注: 本文來自尚硅谷-宋紅康僅用來學習備份
6.1 數值型數組特征值統計
- 這里的特征值涉及到:平均值、最大值、最小值、總和等
**舉例1:**數組統計:求總和、均值
public class TestArrayElementSum {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arr = {4,5,6,1,9};//求總和、均值int sum = 0;//因為0加上任何數都不影響結果for(int i=0; i<arr.length; i++){sum += arr[i];}double avg = (double)sum/arr.length;System.out.println("sum = " + sum);System.out.println("avg = " + avg);}
}
**舉例2:**求數組元素的總乘積
public class TestArrayElementMul {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arr = {4,5,6,1,9};//求總乘積long result = 1;//因為1乘以任何數都不影響結果for(int i=0; i<arr.length; i++){result *= arr[i];}System.out.println("result = " + result);}
}
**舉例3:**求數組元素中偶數的個數
public class TestArrayElementEvenCount {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arr = {4,5,6,1,9};//統計偶數個數int evenCount = 0;for(int i=0; i<arr.length; i++){if(arr[i]%2==0){evenCount++;}}System.out.println("evenCount = " + evenCount);}
}
**舉例4:**求數組元素的最大值

public class TestArrayMax {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arr = {4,5,6,1,9};//找最大值int max = arr[0];for(int i=1; i<arr.length; i++){//此處i從1開始,是max不需要與arr[0]再比較一次了if(arr[i] > max){max = arr[i];}}System.out.println("max = " + max);}
}
**舉例5:**找最值及其第一次出現的下標
public class TestMaxIndex {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arr = {4,5,6,1,9};//找最大值以及第一個最大值下標int max = arr[0];int index = 0;for(int i=1; i<arr.length; i++){if(arr[i] > max){max = arr[i];index = i;}}System.out.println("max = " + max);System.out.println("index = " + index);}
}
**舉例6:**找最值及其所有最值的下標
public class Test13AllMaxIndex {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arr = {4,5,6,1,9,9,3};//找最大值int max = arr[0];for(int i=1; i<arr.length; i++){if(arr[i] > max){max = arr[i];}}System.out.println("最大值是:" + max);System.out.print("最大值的下標有:");//遍歷數組,看哪些元素和最大值是一樣的for(int i=0; i<arr.length; i++){if(max == arr[i]){System.out.print(i+"\t");}}System.out.println();}
}
優化
public class Test13AllMaxIndex2 {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arr = {4,5,6,1,9,9,3};//找最大值int max = arr[0];String index = "0";for(int i=1; i<arr.length; i++){if(arr[i] > max){max = arr[i];index = i + "";}else if(arr[i] == max){index += "," + i;}}System.out.println("最大值是" + max);System.out.println("最大值的下標是[" + index+"]");}
}
**舉例7(難):**輸入一個整形數組,數組里有正數也有負數。數組中連續的一個或多個整數組成一個子數組,每個子數組都有一個和。求所有子數組的和的最大值。要求時間復雜度為O(n)。
例如:輸入的數組為1, -2, 3, -10, -4, 7, 2, -5,和最大的子數組為3, 10, -4, 7, 2,因此輸出為該子數組的和18。
public class Test5 {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arr = new int[]{1, -2, 3, 10, -4, 7, 2, -5};int i = getGreatestSum(arr);System.out.println(i);}public static int getGreatestSum(int[] arr){int greatestSum = 0;if(arr == null || arr.length == 0){return 0;}int temp = greatestSum;for(int i = 0;i < arr.length;i++){temp += arr[i];if(temp < 0){temp = 0;}if(temp > greatestSum){greatestSum = temp;}}if(greatestSum == 0){greatestSum = arr[0];for(int i = 1;i < arr.length;i++){if(greatestSum < arr[i]){greatestSum = arr[i];}}}return greatestSum;}
}
舉例8:評委打分
分析以下需求,并用代碼實現:
(1)在編程競賽中,有10位評委為參賽的選手打分,分數分別為:5,4,6,8,9,0,1,2,7,3
(2)求選手的最后得分(去掉一個最高分和一個最低分后其余8位評委打分的平均值)
/*** @author 尚硅谷-宋紅康* @create 10:03*/
public class ArrayExer {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] scores = {5,4,6,8,9,0,1,2,7,3};int max = scores[0];int min = scores[0];int sum = 0;for(int i = 0;i < scores.length;i++){if(max < scores[i]){max = scores[i];}if(min > scores[i]){min = scores[i];}sum += scores[i];}double avg = (double)(sum - max - min) / (scores.length - 2);System.out.println("選手去掉最高分和最低分之后的平均分為:" + avg);}
}
6.2 數組元素的賦值與數組復制
**舉例1:**楊輝三角

