一、概述?
1.1緩存介紹
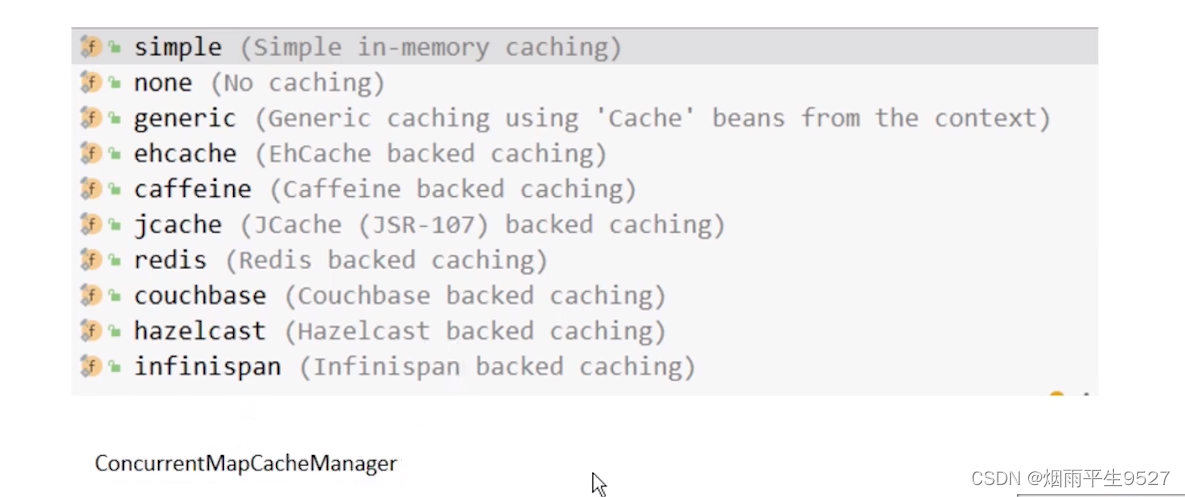
Spring提供了一套cache緩存抽象(注解/接口),使基于spring緩存的使用與實現解耦
- 默認實現,Spring JDK ConcurrentMap-based?Cache
- 第三方實現,caffeine/Ehcache/Redis等
https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/reference/html/integration.html#cache
Spring將緩存應用于方法,從而根據緩存中可用信息減少方法執行次數
即,每次調用目標方法時,spring基于緩存行為,檢查是否包含緩存數據。有則直接返回緩存結果,而不再實際調用目標方法。沒有則調用目標方法,并將方法返回結果置于緩存。從而下次調用目標方法時,基于緩存行為直接返回緩存結果
由于需要的數據對象已經保存在內存,從而可極大減少CPU執行/降低IO操作/減少數據庫請求等?
緩存數據,必須可重復使用;對于業務,緩存邏輯必須透明。即,不實際調用目標方法不會造成任何業務影響
Spring緩存基于AOP切面的實現
 1.2SpringCache 特點
1.2SpringCache 特點
- 通過少量的配置annotation 即可使得既有代碼支持緩存
- 支持開箱即用Out-Of-The-Box, 即不用安裝和部署額外第三方組件即可使用緩存
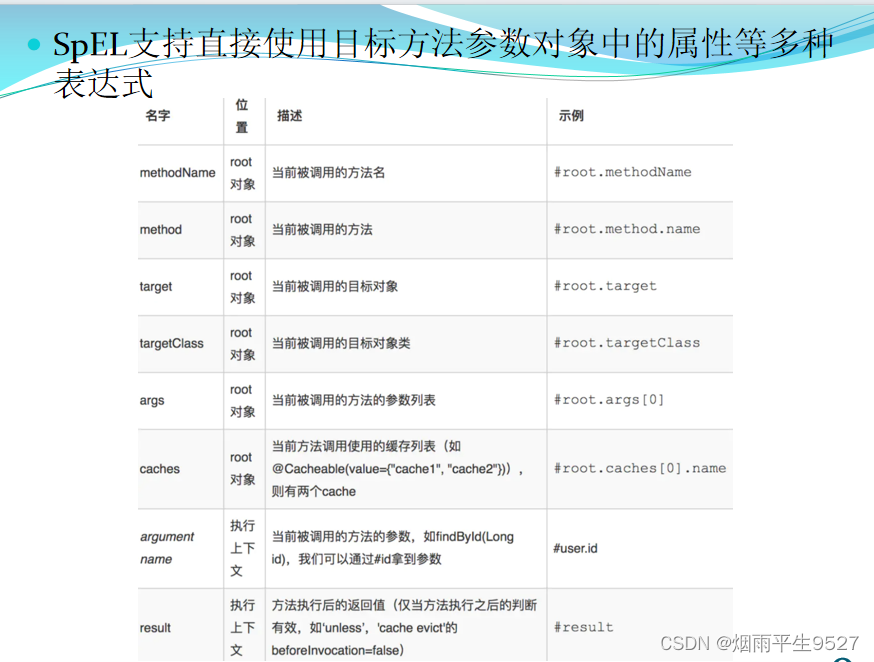
- 支持 Spring Express Language,能使用對象的任何屬性或者方法來定義緩存的key和condition
- 支持AspectJ,并通過其實現任何方法的緩存支持
- 支持自定義key和自定義緩存管理者,具有相當的靈活性和擴展性
- 支持各種緩存實現,如對象,對象列表,默認基ConcurrentMap實現的 ConcurrentMapCache, 同時支持其他緩存實現
綜合來說,springCacho并不像正常緩存那樣存儲數和返回結果作為一個鍵值對存放在緩存中,等到下等數和返回結果作為一個新的參數來調用該方法時,將會把該方法參法,而是直接從緩存中獲取結果進行返回,從而實現緩存的效果
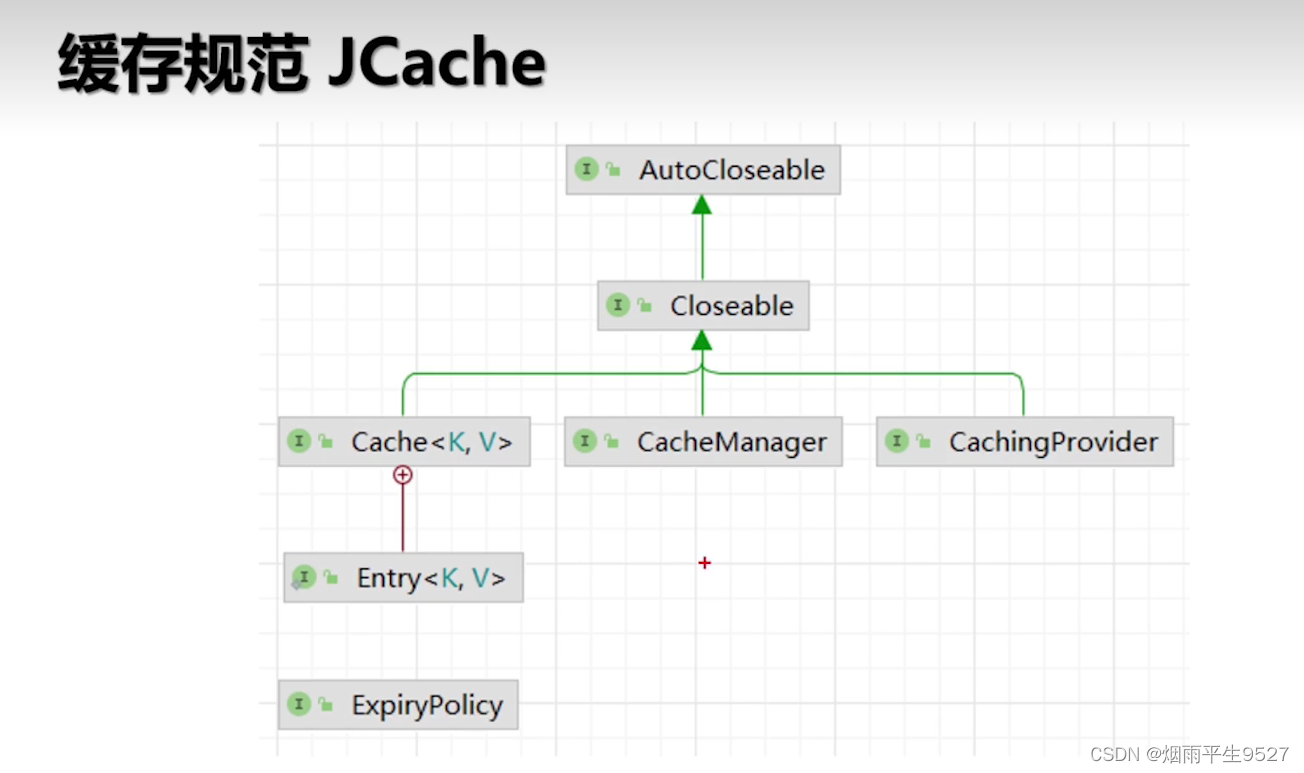
1.3幾個重要注解
@EnableCaching
@Cacheable
- ·該注解用于標記緩存,就是對使用注解的位置進行緩存
- ·該注解可以在方法或者類上進行標記,在類上標記時,該類所有方法都支持緩存
@Cacheable使用時通常搭配三個屬性使用
- ·value,用來指定Cache的名稱,就是存儲哪個Cache上,簡單來說是cache的命名空間或者大的前綴
- ·key,用于指定生成緩存對應的key,如果沒指定,則會默認策略生成key,也可以使用springEL編寫,默認是方法參數組合


// 使用@Cacheable注解對findUser方法進行緩存,緩存名稱為"users",緩存的key為用戶的id
@Cacheable(value="users", key="#user.id")
public User findUser(User user){return user;
}// 使用@Cacheable注解對findUser方法進行緩存,緩存名稱為"users",緩存的key為方法參數id
@Cacheable(value="users", key="#root.args[0]")
public User findUser(String id){return user;
}
- condition,用來指定當前緩存的觸發條件,可以使用springEL編寫,如下代碼,則當user.id為偶數時才會觸發緩存 會觸發緩存

@Cacheable(value="users", key="#user.id",condition="#user.id%2==0")
public User findUser(User user){return user;
}
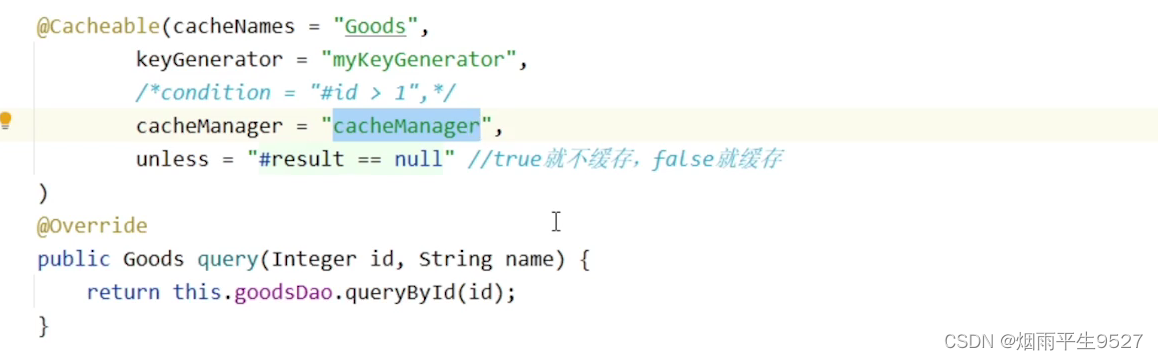
cacheManager
cacheManager, 用于指定當前方法或類使用緩存時的配置管理器,通過cacheManager的配置,可以為不同的方法使用不同的緩存策略,比如有的對象的緩存時間短,有的緩存的長,可以通過自定義配置 cacheManager來實現
@Configuration // 聲明這是一個配置類
@EnableCaching // 開啟緩存功能
