1、什么是模型IO
????????模型 I/O(Model I/O) 是 LangChain 框架中最核心的模塊之一,負責處理與語言模型(LLM)交互的輸入構建、模型調用和輸出解析全流程。它主要分為三個模塊:Prompts(輸入構建)、Language Models(模型調用)、Output Parsers(輸出解析)

2、提示詞模板
????????提示詞可以被視為向大語言模型提出的請求,它們表明了使用者希望模型給出何種反應。提示詞的質量直接影響模型的回答質量,決定了模型能否成功完成更復雜的任務。
????????在 LangChain 框架中, 提示詞是由 "提示詞模板" (PromptTemplate ) 這個包裝器對象生成的。每一個 PromptTemplate 類的實例都定義了一種特定類型的提示詞格式 和 生成規則。 在 LangChain 中, 要想構造提示詞, 就必須學會使用這個包裝器對象。
? ? ? ? 提示詞的模板通常包含(不限于):明確的指令、用戶輸入、少量實例,如下圖:
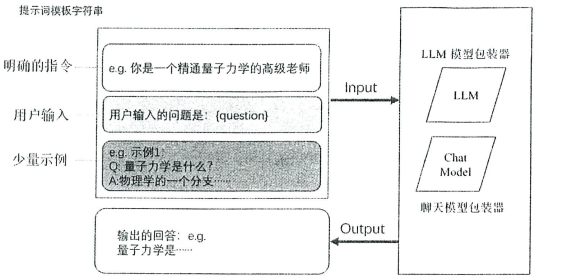
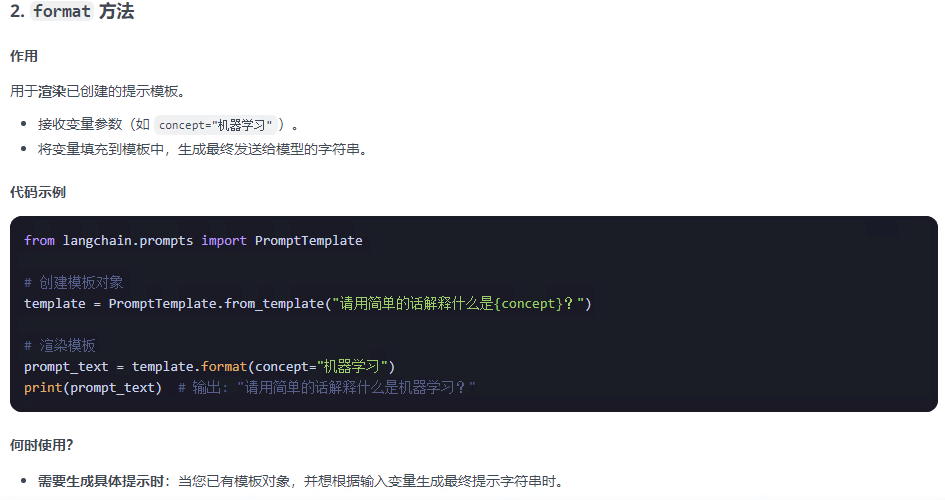
2.1 提示詞模板提供了兩種方法:from_format和format? ? ??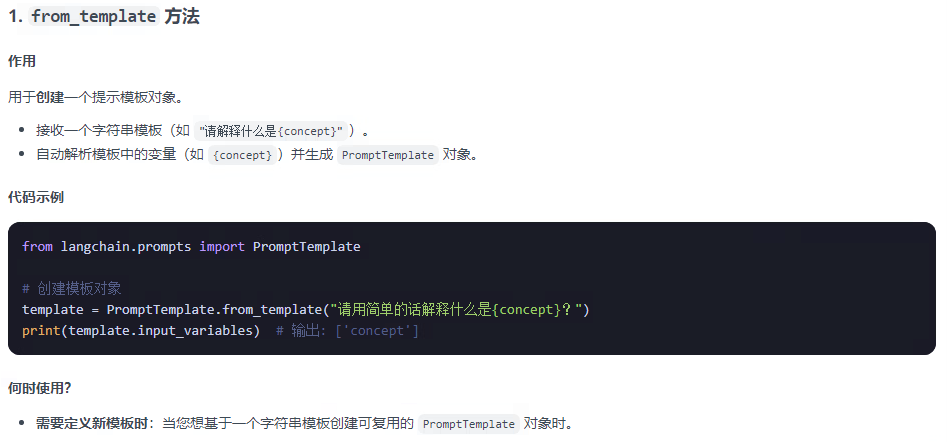

from_format是創建一個模板,模板中可能有需要填充的參數
format的是將模板格式化,填充需要的參數
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate# 創建一個提示詞模板
template = """
你是一個有用的助手。
用戶的名字是 {name}。
用戶的問題是: {question}
請用詳細的回答這個問題。
"""
print("\n=== formatted_prompt1 ===")
prompt_template = PromptTemplate.from_template(template)
formatted_prompt1 = prompt_template.format(name="張三", question="什么是人工智能?")
print(formatted_prompt1)print("\n=== formatted_prompt2 ===")
formatted_prompt2 = prompt_template.format(name="李四", question="機器學習和深度學習有什么區別?")
print(formatted_prompt2)# 展示另一種使用from_template的方式
print("\n=== 直接使用from_template并傳入參數 ===")
prompt_template3 = PromptTemplate.from_template("""
你是一個有用的助手。
用戶的名字是 {name}。
用戶的問題是: {question}
請用詳細的回答這個問題。
""")# 直接在from_template中定義模板并格式化
formatted_prompt3 = prompt_template3.format(name="王五", question="Python中類和對象的概念是什么?")
