前言
歡迎來到我的博客
個人主頁:北嶺敲鍵盤的荒漠貓-CSDN博客
一、Django視圖是什么?
視圖(View) 是Django處理HTTP請求的核心組件。它接收一個HttpRequest對象,處理業務邏輯,并返回一個HttpResponse對象(如網頁、JSON數據、重定向等)。
1. 視圖的兩種寫法
-
函數視圖(FBV,Function-Based Views) :用Python函數實現。
from django.http import HttpResponsedef hello(request):return HttpResponse("Hello World!")
-
類視圖(CBV,Class-Based Views) :用類的方法處理請求(更結構化,適合復用)。
from django.views import View from django.http import HttpResponseclass HelloView(View):def get(self, request):return HttpResponse("GET請求示例")def post(self, request):return HttpResponse("POST請求示例")
二、編寫第一個視圖:詳細步驟
1. 創建視圖函數
在views.py中定義一個處理請求的函數:
# myapp/views.py
from django.http import HttpResponsedef home_page(request):return HttpResponse("<h1>歡迎來到我的網站!</h1>")
2. 配置URL路由
在urls.py中將URL路徑映射到視圖:
# myproject/urls.py
from django.urls import path
from myapp import viewsurlpatterns = [path('', views.home_page, name='home'), # 根路徑指向home_page視圖
]
3. 運行開發服務器
python manage.py runserver
訪問 [http://127.0.0.1:8000](http://127.0.0.1:8000) 即可看到頁面。
三、深入理解請求(HttpRequest)和響應(HttpResponse)
1. HttpRequest對象:包含請求的所有信息
-
常用屬性:
request.method:請求方法(GET、POST等)request.GET:GET請求的參數(字典形式)request.POST:POST請求的表單數據request.FILES:上傳的文件request.user:當前登錄用戶(需啟用認證中間件)
-
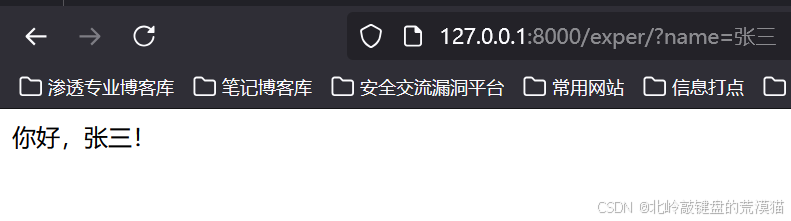
示例:處理GET請求參數
def greet(request):name = request.GET.get('name', '游客') # 獲取name參數,默認值'游客'return HttpResponse(f"你好,{name}!")
?
2. HttpResponse對象:返回內容給瀏覽器
-
常見用法:
- 返回文本:
HttpResponse("文本內容") - 返回HTML:
HttpResponse("<h1>標題</h1>") - 返回JSON:
JsonResponse({'data': 'xxx'}) - 重定向:
HttpResponseRedirect('/new-url/')
- 返回文本:
-
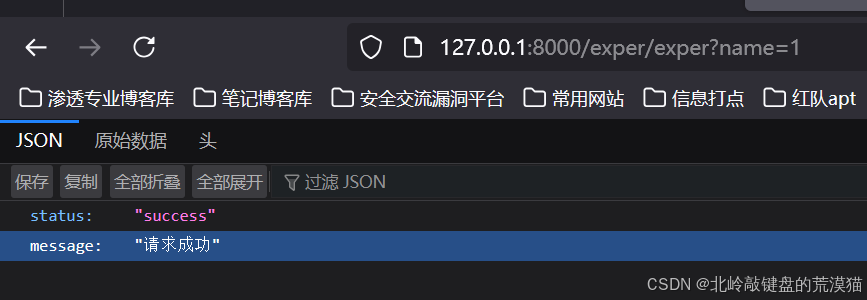
示例:返回JSON數據
from django.http import JsonResponsedef json_example(request):data = {'status': 'success', 'message': '請求成功'}return JsonResponse(data)
四、函數視圖(FBV)的完整流程
1. 處理GET和POST請求
def contact(request):if request.method == 'POST':# 處理表單提交name = request.POST.get('name')email = request.POST.get('email')print(f"收到來自{name} ({email}) 的消息")return HttpResponseRedirect('/thanks/') # 重定向到感謝頁面else:# 顯示空表單return render(request, 'contact.html')
2. 渲染模板(Template)
使用render()函數將數據傳遞到HTML模板:
from django.shortcuts import renderdef article_list(request):articles = Article.objects.all() # 假設Article是模型return render(request, 'articles/list.html', {'articles': articles})
模板文件 articles/list.html:
{% for article in articles %}<h2>{{ article.title }}</h2><p>{{ article.content }}</p>
{% endfor %}
五、類視圖(CBV)的用法詳解
1. 基本結構
from django.views import View
from django.http import HttpResponseclass MyView(View):def get(self, request):# 處理GET請求return HttpResponse("GET請求")def post(self, request):# 處理POST請求return HttpResponse("POST請求")
2. 在URL中使用類視圖
# urls.py
urlpatterns = [path('myview/', MyView.as_view(), name='my-view'),
]
3. 類視圖的優勢:復用與擴展
- 繼承內置通用視圖(如
ListView,DetailView) - 重寫方法自定義行為:
class ArticleListView(ListView):model = Article # 關聯模型template_name = 'articles/list.html' # 指定模板context_object_name = 'article_list' # 模板中使用的變量名def get_queryset(self):# 過濾已發布的文章return Article.objects.filter(status='published')