public class SpringCacheConfig {@Bean // 定義一個Bean對象public CacheManager cacheManager() {// 創建Caffeine緩存管理器CaffeineCacheManager manager = new CaffeineCacheManager();// 創建緩存配置策略Cache<Object, Object> cache = Caffeine.newBuilder().expireAfterWrite(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS) // 設置緩存過期時間為5秒.maximumSize(200) // 設置緩存最大容量為200個元素.build();// 為指定名稱的緩存,指定配置manager.registerCustomCache("user", cache);// 允許緩存值為空的鍵值對。避免緩存穿透manager.setAllowNullValues(true);// 將管理器注入容器,替換默認管理器對象return manager;}
}
@CachePut
該注解將標記的方法的返回值放入緩存中,使用方法與@Cacheable一樣,通常@CachePut放在數據更新的操作上,舉例來說,當getByUserid這樣一方法上使用了以userid為key的緩存時,如果更新了這條數據,該key對應的數據是不是要同步變更呢?
答案是肯的,于是,我們就需要在更新數據的地方添加@CachePut注解,當updateByUserid觸發之后,getByUserid上面的key對應的緩存對象數據也能同步變更

@CacheEvict
- ·該注解用于清理緩存數據
- ·使用在類上時,清除該類所有方法的緩存
- ·@CacheEvict同樣擁有@Cacheable三個屬性,同時還有一個allEntries屬性,該屬性默認為false,當為true時,刪除該值所有緩存
@CacheEvict在實際使用中需要重點關注,比如一開始我們給用戶組,角色,部門等與用戶查詢相關的業務上面添加了key的時候,當一個userid對應的這條數據被清理的時候,那么關聯的key,即所說的用戶組,部門角色等關聯的用戶數據都需要一同清理
 caching
caching
-
組合多個cache注解一起使用

-
允許在同一方法上使用以上3個注解的組合


@CacheConfig

補充說明
以上簡單介紹了springcache中的幾個重要注解,以及各自的作用,通常來講,在開發過程中,使用springcache也就是在這些注解打交道,里面有一個點值得注意就是,關于方法級別上的key的使用規范和命名規范問題,這里可以關注和參考下springEL的寫法規范
二、與springboot的整合(redis版)
2.0應用場景
redis 應用場景
1.利用redis中字符串類型完成項目中手機驗證碼存儲的實現
2.利用redis中字符串類型完成具有失效性業務功能12306 淘寶 訂單還有:40分鐘
3.利用redis 分布式集群系統中Session共享 memcache 內存數據存儲上限 數據類型比較簡單 redis 內存 數據上限 數據類型豐富
4.利用redis 可排序set類型元素 分數排行榜之功能 dangdang 銷量排行 sales (商品id,商品銷量)
5.利用redis 分布式緩存 實現
6.利用redis存儲認證之后token信息 微信小程序 微信公眾號 用戶 openid令牌( token)超時
7.利用redis 解決分布式集群系統中分布式鎖問題 redistrict單線程序 n=20定義
2.1添加pom依賴
需要說明的是,springcache提供了多種緩存的實現,其中與redis的整合比較符合大家對redis的使用習慣,同時也更進一步了解springcache在redis中存儲的結構,因此這里需引入springboot-redis的依賴
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId></dependency>
2.2yml依賴
spring:application:name: redis-examplesjackson:default-property-inclusion: non_null # springmvc忽略空值屬性data:redis:host: port: password: database: 1cache: # 整合cache redis。代碼聲明詳細配置時無效redis:cache-null-values: true # 默認值,可省略。緩存空數據,避免緩存穿透time-to-live: 50000 # 單位毫秒,50秒logging:level:root: warncom:yanyu:springcache: debugpattern:console: '%-5level %C.%M[%line] - %msg%n'
server:port: 80832.3自定義cacheManager
import java.time.Duration;@Configuration
@EnableCaching
@Slf4j
