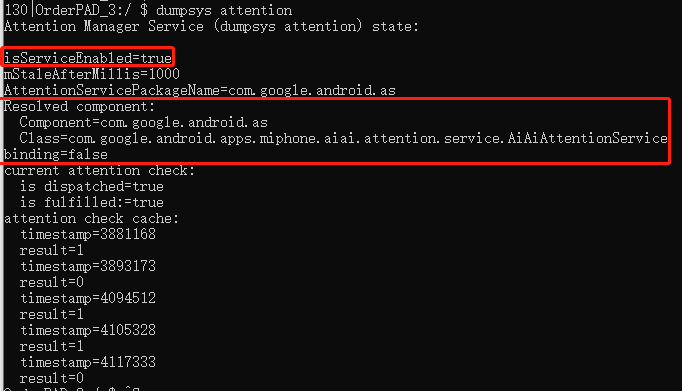
AttentionManagerService是framework中用來實現屏幕感知的一個系統級服務,他繼承于systemserver。我們可以通過dumpsys?attention來獲取他的一些信息。
如下針對屏幕感知的功能的引入來針對這個服務進行一個介紹。
1、屏幕感知Settings UI實現
屏幕感知的功能在A14上面默認都支持,其入口在設置->顯示->屏幕超時->屏幕感知。
根據其描述他會檢測到如果你在定制屏幕看,就會阻止屏幕超時息屏。
Settings UI控制代碼:AdaptiveSleepPreferenceController.java
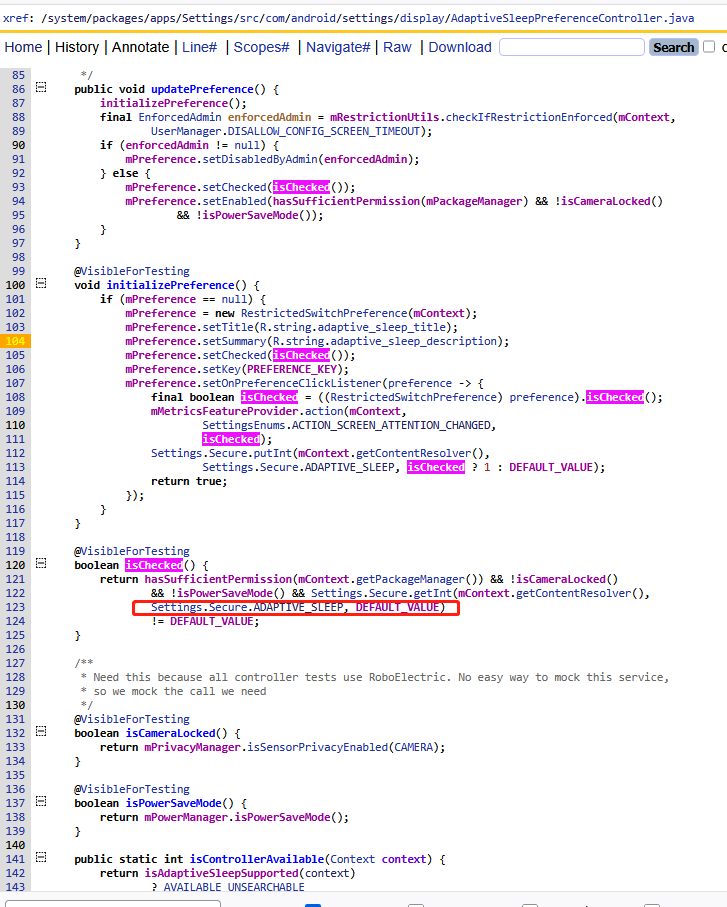
如上的開關看起來是在isChecked這里實現,主要判斷了一些條件來進行顯示,這個開關的key是:adaptive_sleep,為1表示此功能開啟
2、屏幕感知FW Client實現
通過搜索ADAPTIVE_SLEEP發現fw只有如下一個地方在使用:
//frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/power/AttentionDetector.java
public class AttentionDetector {private static final String TAG = "AttentionDetector";private static final boolean DEBUG = false;private Context mContext;private boolean mIsSettingEnabled;@VisibleForTestingAttentionCallbackInternalImpl mCallback;public AttentionDetector(Runnable onUserAttention, Object lock) {mOnUserAttention = onUserAttention;mLock = lock;mRequested = new AtomicBoolean(false);mRequestId = 0;// Device starts with an awake state upon boot.mWakefulness = PowerManagerInternal.WAKEFULNESS_AWAKE;}@VisibleForTestingvoid updateEnabledFromSettings(Context context) {//判斷Settings的屏幕感知功能是否使能mIsSettingEnabled = Settings.Secure.getIntForUser(context.getContentResolver(),Settings.Secure.ADAPTIVE_SLEEP, 0, UserHandle.USER_CURRENT) == 1;}//屏幕感知核心功能,PowerManagerService#updateUserActivitySummaryLocked會調用到這里//即PowerManagerService在進行屏幕喚醒或者息屏以及應用鎖持有計算的時候進行調用,因此這里會影響屏幕超時息屏的邏輯 To be called in {@link PowerManagerService#updateUserActivitySummaryLocked} public long updateUserActivity(long nextScreenDimming, long dimDurationMillis) {// 1. 前置條件檢查:滿足任一條件則直接返回原定的變暗時間if (nextScreenDimming == mLastActedOnNextScreenDimming // 已處理過相同變暗時間|| !mIsSettingEnabled // 功能未啟用|| !isAttentionServiceSupported() // 設備不支持注意力檢測服務|| mWindowManager.isKeyguardShowingAndNotOccluded()) { // 當前處于鎖屏狀態return nextScreenDimming;}// 2. 