六、通用視圖(Generic Views)快速入門
Django內置了處理常見場景的類視圖,極大簡化代碼。
概念:
通用視圖(Generic Views)是Django為解決Web開發中重復模式設計的"快捷工具包",它能讓你用極簡代碼實現以下常見功能:
- 顯示對象列表(如商品列表、文章列表)
- 展示單個對象詳情(如用戶詳情頁)
- 處理表單創建/修改對象(如新建訂單)
- 日期歸檔頁面(如按月份展示文章)
- 刪除對象前的確認操作
傳統函數視圖需要手動處理數據庫查詢、模板渲染等細節,而通用視圖通過"約定優于配置"原則自動完成這些基礎工作
1. ListView:顯示對象列表
from django.views.generic import ListViewclass BookListView(ListView):model = Book # 自動獲取所有Book對象template_name = 'books/book_list.html' # 默認模板:books/book_list.htmlcontext_object_name = 'books' # 模板中變量名(默認object_list)
2. DetailView:顯示單個對象詳情
from django.views.generic import DetailViewclass BookDetailView(DetailView):model = Book# 默認模板:books/book_detail.html# 通過URL中的pk或slug獲取對象(如 /books/1/)
3. 表單處理:CreateView/UpdateView
from django.views.generic.edit import CreateView
from django.urls import reverse_lazyclass BookCreateView(CreateView):model = Bookfields = ['title', 'author', 'price'] # 表單字段template_name = 'books/book_form.html'success_url = reverse_lazy('book-list') # 提交成功后跳轉的URL
七、實際場景案例
1. 用戶登錄視圖
from django.contrib.auth import authenticate, login
from django.shortcuts import render, redirectdef login_view(request):if request.method == 'POST':username = request.POST['username']password = request.POST['password']user = authenticate(request, username=username, password=password)if user is not None:login(request, user)return redirect('home')else:return render(request, 'login.html', {'error': '用戶名或密碼錯誤'})return render(request, 'login.html')
2. 文件上傳
def upload_file(request):if request.method == 'POST' and request.FILES['file']:uploaded_file = request.FILES['file']# 保存文件到服務器with open(f'uploads/{uploaded_file.name}', 'wb+') as destination:for chunk in uploaded_file.chunks():destination.write(chunk)return HttpResponse("文件上傳成功!")return render(request, 'upload.html')
八、常見問題與調試技巧
1. 404錯誤處理
- 使用
get_object_or_404替代get:from django.shortcuts import get_object_or_404def book_detail(request, pk):book = get_object_or_404(Book, pk=pk)return render(request, 'books/detail.html', {'book': book})
2. 調試視圖
- 打印請求信息:
def debug_view(request):print("請求方法:", request.method)print("GET參數:", request.GET)print("用戶:", request.user)return HttpResponse("查看控制臺輸出")
3. 單元測試
from django.test import TestCase, Clientclass ViewTests(TestCase):def test_home_page(self):client = Client()response = client.get('/')self.assertEqual(response.status_code, 200)self.assertContains(response, "歡迎")
九、最佳實踐總結
-
選擇合適的視圖類型:
- 簡單邏輯用函數視圖(FBV)
- 復雜或重復邏輯用類視圖(CBV)
-
保持視圖簡潔:
- 業務邏輯抽離到單獨模塊(如
utils.py) - 使用通用視圖減少重復代碼
- 業務邏輯抽離到單獨模塊(如
-
安全注意事項:
- 始終驗證用戶輸入
- 使用
@login_required限制敏感操作 - 啟用CSRF保護(表單中加
{% csrf_token %})
-
性能優化:
- 使用
select_related和prefetch_related優化數據庫查詢 - 緩存頻繁訪問的視圖(如使用
@cache_page裝飾器)
- 使用

)
)




)
![STM32單片機入門學習——第26節: [9-2] USART串口外設](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/STM32單片機入門學習——第26節: [9-2] USART串口外設)
)

)


)


)

)