public class SpringCacheConfig {// 按默認jdk序列化對象。未聲明全局配置,緩存數據永不過期/*@Beanpublic CacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory cf) {// 全局配置RedisCacheConfiguration configG = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig().entryTtl(Duration.ofSeconds(120L));// 獨立配置RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig().entryTtl(Duration.ofSeconds(60L));RedisCacheManager manager = RedisCacheManager.builder(cf).cacheDefaults(configG).withCacheConfiguration("user", config).build();return manager;}*/// -----------------------------------// 持基于jackson的序列化,以及自定義緩存策略@Beanpublic CacheManager cacheManager(Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Object> serializer,RedisConnectionFactory cf) {// 全局配置:設置默認的緩存配置,包括過期時間和序列化方式RedisCacheConfiguration defaults = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig() // 獲取默認的緩存配置.entryTtl(Duration.ofMinutes(4)) // 設置緩存過期時間為4分鐘.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(serializer)); // 使用指定的序列化器進行序列化// 獨立的緩存配置:為特定的緩存區域設置配置,包括過期時間和序列化方式RedisCacheConfiguration userR = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig() // 獲取默認的緩存配置.entryTtl(Duration.ofMinutes(2)) // 設置緩存過期時間為2分鐘.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(serializer)); // 使用指定的序列化器進行序列化// 基于全局配置/獨立配置,創建redis緩存管理器RedisCacheManager manager = RedisCacheManager.builder(cf).cacheDefaults(defaults) // 應用全局配置.withCacheConfiguration("user", userR) // 為"user"緩存區域應用獨立配置.build(); // 構建緩存管理器實例return manager; // 返回緩存管理器實例}// 全局jackson-redis序列化配置。可直接注入到容器覆蓋默認配置@Beanpublic Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Object> jackson2JsonRedisSerializer() {// 創建 ObjectMapper 對象,用于配置序列化和反序列化的規則ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();// 設置序列化時忽略空值屬性mapper.setSerializationInclusion(JsonInclude.Include.NON_NULL);// 設置反序列化時忽略不存在的屬性,避免異常mapper.disable(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES);// 設置屬性訪問權限為任意可見性mapper.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);// 設置多態類型驗證器,允許子類作為父類處理PolymorphicTypeValidator ptv = BasicPolymorphicTypeValidator.builder().allowIfSubType(Object.class).build();// 激活默認的多態類型處理方式mapper.activateDefaultTyping(ptv, ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);// 設置日期時間序列化為 ISO 字符串格式,而非對象mapper.disable(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS);// 