特征箱線圖
- 1.11 數值型特征填充前后的分布對比
- 1.12 時序特征分析
- 1.13 用熱圖分析數值型特征之間的相關性
- 2. 數據處理
- 2.1 正態化 SalePrice
- 2.2 時序特征處理
- 2.3 特征融合
- 2.4 填充特征值
- 2.5 連續性數據正態化
- 2.5 編碼數據集后切分數據集
- 3. 模型搭建
- 3.1 模型搭建與超參數調整
- 3.2 模型交叉驗證
- 3.3 特征重要性分析
- 3.4 數值預測
- 4. 參考文獻
這是接觸Kaggle競賽的第一個題目,借鑒了其他人可視化分析和特征分析的技巧(文末附鏈接)。本次提交到Kaggle的得分是0.13227,排名1209(提交日期:2024年6月30日)。

思路簡圖:
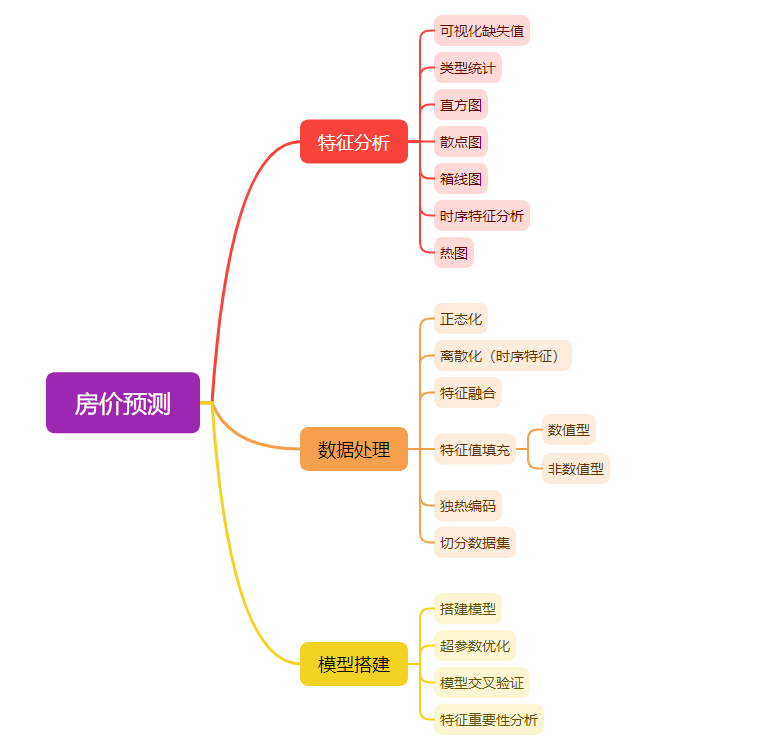
1. 特征分析
1.1 數據集導入
將訓練集與測試集合并,方便更準確地分析數據特征。
train = pd.read_csv("D:\\Desktop\\kaggle數據集\\house-prices-advanced-regression-techniques\\train.csv")
test = pd.read_csv("D:\\Desktop\\kaggle數據集\\house-prices-advanced-regression-techniques\\test.csv")
Id = test['Id']
print("訓練集大小{}".format(train.shape))
print("測試集大小{}".format(test.shape))
# 合并訓練集與測試集,方便更準確地分析數據特征
datas = pd.concat([train, test], ignore_index=True)
# 刪除Id列
datas.drop("Id", axis= 1, inplace=True)
訓練集大小(1460, 81)
測試集大小(1459, 80)
1.2 統計缺失值
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 統計數據集中的值的空缺情況(以列為統計單位)
# isnull():檢查所有數據集,如果是缺失值則返回True,否則返回False
# .sum():計算每列中True的數量
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
datas.isnull().sum().sort_values(ascending = False).head(40)
PoolQC 2909
MiscFeature 2814
Alley 2721
Fence 2348
MasVnrType 1766
SalePrice 1459
FireplaceQu 1420
LotFrontage 486
GarageFinish 159
GarageQual 159
GarageCond 159
GarageYrBlt 159
GarageType 157
BsmtCond 82
BsmtExposure 82
BsmtQual 81
BsmtFinType2 80
BsmtFinType1 79
MasVnrArea 23
MSZoning 4
BsmtHalfBath 2
Utilities 2
BsmtFullBath 2
Functional 2
Exterior2nd 1
Exterior1st 1
GarageArea 1
GarageCars 1
SaleType 1
KitchenQual 1
BsmtFinSF1 1
Electrical 1
BsmtFinSF2 1
BsmtUnfSF 1
TotalBsmtSF 1
TotRmsAbvGrd 0
Fireplaces 0
SaleCondition 0
PavedDrive 0
MoSold 0
dtype: int64
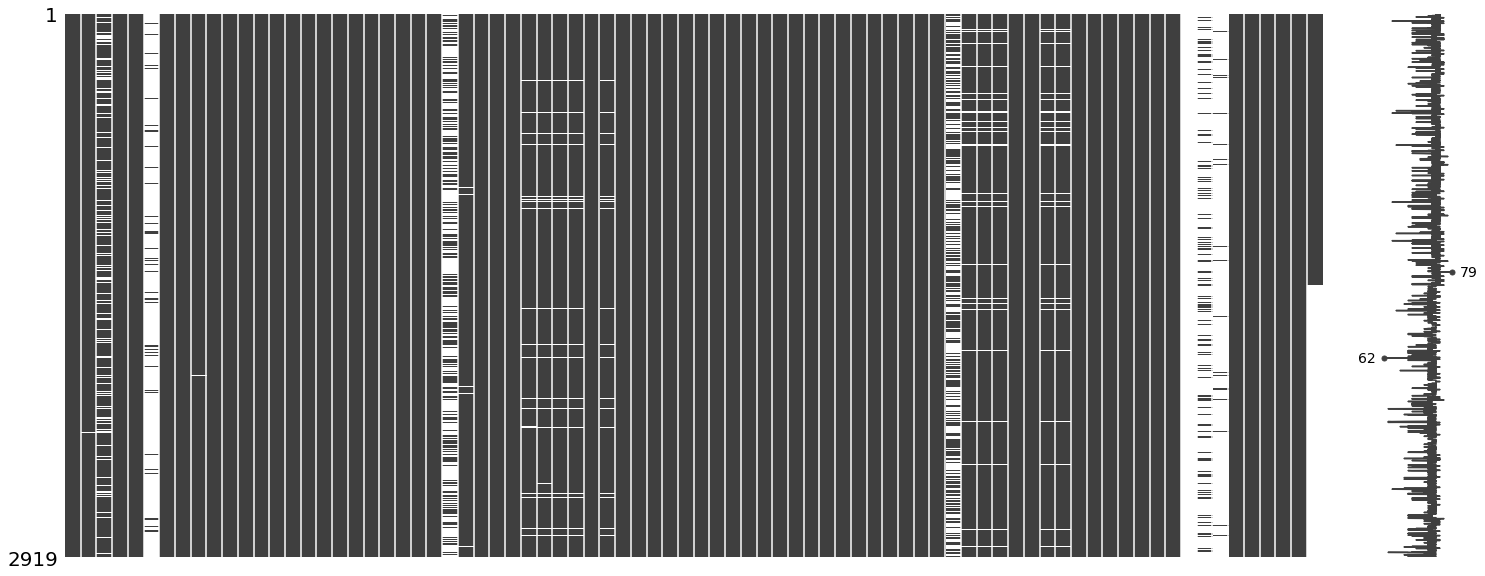
1.3 可視化缺失值
右側的微線圖概括了數據完整性的一般形狀,并標明了具有最多空值(最靠近左側,數值表示的該行中非空值的數量)和最少空值(最靠近右側)的行。
msno.matrix(datas)
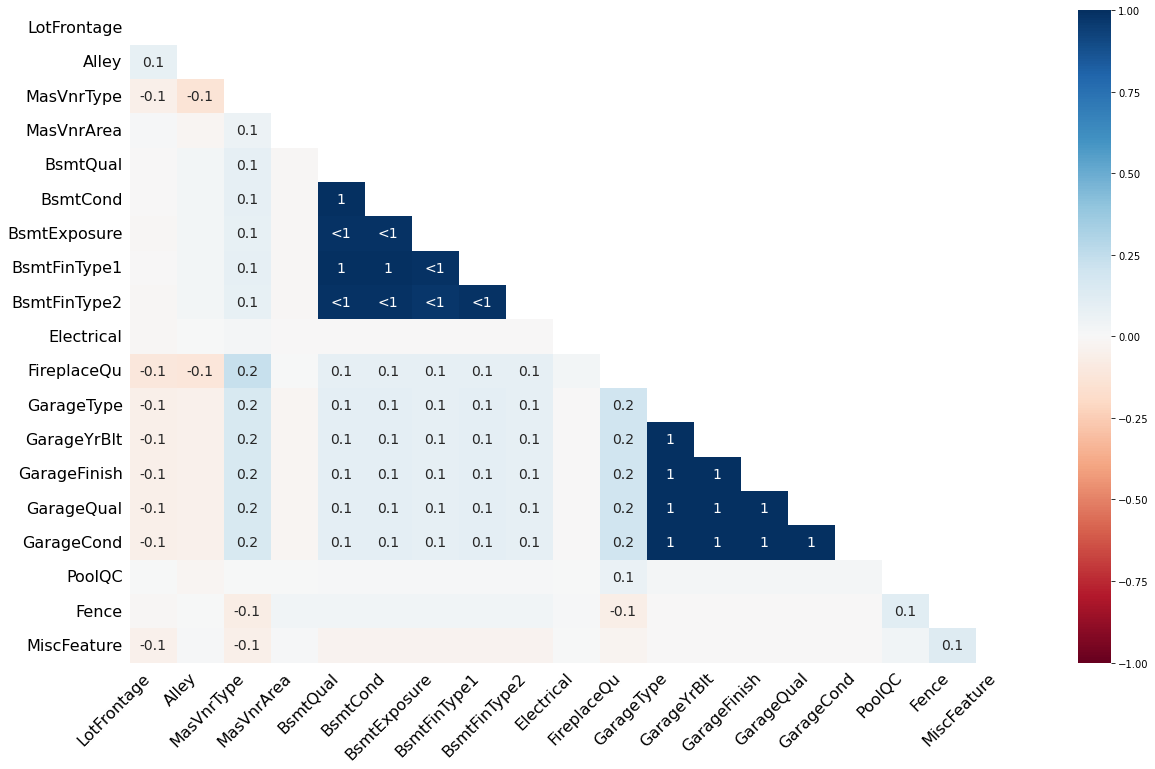
1.4 缺失值相關性分析
用熱圖顯示數據集中缺失值之間的相關性
- 1:表示兩個特征的缺失模式完全相同,即其中一個缺失時,另一個也缺失
- -1:表示一個特征有缺失值時,另一個特征沒有缺失值
- 0: 表示兩個特征的缺失值模式不相關
msno.heatmap(train)
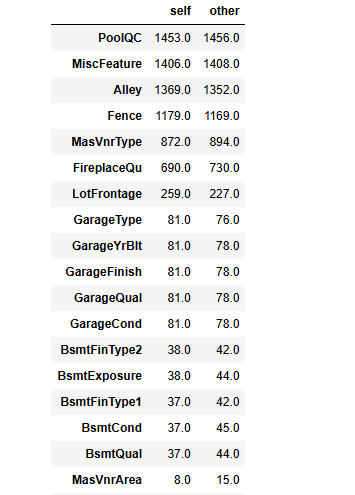
1.5 訓練集和測試集缺失數據對比
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 比較兩個dataframe(train和test)的數據類型,需確保兩個數據集具有相同的列標簽
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
train_dtype = train_dtype.drop('SalePrice')
train_dtype.compare(test_dtype)
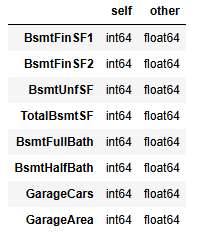
由對比結果可知數據類型都是int64和float64的區別,對結果影響不大。
# 缺失值對比
null_train = train.isnull().sum()
null_test = test.isnull().sum()
null_train = null_train.drop('SalePrice')
null_comp = null_train.compare(null_test).sort_values(['self'], ascending=[False])
null_comp
(局部,未截完整)
1.6 統計特征的數據類型
- 數值型特征
- 1.1 離散特征(唯一值(多個重復值只取一個)數量小于25(可視情況而定))
- 1.2 連續特征(‘Id’列不計入)
- 非數值型數據