print(formatted_prompt3)# 展示PromptTemplate的其他常用屬性和方法
print("\n=== PromptTemplate屬性和方法 ===")
print(f"輸入變量: {prompt_template.input_variables}")
print(f"模板字符串: {prompt_template.template}")2.2 langchain定義的內部模板
? ? ? ? langchain定義了一些內置的提示詞模板,可以通過入參使用。定義在langchain.chains.api.prompt,執行其內容如下:
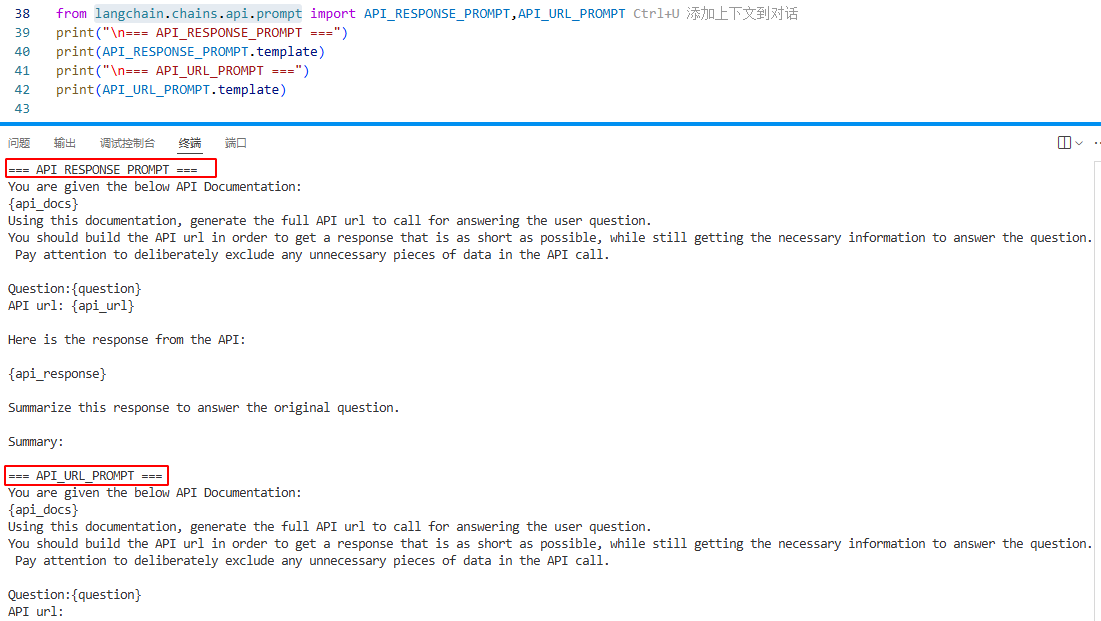
2.3 提示詞模板包裝器
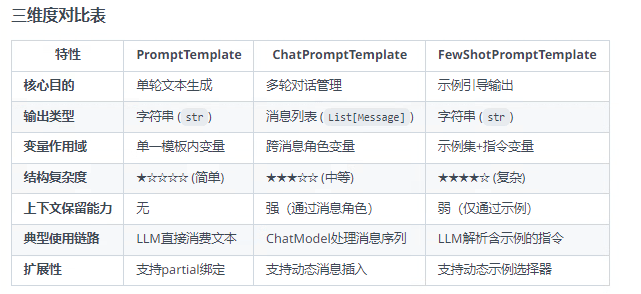
????????提示詞模板包裝器分為兩類:PromotTemplate包裝器 和 ChatPromptTemplate包裝器兩類,FewShotPromptTemplate是PromotTemplate的擴展,以下總結整理這三種包裝器:
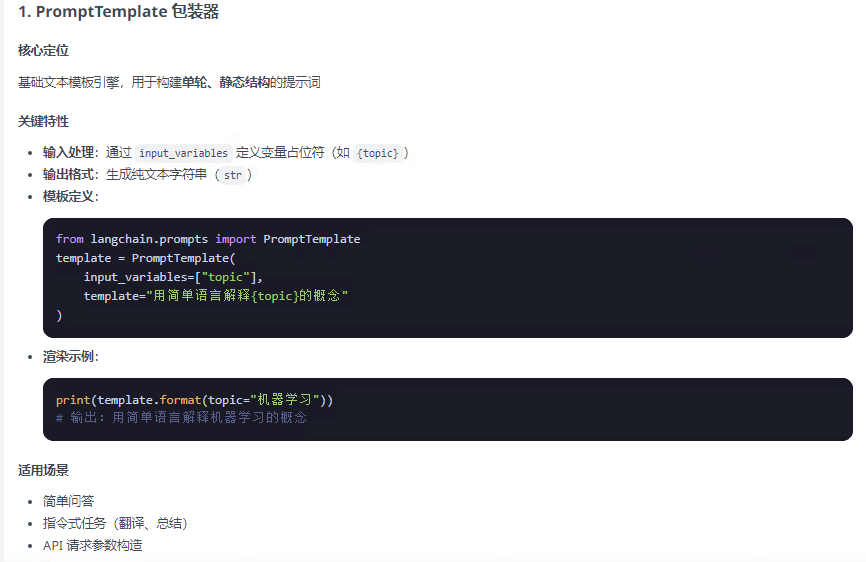
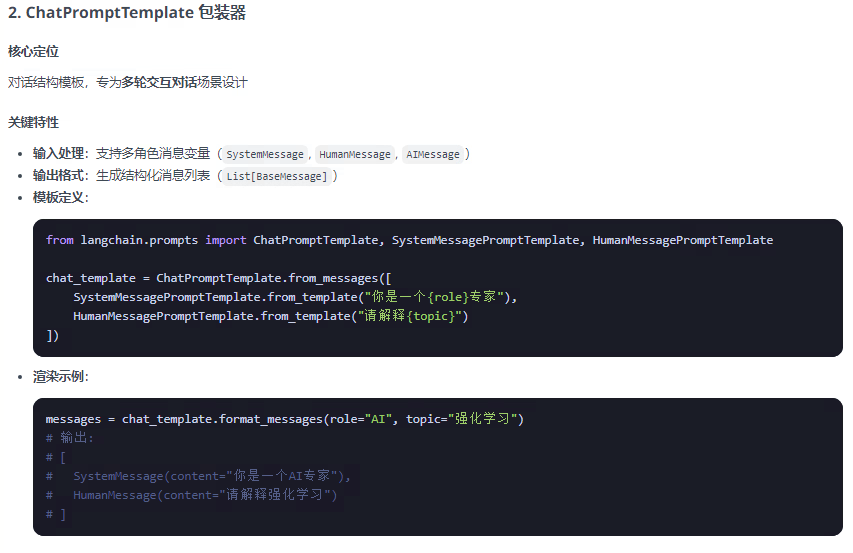

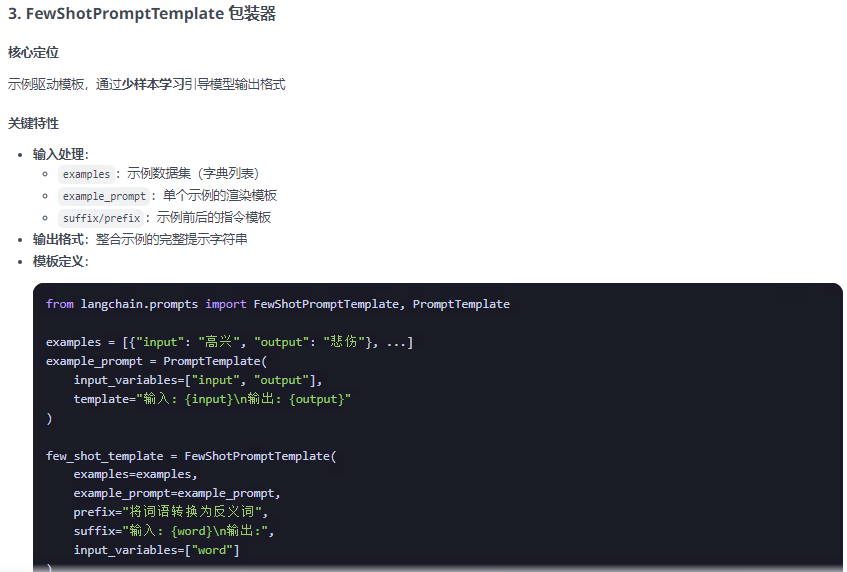
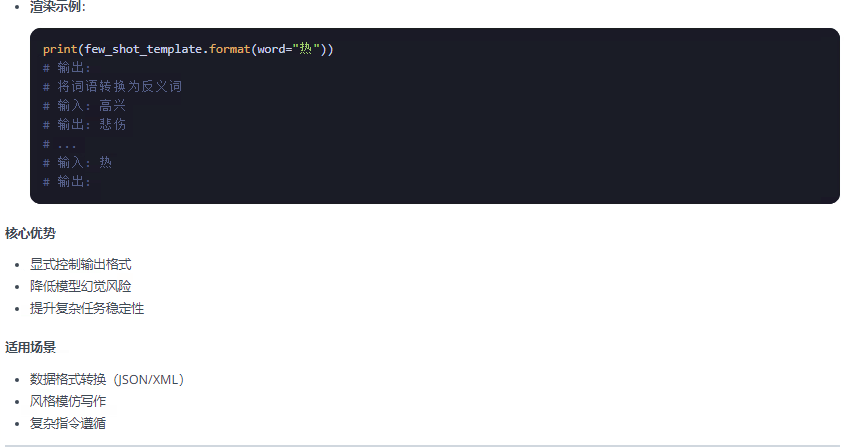
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate, ChatPromptTemplate, FewShotPromptTemplate
from langchain.prompts.example_selector import LengthBasedExampleSelector# 1. PromptTemplate - 基礎提示模板
print("=== 1. PromptTemplate - 基礎提示模板 ===")
template = """
你是一個{role}。
請回答以下問題: {question}
"""prompt_template = PromptTemplate.from_template(template)
formatted_prompt = prompt_template.format(role="AI助手", question="什么是機器學習?")
print(formatted_prompt)# 2. ChatPromptTemplate - 聊天提示模板
print("\n=== 2. ChatPromptTemplate - 聊天提示模板 ===")
chat_template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([("system", "你是一個{role},你的名字是{name}"),("human", "你好,{greeting}"),("ai", "你好!很高興見到你。"),("human", "{question}")
])chat_prompt = chat_template.format_messages(role="專業的技術顧問",name="TechExpert",greeting="我想了解一些技術知識",question="請解釋一下深度學習的基本概念"
