? ? ? ? Vue生命周期常用的onMounted掛載后執行和onUnmounted卸載前以及onupdated更新后實際上用react對比就是useEffect,而且掛載順序也是子組件先于父組件然后往外的棧結構,先進后出。
? ? 1.Vue的生命周期
<template><h2>當前求和為{{ sum }}</h2><button @click="add">點為sum+1</button>
</template>
<script setup name="Person" lang="ts">import { ref,onBeforeMount,onMounted, onUpdated,onBeforeUpdate,onBeforeUnmount,onUnmounted} from 'vue';let sum =ref(0)const add=()=>{sum.value+=1}//創建console.log('組件創建');//掛載onBeforeMount(()=>{console.log('租借掛載之前');})//掛載完畢onMounted(()=>{console.log('person掛載完畢');})//更新前onBeforeUpdate(()=>{console.log('更新前');})//更新完畢onUpdated(()=>{console.log(' 更新后', )})//卸載前onBeforeUnmount(()=>{console.log(' 卸載前', )})//卸載后onUnmounted(()=>{console.log(' 卸載后', )})
</script>
<!-- scoped局部樣式 類似于module.css -->
<style scoped>
</style>? ? ? ? 這些就是vue3的生命周期常用的掛載前掛載后以及更新后。
2.watchEffect
? ? ? ? watch監聽方法可以監聽多個需要用[{}]這樣寫法,而且如果對象的屬性需要函數式也就是()=>person.car這種。
? ? ? ? watchEffect可以自己分析監聽數據,只要里面的數據發生改變就會重新執行函數而且上來就會執行一次。
<template><h1>水位達到60度或者水位達到80cm 服務器發送請求</h1><h2>當前水溫為{{ temp }}</h2><h2>當前水位{{ height}}</h2><button @click="changetemp">水溫加10</button><button @click="changeheight">水位加10</button>
</template>
<script setup name="Person" lang="ts">import { ref,watch,watchEffect } from 'vue';let temp =ref(10)let height=ref(0)const changetemp=()=>{temp.value+=10}const changeheight=()=>{height.value+=10}//監視//watch必須指定監視誰// watch([temp,height],(value)=>{// let [newtemp,newheight] = value// if(newtemp>=60||newheight>=80){// console.log('發送請求');// }// })//watchEffect可以直接用回自己分析監視誰?// 響應式的追蹤其依賴 并且依賴更改之后重新執行函數//上來就會執行一次watchEffect(()=>{if(temp.value>=60||height.value>=80){console.log('發送請求'); }})
</script>
<style>
</style>3.hooks和props傳遞
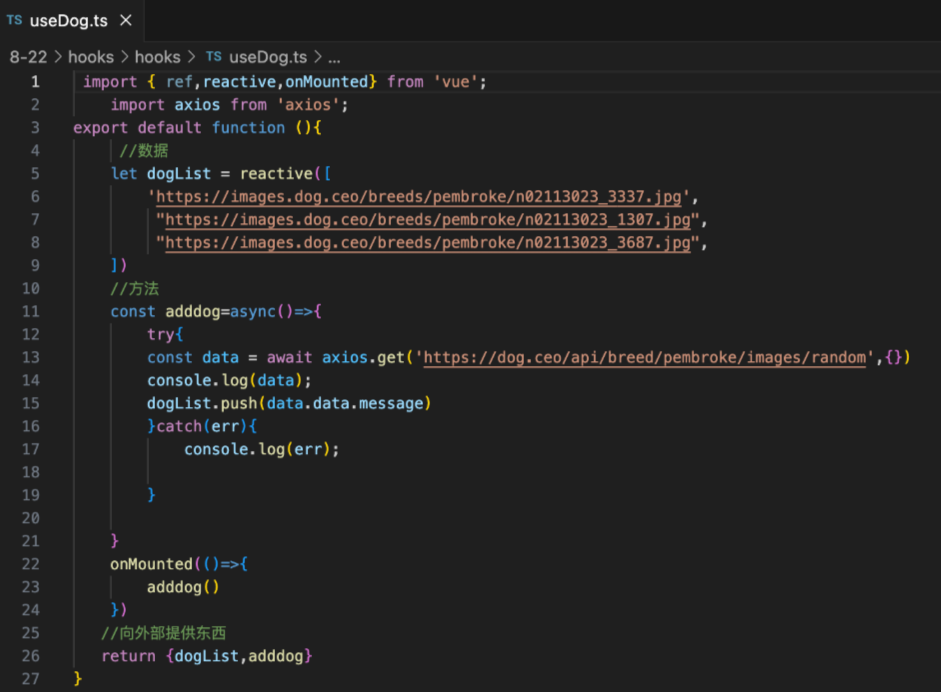
? ? ? ? hooks當我們操作的方法和數據很多組件要使用或者很明顯重復代碼過多,那么就可以提取到一個ts文件也就是包裹一個匿名函數里面,文件名use開頭。
????????
? ? ? ? 組件之間的props傳遞也是和react一樣,只不過需要用defineProps()傳遞如果沒有指定類型那么就需要指定接收的屬性名,如果指名了接收的數據類型就可以參數可以為().? ?