# 在 pandas 中,如果一個列的數據類型無法確定為數值型,則會被標記為 '0'
numerical_features = [col for col in datas.columns if datas[col].dtypes != 'O']
discrete_features = [col for col in numerical_features if len(datas[col].unique()) < 25]
continuous_features = [feature for feature in numerical_features if feature not in discrete_features]
non_numerical_features = [col for col in datas.columns if datas[col].dtype == 'O']print("Total Number of Numerical Columns : ",len(numerical_features))
print("Number of discrete features : ",len(discrete_features))
print("No of continuous features are : ", len(continuous_features))
print("Number of non-numeric features : ",len(non_numerical_features))print("離散型數據: ",discrete_features)
print("連續型數據:", continuous_features)
print("非數值型數據:",non_numerical_features)
Total Number of Numerical Columns : 37
Number of discrete features : 15
No of continuous features are : 22
Number of non-numeric features : 43
離散型數據: ['MSSubClass', 'OverallQual', 'OverallCond', 'BsmtFullBath', 'BsmtHalfBath', 'FullBath', 'HalfBath', 'BedroomAbvGr', 'KitchenAbvGr', 'TotRmsAbvGrd', 'Fireplaces', 'GarageCars', 'PoolArea', 'MoSold', 'YrSold']
連續型數據: ['LotFrontage', 'LotArea', 'YearBuilt', 'YearRemodAdd', 'MasVnrArea', 'BsmtFinSF1', 'BsmtFinSF2', 'BsmtUnfSF', 'TotalBsmtSF', '1stFlrSF', '2ndFlrSF', 'LowQualFinSF', 'GrLivArea', 'GarageYrBlt', 'GarageArea', 'WoodDeckSF', 'OpenPorchSF', 'EnclosedPorch', '3SsnPorch', 'ScreenPorch', 'MiscVal', 'SalePrice']
非數值型數據: ['MSZoning', 'Street', 'Alley', 'LotShape', 'LandContour', 'Utilities', 'LotConfig', 'LandSlope', 'Neighborhood', 'Condition1', 'Condition2', 'BldgType', 'HouseStyle', 'RoofStyle', 'RoofMatl', 'Exterior1st', 'Exterior2nd', 'MasVnrType', 'ExterQual', 'ExterCond', 'Foundation', 'BsmtQual', 'BsmtCond', 'BsmtExposure', 'BsmtFinType1', 'BsmtFinType2', 'Heating', 'HeatingQC', 'CentralAir', 'Electrical', 'KitchenQual', 'Functional', 'FireplaceQu', 'GarageType', 'GarageFinish', 'GarageQual', 'GarageCond', 'PavedDrive', 'PoolQC', 'Fence', 'MiscFeature', 'SaleType', 'SaleCondition']
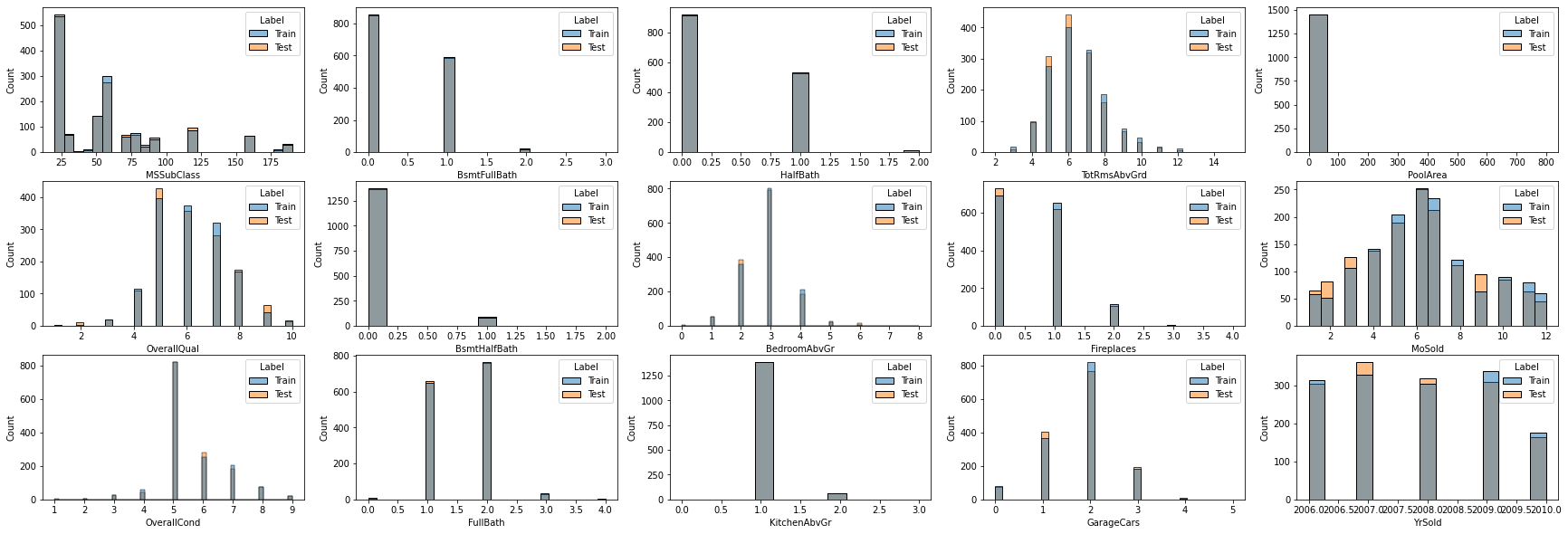
1.7 數值型特征分布直方圖
離散數據分布直方圖
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 添加 Label 列用于標識訓練集和測試集
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
datas['Label'] = "Test"
datas['Label'][:1460] = "Train"
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 離散數據直方圖
# sharex=False:子圖的x軸不共享,每個子圖可以獨立設置自己的x軸屬性
# hue='Label':根據 Label 列的值為直方圖上色,不同的 Label 值會分配不同顏色
# ax=axes[i%3,i//3]:確保了直方圖可以在一個3xN的網格中均勻分布
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
fig, axes = plt.subplots(3, 5, figsize=(30, 10), sharex=False)
for i, feature in enumerate(discrete_features):sns.histplot(data=datas, x=feature, hue='Label', ax=axes[i%3, i//3])