)for message in chat_prompt:print(f"{message.type}: {message.content}")# 3. FewShotPromptTemplate - 少樣本提示模板
print("\n=== 3. FewShotPromptTemplate - 少樣本提示模板 ===")# 定義示例
examples = [{"input": "什么是人工智能?","output": "人工智能是計算機科學的一個分支,旨在創建能夠執行通常需要人類智能的任務的機器。"},{"input": "機器學習是什么?","output": "機器學習是人工智能的一個子集,它使計算機能夠從數據中學習并做出決策或預測,而無需明確編程。"}
]# 創建基礎模板
example_prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template("問題: {input}\n答案: {output}"
)# 創建FewShotPromptTemplate
few_shot_prompt = FewShotPromptTemplate(examples=examples,example_prompt=example_prompt,suffix="問題: {input}\n答案: ",input_variables=["input"]
)formatted_few_shot = few_shot_prompt.format(input="深度學習和機器學習有什么區別?"
)
print(formatted_few_shot)# 4. 帶有示例選擇器的FewShotPromptTemplate
print("\n=== 4. 帶有示例選擇器的FewShotPromptTemplate ===")# 添加更多示例
more_examples = examples + [{"input": "什么是神經網絡?","output": "神經網絡是一種模擬人腦神經元結構的計算模型,由相互連接的節點(神經元)組成。"},{"input": "什么是自然語言處理?","output": "自然語言處理是人工智能的一個領域,專注于計算機與人類語言之間的交互,包括理解和生成文本。"}
]# 使用LengthBasedExampleSelector根據輸入長度選擇示例
example_selector = LengthBasedExampleSelector(examples=more_examples,example_prompt=example_prompt,max_length=50 # 根據輸入長度限制示例數量
)few_shot_prompt_with_selector = FewShotPromptTemplate(example_selector=example_selector,example_prompt=example_prompt,suffix="問題: {input}\n答案: ",input_variables=["input"]
)formatted_selector_prompt = few_shot_prompt_with_selector.format(input="請簡要解釋Transformer模型在NLP中的作用"
)
print(formatted_selector_prompt)
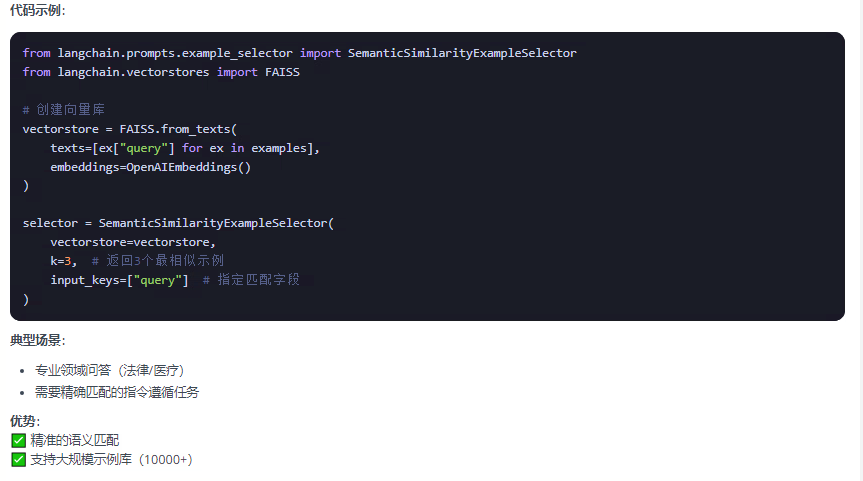