計算關鍵時間節點final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis(); // 當前系統啟動時間(毫秒)final long whenToCheck = nextScreenDimming - mPreDimCheckDurationMillis; // 檢測觸發時間(變暗前提前量)final long whenToStopExtending = mLastUserActivityTime + mMaximumExtensionMillis; // 最長可延時時限// 3. 時間窗口判斷邏輯if (now < whenToCheck) { // 未到檢測時間:返回下次應檢測的時間點(DEBUG模式輸出日志)if (DEBUG) Slog.d(TAG, "Do not check for attention yet, wait " + (whenToCheck - now));return whenToCheck;} else if (whenToStopExtending < whenToCheck) {// 超過最大延時時長:放棄檢測直接允許變暗(安全策略)if (DEBUG) Slog.d(TAG, "Let device sleep to avoid false results...");return nextScreenDimming;} else if (mRequested.get()) {// 已有未完成的檢測請求:等待當前請求完成if (DEBUG) Slog.d(TAG, "Pending attention callback with ID=" + mCallback.mId + ", wait.");return whenToCheck;}// 4. 發起屏幕感知檢測請求mRequested.set(true); // 標記請求狀態mRequestId++; // 生成唯一請求IDmLastActedOnNextScreenDimming = nextScreenDimming; // 記錄當前處理的變暗時間mCallback = new AttentionCallbackInternalImpl(mRequestId); // 創建回調實例// 5. 計算實際檢測超時時間(取配置值與剩余變暗時間的較小值)mEffectivePostDimTimeoutMillis = Math.min(mRequestedPostDimTimeoutMillis, dimDurationMillis);// 6. 調用系統服務檢測用戶注意力Slog.v(TAG, "Checking user attention, ID: " + mRequestId);final boolean sent = mAttentionManager.checkAttention(mPreDimCheckDurationMillis + mEffectivePostDimTimeoutMillis,mCallback);// 7. 請求失敗處理if (!sent) {mRequested.set(false); // 重置請求狀態}return whenToCheck; // 返回建議的下次檢測時間}
}綜上最核心的方法如下:
1)Attention注意力檢查請求
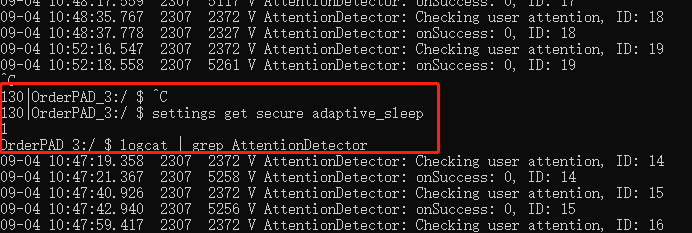
每次從pms那邊過來就會請求一次是否有人眼盯著屏幕看,每次請求都有唯一標準ID,可以參考如下日志:
130|OrderPAD_3:/ $ logcat | grep -E "AttentionManagerService|AttentionDetector"
09-04 11:22:26.250 2307 2372 V AttentionDetector: Checking user attention, ID: 40
09-04 11:22:28.258 2307 3160 V AttentionDetector: onSuccess: 0, ID: 40
09-04 11:23:08.249 2307 2372 V AttentionDetector: Checking user attention, ID: 41
09-04 11:23:10.258 2307 2409 V AttentionDetector: onSuccess: 0, ID: 41
09-04 11:23:42.238 2307 2372 V AttentionDetector: Checking user attention, ID: 42