注冊 JavaTimeModule,支持 Java 8 日期時間類型mapper.registerModule(new JavaTimeModule());// 創建 Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer 對象,并設置 ObjectMapper 對象Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer serializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(mapper, Object.class);return serializer;}// ------------------------------------@Bean("cum") // 定義一個名為"cum"的Beanpublic RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory cf) {// 創建 ObjectMapper 對象,用于配置序列化和反序列化的規則ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();// 設置反序列化時忽略不存在的屬性,避免異常objectMapper.disable(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_IGNORED_PROPERTIES);objectMapper.disable(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES);// 設置序列化時忽略空值屬性objectMapper.setSerializationInclusion(JsonInclude.Include.NON_NULL);// 設置屬性訪問權限為任意可見性objectMapper.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);// 按ISO字符串序列化/反序列化日期時間,而非對象objectMapper.disable(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS);// 注冊 JavaTimeModule,支持 Java 8 日期時間類型objectMapper.registerModule(new JavaTimeModule());// 創建 Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer 對象,并設置 ObjectMapper 對象Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer serializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(objectMapper, Object.class);// 創建 RedisTemplate 對象,并設置序列化器、連接工廠等屬性RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(serializer);redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(serializer);redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(serializer);redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(serializer);redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(cf);return redisTemplate;}// ---------------------------------------------// 也可自定義RedisTemplate注入/*@Beanpublic RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory cf) {Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Object> serializer =new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(Object.class);ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();objectMapper.disable(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_IGNORED_PROPERTIES);objectMapper.disable(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES);objectMapper.setSerializationInclusion(JsonInclude.Include.NON_NULL);objectMapper.