目錄
線程(上)
1. 線程的創建方式
Thread類常用構造方法
Thread類常用成員方法
Thread類常用靜態方法
示例
總結
2. 線程內存模型
3.線程安全
案例
代碼實現
執行結果
線程(上)
1. 線程的創建方式
????????An application that creates an instance of Thread must provide the code that will run in that thread. There are two ways to do this:????????創建Thread 實例的應用程序必須提供將在該線程中運行的代碼。 有兩種方法可以做到這一點:????????-Provide a Runnable object. The Runnable interface defines a single method, run, meant to contain the code executed in the thread.????????-提供可運行的對象。 Runnable 接口定義了一個方法 run ,旨在包含在線程中執行的代碼。????????-Subclass Thread. The Thread class itself implements Runnable, though its run method does nothing.????????-子類線程。 Thread 類本身實現了 Runnable ,盡管它的 run 方法不執行任何操作。
Thread類常用構造方法
public Thread (); // 創建一個線程public Thread ( String name ); // 創建一個依據名稱的線程public Thread ( Runnable target ); // 根據給定的線程任務創建一個線程public Thread ( Runnable target , String name ); // 根據給定的線程任務和名稱創建一個線程
Thread類常用成員方法
public synchronized void start (); // 啟動線程但不一定會執行public final String getName (); // 獲取線程名稱public final synchronized void setName ( String name ); // 設置線程的名稱public final void setPriority ( int newPriority ); // 設置線程的優先級public final int getPriority (); // 獲取線程的優先級public final void join () throws InterruptedException ; // 等待線程執行完成// 等待線程執行給定的時間 ( 單位毫秒 )public final synchronized void join ( long millis ) throwsInterruptedException ;// 等待線程執行給定的時間 ( 單位毫秒、納秒 )public final synchronized void join ( long millis , int nanos ) throwsInterruptedException ;public long getId (); // 獲取線程的 IDpublic State getState (); // 獲取線程的狀態public boolean isInterrupted (); // 檢測線程是否被打斷public void interrupt (); // 打斷線程
Thread類常用靜態方法
public static native Thread currentThread (); // 獲取當前運行的線程public static boolean interrupted (); // 檢測當前運行的線程是否被打斷public static native void yield (); // 暫停當前運行的線程,然后再與其他線程爭搶資源,稱為線程禮讓// 使當前線程睡眠給定的時間(單位毫秒)public static native void sleep ( long millis ) throws InterruptedException ;// 使當前線程睡眠給定的時間(單位毫秒、納秒)public static void sleep ( long millis , int nanos ) throwsInterruptedException ;
示例
public class CreateDemo {????????public static void main ( String [] args ) {????????????????Thread t1 = new SubThread ( "inherit" ); // 通過繼承實現的線程????????????????Thread t2 = new Thread ( new ThreadTask (), "interface" ); // 通過實現????????????????Runnable接口實現的線程????????????????t1 . start (); //start 方法只是告訴 JVM 線程 t1 已經準備好了,隨時可以調度執行????????????????try {????????????????????????t1 . join (); // 等待線程 t1 執行完成????????????????????????t1 . join ( 1000 ); // 等待線程 t1 執行 1 秒????????????????????????// 1毫秒 = 1000微秒 = 1000000 納秒????????????????????????t1 . join ( 1000 , 50000 ); // 等待線程 t1 執行 1.5 秒????????????????} catch ( InterruptedException e ) {????????????????????????e . printStackTrace ();????????????????}????????????????t2 . start ();????????}????????static class SubThread extends Thread {????????????????public SubThread () {????????????????}????????????????public SubThread ( String name ) {????????????????????????super ( name );????????????????}????????????????@Override????????????????public void run () {????????????????????????try {????????????????????????????????Thread . sleep ( 2000 );????????????????????????} catch ( InterruptedException e ) {????????????????????????????????e . printStackTrace ();????????????????????????}????????????????????????System . out . println ( getName () + "=>This is SubThread" );????????????????}????????}????????static class ThreadTask implements Runnable {????????????????@Override????????????????public void run () {????????????????????????Thread thread = Thread . currentThread ();???????????????????????String name = thread . getName ();????????????????????????System . out . println ( name + "=>This is Implementation" );????????????????}????????}}
總結
????????創建線程有兩種方式:實現 Runable 接口和繼承 Thread 。相較于繼承 Thread ,實現 Runable 接口更具有優勢,在實現接口的同時還可以繼承自其他的父類,避免了Java 中類單繼承的局限性;同時Runable 接口的實現可以被多個線程重用,但繼承 Thread 無法做到;后續學到的線程池中支持Runable 接口但不支持 Thread
2. 線程內存模型
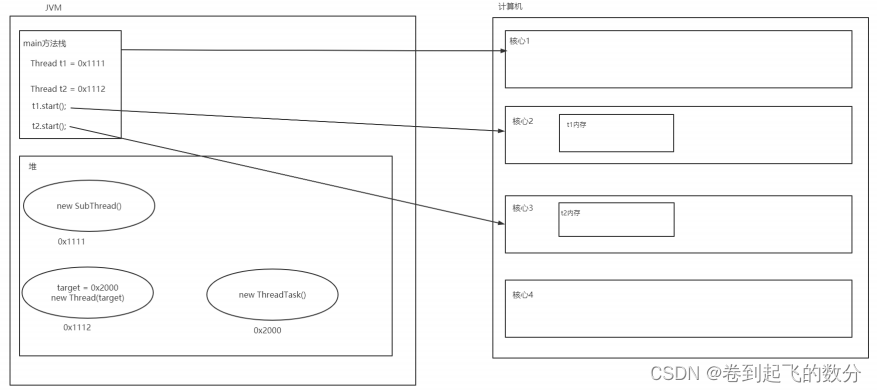
3.線程安全
案例
某火車站有 10 張火車票在 3 個窗口售賣
代碼實現
public class SaleThreadTest {????????public static void main ( String [] args ) {????????????????SaleTask task = new SaleTask ();????????????????Thread t1 = new Thread ( task , " 窗口 1" );????????????????Thread t2 = new Thread ( task , " 窗口 2" );????????????????Thread t3 = new Thread ( task , " 窗口 3" );????????????????t1 . start ();????????????????t2 . start ();????????????????t3 . start ();????????}static class SaleTask implements Runnable {????????private int totalTickets = 10 ; // 售賣 10 張火車票????????@Override????????public void run () {????????????????while ( true ){????????????????????????String name = Thread . currentThread (). getName ();????????????????????????System . out . println ( name + " 售賣火車票: " + totalTickets );????????????????????????totalTickets -- ;????????????????????????if ( totalTickets <= 0 ) break ;????????????????????????????????try {????????????????????????????????????????Thread . sleep ( 100L );????????????????????????????????} catch ( InterruptedException e ) {????????????????????????????????????????e . printStackTrace ();????????????????????????????????}????????????????????????}????????????????}????????}}
執行結果

從結果中可以看出,同一張火車票被賣了多次,這是由于線程之間獲取信息不同步導致。
更多參考:
Java SE入門及基礎(60)& 線程的實現(下) & 線程的同步(synchronized 和 Lock 的實現) & 線程通信 & 線程狀態-CSDN博客






: 基于FT2232HL實現的jtag下載器硬件+jtag的通信引腳說明)
)

 | 服務端請求偽造 SSRF)

2024.6.24~2024.6.30)
)






)