09-04 11:23:44.246 2307 4514 V AttentionDetector: onSuccess: 0, ID: 42
09-04 11:27:38.810 2307 2372 V AttentionDetector: Checking user attention, ID: 43
09-04 11:27:40.831 2307 3177 V AttentionDetector: onSuccess: 0, ID: 43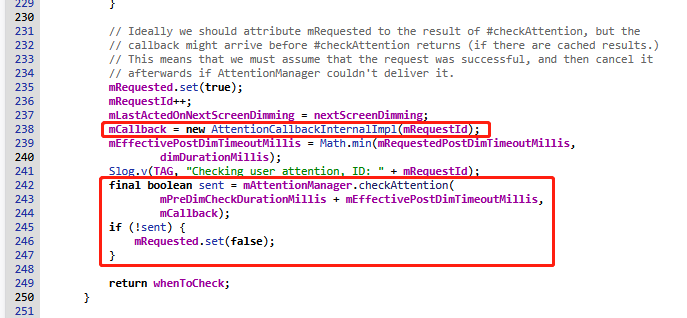
2)Attention檢查結果返回
//frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/power/AttentionDetector.java
@Override
public void onSuccess(int result, long timestamp) {// 1. 日志記錄檢測結果(VERBOSE級別日志,包含結果碼和請求ID)Slog.v(TAG, "onSuccess: " + result + ", ID: " + mId);// 2. 防循環處理:驗證請求ID有效性并原子性重置請求狀態// - mId == mRequestId:確保回調匹配當前最新請求(避免舊請求干擾)// - mRequested.getAndSet(false):原子操作標記請求已完成if (mId == mRequestId && mRequested.getAndSet(false)) {// 3. 同步鎖保護關鍵代碼塊(防止多線程競爭條件)synchronized (mLock) {// 4. 設備狀態檢查:若非喚醒狀態則直接返回(如已進入休眠)if (mWakefulness != PowerManagerInternal.WAKEFULNESS_AWAKE) {if (DEBUG) Slog.d(TAG, "Device slept before receiving callback.");return;}// 5. 根據檢測結果執行分支邏輯if (result == AttentionService.ATTENTION_SUCCESS_PRESENT) {// 5.1 檢測到用戶注意力:觸發延屏操作(如執行mOnUserAttention回調)mOnUserAttention.run();} else {// 5.2 未檢測到注意力:重置連續延屏計數(統計上報邏輯)resetConsecutiveExtensionCount();}}}
}
3、屏幕感知FW Service實現
在此回到attention的檢查請求,是直接調用了mAttentionManager.checkAttention,根據經驗,其實就是調用到了AttentionManagerService.java如下代碼:
//frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/attention/AttentionManagerService.java
boolean checkAttention(long timeout, AttentionCallbackInternal callbackInternal) {Objects.requireNonNull(callbackInternal);//流程1:服務可用性檢查(三級防御式編程)if (!mIsServiceEnabled) { // 設備硬件不支持該服務Slog.w(LOG_TAG, "Trying to call checkAttention() on an unsupported device.");return false;}if (!isServiceAvailable()) { // 服務進程未就緒Slog.w(LOG_TAG, "Service is not available at this moment.");return false;}// 攝像頭被系統級禁用if (mPrivacyManager.isSensorPrivacyEnabled(SensorPrivacyManager.Sensors.CAMERA)) {Slog.w(LOG_TAG, "Camera is locked by a toggle.");return false;}// 電源狀態檢查:屏幕關閉或省電模式下禁止檢測if (!mPowerManager.isInteractive() || mPowerManager.isPowerSaveMode()) {return false;}//流程2: 服務綁定與緩存管理(線程安全),這里其實要去發送intent移交其他組件來實現Attention檢查synchronized (mLock) {freeIfInactiveLocked();bindLocked();}// 阻塞等待intent那邊組件完全啟動final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();awaitServiceBinding(Math.min(SERVICE_BINDING_WAIT_MILLIS, timeout));//流程3:核心業務邏synchronized (mLock) {final AttentionCheckCache cache = mAttentionCheckCacheBuffer == null ? null : mAttentionCheckCacheBuffer.getLast();if (cache != null && now < cache.mLastComputed + mStaleAfterMillis) {callbackInternal.onSuccess(cache.mResult, cache.mTimestamp); return true;}//請求限流:同一時間只允許一個未完成的請求if (mCurrentAttentionCheck != null) {if (!mCurrentAttentionCheck.mIsDispatched || ! mCurrentAttentionCheck.mIsFulfilled) return false;}//創建新檢測請求:其實把Attention請求的實現轉移給到了前面流程2啟動的intent的組件來實現mCurrentAttentionCheck = new AttentionCheck(callbackInternal, this);if (mService != null) {try {cancelAfterTimeoutLocked(timeout); mService.checkAttention(mCurrentAttentionCheck.mIAttentionCallback); mCurrentAttentionCheck.mIsDispatched = true;} catch (RemoteException e) {Slog.e(LOG_TAG, "Cannot call into the AttentionService");return false;}}return true;}
}
AttentionManagerService實現的checkAttention方法來看,貌似他也沒有來實現具體邏輯,而是作為一個中間人也去調用了一個mService.checkAttention里面去進行調用,它已經是一個系統級服務了,為什么還存在一個mService呢?先劇透一下,他其實依賴其他com.google.android.as來完成attention注意力感知的邏輯實現。
1)綁定google as服務
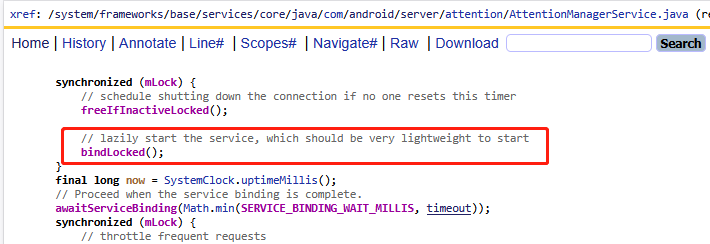
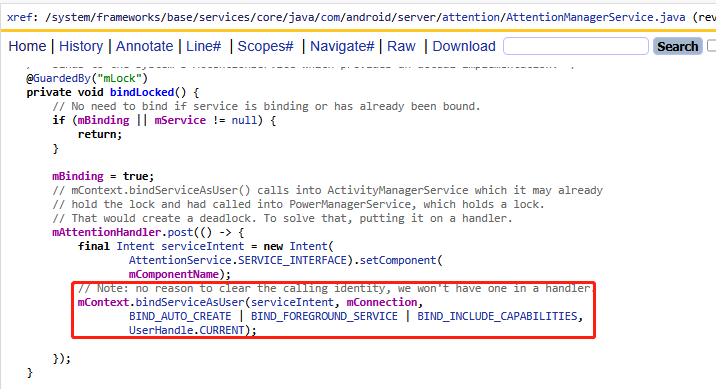
在checkAttention方法中通過bindLocked去綁定google as服務,其實就是普通的一個服務綁定,這里傳遞了mConnection來接收Binder對端,他的定義如下:
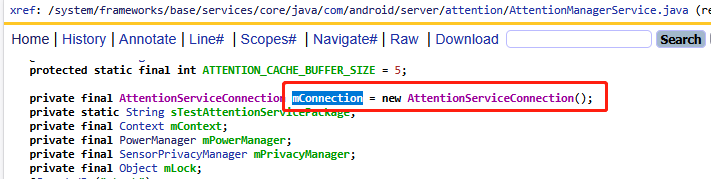

google as服務綁定成功,拿到service并賦值給mService,后續的checkAttention通過google as服務區實現
2)調用google as服務
這里發現了兩處去調用google as服務的,但是基本實現邏輯基本一致:
- 服務綁定成功的時候觸發一次handlePendingCallbackLocked

- PMS間歇式調用checkAttention/如果mService不為null直接請求
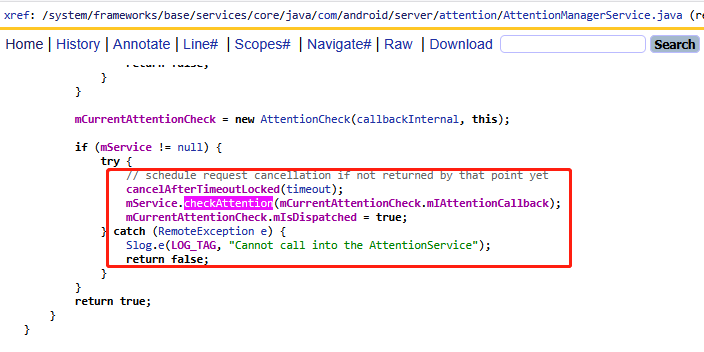
如上兩種場景其實就是綁定服務后的第一次觸發和后面的輪詢觸發。原理都一致。
3)為什么是google as服務?