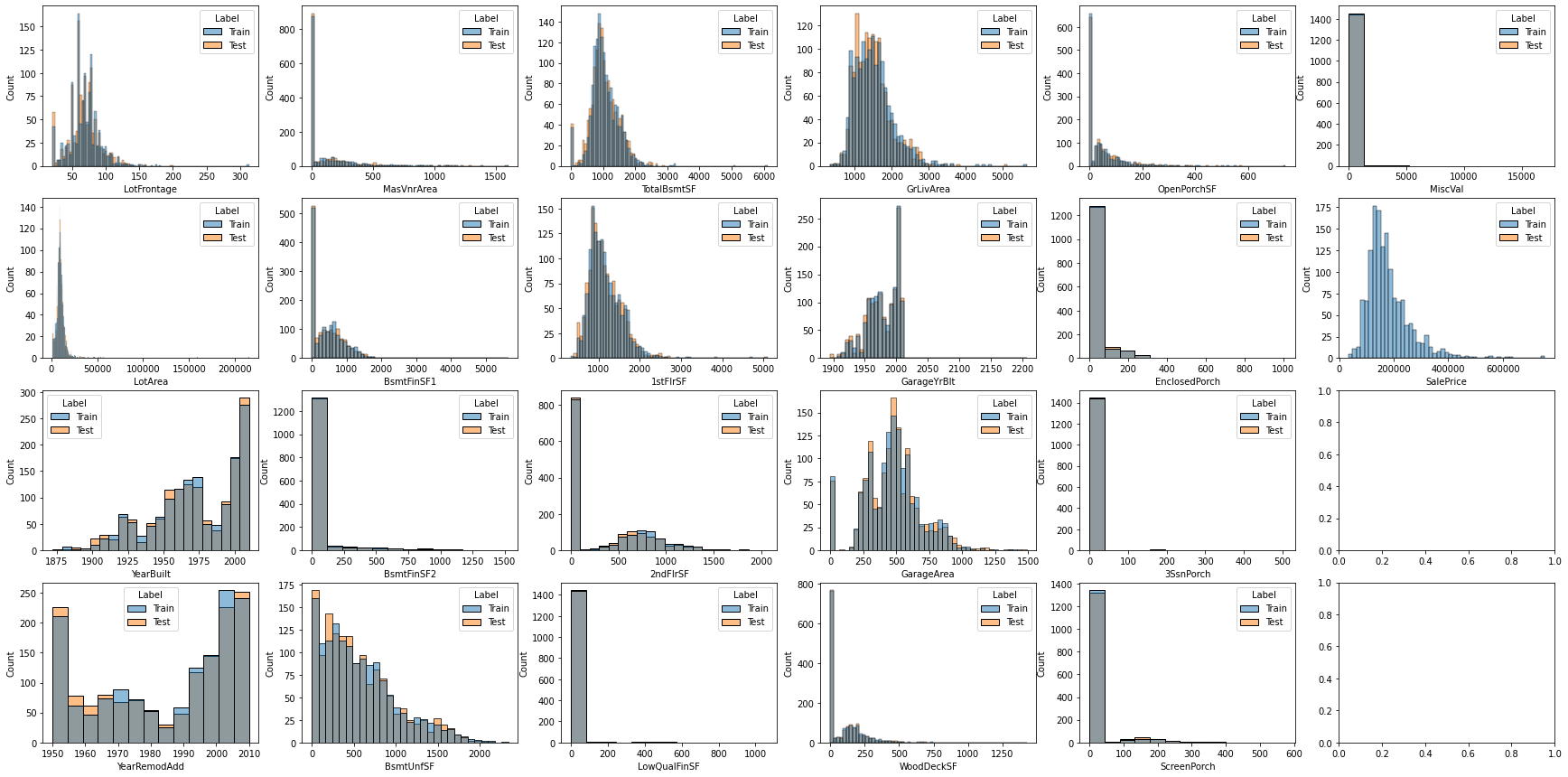
連續數據分布直方圖
fig,axes = plt.subplots(nrows = 4, ncols = 6, figsize=(30,15), sharex=False)
for i, feature in enumerate(continuous_features):sns.histplot(data=datas, x=feature, hue='Label',ax=axes[i%4,i//4])
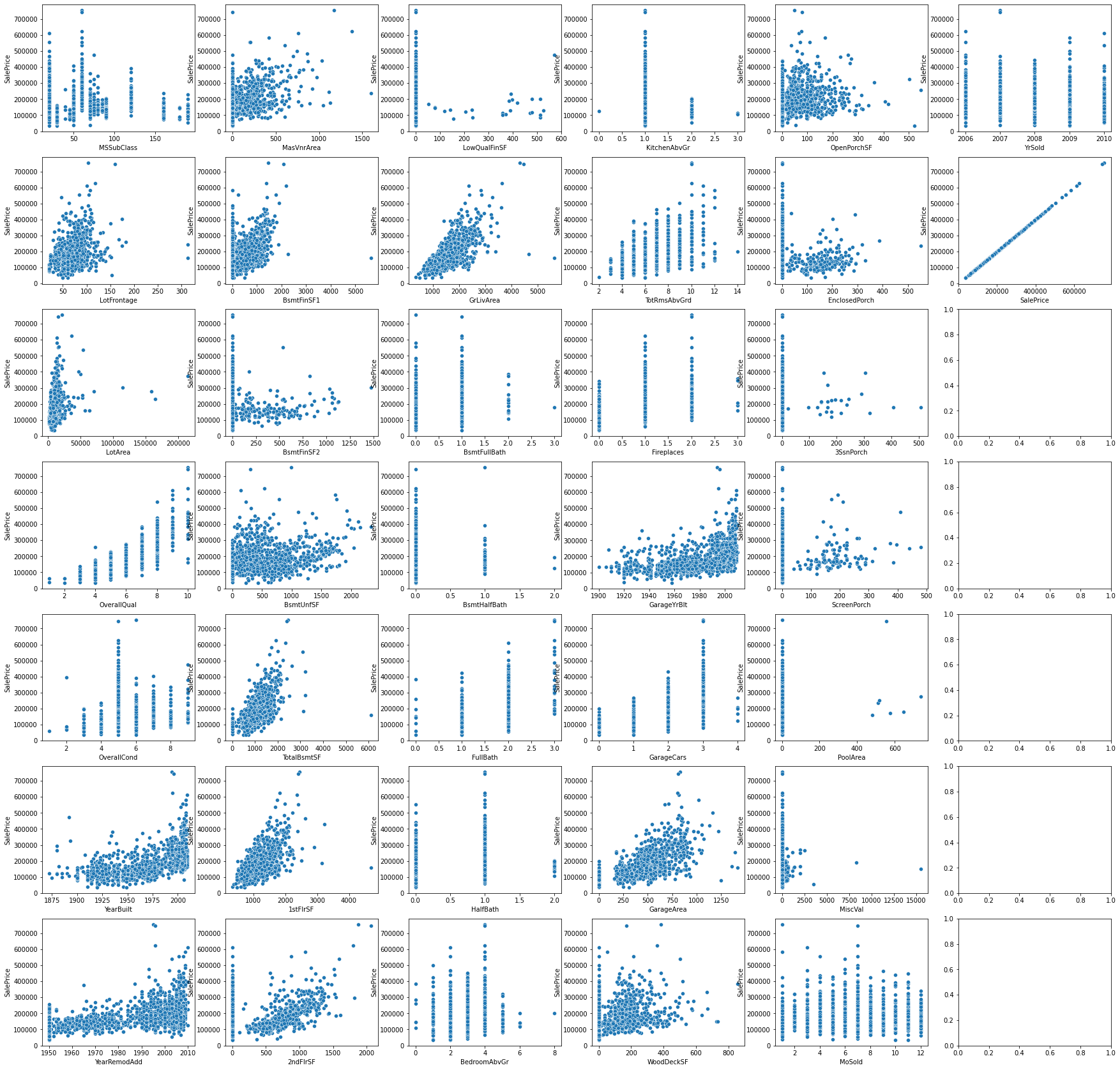
1.8 數值型特征與房價的線性關系
fig, axes = plt.subplots(7, 6, figsize=(30, 30), sharex=False)
for i, feature in enumerate(numerical_features):sns.scatterplot(data = datas, x = feature, y="SalePrice", ax=axes[i%7, i//7])
1.9 非數值型特征的分布直方圖
f,axes = plt.subplots(7, 7, figsize=(30,30),sharex=False)
for i,feature in enumerate(non_numerical_features):sns.countplot(data=datas, x=feature, hue="Label", ax=axes[i%7,i//7])
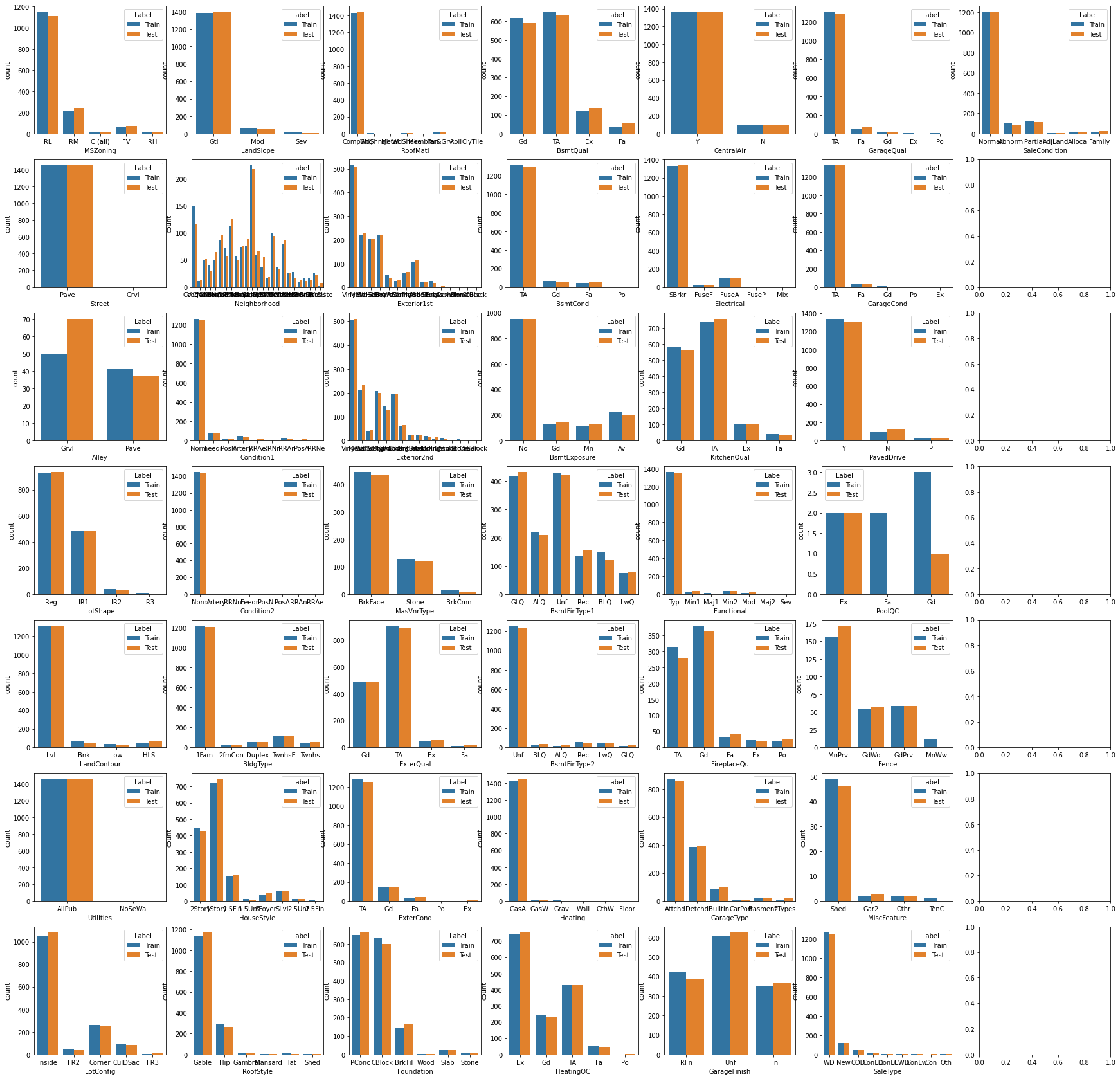
1.10 非數值型特征箱線圖
對每個箱線圖內部按照 SalePric 對不同的特征值進行降序排序。
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# groupby(feature)['SalePrice'].median():計算每個 feature 分組的SalePrice中位數
# items():將結果轉換為一個包含鍵值對的迭代器(迭代器中的每個元素都是一個二元組),二元組形式:(特征值,中位數)
# x[1]:根據二元組的第二個值進行排序
# reverse = True:降序
# x[0] for x in sort_list:提取二元組的第一個值(鍵)即特征值
# order=order_list:按 order_list 中的順序排列 x 軸的分類
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
fig, axes = plt.subplots(7,7 , figsize=(30, 30), sharex=False)
for i, feature in enumerate(non_numerical_features):sort_list = sorted(datas.groupby(feature)['SalePrice'].median().items(), key = lambda x:x[1], reverse = True)order_list = [x[0] for x in sort_list ]sns.boxplot(data = datas, x = feature, y = 'SalePrice', order=order_list, ax=axes[i%7, i//7])
plt.show()
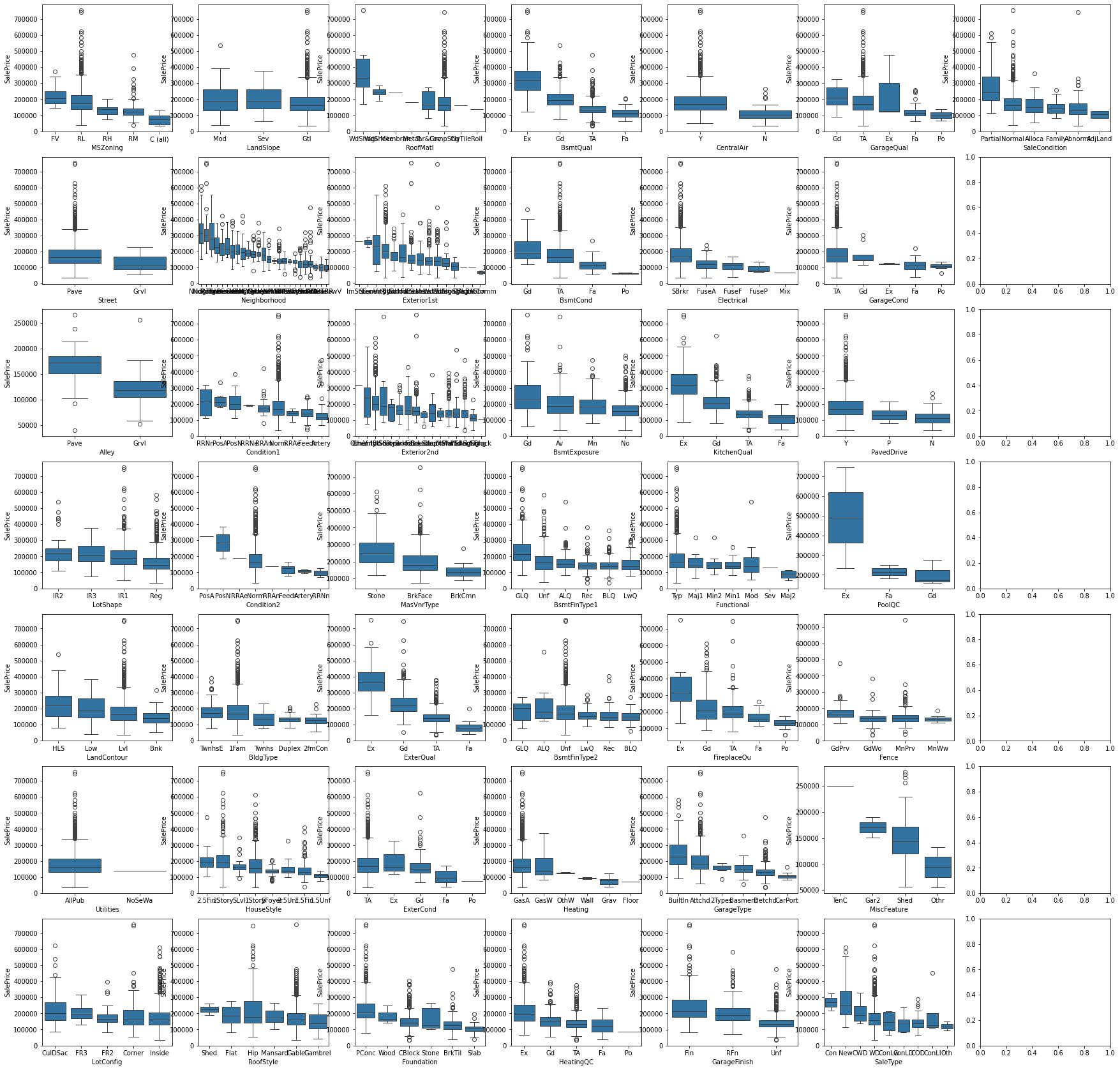
1.11 數值型特征填充前后的分布對比
# 原數值數據數據(有數據缺失的列)與使用均值、眾數和中位數填充后的數據分布對比
null_numerical_features = [col for col in datas.columns if datas[col].isnull().sum()>0 and col not in non_numerical_features]
plt.figure(figsize=(30, 20))for i, var in enumerate(null_numerical_features):plt.subplot(4,3,i+1)sns.distplot(datas[var], bins=20, kde_kws={'linewidth':3,'color':'yellow'}, label="original")sns.distplot(datas[var].fillna(datas[var].mean()), bins=20, kde_kws={'linewidth':2,'color':'red'}, label="mean")sns.distplot(datas[var].fillna(datas[var].median()), bins=20, kde_kws={'linewidth':2,'color':'green'}, label="median")sns.distplot(datas[var].fillna(datas[var].mode()[0]), bins=20, kde_kws={'linewidth':2,'color':'blue'}, label="mode")
1.12 時序特征分析
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# YrSold是離散型數據,YearBuilt(建房日期),YearRemodAdd(改造日期),GarageYrBlt(車庫修建日期)是連續型數據
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
year_feature = [col for col in datas.columns if "Yr" in col or 'Year' in col]
year_feature
['YearBuilt', 'YearRemodAdd', 'GarageYrBlt', 'YrSold']
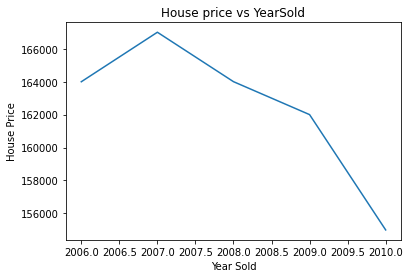
# 查看YrSold與售價的關系
datas.groupby('YrSold')['SalePrice'].median().plot()