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);PolymorphicTypeValidator ptv =BasicPolymorphicTypeValidator.builder().allowIfSubType(Object.class).build();objectMapper.activateDefaultTyping(ptv, ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);serializer.setObjectMapper(objectMapper);RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(serializer);redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(serializer);redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(serializer);redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(serializer);redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(cf);return redisTemplate;}*//*@Beanpublic CacheManager cacheManager(RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate,RedisConnectionFactory cf) {// 全局配置RedisCacheConfiguration defaults = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig().entryTtl(Duration.ofMinutes(4)).serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(redisTemplate.getValueSerializer()));// 獨立的緩存配置RedisCacheConfiguration userR = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig().entryTtl(Duration.ofMinutes(2)).serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(redisTemplate.getValueSerializer()));// 基于全局配置/獨立配置,創建redis緩存管理器RedisCacheManager manager = RedisCacheManager.builder(cf).cacheDefaults(defaults).withCacheConfiguration("user", userR).build();return manager;}*/// -------------------------------}
2.4搭建基本框架
見3.5
2.5測試
GET http://localhost:8083/api/users/1
###
GET http://localhost:8083/api/users/2
###PATCH http://localhost:8083/api/users
Content-Type: application/json{"id": "1","name": "小明","detail": "956"
}
###
DELETE http://localhost:8083/api/users/1
###
GET http://localhost:8083/api/users###
GET http://localhost:8083/api/userdtos/1###
POST http://localhost:8083/api/userdto/1三、與springboot的整合(Caffeine版)
2.1Caffeine介紹

2.2添加依賴
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>com.github.ben-manes.caffeine</groupId><artifactId>caffeine</artifactId></dependency>2.3添加yml配置