<template><ul><li v-for="item in x.personlist" :key="item.id">{{ item.name }}--{{ item.age }}</li></ul><h2>{{ x.a }}</h2>
</template>
<script setup name="Person" lang="ts">import { ref,watch,watchEffect,defineExpose,defineProps,withDefaults} from 'vue';import type { Person } from '@/types';//接收數組并且保存到x變量上//let x = defineProps(['personlist'])//可以聲明類型 這里傳什么接收什么//let x = defineProps<{personlist:Person[],a:number}>()//可以設置默認值let x =withDefaults(defineProps<{personlist?:Person[],a:number}>(),{personlist:()=>[{id:'a',name:'s',age:1}],a:2})
</script>
<!-- scoped局部樣式 類似于module.css -->
<style scoped>
</style>4.路由組件的參數傳遞
? ? ? ? vue3的路由組件定義以及跳轉連接link和react幾乎一致,
//創建一個路由器并且暴露出去
import { createRouter,createWebHistory } from "vue-router";
//創建路由器
import Home from "@/components/Home.vue";
import News from "@/components/News.vue";
import About from "@/components/About.vue";
import Detail from "@/components/Detail.vue";
const router = createRouter({history:createWebHistory(),routes:[//一個個路由規則{path:'/home',component:Home},{path:'/about',component:About},{path:'/news',component:News,children:[{name:'xiang',path:'detail',component:Detail,//第一種寫法//props:true//將所有params參數作為props傳遞給組件//第二種寫法 可以指定queryprops(route){return route.query}}]}]
})
/*history兩種模式url更加美觀 接近傳統完整的url 不加#vue3 createWebhistrry() React缺點 上線需要服務端配合 否則刷新會404<createBrowserRouter></createBrowserRouter><Router Provider></Router>hash模式url帶有# SEO優化方面相對較差createWebHashhsitory
*/
//暴露操作
export default router? ? ? ? 也是兩種路由表模式一種是createWebhistory另一種是hash模式多了個#和react的createBrowserRouter以及createHashrouter差不多,然后嵌套路由也是直接children直接寫。
????????子路由展示區域需要用RouterView,React用outlet組件。RouterLinkl跳轉路徑組件,然后就是傳遞參數,父路由組件路由像子路由組件傳遞參數。比較繁瑣而且在寫項目的時候沒有使用過,只是前端像后端發送請求會攜帶參數,比如/:id不過一般都是在get('',{id;})這樣攜帶,params參數。
<template><h1>我是news</h1><ul><li v-for="item in newslist" :key="item.id"><!-- 第一種寫法 query傳遞參數 --><RouterLink :to="/news/detail?id=${item.id}&title=${item.title}">{{ item.title }}--{{ item.content }}</RouterLink><!-- 第二種寫法query --><!-- <RouterLink :to="{path:'/news/detail',query:{id:item.id,title:item.title}}">{{ item.title }}--{{ item.content }}</RouterLink> --><!-- params傳遞 第一種寫法 params傳遞需要占位--><!-- <RouterLink :to="/news/detail/${item.id}/${item.title}">{{ item.title }}--{{ item.content }}</RouterLink> --><!-- 需要在定義路由的時候接收/:id/:title --><!-- 第二種寫法 如果使用to的對象寫法必須使用name配置項不能用path 需要用name 不能傳數組--><!-- <RouterLink :to="{name:'xiang',params:{id:item.id,title:item.title}}">{{ item.title }}--{{ item.content }}</RouterLink> --><!-- 路由規則props配置 props:true --></li></ul><div><RouterView></RouterView></div></template><script setup name="News" lang="ts">import { reactive } from 'vue';import { RouterView, RouterLink} from 'vue-router';const newslist=reactive([{id:1,title:'十種食物',content:'系懶覺'},{id:2,title:'十種測試',content:'系懶覺'},{id:3,title:'好消息',content:'震驚'},{id:4,title:'壞消息',content:'周一'}])
</script>
<style>
</style>? ? ? ? 兩種一種是query一種是params,寫法是固定的,不用記憶。接收的話用useRoute鉤子
<template><ul><!-- <li>{{ query.id }}</li><li>{{ query.title }}</li> --><li>{{ x.id }}</li><li>{{ x.title }}</li></ul>
</template><script setup name="Detail" lang="ts">import { reactive, toRefs ,defineProps} from 'vue';//從響應式對象結構屬性需要加toRefs包裹不然丟失響應功能import { RouterView, useRoute} from 'vue-router';//獲取父路由組件通過路徑傳遞query的參數// let data = useRoute()// let {query}=toRefs(data)//獲取params參數// let data = useRoute()// let {params}=toRefs(data)let x = defineProps(['id','title'])console.log(x);</script>
<style>
</style>? ? ? ? 如果在定義路由組件規則的時候聲明props:true那么可以用接收props的方式接收params參數,如果props(route){return route.query}可以用接收props方式接收query參數。
????????













![week3-[二維數組]小方塊](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/week3-[二維數組]小方塊)


)
)