plt.xlabel('Year Sold')
plt.ylabel('House Price')
plt.title('House price vs YearSold')
# 繪制其他三個特征與銷售價格的散點對應圖
for feature in year_feature:if feature != 'YrSold':hs = datas.copy()plt.scatter(hs[feature],hs['SalePrice'])plt.xlabel(feature)plt.ylabel('SalePrice')
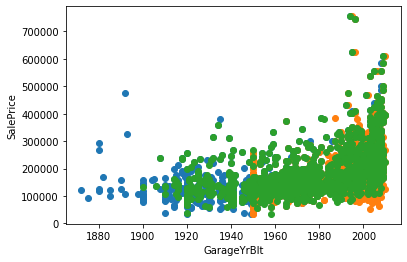
可以發現隨著時間增加(即建造的時間越近),價格也逐漸增加。
1.13 用熱圖分析數值型特征之間的相關性
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# cmap="YlGnBu":指定從黃綠色(正相關)到藍綠色(負相關)的顏色漸變
# linewidths=.5:邊框寬度為0.5
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
plt.figure(figsize=(20,10))
numeric_features = train.select_dtypes(include=[float, int])
sns.heatmap(numeric_features.corr(), cmap="YlGnBu", linewidths=.5)
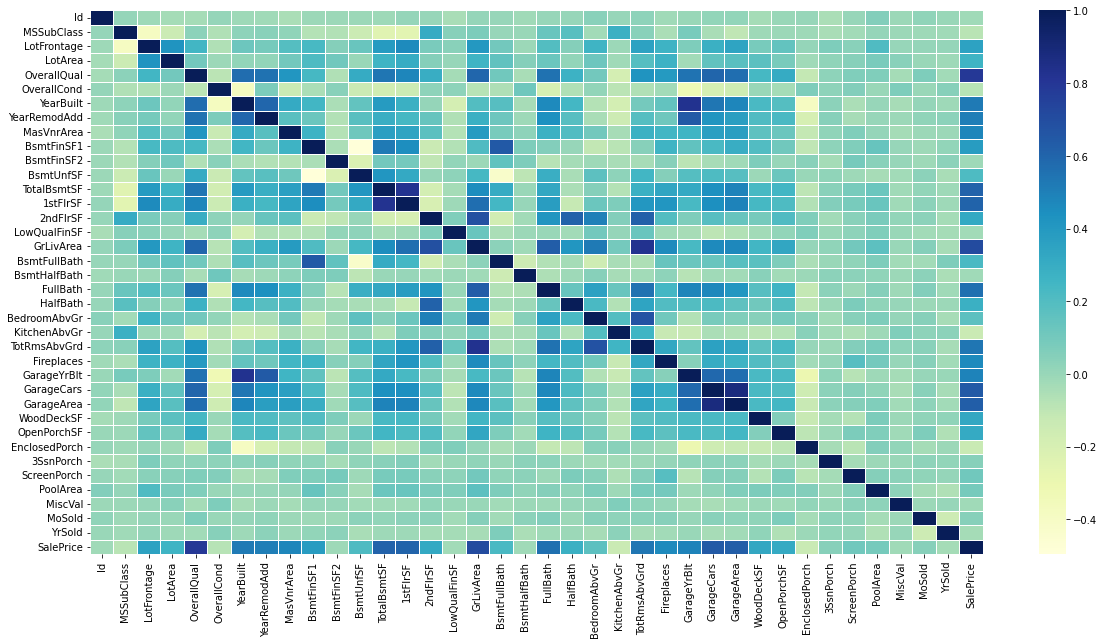
2. 數據處理
2.1 正態化 SalePrice
- n p . l o g 1 ( ) np.log1() np.log1():即計算 l n ( 1 + x ) ln(1 + x) ln(1+x),使用該函數比直接使用 n p . l o g ( 1 + x ) np.log(1 + x) np.log(1+x) 計算的精度要高。注意:np.log() 函數指的是計算自然對數)。
- n p . e x p m 1 ( ) np.expm1() np.expm1():即計算 e x ? 1 e^x-1 ex?1,使用該函數比直接計算 e x ? 1 e^x-1 ex?1 的精度要高。
二者互為反函數,使用 n p . l o g 1 ( ) np.log1() np.log1() 將 SalePrice 平滑化(正態化)后,最后得到的預測值需要用 n p . e x p m 1 ( ) np.expm1() np.expm1() 進行轉換。
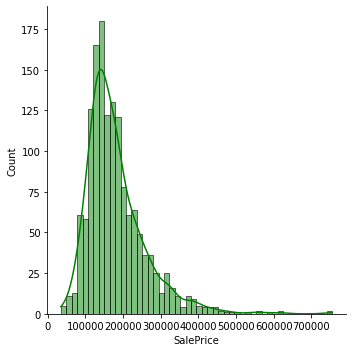
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 繪制SalePrice的特征分布
# displot:用于繪制直方圖和核密度估計圖
# kde:用于在直方圖上疊加核密度估計曲線
# .skew():算數據集的偏度,偏度是統計數據分布的不對稱性的度量
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
sns.displot(datas['SalePrice'], color='g', bins=50, kde=True)
print("SalePrice的偏度:{:.2f}".format(datas['SalePrice'].skew()))
SalePrice的偏度:1.88
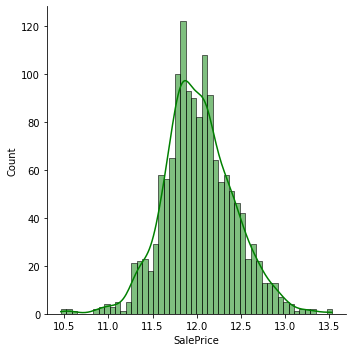
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 使用 np.log1() 將其平滑化(正態化)
# 偏度為1.88,SalePrice 的數據分布顯著偏離正態,正常的數據應該是接近于正態分布的
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
datas['SalePrice'] = np.log1p(datas['SalePrice'])
sns.displot(datas['SalePrice'], color='g', bins=50, kde=True)
print("正態化后 SalePrice 的偏度:{:.2f}".format(datas['SalePrice'].skew()))
正態化后 SalePrice 的偏度:0.12
2.2 時序特征處理
將時序特征離散化(用 YrSold 減去 YearBuilt、YearRemodAdd和GarageYrBlt 的時間),YrSold本身離散不用管。時序特征中 GarageYrBlt 數據有缺失,用中位數補足。
for feature in ['YearBuilt','YearRemodAdd','GarageYrBlt']:datas[feature]=datas['YrSold']-datas[feature]
datas['GarageYrBlt'].fillna(datas['GarageYrBlt'].median(), inplace = True)
2.3 特征融合
從非數值型特征的分布直方圖中可以發現 GarageQual 特征的 Ex 和 Po 占比非常小(如下圖),所以將這兩個特征值統稱為 other(其他列暫不使用,還不知道效果如何)。
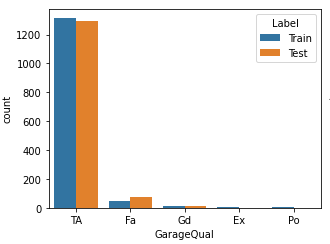
# mask是一個布爾索引數組,長度與列 cGarageQual 的長度相同
# datas['GarageQual'][mask]:選擇列 GarageQual 中所有 mask 為 True 的元素,
mask = datas['GarageQual'].isin(['Ex', 'Po'])
datas['GarageQual'][mask] = 'Other'
2.4 填充特征值
缺失最多的特征 PoolQC(泳池質量)并不代表數據缺失,而是沒有泳池,因此不能簡單地直接刪除該列,這里用None替換掉Nan。