spring:cache:caffeine: # 如果在代碼聲明配置并注入緩存管理器,此處配置無效spec: expireAfterWrite=240s, maximumSize=200 # 設置Caffeine緩存的配置參數,過期時間為240秒,最大容量為200個元素logging:level: # 設置日志級別root: warn # 根日志級別為警告級別com:example: debug # 對于com.example包下的日志級別為調試級別pattern: # 設置日志輸出格式console: '%-5level %C.%M[%line] - %msg%n' # 控制臺日志輸出格式,包括日志級別、類名、方法名、行號和日志信息
2.4自定義cacheManager
@Configuration // 聲明這是一個配置類
@EnableCaching // 開啟緩存功能
public class SpringCacheConfig {@Bean // 定義一個Bean對象public CacheManager cacheManager() {// 創建Caffeine緩存管理器CaffeineCacheManager manager = new CaffeineCacheManager();// 創建緩存配置策略Cache<Object, Object> cache = Caffeine.newBuilder().expireAfterWrite(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS) // 設置緩存過期時間為5秒.maximumSize(200) // 設置緩存最大容量為200個元素.build();// 為指定名稱的緩存,指定配置manager.registerCustomCache("user", cache);// 允許緩存值為空的鍵值對。避免緩存穿透manager.setAllowNullValues(true);// 將管理器注入容器,替換默認管理器對象return manager;}
}
2.5搭建基礎框架
entity
@Getter
@Setter
@ToString
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Builder
public class Address {private int id;private String detail;private User user;
}@Getter
@Setter
@ToString
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Builder
public class User {private Long id;private String name;
}mapper
@Repository // 標記為Spring框架的持久層組件
public class UserMapper {private static final List<User> USERS; // 靜態用戶列表static { // 靜態代碼塊,用于初始化用戶列表User u1 = User.builder().id(1L).name("BO").build(); // 創建用戶1User u2 = User.builder().id(2L).name("SUN").build(); // 創建用戶2USERS = new ArrayList<>(); // 初始化用戶列表USERS.add(u1); // 添加用戶1到列表USERS.add(u2); // 添加用戶2到列表}// 根據用戶ID獲取用戶信息public User getUser(long uid) {return USERS.stream() // 使用Java 8的Stream API進行過濾操作.filter(u -> u.getId() == uid) // 過濾出ID等于給定ID的用戶.findFirst() // 獲取第一個匹配的用戶(如果存在).orElse(null); // 如果沒有匹配的用戶,返回null}// 更新用戶信息public User updateUser(User user) {for (int i = 0; i < USERS.size(); i++) { // 遍歷用戶列表if (Objects.equals(user.getId(), USERS.get(i).getId())) { // 如果找到匹配的用戶IDUSERS.set(i, user); // 更新用戶信息}}return user; // 返回更新后的用戶信息}// 獲取所有用戶信息public List<User> listUsers() {return USERS; // 返回用戶列表}
}
service
@Service // 標記為Spring框架的服務層組件
@Slf4j // 使用Lombok提供的日志功能