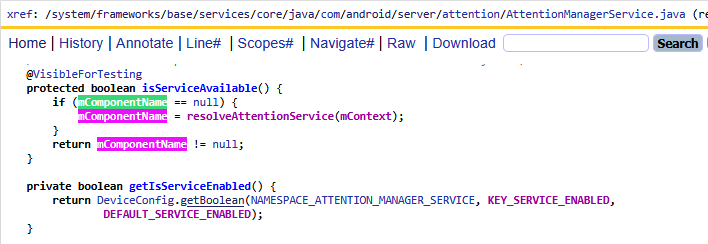
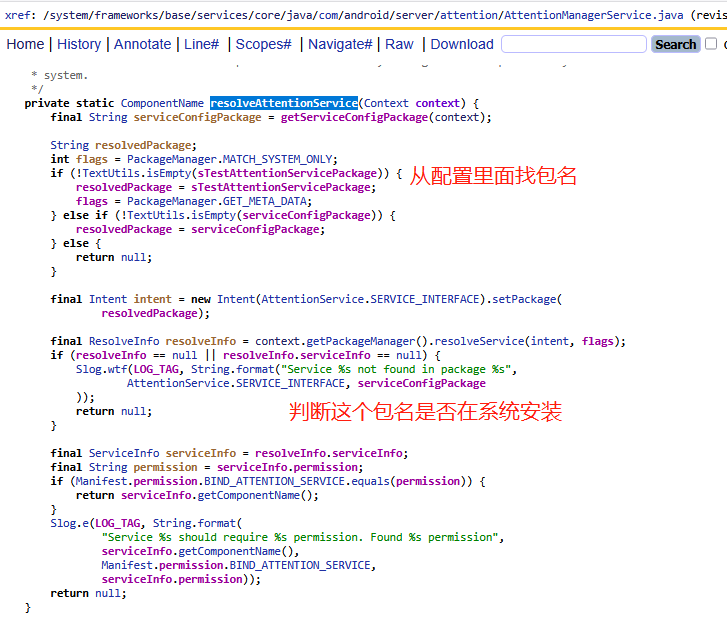
從第一小節的bindLocked方法可以看到她并不是隱式的去啟動attention服務,而是直接指定了包名:
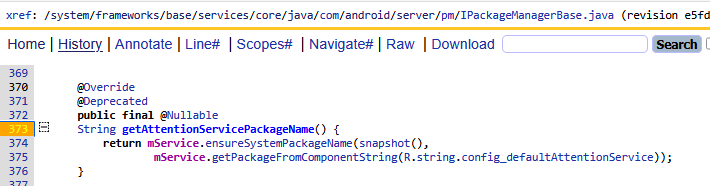
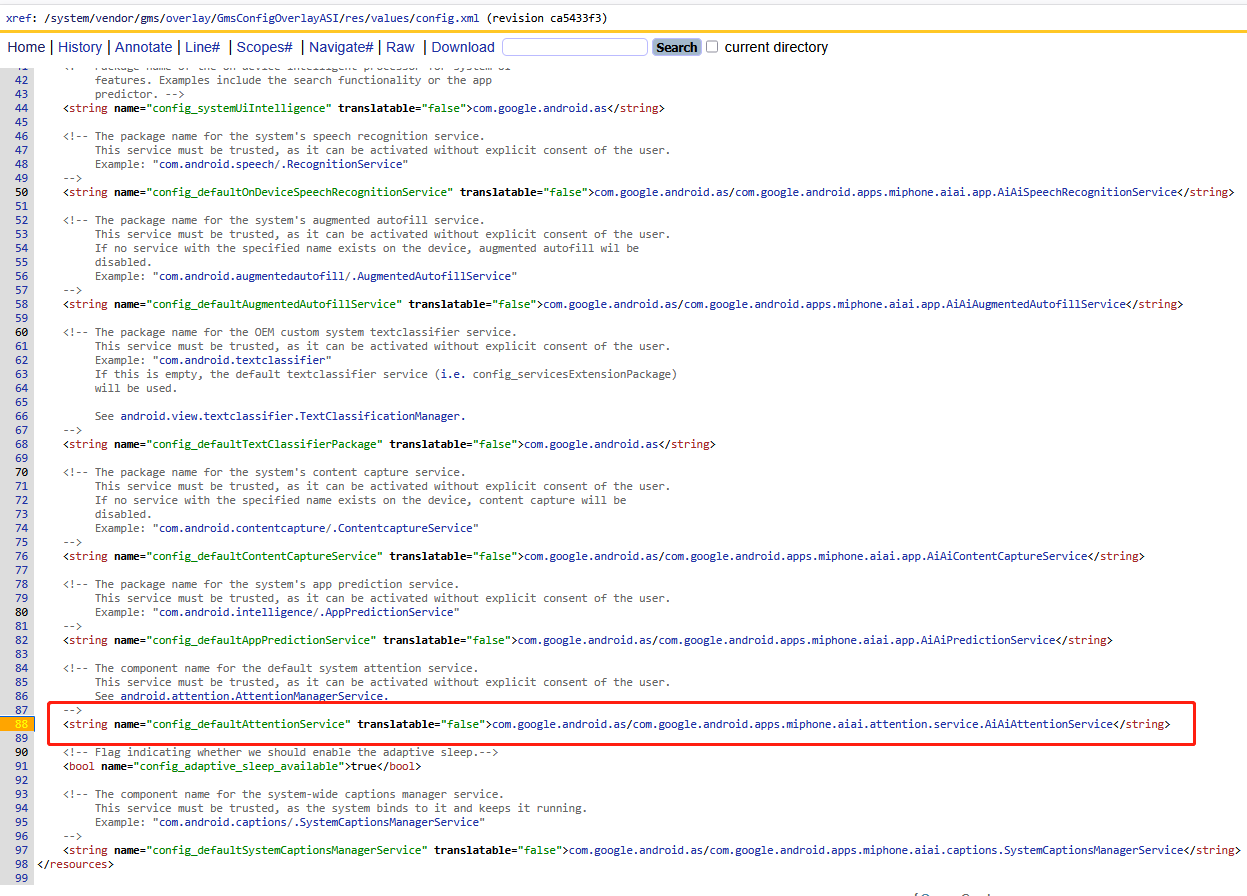
final Intent serviceIntent = new Intent(AttentionService.SERVICE_INTERFACE).setComponent(mComponentName);這里的mComponentName到底是誰?通過dump出來的答案就是
AttentionServicePackageName=com.google.android.as