案例:使用二維數組打印一個 10 行楊輝三角。
提示:
- 第一行有 1 個元素, 第 n 行有 n 個元素
- 每一行的第一個元素和最后一個元素都是 1
- 從第三行開始, 對于非第一個元素和最后一個元素的元素。即:
yanghui[i][j] = yanghui[i-1][j-1] + yanghui[i-1][j];
public class YangHuiTest {public static void main(String[] args) {//1. 創建二維數組int[][] yangHui = new int[10][];//2.使用循環結構,初始化外層數組元素for(int i = 0;i < yangHui.length;i++){yangHui[i] = new int[i + 1];//3. 給數組的元素賦值//3.1 給數組每行的首末元素賦值為1yangHui[i][0] = yangHui[i][i] = 1;//3.2 給數組每行的非首末元素賦值//if(i >= 2){for(int j = 1;j < yangHui[i].length - 1;j++){ //j從每行的第2個元素開始,到倒數第2個元素結束yangHui[i][j] = yangHui[i - 1][j] + yangHui[i - 1][j - 1];}//}}//遍歷二維數組for (int i = 0; i < yangHui.length; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < yangHui[i].length; j++) {System.out.print(yangHui[i][j] + "\t");}System.out.println();}}
}
**舉例2:**使用簡單數組
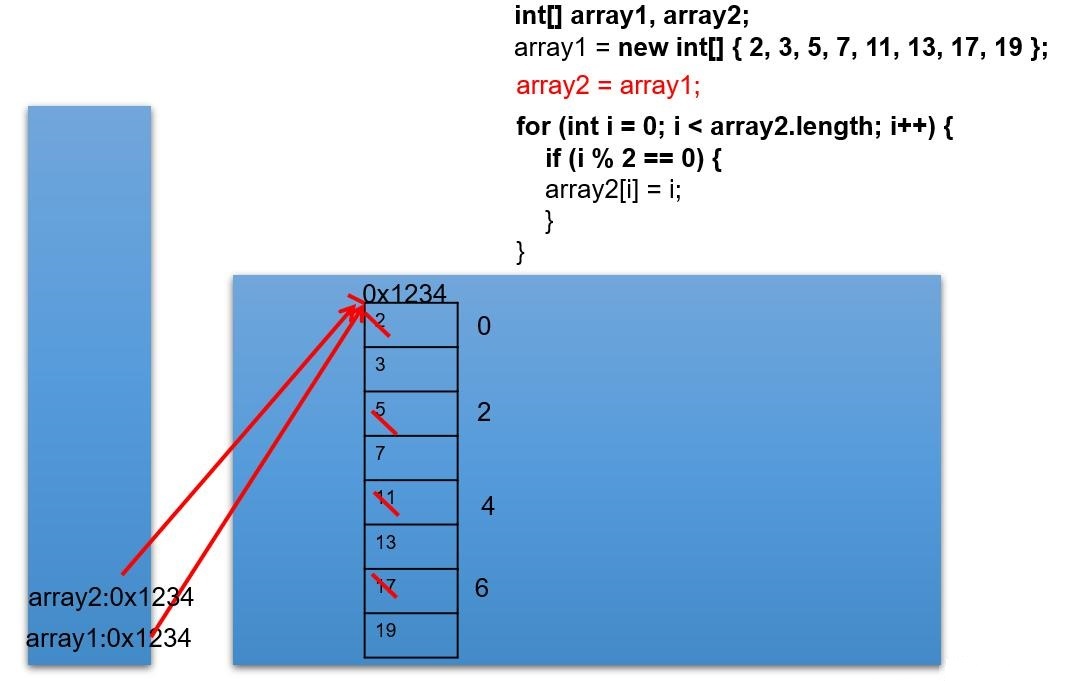
(1)創建一個名為ArrayTest的類,在main()方法中聲明array1和array2兩個變量,他們是int[]類型的數組。
(2)使用大括號{},把array1初始化為8個素數:2,3,5,7,11,13,17,19。
(3)顯示array1的內容。
(4)賦值array2變量等于array1,修改array2中的偶索引元素,使其等于索引值(如array[0]=0,array[2]=2)。打印出array1。 array2 = array1;
**思考:**array1和array2是什么關系?
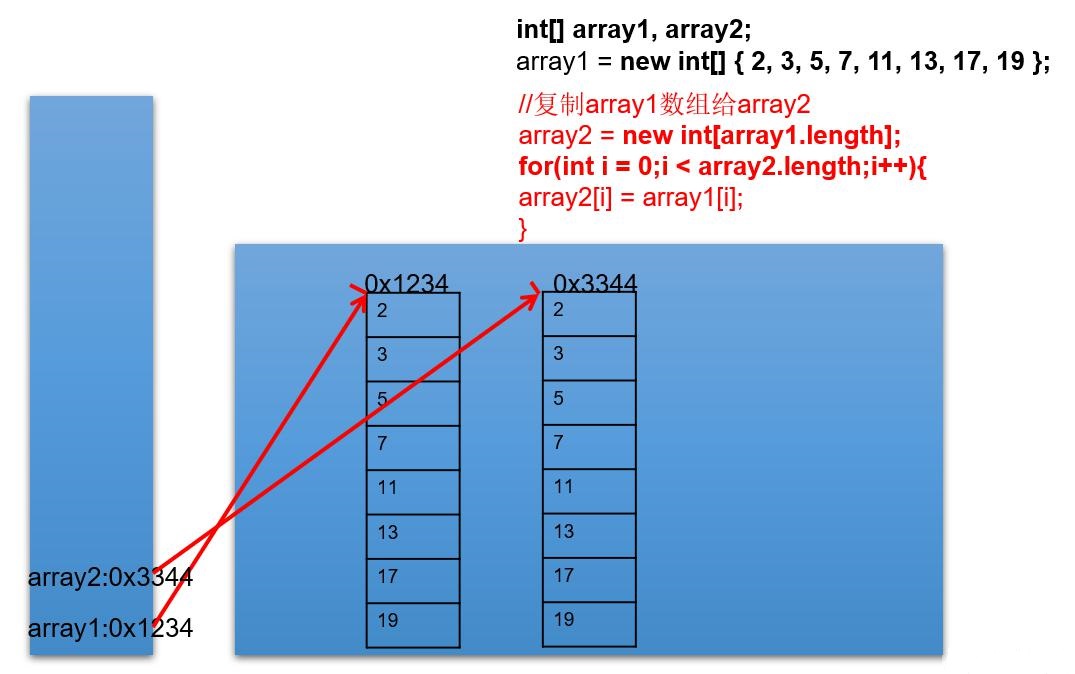
**拓展:**修改題目,實現array2對array1數組的復制
**舉例3:**一個數組,讓數組的每個元素去除第一個元素,得到的商作為被除數所在位置的新值。
public class Test3 {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arr = new int[]{12,43,65,3,-8,64,2};// for(int i = 0;i < arr.length;i++){
// arr[i] = arr[i] / arr[0];
// }for(int i = arr.length -1;i >= 0;i--){arr[i] = arr[i] / arr[0];}//遍歷arrfor(int i = 0;i < arr.length;i++){System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");}}
}
**舉例4:**創建一個長度為6的int型數組,要求數組元素的值都在1-30之間,且是隨機賦值。同時,要求元素的值各不相同。
public class Test4 {// 5-67 Math.random() * 63 + 5;@Testpublic void test1() {int[] arr = new int[6];for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {// [0,1) [0,30) [1,31)arr[i] = (int) (Math.random() * 30) + 1;boolean flag = false;while (true) {for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {if (arr[i] == arr[j]) {flag = true;break;}}if (flag) {arr[i] = (int) (Math.random() * 30) + 1;flag = false;continue;}break;}}for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {System.out.println(arr[i]);}}//更優的方法@Testpublic void test2(){int[] arr = new int[6];for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {// [0,1) [0,30) [1,31)arr[i] = (int) (Math.random() * 30) + 1;for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {if (arr[i] == arr[j]) {i--;break;}}}for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {System.out.println(arr[i]);}}
}
**舉例5:**撲克牌
案例:遍歷撲克牌
遍歷撲克牌,效果如圖所示:

提示:使用兩個字符串數組,分別保存花色和點數,再用一個字符串數組保存最后的撲克牌。
String[] hua = {“黑桃”,“紅桃”,“梅花”,“方片”};
String[] dian = {“A”,“2”,“3”,“4”,“5”,“6”,“7”,“8”,“9”,“10”,“J”,“Q”,“K”};
package com.atguigu3.common_algorithm.exer5;/*** @author 尚硅谷-宋紅康* @create 17:16*/
public class ArrayExer05 {public static void main(String[] args) {String[] hua = {"黑桃","紅桃","梅花","方片"};String[] dian = {"A","2","3","4","5","6","7","8","9","10","J","Q","K"};String[] pai = new String[hua.length * dian.length];int k = 0;for(int i = 0;i < hua.length;i++){for(int j = 0;j < dian.length;j++){pai[k++] = hua[i] + dian[j];}}for (int i = 0; i < pai.length; i++) {System.out.print(pai[i] + " ");if(i % 13 == 12){System.out.println();}}}
}拓展:在上述基礎上,增加大王、小王。
**舉例6:**回形數
從鍵盤輸入一個整數(1~20) ,則以該數字為矩陣的大小,把1,2,3…n*n 的數字按照順時針螺旋的形式填入其中。
例如: 輸入數字2,則程序輸出:
1 2
4 3
輸入數字3,則程序輸出:
1 2 3
8 9 4
7 6 5
輸入數字4, 則程序輸出:
1 2 3 4
12 13 14 5
11 16 15 6
10 9 8 7
//方式1
public class RectangleTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("輸入一個數字");int len = scanner.nextInt();int[][] arr = new int[len][len];int s = len * len;/** k = 1:向右* k = 2:向下* k = 3:向左* k = 4:向上*/int k = 1;int i = 0,j = 0;for(int m = 1;m <= s;m++){if(k == 1){if(j < len && arr[i][j] == 0){arr[i][j++] = m;}else{k = 2;i++; j--;m--;}}else if(k == 2){if(i < len && arr[i][j] == 0){arr[i++][j] = m;}else{k = 3;i--;j--;m--;}}else if(k == 3){if(j >= 0 && arr[i][j] == 0){arr[i][j--] = m;}else{k = 4;i--;j++;m--;}}else if(k == 4){if(i >= 0 && arr[i][j] == 0){arr[i--][j] = m;}else{k = 1;i++;j++;m--;}}}//遍歷for(int m = 0;m < arr.length;m++){for(int n = 0;n < arr[m].length;n++){System.out.print(arr[m][n] + "\t");}System.out.println();}}
}
//方式2
/*01 02 03 04 05 06 07 24 25 26 27 28 29 08 23 40 41 42 43 30 09 22 39 48 49 44 31 10 21 38 47 46 45 32 11 20 37 36 35 34 33 12 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 */
public class RectangleTest1 {public static void main(String[] args) {int n = 7;int[][] arr = new int[n][n];int count = 0; //要顯示的數據int maxX = n-1; //x軸的最大下標int maxY = n-1; //Y軸的最大下標int minX = 0; //x軸的最小下標int minY = 0; //Y軸的最小下標while(minX<=maxX) {for(int x=minX;x<=maxX;x++) {arr[minY][x] = ++count;}minY++;for(int y=minY;y<=maxY;y++) {arr[y][maxX] = ++count;}maxX--;for(int x=maxX;x>=minX;x--) {arr[maxY][x] = ++count;}maxY--;for(int y=maxY;y>=minY;y--) {arr[y][minX] = ++count;}minX++;}for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++) {for(int j=0;j<arr.length;j++) {String space = (arr[i][j]+"").length()==1 ? "0":"";System.out.print(space+arr[i][j]+" ");}System.out.println();}}
}
6.3 數組元素的反轉
**實現思想:**數組對稱位置的元素互換。