public class UserService {@Autowired // 自動注入UserMapper對象private UserMapper userMapper;@Cacheable(value = "user", key = "#uid") // 緩存用戶信息,key為用戶IDpublic User getUser(long uid) {User user = userMapper.getUser(uid); // 從UserMapper獲取用戶信息log.debug("called UserService getUser() user: {}", user); // 記錄調試日志return user; // 返回用戶信息}@Cacheable(value = "users") // 緩存所有用戶信息public List<User> listUsers() {return userMapper.listUsers(); // 從UserMapper獲取所有用戶信息}@CachePut(value = "user", key = "#user.id") // 更新緩存中的用戶信息// 以鍵值對緩存一個集合對象時,緩存對象是一個整體。無法修改其中某一個元素// 因此清空整個集合緩存@CacheEvict(value = "users", allEntries = true)public User updateUser(User user) {User u = userMapper.updateUser(user); // 更新用戶信息log.debug("updateUser(), user: {}", u); // 記錄調試日志return user; // 返回更新后的用戶信息}@CacheEvict(value = "user", key = "#uid") // 刪除緩存中的用戶信息public void delUser(long uid) {// 從緩存刪除,沒有調用模擬的持久層刪除// 因此會實際調用getUser()方法,重新從持久層獲取}
}
controller
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/")
public class MyController {@Autowiredprivate UserService userService;@GetMapping("users/{uid}")public User getUser(@PathVariable long uid) {return userService.getUser(uid);}@GetMapping("users")public List<User> listUsers() {return userService.listUsers();}@PatchMapping("users")public User patchUser(@RequestBody User user) {return userService.updateUser(user);}@DeleteMapping("users/{uid}")public void delUser(@PathVariable long uid) {userService.delUser(uid);}
}測試
GET http://localhost:8081/api/users/1
###
GET http://localhost:8081/api/users/2
###PATCH http://localhost:8081/api/users
Content-Type: application/json{"id": "1","name": "LIU"
}
###
DELETE http://localhost:8081/api/users/1
###
GET http://localhost:8081/api/users四、Ecache緩存
4.1Ecache緩存
- 基于Java的開源的使用最廣泛的緩存組件;
- 使用簡單,一個jar包,簡單配置,即可使用;
- 可以進程內緩存(內存),也可以進程外緩存(磁盤上持久化);
- 目前已經有三個系列版本,1.x(已經過時不用)、2.x和3.x;
- 著名的Hibernate、Shiro里面的緩存就采用了Ecache;
- Ecache還可以支持集群;
4.2使用場景
- 比較適合緩存一些不經常改變的數據;
- 對數據實時性要求不高的場景,多臺應用服務器中的緩存是不能進行實時同步的;
- 可以作為其他緩存如Redis的輔助方案,比如做Redis的二級緩存,作為Redis緩存宕機導致大量請求讀數據庫的解決方案;
4.3使用
添加相關依賴
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/net.sf.ehcache/ehcache --><dependency><groupId>net.sf.ehcache</groupId><artifactId>ehcache</artifactId><version>2.10.4</version></dependency>ehchche配置,關于ehcache的使用,大家可自行查找一下相關資料補習一下,用起來很簡單,只要xml的配置文件沒問題就可以,更深入的其實都在hcache的配置文件中,作為本地的堆緩存,在應對數據量不是特別大的場景,使用ehcache是個不錯的選擇,一般是配合redis和其他的緩存工具以一起使用,這里直接貼上,提供參考,