datas['PoolQC'].fillna("None", inplace=True)
排查數據缺失列,如果是數值型特征則根據數據 [1.11 數值型特征填充前后的分布對比] 選擇中位數、眾數還是平均數填充(多數情況下離散型用眾數或中位數,連續型用中位數或平均數)。
如果是非數值型數據分兩種情況:
- 缺失較多,使用 None 填充(新加一個類)
- 缺失較少,使用眾數(最大類別)填充
# -------------------------------------------------非數值型數據----------------------------------------------#
datas['MiscFeature'].fillna('None', inplace=True)
datas['Alley'].fillna('None', inplace=True)
datas['Fence'].fillna('None', inplace=True)
datas['MasVnrType'].fillna('None', inplace=True)
datas['FireplaceQu'].fillna('None', inplace=True)
datas['GarageQual'].fillna('None', inplace=True)
datas['GarageCond'].fillna('None', inplace=True)
datas['GarageFinish'].fillna('None', inplace=True)
datas['GarageType'].fillna('None', inplace=True)
datas['BsmtCond'].fillna('None', inplace=True)
datas['BsmtExposure'].fillna('None', inplace=True)
datas['BsmtQual'].fillna('None', inplace=True)
datas['BsmtFinType1'].fillna('None', inplace=True)
datas['BsmtFinType2'].fillna('None', inplace=True)# mode()[0]:計算該列的眾數并取第一個值
datas['MSZoning'].fillna(datas['MSZoning'].mode()[0], inplace=True)
datas['Utilities'].fillna(datas['Utilities'].mode()[0], inplace=True)
datas['Functional'].fillna(datas['Functional'].mode()[0], inplace=True)
datas['Electrical'].fillna(datas['Electrical'].mode()[0], inplace=True)
datas['Exterior2nd'].fillna(datas['Exterior2nd'].mode()[0], inplace=True)
datas['Exterior1st'].fillna(datas['Exterior1st'].mode()[0], inplace=True)
datas['SaleType'].fillna(datas['SaleType'].mode()[0], inplace=True)
datas['KitchenQual'].fillna(datas['KitchenQual'].mode()[0], inplace=True)#--------------------------------------------------數值型數據------------------------------------------------#
datas['MasVnrArea'].fillna(datas['MasVnrArea'].mean(), inplace = True)
datas['LotFrontage'].fillna(datas['LotFrontage'].mean(), inplace = True)
datas['BsmtFullBath'].fillna(datas['BsmtFullBath'].median(), inplace = True)
datas['BsmtHalfBath'].fillna(datas['BsmtHalfBath'].median(), inplace = True)
datas['BsmtFinSF1'].fillna(datas['BsmtFinSF1'].median(), inplace = True)
datas['GarageCars'].fillna(datas['GarageCars'].mean(), inplace = True)
datas['GarageArea'].fillna(datas['GarageArea'].mean(), inplace = True)
datas['TotalBsmtSF'].fillna(datas['TotalBsmtSF'].mean(), inplace = True)
datas['BsmtUnfSF'].fillna(datas['BsmtUnfSF'].mean(), inplace = True)
datas['BsmtFinSF2'].fillna(datas['BsmtFinSF2'].median(), inplace = True)
數據填充完之后確認一下是否還有遺漏的數據
datas.isnull().sum().sort_values(ascending = False).head(10)
SalePrice 1459
MSZoning 0
GarageYrBlt 0
GarageType 0
FireplaceQu 0
Fireplaces 0
Functional 0
TotRmsAbvGrd 0
KitchenQual 0
KitchenAbvGr 0
dtype: int64
2.5 連續性數據正態化
數據填充完畢后,重新挑選出連續型數值特征,觀察其分布情況。