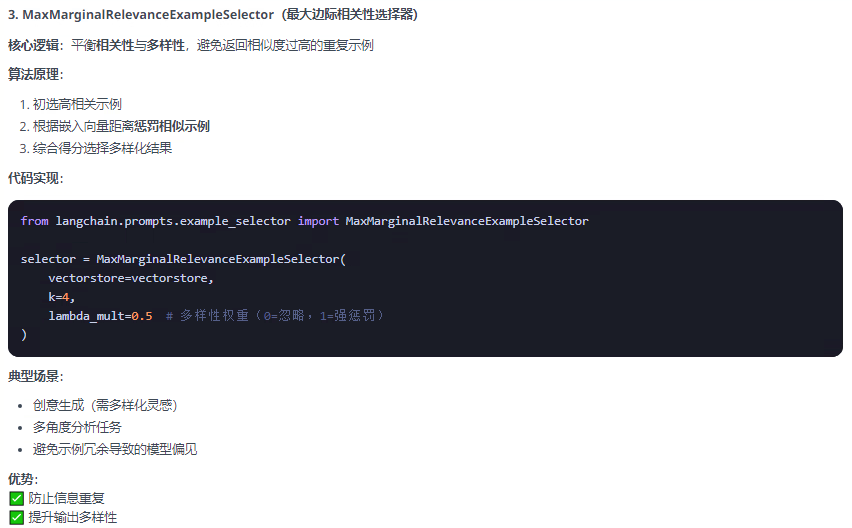
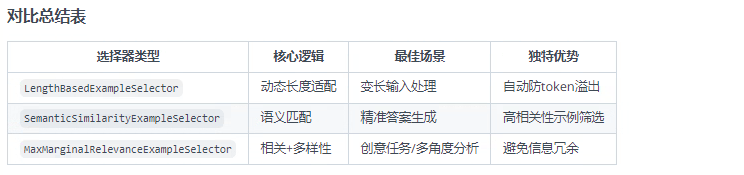
2.4 示例選擇器
作用:在少樣本學習模板(FewShotPromptTemplate)中智能篩選示例,解決兩大關鍵問題:
上下文窗口限制:避免示例過多導致 token 超限
相關性優化:選擇與當前查詢最相關的示例
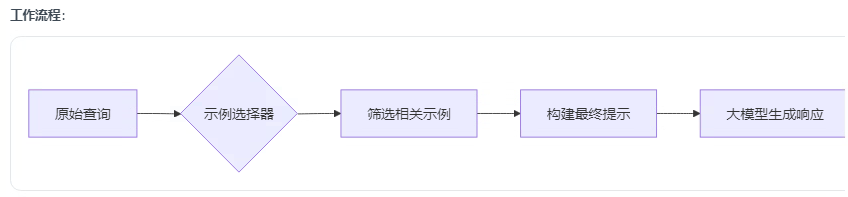
以下列舉常用的三個示例選擇器,以及demo:
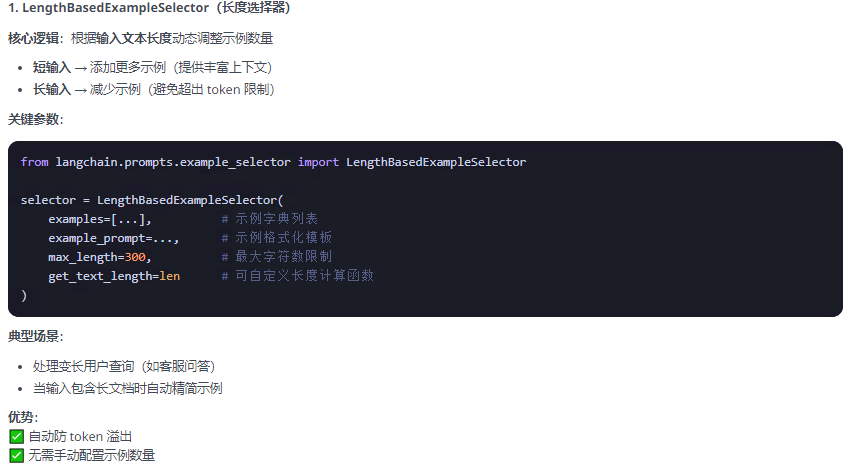
max_length 參數限制的是 最終生成提示詞(prompt)的總長度
包含所有元素的完整提示長度:
用戶當前輸入文本(input)
所有被選中的示例(examples)
提示前綴(prefix,如系統指令)
提示后綴(suffix,如回答格式要求)
計算方式
總長度 = len(prefix) + len(所有示例文本) + len(input) + len(suffix)
import os
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate, FewShotPromptTemplate
from langchain.prompts.example_selector import (LengthBasedExampleSelector,SemanticSimilarityExampleSelector,MaxMarginalRelevanceExampleSelector
)
from langchain.vectorstores import FAISS
from langchain_community.embeddings import DashScopeEmbeddings# 設置API密鑰
api_key = os.getenv("DASHSCOPE_API_KEY")# 定義示例數據
examples = [{"question": "什么是人工智能?","answer": "人工智能是計算機科學的一個分支,旨在創建能夠執行通常需要人類智能的任務的機器。"},{"question": "機器學習是什么?","answer": "機器學習是人工智能的一個子集,它使計算機能夠從數據中學習并做出決策或預測,而無需明確編程。"},{"question": "什么是深度學習?","answer": "深度學習是機器學習的一個子集,使用多層神經網絡來模擬人腦處理信息的方式。"},{"question": "什么是神經網絡?","answer": "神經網絡是一種模擬人腦神經元結構的計算模型,由相互連接的節點(神經元)組成。"},{"question": "什么是自然語言處理?","answer": "自然語言處理是人工智能的一個領域,專注于計算機與人類語言之間的交互,包括理解和生成文本。"}
]# 創建基礎模板
example_prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template("問題: {question}\n答案: {answer}"
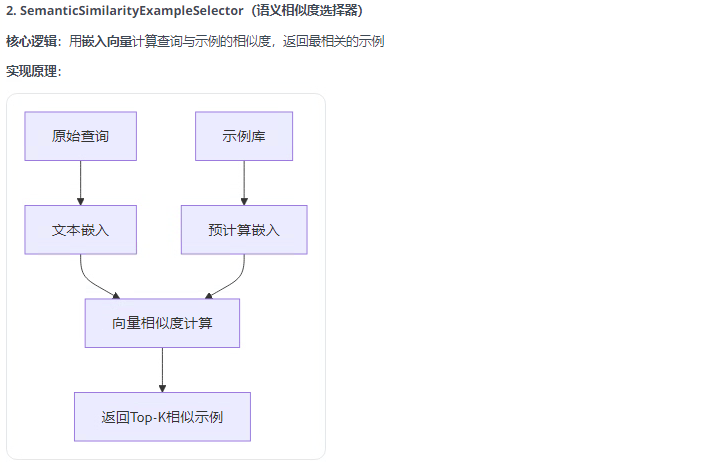
)print("=== 1. LengthBasedExampleSelector - 基于長度的示例選擇器 ===")
