題目
給定一個整數數組 nums 和一個目標值 target,請你在該數組中找出和為目標值的那 兩個 整數,并返回他們的數組下標。
你可以假設每種輸入只會對應一個答案。但是,數組中同一個元素不能使用兩遍。
示例:
給定 nums = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9
因為 nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9
所以返回 [0, 1]
思路
暴力的解法是兩層for循環查找,時間復雜度是O(n^2)。
public class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++) {
if (nums[i] + nums[j] == target) {
return new int[] {i, j};
}
}
}
// 按照題目描述,這里不會運行到,因為總是會有一個解
throw new IllegalArgumentException(“No two sum solution”);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {Solution solution = new Solution();int[] nums = {2, 7, 11, 15};int target = 9;int[] result = solution.twoSum(nums, target);System.out.println("Indices: [" + result[0] + ", " + result[1] + "]");
}
}
當我們需要查詢一個元素是否出現過,或者一個元素是否在集合里的時候,就要第一時間想到哈希法。
需要使用 key value結構來存放,key來存元素,value來存下標,那么使用map正合適。
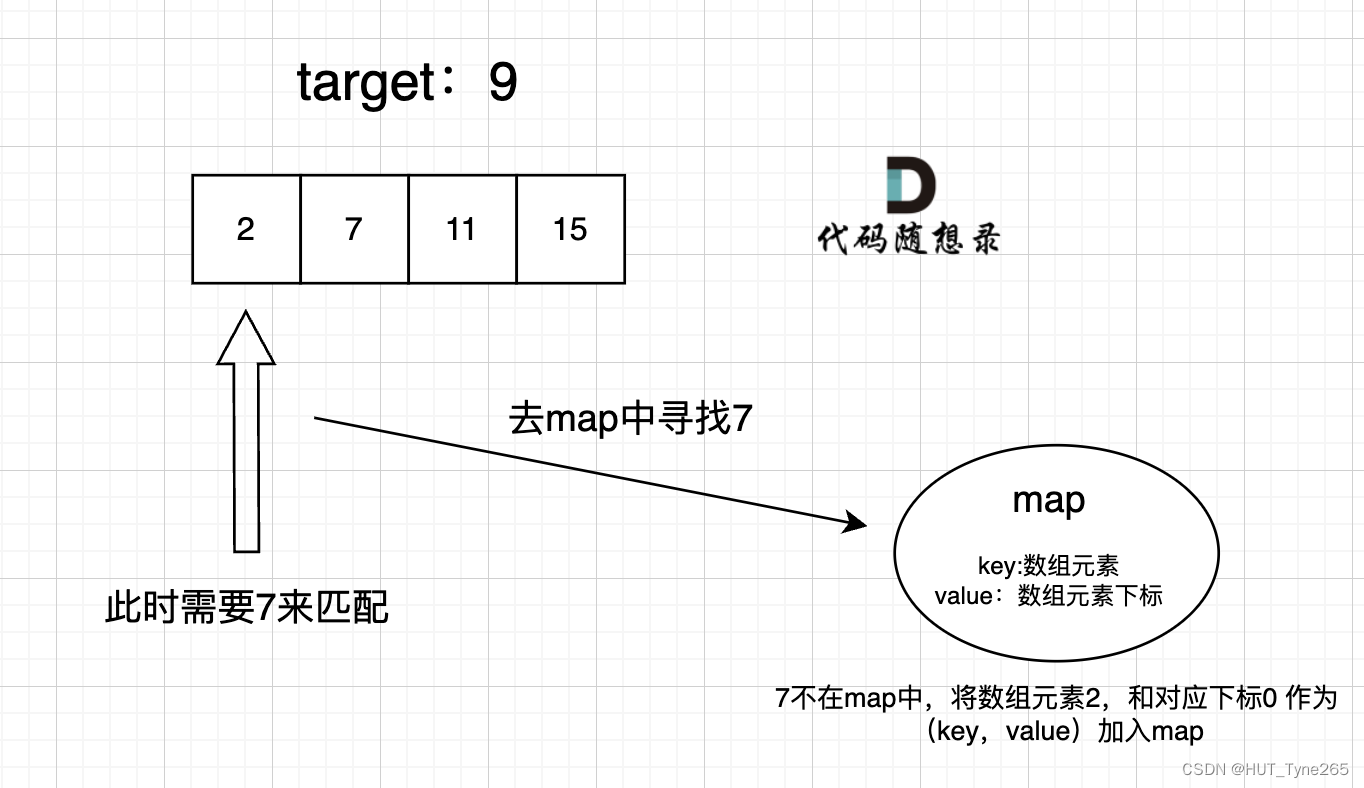
 C++代碼:
C++代碼:
class Solution {
public:
vector twoSum(vector& nums, int target) {
std::unordered_map <int,int> map;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
// 遍歷當前元素,并在map中尋找是否有匹配的key
auto iter = map.find(target - nums[i]);
if(iter != map.end()) {
return {iter->second, i};
}
// 如果沒找到匹配對,就把訪問過的元素和下標加入到map中
map.insert(pair<int, int>(nums[i], i));
}
return {};
}
};
時間復雜度: O(n)
空間復雜度: O(n)
Java
//使用哈希表
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int[] res = new int[2];
if(nums == null || nums.length == 0){
return res;
}
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
int temp = target - nums[i]; // 遍歷當前元素,并在map中尋找是否有匹配的key
if(map.containsKey(temp)){
res[1] = i;
res[0] = map.get(temp);
break;
}
map.put(nums[i], i); // 如果沒找到匹配對,就把訪問過的元素和下標加入到map中
}
return res;
}
//使用雙指針
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int m=0,n=0,k,board=0;
int[] res=new int[2];
int[] tmp1=new int[nums.length];
//備份原本下標的nums數組
System.arraycopy(nums,0,tmp1,0,nums.length);
//將nums排序
Arrays.sort(nums);
//雙指針
for(int i=0,j=nums.length-1;i<j;){
if(nums[i]+nums[j]<target)
i++;
else if(nums[i]+nums[j]>target)
j–;
else if(nums[i]+nums[j]==target){
m=i;
n=j;
break;
}
}
//找到nums[m]在tmp1數組中的下標
for(k=0;k<nums.length;k++){
if(tmp1[k]==nums[m]){
res[0]=k;
break;
}
}
//找到nums[n]在tmp1數組中的下標
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
if(tmp1[i]==nums[n]&&i!=k)
res[1]=i;
}
return res;
}

 葉子游戲新聞)





)

 Object Pascal 學習筆記---第14章泛型第1節(泛型鍵值對))

)
:文件管理部分)





)
