?中介者模式讓多對多的復雜引用關系變成一對多,同時能通過中間類來封裝多個類中的行為,觀察者模式在目標狀態更新時能自動通知給訂閱者,模版方法模式則是控制方法的執行順序,子類在不改變算法的結構基礎上可以擴展功能實現。
1 中介者模式
需求:1)系統中對象之間存在復雜的引用關系,比如一對多,多對多等。系統結構耦合度很高,結構混亂且難以理解。2)想通過一個中間類來封裝多個類中的行為,而又不想生成太多的子類。在中間類中定義對象交互的公共行為。
1.1 中介者模式介紹
用一個中介對象來封裝一系列的對象交互。使得各個對象不需要顯式地相互引用,從而使其耦合度松散,而且可以獨立地改變它們之間的交互。
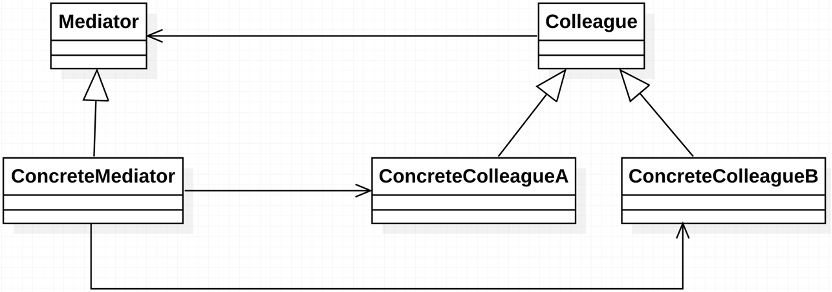
圖 中介者模式 UML
需求描述:在前端開發中,有三個組件 Button、View, 及Text. View 用來展示信息,Text 用于輸入編輯信息,Button用來提交更新。用戶在Text輸入好內容后,點擊Button后,內容會更新到View. 而點擊View時,會把內容輸入到Text。

圖 需求分析圖
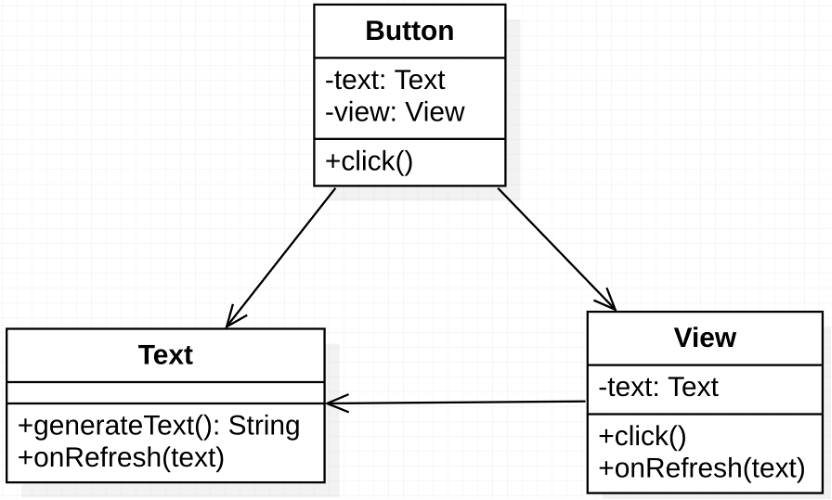
圖 需求分析UML
public class NoMediatorPattern {public static void main(String[] args) {Text text = new Text();Button button = new Button();View view = new View();button.setText(text);button.setView(view);view.setText(text);button.click();view.click();button.click();}private static class Button {private Text text;private View view;public void setText(Text text) {this.text = text;}public void setView(View view) {this.view = view;}void click() {if (text != null && view != null) {view.onRefresh(text.generateText());}}}private static class Text {private String content;private String generateText() {if (content == null) content = "";Random random = new Random();content += random.nextInt();return content;}void onRefresh(String text) {content = text;}}private static class View{private Text text;private String content;public void setText(Text text) {this.text = text;}void click() {if (text != null) {text.onRefresh(content);}}void onRefresh(String text) {this.content = text; // 更新信息System.out.println("View中顯示信息:" + text);}}}上面代碼中,需要考慮Button 與 Text、View,View 與Text 的交互。這使得系統邏輯變得更復雜。
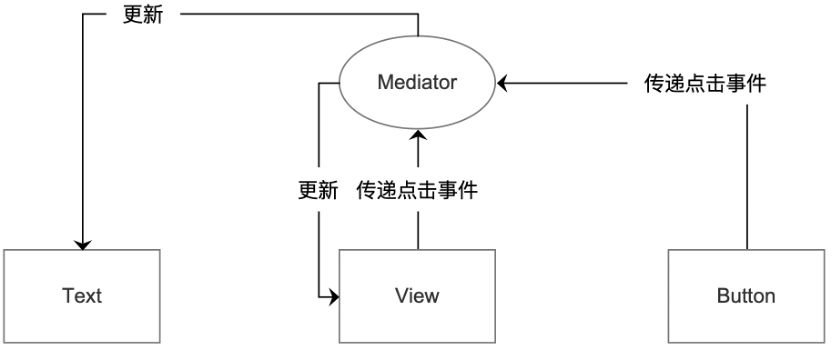
圖 中介者模式思維下的需求分析
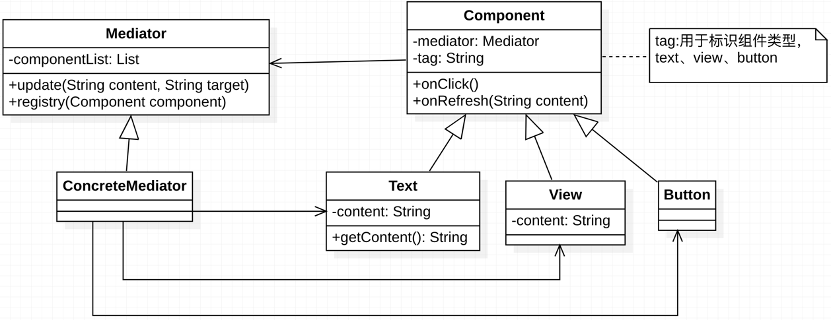
圖 中介者模式思維下的 UML
中介者模式下,只需要考慮中介者與各同事類的交互。
public class MediatorPattern {public static void main(String[] args) {Mediator mediator = new ContentMediator();Component text = new Text(mediator, "text");Component button = new Button(mediator,"button");Component view = new View(mediator,"view");mediator.registry(text);mediator.registry(button);mediator.registry(view);button.onClick();button.onClick();view.onClick();button.onClick();}private static abstract class Mediator {protected final Set<Component> components = new HashSet<>();public void registry(Component component) {if (component != null) {components.add(component);}}abstract void update(String content,String target);}private static class ContentMediator extends Mediator{@Overridepublic void update(String content,String target) {if (content == null) {Text text = getText();if (text == null) throw new RuntimeException("沒有更新內容");content = text.getContent();}for (Component component : components) {if (component.getTag().equals(target)) {component.onRefresh(content);}}}private Text getText() {for (Component component : components) {if ("text".equals(component.getTag())) return (Text) component;}return null;}}private static abstract class Component {protected final Mediator mediator;private final String tag;protected Component(Mediator mediator, String tag) {this.mediator = mediator;this.tag = tag;}public String getTag() {return tag;}abstract void onClick();abstract void onRefresh(String content);}private static class Text extends Component {private String content;protected Text(Mediator mediator, String tag) {super(mediator, tag);}@Overridevoid onClick() { // 輸入操作throw new RuntimeException("暫不支持Text的點擊事件");}@Overridevoid onRefresh(String content) {this.content = content;}public String getContent() {Random random = new Random();String temp = content;if (temp == null) temp = "";temp += random.nextInt() + "@";content = null;return temp;}}private static class View extends Component {private String content;protected View(Mediator mediator, String tag) {super(mediator, tag);}@Overridevoid onClick() {mediator.update(content,"text");}@Overridevoid onRefresh(String content) {this.content = content;System.out.println("view更新:"+ content);}}private static class Button extends Component {protected Button(Mediator mediator, String tag) {super(mediator, tag);}@Overridevoid onClick() {mediator.update(null,"view");}@Overridevoid onRefresh(String content) {throw new RuntimeException("暫不支持Button的更新操作");}}}1.2 優缺點
優點:
- 簡化了對象之間的交互,將原本多對多的交互改成一對多。使得對象之間解耦。
- 可以通過中介者類來擴展對象的交互行為,當需要添加或改變交互行為時,只需要添加對應的中介者子類即可,符合開閉原則。
- 同事類可以更專注自身業務,而不必關心與其他同事類的交互。
缺點:
- 中介者類包含同事類之間大量的交互細節,使得該類變得非常復雜,不符合單一職責原則。
- 中介者類與同事類的耦合度高。
2 觀察者模式
需求:當目標更新時,能自動通知給訂閱者。
2.1 觀察者模式介紹
當目標對象的狀態發生改變時,它的所有觀察者都會收到通知。
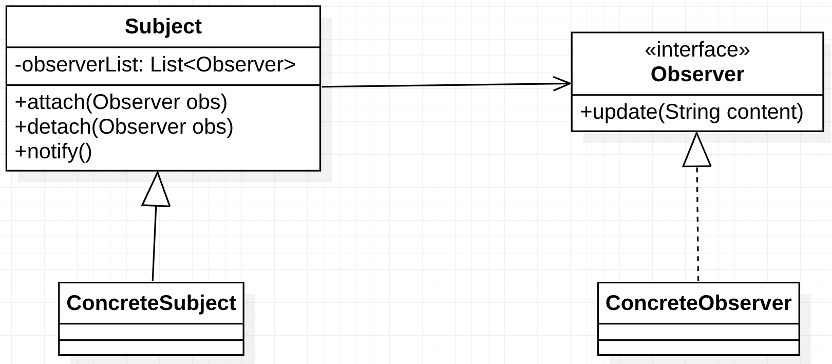
圖 觀察者模式 UML