# LengthBasedExampleSelector根據輸入長度選擇示例數量
length_selector = LengthBasedExampleSelector(examples=examples,example_prompt=example_prompt,max_length=10 # 根據輸入長度限制示例數量
)few_shot_prompt_length = FewShotPromptTemplate(example_selector=length_selector,example_prompt=example_prompt,suffix="問題: {input}\n答案: ",input_variables=["input"]
)# 短輸入 - 會選擇更多示例
short_input = "AI"
print(f"輸入: {short_input}")
print(f"選擇的示例:\n{few_shot_prompt_length.format(input=short_input)}")# 長輸入 - 會選擇較少示例
long_input = "請詳細解釋人工智能、機器學習和深度學習之間的關系和區別"
print(f"\n輸入: {long_input}")
print(f"選擇的示例:\n{few_shot_prompt_length.format(input=long_input)}")print("\n=== 2. SemanticSimilarityExampleSelector - 基于語義相似度的示例選擇器 ===")
# SemanticSimilarityExampleSelector基于語義相似度選擇示例
# 注意:這需要API密鑰來創建嵌入模型
try:embeddings = DashScopeEmbeddings(model="text-embedding-v1",dashscope_api_key=api_key)similarity_selector = SemanticSimilarityExampleSelector.from_examples(examples,embeddings,FAISS,k=2 # 選擇2個最相似的示例)few_shot_prompt_similarity = FewShotPromptTemplate(example_selector=similarity_selector,example_prompt=example_prompt,suffix="問題: {input}\n答案: ",input_variables=["input"])# 輸入與示例相似的問題similar_input = "什么是機器學習算法?"print(f"輸入: {similar_input}")print(f"選擇的示例:\n{few_shot_prompt_similarity.format(input=similar_input)}")except Exception as e:print(f"注意:SemanticSimilarityExampleSelector需要有效的API密鑰。錯誤信息: {e}")print("\n=== 3. MaxMarginalRelevanceExampleSelector - 最大邊緣相關性示例選擇器 ===")