numerical_features = [col for col in datas.columns if datas[col].dtypes != 'O']
discrete_features = [col for col in numerical_features if len(datas[col].unique()) < 25 and col not in ['Id']]
continuous_features = [feature for feature in numerical_features if feature not in discrete_features+['Id']]
fig,axes = plt.subplots(nrows = 4, ncols = 6, figsize=(30,15), sharex=False)
for i, feature in enumerate(continuous_features):sns.histplot(data=datas, x=feature, hue='Label',ax=axes[i%4,i//4])
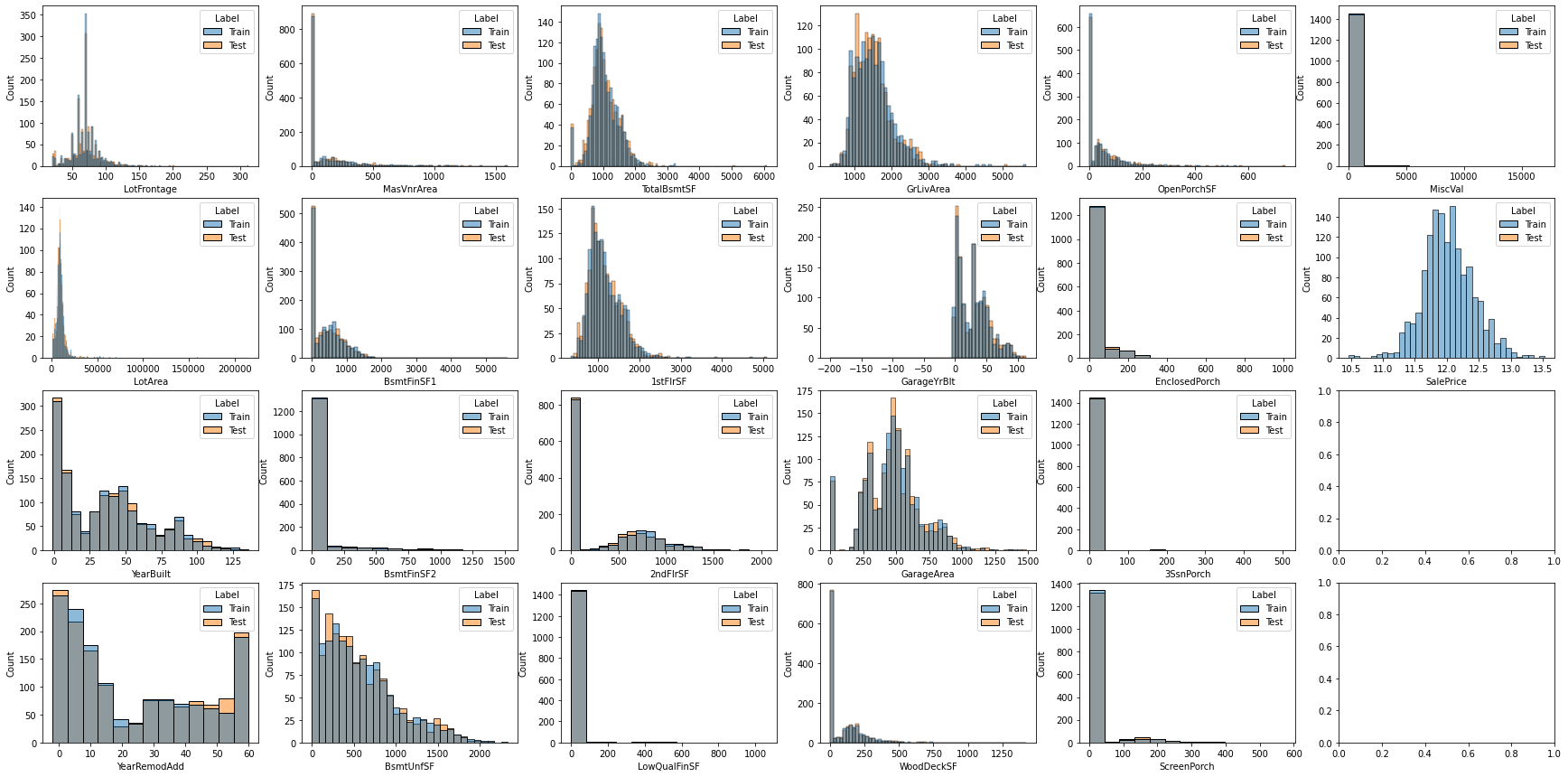
通過直方圖可以直觀地看出數值的分布是否符合正態分布,再分別計算偏度,通過偏度查看數據的偏離情況。
# 計算偏度
skewed_features = datas[continuous_features].apply(lambda x:x.skew()).sort_values(ascending=False)
print(skewed_features)
MiscVal 21.958480
LotArea 12.829025
LowQualFinSF 12.094977
3SsnPorch 11.381914
BsmtFinSF2 4.148275
EnclosedPorch 4.005950
ScreenPorch 3.948723
MasVnrArea 2.612892
OpenPorchSF 2.536417
WoodDeckSF 1.843380
LotFrontage 1.646420
1stFlrSF 1.470360
BsmtFinSF1 1.426111
GrLivArea 1.270010
TotalBsmtSF 1.163082
BsmtUnfSF 0.919981
2ndFlrSF 0.862118
YearBuilt 0.598917
YearRemodAdd 0.450458
GarageYrBlt 0.392261
GarageArea 0.241342
SalePrice 0.121347
dtype: float64
這里將偏度大于 1.5 的特征進行正態化,值設得太大的話正態化之后會導致原本0-1之間的特征的偏度過于小(-4左右)而出現左偏斜(即數據集中有較多較小的值)。
# 如果偏度的絕對值大于1.5,則用np.log1p進行處理【注:并不保證處理后偏度就會小于1.5,只能是使數據盡量符合正態分布】
# 需要正則化的特征列
log_list=[]
for feature, skew_value in skewed_features.items():if skew_value > 1.5:log_list.append(feature)
log_list# 正則化
for i in log_list:datas[i] = np.log1p(datas[i])# 檢查正則化情況
skewed_features = datas[continuous_features].apply(lambda x:x.skew()).sort_values(ascending=False)
print(skewed_features)
3SsnPorch 8.829794
LowQualFinSF 8.562091
MiscVal 5.216665
ScreenPorch 2.947420
BsmtFinSF2 2.463749
EnclosedPorch 1.962089
1stFlrSF 1.470360
BsmtFinSF1 1.426111
GrLivArea 1.270010
TotalBsmtSF 1.163082
BsmtUnfSF 0.919981
2ndFlrSF 0.862118
YearBuilt 0.598917
MasVnrArea 0.504832
YearRemodAdd 0.450458
GarageYrBlt 0.392261
GarageArea 0.241342
WoodDeckSF 0.158114
SalePrice 0.121347
OpenPorchSF -0.041819
LotArea -0.505010
LotFrontage -1.019985
dtype: float64
由結果可知,3SsnPorch、LowQualFinSF 和 MiscVal 的偏度還是太大(正偏度值大于2通常被認為是嚴重的右偏斜),但此時不宜再對這三個特征再次進行正態化,否則可能會導致數據失真。
2.5 編碼數據集后切分數據集
# 刪除Label列后對數據集進行獨熱(One-hot)編碼
datas.drop('Label', axis=1, inplace=True)
datas = pd.get_dummies(datas, dtype=int)
# 切分訓練集和測試集
new_train= datas.iloc[:len(train), :]
new_test = datas.iloc[len(train):, :]
X_train = new_train.drop('SalePrice', axis=1)
Y_train = new_train['SalePrice']
X_test = new_test.drop('SalePrice', axis=1)
3. 模型搭建
3.1 模型搭建與超參數調整
import optuna
from sklearn.linear_model import Ridge
from xgboost import XGBRegressor
from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingRegressor
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score"""