public class ObserverPattern {public static void main(String[] args) {Subject subject = new School();Observer observer1 = new Teacher();Observer observer2 = new Student();subject.attach(observer1);subject.attach(observer2);subject.notifyObserverList("快高考啦!");subject.notifyObserverList("六一放假");}private static abstract class Subject {protected final Set<Observer> observerList = new HashSet<>();public void attach(Observer observer) {observerList.add(observer);}public void detach(Observer observer) {observerList.remove(observer);}public void notifyObserverList(String content) {beforeNotify(content);for (Observer observer : observerList) observer.update(content);afterNotify(content);}public abstract void beforeNotify(String content);public abstract void afterNotify(String content);}private static class School extends Subject {@Overridepublic void beforeNotify(String content) {System.out.println("通知時間:" + new Date());}@Overridepublic void afterNotify(String content) {System.out.println("通知完成");}}private interface Observer {void update(String content);}private static class Student implements Observer {@Overridepublic void update(String content) {if (content.contains("放假")) System.out.println("學生,耶耶耶!");else System.out.println("學生,哦哦哦");}}private static class Teacher implements Observer {@Overridepublic void update(String content) {System.out.println("老師,收到:" + content);}}}2.2 優缺點
優點:
- 當目標狀態更新時,能自動發生通知給訂閱者。
- 觀察者與被觀察者耦合度低,符合依賴倒置原則。
缺點:
- 當觀察者數量較多時,通知耗時會加長。一個觀察者的卡頓會影響整體執行效率
3 模版方法模式
需求:對方法的執行順序有要求,而某些特定方法由子類去實現。例如想寫排序算法,算法內部中方法的執行順序相同,但具體排序算法由不同子類實現。
3.1 模版方法模式介紹
定義一個操作中的算法框架,將一些步驟延遲到子類中,子類在不改變算法的結構基礎上重定義該算法的某些特定步驟。
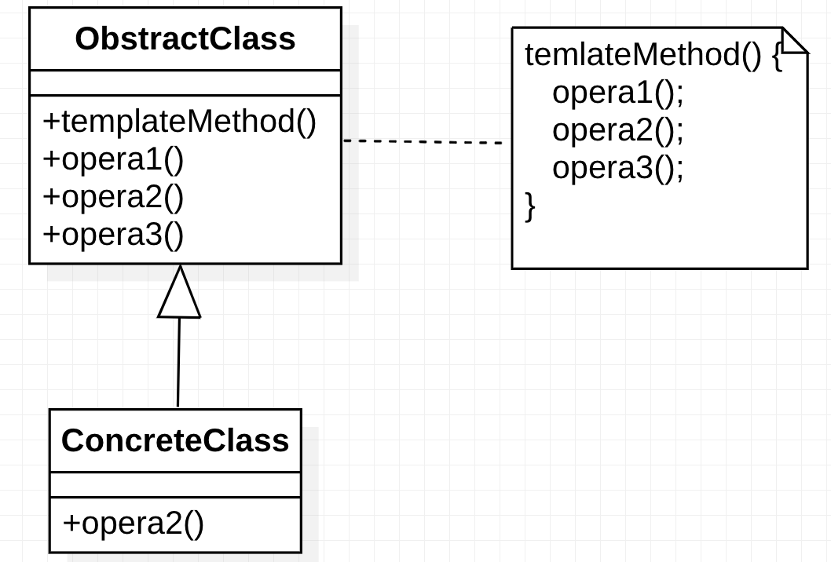
圖 模版方法模式 UML
public class TemplateMethodPattern {public static void main(String[] args) {Worker programmer = new Programmer();programmer.work();}private static abstract class Worker {public void work() {punch("上班");duty();punch("下班");}protected abstract void duty();protected void punch(String content) {System.out.println("打卡:" + content);}}private static class Programmer extends Worker {@Overrideprotected void duty() {System.out.println("寫bug AND 解決bug");}}}3.2 優缺點
優點:
- 可以控制方法執行順序,當要增加新的方法實現時,只需要添加特定子類。符合開閉原則及里氏替換原則。
缺點:
- 增加了類的個數。




【1 Fuse】)


 ----------- 環境搭建)





![[數據集][目標檢測]貓狗檢測數據集VOC+YOLO格式8291張2類別](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[數據集][目標檢測]貓狗檢測數據集VOC+YOLO格式8291張2類別)