# MaxMarginalRelevanceExampleSelector選擇既相似又多樣化的示例
try:mmr_selector = MaxMarginalRelevanceExampleSelector.from_examples(examples,embeddings,FAISS,k=3, # 選擇3個示例fetch_k=5 # 從5個候選示例中選擇3個)few_shot_prompt_mmr = FewShotPromptTemplate(example_selector=mmr_selector,example_prompt=example_prompt,suffix="問題: {input}\n答案: ",input_variables=["input"])# 輸入一個綜合性問題mmr_input = "請解釋AI技術在現代科技中的應用"print(f"輸入: {mmr_input}")print(f"選擇的示例:\n{few_shot_prompt_mmr.format(input=mmr_input)}")except Exception as e:print(f"注意:MaxMarginalRelevanceExampleSelector需要有效的API密鑰。錯誤信息: {e}")#print("\n=== 4. 三種選擇器的對比總結 ===")
comparison = """
1. LengthBasedExampleSelector:- 根據輸入長度選擇示例數量- 輸入越短,選擇的示例越多- 輸入越長,選擇的示例越少- 不需要API密鑰或嵌入模型- 適用于需要根據上下文長度調整示例數量的場景2. SemanticSimilarityExampleSelector:- 基于語義相似度選擇最相關的示例- 需要嵌入模型和API密鑰- 選擇與輸入最相似的示例- 適用于需要相關示例來指導輸出的場景3. MaxMarginalRelevanceExampleSelector:- 選擇既相關又多樣化的示例- 需要嵌入模型和API密鑰- 首先選擇最相似的示例,然后增加多樣性- 適用于需要平衡相關性和多樣性的場景
"""
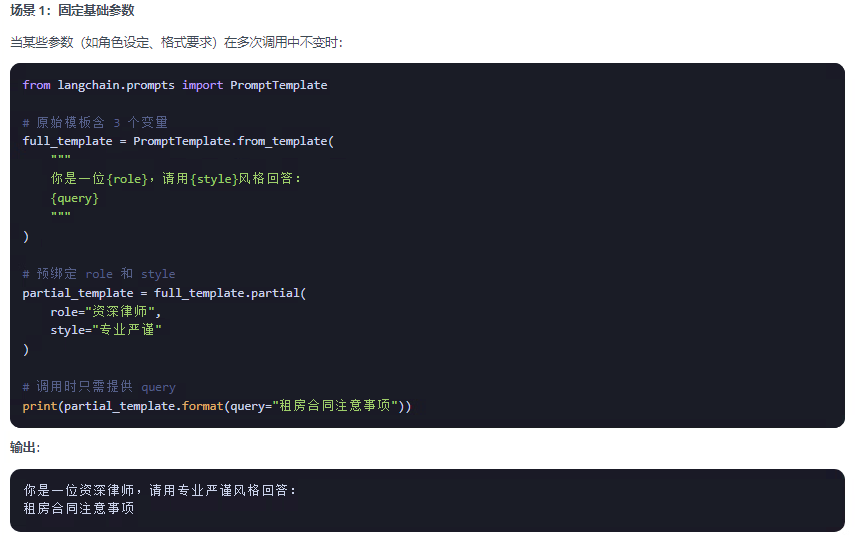
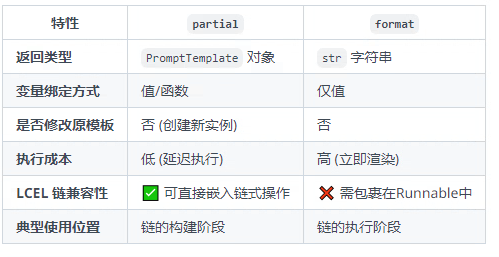
#print(comparison)2.5 partial的使用
????????partial 主要用于 提前綁定提示模板變量,實現模板的預配置和復用,是構建高效鏈(Chain)的關鍵技術。
????????解決三大問題:
1、變量預綁定:將部分模板變量提前固定,簡化運行時輸入
2、模板復用:創建可配置的模板實例,避免重復定義
3、動態適配:結合函數實現運行時動態變量生成
以下列舉幾個使用場景:
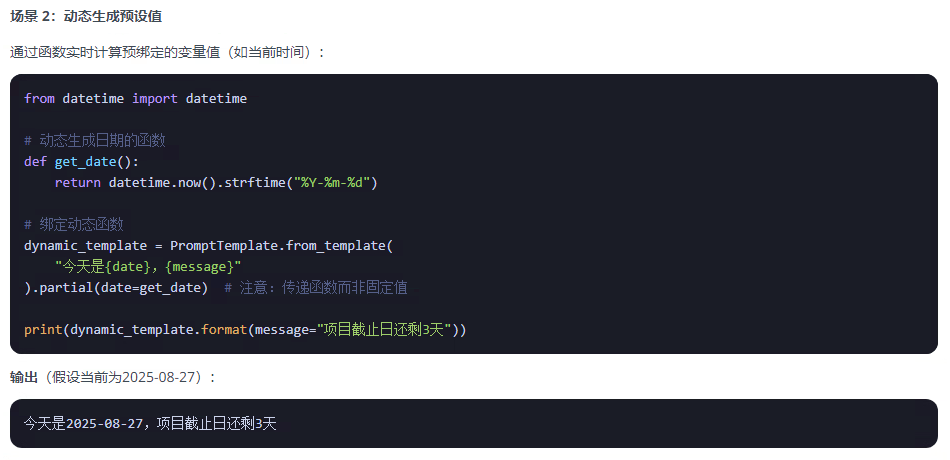
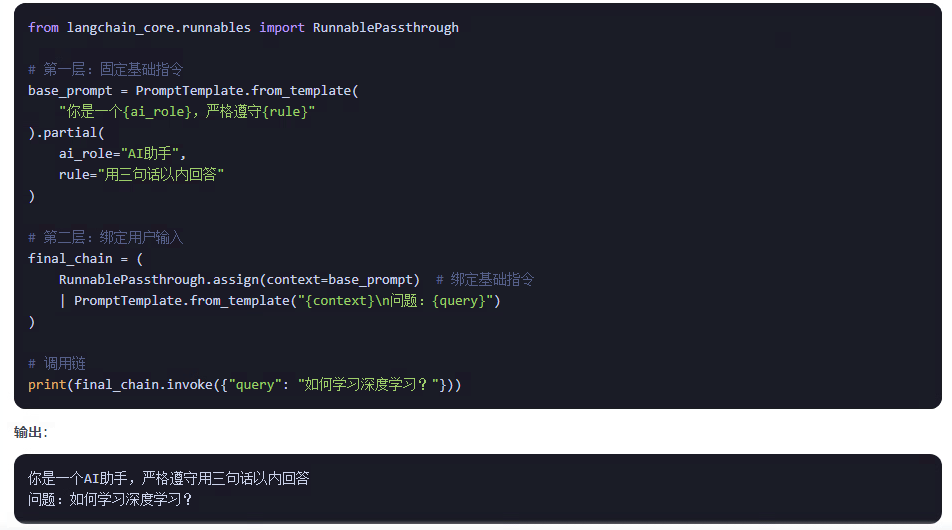
????????在使用上能感覺出partial和format有一些相似,他們有什么區別呢?
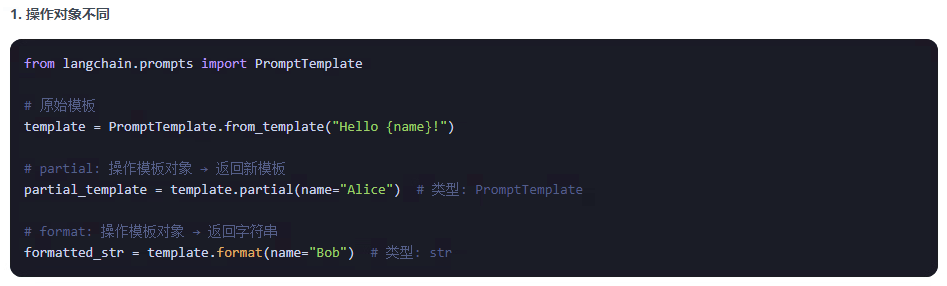
他們的返回值不同
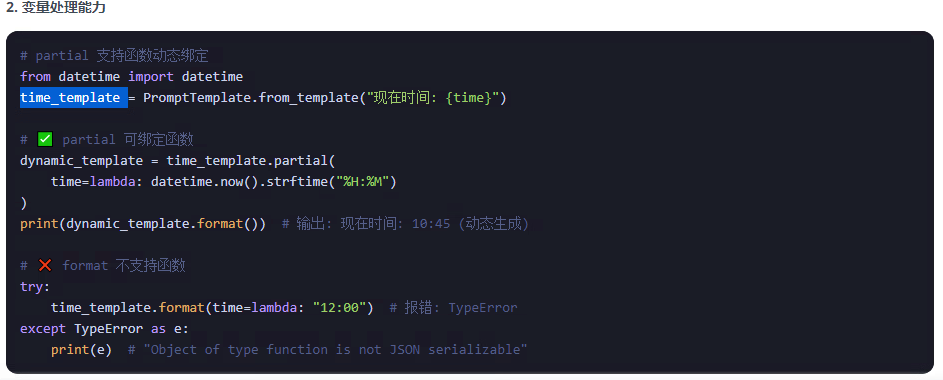
partial的入參可以添加函數
差異總結表如下:
3、輸出解析器
3.1 輸出解析器的功能和使用
????????輸出解析器具有兩大功能:添加 提示詞模板的輸出指令 和 解析輸出格式。看到這里你也許會感到很奇怪,解析輸出格式很好理解,但是輸出解析器跟提示詞模板有什么關系呢?