定義超參數優化函數
Params:objective:待優化的評估函數
Returns:params:最佳超參數組合
"""
def tune(objective):# 創建了一個 Optuna 的 Study 對象,用于管理一次超參數優化的過程# direction='maximize' 表示優化的目標是最大化目標函數的返回值(返回值是負的均方根誤差)study = optuna.create_study(direction='maximize')# 使用 study 對象的 optimize 方法來執行優化過程# n_trials=100:指定了進行優化的試驗次數study.optimize(objective, n_trials=10)params = study.best_params# 獲取經過優化后的最佳得分((目標函數的返回值))best_score = study.best_valueprint(f"Best score: {-best_score} \nOptimized parameters: {params}")return params"""
Ridge回歸
Params:trial:是由 Optuna 庫提供的對象,用于在超參數優化過程中管理參數的提議和跟蹤
Returns:score:交叉驗證評分
"""
def ridge_objective(trial):# 0.1 是超參數的下界,20 是超參數的上界。Optuna 會在指定的范圍內為超參數 alpha 提出一個值_alpha = trial.suggest_float("alpha",0.1,20)ridge = Ridge(alpha=_alpha, random_state=1)score = cross_val_score(ridge,X_train,Y_train, cv=10, scoring="neg_root_mean_squared_error").mean()return score"""
梯度增強樹回歸
Params:trial:是由 Optuna 庫提供的對象,用于在超參數優化過程中管理參數的提議和跟蹤
Returns:score:交叉驗證評分
"""
def gbr_objective(trial):_n_estimators = trial.suggest_int("n_estimators", 50, 2000)_learning_rate = trial.suggest_float("learning_rate", 0.01, 1)_max_depth = trial.suggest_int("max_depth", 1, 20)
# _min_samp_split = trial.suggest_int("min_samples_split", 2, 20)
# _min_samples_leaf = trial.suggest_int("min_samples_leaf", 2, 20)
# _max_features = trial.suggest_int("max_features", 10, 50)gbr = GradientBoostingRegressor(n_estimators=_n_estimators,learning_rate=_learning_rate,max_depth=_max_depth,
# max_features=_max_features,
# min_samples_leaf=_min_samples_leaf,
# min_samples_split=_min_samp_split,random_state=1,)score = cross_val_score(gbr, X_train,Y_train, cv=10, scoring="neg_root_mean_squared_error").mean()return score"""
XGBoost回歸模型
Params:trial:是由 Optuna 庫提供的對象,用于在超參數優化過程中管理參數的提議和跟蹤
Returns:score:交叉驗證評分
"""
def xgb_objective(trial):_n_estimators = trial.suggest_int("n_estimators", 50, 2000)_max_depth = trial.suggest_int("max_depth", 1, 20)_learning_rate = trial.suggest_float("learning_rate", 0.01, 1)
# _gamma = trial.suggest_float("gamma", 0.01, 1)
# _min_child_weight = trial.suggest_float("min_child_weight", 0.1, 10)
# _subsample = trial.suggest_float('subsample', 0.01, 1)
# _reg_alpha = trial.suggest_float('reg_alpha', 0.01, 10)
# _reg_lambda = trial.suggest_float('reg_lambda', 0.01, 10)xgboost = XGBRegressor(n_estimators=_n_estimators,max_depth=_max_depth, learning_rate=_learning_rate,
# gamma=_gamma,
# min_child_weight=_min_child_weight,
# subsample=_subsample,
# reg_alpha=_reg_alpha,
# reg_lambda=_reg_lambda,
# random_state=1,)score = cross_val_score(xgboost, X_train, Y_train, cv=10, scoring="neg_root_mean_squared_error").mean()return score
尋找最佳參數,運行下面代碼很耗時,可適當減少不重要參數的調優。本地調優后官網提交時不用再次運行,直接用本地運行的最佳參數即可。