public class TestArrayReverse1 {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arr = {1,2,3,4,5};System.out.println("反轉之前:");for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {System.out.println(arr[i]);}//反轉/*思路:首尾對應位置的元素交換(1)確定交換幾次次數 = 數組.length / 2(2)誰和誰交換for(int i=0; i<次數; i++){int temp = arr[i];arr[i] = arr[arr.length-1-i];arr[arr.length-1-i] = temp;}*/for(int i=0; i<arr.length/2; i++){int temp = arr[i];arr[i] = arr[arr.length-1-i];arr[arr.length-1-i] = temp;}System.out.println("反轉之后:");for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {System.out.println(arr[i]);}}}
或

public class TestArrayReverse2 {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arr = {1,2,3,4,5};System.out.println("反轉之前:");for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {System.out.println(arr[i]);}//反轉//左右對稱位置交換for(int left=0,right=arr.length-1; left<right; left++,right--){//首 與 尾交換int temp = arr[left];arr[left] = arr[right];arr[right] = temp;}System.out.println("反轉之后:");for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {System.out.println(arr[i]);}}
}
6.4 數組的擴容與縮容
數組的擴容
題目:現有數組 int[] arr = new int[]{1,2,3,4,5}; ,現將數組長度擴容1倍,并將10,20,30三個數據添加到arr數組中,如何操作?
public class ArrTest1 {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arr = new int[]{1,2,3,4,5};int[] newArr = new int[arr.length << 1];for(int i = 0;i < arr.length;i++){newArr[i] = arr[i];}newArr[arr.length] = 10;newArr[arr.length + 1] = 20;newArr[arr.length + 2] = 30;arr = newArr;//遍歷arrfor (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {System.out.println(arr[i]);}}
}
數組的縮容
題目:現有數組 int[] arr={1,2,3,4,5,6,7}。現需刪除數組中索引為4的元素。
public class ArrTest2 {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7};//刪除數組中索引為4的元素int delIndex = 4;//方案1:/*//創建新數組int[] newArr = new int[arr.length - 1];for (int i = 0; i < delIndex; i++) {newArr[i] = arr[i];}for (int i = delIndex + 1; i < arr.length; i++) {newArr[i - 1] = arr[i];}arr = newArr;for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {System.out.println(arr[i]);}*///方案2:for (int i = delIndex; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {arr[i] = arr[i + 1];}arr[arr.length - 1] = 0;for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {System.out.println(arr[i]);}}
}

![[ctfshow web入門] web29](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[ctfshow web入門] web29)

![【GESP】C++二級練習 luogu-B3721 [語言月賽202303] Stone Gambling S](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/【GESP】C++二級練習 luogu-B3721 [語言月賽202303] Stone Gambling S)

:樹的直徑與重心)




)
)




)
![STM32單片機入門學習——第26節: [9-2] USART串口外設](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/STM32單片機入門學習——第26節: [9-2] USART串口外設)
)