確實, 從名字上看, 輸出解析器 (OutputParser) 似乎與提示詞模板沒有關系, 因為它聽起來更像用于處理和解析輸出的工具。然而實際上,輸出解析器是通過改變提示詞模板,即增加輸出指令,來指導模型按照特定格式輸出內容的。換句話說,原本的提示詞模板中不包含輸出指令,如果你想得到某種特定格式的輸出結果,就得使用輸出解析器。這樣做的目的是分離提示詞模板的輸入和輸出,輸出解析器會把增加"輸出指令"這件事做好。如果不要求模型按照特定的格式輸出結果,則保持原提示詞模板即可。
? ? ? ? ?輸出解析器的便利性體現在, 你想要某種輸出格式時不需要手動寫入輸出指令,而是導入預設的輸出解析器即可。除了預設大量的輸出指令, 輸出解析器的 parse 方法還支持將模型的輸出解析為對應的數據格式。總的來說,輸出解析器已經寫好了輸出指令(注入提示詞模板的字符串),也寫好了輸出數據的格式處理函數,開發者不需要"重復造輪子"。
? ? ? ? langchain提供了一些預設的輸出解析器,如下圖:

下面使用CommaSeparatedListOutputParser舉個例子,CommaSeparatedListOutputParser是一個定義的類用于解析以逗號分隔的列表類型的輸出。
from langchain.output_parsers import CommaSeparatedListOutputParser
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate# 創建CommaSeparatedListOutputParser實例
output_parser = CommaSeparatedListOutputParser()# 查看格式化指令
format_instructions = output_parser.get_format_instructions()
print("格式化指令:")
print(format_instructions)
print()# 創建提示模板
prompt_template = PromptTemplate(template="列出5個{topic}。{format_instructions}",input_variables=["topic"],partial_variables={"format_instructions": format_instructions}
)# 生成提示
prompt = prompt_template.format(topic="編程語言")
print("生成的提示:")
print(prompt)
print()# 模擬LLM的輸出(實際使用時這里會是真實的LLM調用結果)
llm_output = "Python, Java, JavaScript, C++, Go"# 使用CommaSeparatedListOutputParser解析輸出
parsed_output = output_parser.parse(llm_output)
print("解析后的結果:")
print(type(parsed_output))
print(parsed_output)
print()# 遍歷解析后的列表
print("逐項輸出:")
for i, item in enumerate(parsed_output, 1):print(f"{i}. {item.strip()}")print()
print("="*50)# 另一個示例:解析水果列表
prompt_template2 = PromptTemplate(template="列舉一些{category}。{format_instructions}",input_variables=["category"],partial_variables={"format_instructions": format_instructions}
)prompt2 = prompt_template2.format(category="熱帶水果")
print("第二個提示:")
print(prompt2)
print()# 模擬LLM輸出
llm_output2 = "芒果, 菠蘿, 香蕉, 椰子, 火龍果, 山竹, 榴蓮"# 解析輸出
parsed_output2 = output_parser.parse(llm_output2)
print("解析后的熱帶水果列表:")
print(parsed_output2)
print()print("熱帶水果:")
for i, fruit in enumerate(parsed_output2, 1):print(f"{i}. {fruit.strip()}")print()
print("="*50)# 展示錯誤處理
print("錯誤處理示例:")
try:# 嘗試解析無效格式invalid_output = "這是一個無效的列表格式沒有逗號分隔:Your response"parsed_invalid = output_parser.parse(invalid_output)print("解析結果:", parsed_invalid)
except Exception as e:print(f"解析錯誤: {e}")# 正確處理無逗號的情況
print()
print("處理單個項目:")
single_item_output = "Python"
single_parsed = output_parser.parse(single_item_output)
print("單個項目解析結果:", single_parsed)3.2 Pydantic JSON輸出解析器
? ? ? ?pydantic是連接 LLM 非結構化輸出與結構化數據的核心組件,在真實項目中應用率高達 85%(LangChain 官方調研數據)。
????????什么是 Pydantic JSON 輸出解析器? 本質:將 LLM 原始文本輸出自動轉換為 類型安全的 Python 對象 核心組件:
????????Pydantic:數據驗證庫(定義數據結構)
????????JSON:結構化數據格式
????????OutputParser:LangChain 解析接口
import os
from typing import List, Optional
from langchain_community.llms import Tongyi
from langchain.output_parsers import PydanticOutputParser
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
# 更新Pydantic導入方式
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field# 定義一個Pydantic模型來表示我們期望的輸出結構
class PersonInfo(BaseModel):name: str = Field(description="人的姓名")age: int = Field(description="人的年齡")occupation: str = Field(description="人的職業")hobbies: List[str] = Field(description="人的愛好列表")def age_must_be_positive(cls, v):if v <= 0:raise ValueError('年齡必須是正數')return v# 定義另一個Pydantic模型表示更復雜的結構
class PersonDetail(BaseModel):person: PersonInfo = Field(description="個人信息")summary: str = Field(description="對這個人的簡要總結")def main():# 修復API密鑰變量名llm = Tongyi(dashscope_api_key=os.getenv("DASHSCOPE_API_KEY"),model_name="qwen-turbo-latest")# 創建Pydantic輸出解析器parser = PydanticOutputParser(pydantic_object=PersonDetail)# 創建提示模板prompt_template = PromptTemplate(template="請提供以下人物的詳細信息:\n人物: {person_name}\n{format_instructions}\n",input_variables=["person_name"],partial_variables={"format_instructions": parser.get_format_instructions()})# 示例查詢person_name = "愛因斯坦"# 格式化提示詞prompt = prompt_template.format(person_name=person_name)print("提示詞:")print(prompt)print("-" * 50)# 調用大模型response = llm.invoke(prompt)print("大模型原始輸出:")print(response)print("-" * 50)# 使用Pydantic解析器解析輸出try:parsed_output = parser.parse(response)print("解析后的結構化數據:")print(f"姓名: {parsed_output.person.name}")print(f"年齡: {parsed_output.person.age}")print(f"職業: {parsed_output.person.occupation}")print(f"愛好: {', '.join(parsed_output.person.hobbies)}")print(f"總結: {parsed_output.summary}")except Exception as e:print(f"解析失敗: {e}")if __name__ == "__main__":main()3.3?StructuredOutputParser 結構化輸出解析器
????????解釋 StructuredOutputParser 和 ResponseSchema 的含義和使用方法。這兩個組件是 LangChain 中用于結構化輸出解析的核心工具,使語言模型 (LLM) 的輸出能夠被解析為預定義的、類型安全的 Python 對象。