# 設置日志級別為 WARNING,減少輸出信息的數量
# optuna.logging.set_verbosity(optuna.logging.WARNING)ridge_params = tune(ridge_objective)
# Best score: 0.13482720346041538
# Optimized parameters: {'alpha': 14.933121817345844}
# ridge_params = {'alpha': 14.933121817345844}gbr_params = tune(gbr_objective)
# Best score: 0.1388996815131788
# Optimized parameters: {'n_estimators': 928, 'learning_rate': 0.24282934638611978, 'max_depth': 7}
# gbr_params = {'n_estimators': 928, 'learning_rate': 0.24282934638611978, 'max_depth': 7}xbg_params = tune(xgb_objective)
# Best score: 0.12403838351336531
# Optimized parameters: {'n_estimators': 1713, 'max_depth': 3, 'learning_rate': 0.030462678052628034}
# xbg_params = {'n_estimators': 1713, 'max_depth': 3, 'learning_rate': 0.030462678052628034}# **:用于將鍵值對作為關鍵字參數傳遞給函數
ridge = Ridge(**ridge_params, random_state=1)
gbr = GradientBoostingRegressor(**gbr_params, random_state=1)
xgboost = XGBRegressor(**xbg_params, random_state=1)
3.2 模型交叉驗證
ridge_score = np.sqrt(-cross_val_score(ridge, X_train, Y_train, cv=10, scoring='neg_mean_squared_error'))
gbr_score = np.sqrt(-cross_val_score(gbr, X_train, Y_train, cv=10, scoring='neg_mean_squared_error'))
xgboost_score = np.sqrt(-cross_val_score(xgboost, X_train, Y_train, cv=10, scoring='neg_mean_squared_error'))
print(f"ridge_score: {np.mean(ridge_score)}")
print(f"gbr_score: {np.mean(gbr_score)}")
print(f"xgboost_score: {np.mean(xgboost_score)}")
ridge_score: 0.13482720346041538
gbr_score: 0.1388996815131788
xgboost_score: 0.12403838351336531
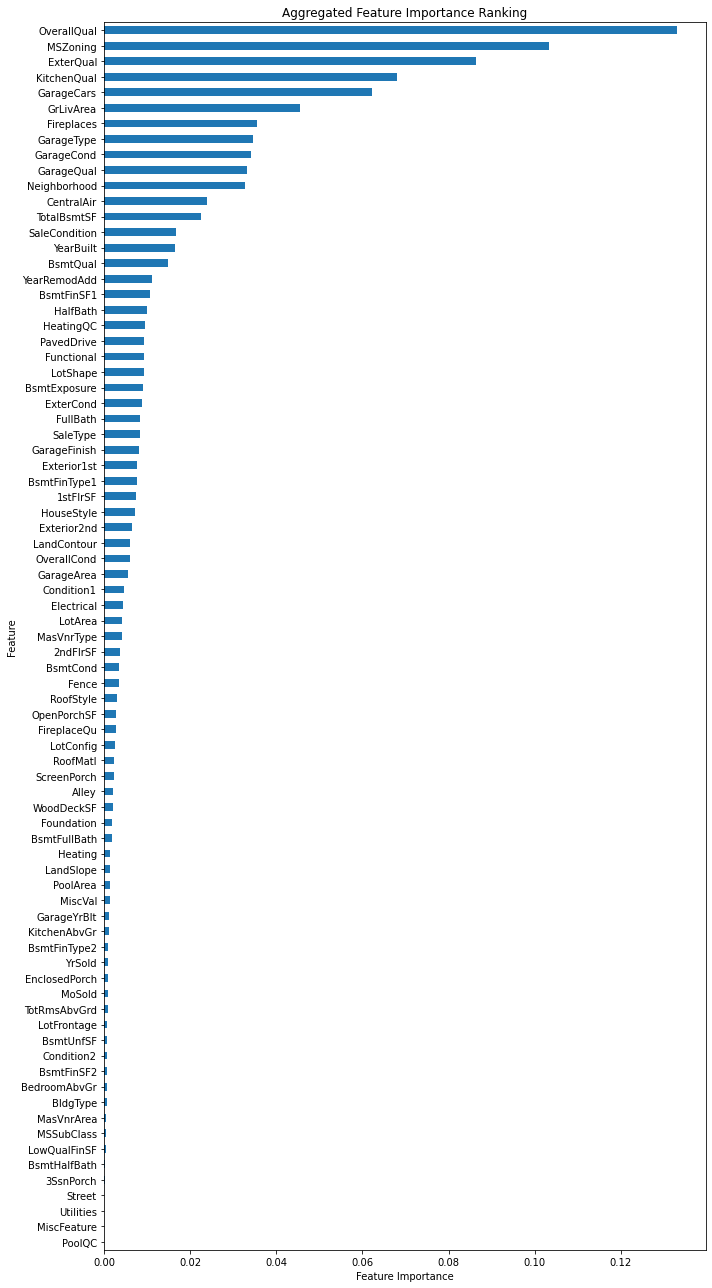
3.3 特征重要性分析
xgboost.fit(X_train, Y_train)
# 刪除 "SalePrice" 方便分析特征重要性
imp_datas = datas.drop("SalePrice", axis=1)# 獲取特征重要性
importance = xgboost.feature_importances_# 創建特征名稱與重要性映射,用于合并獨熱編碼之后的特征
feature_importance = pd.Series(importance, index=imp_datas.columns)# 提取獨熱編碼的特征名
original_feature_names = [col.split('_')[0] for col in imp_datas.columns]# 聚合特征重要性
aggregated_importance = feature_importance.groupby(original_feature_names).sum()plt.figure(figsize=(10, 18))# kind='barh':指定了繪圖類型為水平條形圖
# sort_values()本身是由小到大的排序,但使用 .plot(kind='barh') 時,水平條形圖的 y 軸將顯示由高到低的順序
aggregated_importance.sort_values().plot(kind='barh')
plt.xlabel("Feature Importance")
plt.ylabel('Feature')
plt.title("Aggregated Feature Importance Ranking")
# 調整圖表布局,使其更緊湊
plt.tight_layout()
3.4 數值預測
選擇最佳模型xgboost預測售價。
xgboost.fit(X_train, Y_train)
predictions = np.expm1(xgboost.predict(X_test))
submission = pd.DataFrame({'Id': Id,'SalePrice': predictions})
# submission.to_csv('/kaggle/working/submission.csv', index=False)
print('Submission file created!')
4. 參考文獻
[1] 機器學習/深度學習實戰——kaggle房價預測比賽實戰(數據分析篇)
[2] kaggle簡單實戰——房價預測(xgboost實現)


266)
:xpath和lxml類庫)















)