Resolved component:Component=com.google.android.asClass=com.google.android.apps.miphone.aiai.attention.service.AiAiAttentionService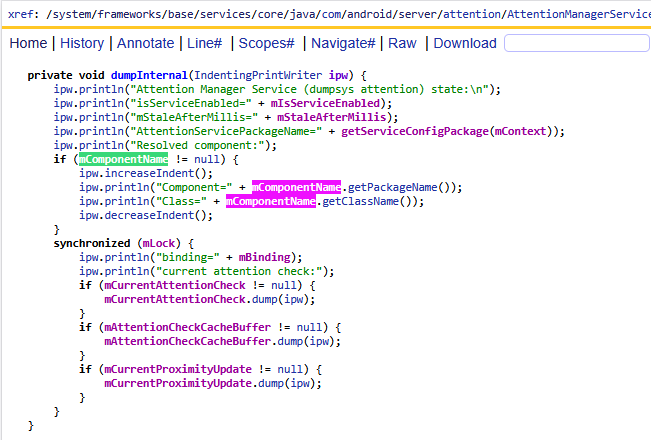
我們接著來研究一下為什么是google as:







:從發現頁到詳情頁——跳轉、傳值與RecyclerView多類型布局)





區別分析)

![[Upscayl圖像增強] docs | 前端 | Electron工具(web->app)](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[Upscayl圖像增強] docs | 前端 | Electron工具(web->app))