????????(1)ResponseSchema(響應模式)
含義:定義你期望從語言模型 (LLM) 輸出中提取的結構化字段。每個 ResponseSchema 描述一個字段的:
名稱 (name):字段的鍵名(如 "name", "age")
描述 (description):提示 LLM 應在此字段中返回什么內容
類型 (type):字段的數據類型(如 string, integer, list)
作用:相當于告訴 LLM:“你的輸出需要包含以下字段,并按照這些要求填充數據”。
(2)StructuredOutputParser(結構化輸出解析器)
含義:將 LLM 的自由文本輸出根據 ResponseSchema 定義的規則自動解析為結構化數據(如字典、Pydantic 模型)。
核心能力:
生成給 LLM 的格式化指令(如 JSON 格式要求)
將 LLM 的文本輸出解析為 Python 對象
自動處理類型轉換和驗證
import os
from typing import List, Optional
from langchain_community.llms import Tongyi
from langchain.output_parsers import StructuredOutputParser, ResponseSchema
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate, ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessagedef main():# 初始化通義千問大模型llm = Tongyi(dashscope_api_key=os.getenv("DASHSCOPE_API_KEY"),model_name="qwen-turbo-latest")# 定義響應結構response_schemas = [ResponseSchema(name="name", description="人物的姓名,只有名字使用英文輸出,其他部分使用中文輸出"),ResponseSchema(name="age", description="人物的年齡,不是出生死亡的年月日,是一個數字"),ResponseSchema(name="occupation", description="人物的職業"),ResponseSchema(name="hobbies", description="人物的愛好列表,以逗號分隔"),ResponseSchema(name="summary", description="對這個人的簡要總結")]# 創建結構化輸出解析器output_parser = StructuredOutputParser.from_response_schemas(response_schemas)# 獲取格式化指令format_instructions = output_parser.get_format_instructions()# 創建提示模板prompt_template = """請提供以下人物的詳細信息:人物: {person_name}{format_instructions}"""# 創建ChatPromptTemplatechat_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([("system", "你是一個 helpful AI 助手"),("user", prompt_template)])# 示例查詢person_name = "愛因斯坦"# 格式化提示詞prompt = chat_prompt.format_messages(person_name=person_name,format_instructions=format_instructions)print("提示詞:")print(prompt[1].content)print("-" * 50)# 調用大模型response = llm.invoke(prompt)print("大模型原始輸出:")print(response)print("-" * 50)# 使用StructuredOutput解析器解析輸出try:parsed_output = output_parser.parse(response)print("解析后的結構化數據:")print(f"姓名: {parsed_output['name']}")print(f"年齡: {parsed_output['age']}")print(f"職業: {parsed_output['occupation']}")print(f"愛好: {parsed_output['hobbies']}")print(f"總結: {parsed_output['summary']}")except Exception as e:print(f"解析失敗: {e}")if __name__ == "__main__":main()4、模型包裝器
????????LangChain 的模型包裝器組件是基于各個模型平臺的 API 協議進行開發的, 主要提供了兩種類型的包裝器。一種是通用的 LLM模型包裝器, 另一種是專門針對 Chat 類型 API 的 Chat Model (聊天模型包裝器)。
4.1 模型包裝器的區別
在 LangChain 的官網文檔中,凡是涉及模型輸入、輸出的鏈(Chain )和代理(Agent)的示例代碼,都會提供兩份。一份是使用LLM模型包裝器的,一份是使用聊天模型包裝器的,這是因為兩者之間存在著細微但是很重要的區別。
(1)輸入的區別
????????對于 LLM 模型包裝器, 其輸入通常是單一的字符串提示詞 (prompt) 。例如,你可以輸入"Translate the following English text to French: '{text}", 然后模型會生成對應的法文翻譯。另外,LLM模型包裝器主要用于文本任務,例如給定一個提示"今天的天氣如何?"模型會生成一個相應的答案"今天的天氣很好。"
????????聊天模型包裝器,其輸入則是一系列的聊天消息。通常這些消息都帶有發言人的標簽 (比如系統、 AI 和人類)。每條消息都有一個 role (角色) 和 content (內容) 。例如, 你可以輸入[{"role": "user", "content": 'Translate the following English text toFrench: "{text}"}], 模型會返回對應的法文翻譯, 但是返回內容包含在 AIMessage(...)內。
(2)輸出的區別
????????對于LLM模型包裝器,其輸出是一個字符串,這個字符串是模型對提示詞的補全。而聊天模型包裝器的輸出是一則聊天消息,是模型對輸入消息的響應。
????????雖然LLM模型包裝器和聊天模型包裝器在處理輸入和輸出的方式上有所不同,但是為了使它們可以混合使用,它們都實現了基礎模型接口。這個接口公開了兩個常見的方法:predict(接收一個字符串并返回一個字符串)和predict messages(接收一則消息并返回一則消息)。這樣,無論你是使用特定的模型,還是創建一個應該匹配其他類型模型的應用,都可以通過這個共享接口來進行操作。
4.2 模型包裝器的案例解釋
以下給出LLM模型包裝器和Chat模型包裝器的示例:
LLM模型包裝器:
import os
from langchain_community.llms import Tongyi# 初始化通義千問大模型
llm = Tongyi(dashscope_api_key=os.getenv("DASHSCOPE_API_KEY"),model_name="qwen-turbo"
)# 簡單調用
response = llm.invoke("你好,介紹一下人工智能")
print("大模型回答:")
print(response)Chat模型包裝器:
import os
from langchain_community.chat_models import ChatTongyi
#from langchain import LLMChain
from langchain.chains import LLMChain
from langchain.prompts.chat import (ChatPromptTemplate,HumanMessagePromptTemplate,SystemMessagePromptTemplate,
)
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser# 從環境變量獲取 DASHSCOPE_API_KEY
api_key = os.getenv('DASHSCOPE_API_KEY')# 檢查是否獲取到 API Key
if not api_key:raise ValueError("請設置 DASHSCOPE_API_KEY 環境變量")# 使用通義千問模型
llm = ChatTongyi(temperature=1,dashscope_api_key=api_key,model_name="qwen-plus")template = ("以下是一段人類與人工智能之間的友好對話。""該人工智能健談,并從其上下文中提供大量具體細節。如果人工智能不知道某個問題的答案,它會如實說明自己不知道。"
)system_message_prompt = SystemMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(template)human_template = "{text}"
human_message_prompt = HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(human_template)chat_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([system_message_prompt, human_message_prompt])chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=chat_prompt)
ret = chain.run(text="你叫張三")
print(ret)
)
:幾種草體的實現方式(透明度剔除,GPU Instaning, 曲面細分+幾何著色器實現))



JavaScript 表單驗證)
)


 - 飛控中的傳感器)





)


)