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="http://ehcache.org/ehcache.xsd"updateCheck="false"><!-- diskStore:ehcache其實是支持內存+磁盤+堆外內存,幾個層級的緩存 --><!-- 在這里設置一下,但是一般不用的 ,這里是基于磁盤的緩存--><diskStore path="java.io.tmpdir/Tmp_EhCache" /><!-- defaultCache,是默認的緩存策略 --><!-- 如果你指定的緩存策略沒有找到,那么就用這個默認的緩存策略 --><!-- external:如果設置為true的話,那么timeout就沒有效果,緩存就會一直存在,一般默認就是false --><!-- maxElementsInMemory:內存中可以緩存多少個緩存條目,在實踐中,你是需要自己去計算的,比如你計算你要緩存的對象是什么?有多大?最多可以緩存多少MB,或者多少個G的數據?除以每個對象的大小,計算出最多可以放多少個對象 --><!-- overflowToDisk:如果內存不夠的時候,是否溢出到磁盤 --><!-- diskPersistent:是否啟用磁盤持久化的機制,在jvm崩潰的時候和重啟之間,不用 --><!-- timeToIdleSeconds:對象最大的閑置的時間,如果超出閑置的時間,可能就會過期,我們這里就不用了,緩存最多閑置5分鐘就被干掉了 --><!-- timeToLiveSeconds:對象最多存活的時間,我們這里也不用,超過這個時間,緩存就過期,就沒了 --><!-- memoryStoreEvictionPolicy:當緩存數量達到了最大的指定條目數的時候,需要采用一定的算法,從緩存中清除一批數據,LRU,最近最少使用算法,最近一段時間內,最少使用的那些數據,就被干掉了 --><defaultCacheeternal="false"maxElementsInMemory="1000"overflowToDisk="false"diskPersistent="false"timeToIdleSeconds="300"timeToLiveSeconds="0"memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU" /><!-- 手動指定的緩存策略 --><!-- 比如你一個應用吧,可能要緩存很多種不同的數據,比如說商品信息,或者是其他的一些數據 --><!-- 對不同的數據,緩存策略可以在這里配置多種 --><cachename="local" eternal="false"maxElementsInMemory="1000"overflowToDisk="false"diskPersistent="false"timeToIdleSeconds="300"timeToLiveSeconds="0"memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU" /><!-- ehcache這種東西,簡單實用,是很快速的,1小時上手可以用在項目里了,沒什么難度的 --> <!-- ehcache這個技術,如果講深了,里面的東西還是很多的,高級的feature,但是我們這里就不涉及了 --> </ehcache>
 接下來是ehcache的配置類和redis的配置類,springbooti在啟動的時候會自動將這兩個配置類納入全局的bean容器管理中,
接下來是ehcache的配置類和redis的配置類,springbooti在啟動的時候會自動將這兩個配置類納入全局的bean容器管理中,
/*** 本地堆緩存配置類* @author asus*/
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class EhcacheConfig {@Beanpublic EhCacheManagerFactoryBean ehCacheManagerFactoryBean() {EhCacheManagerFactoryBean cacheManagerFactoryBean = new EhCacheManagerFactoryBean();cacheManagerFactoryBean.setConfigLocation(new ClassPathResource("ehcache.xml"));cacheManagerFactoryBean.setShared(true);return cacheManagerFactoryBean;}@Beanpublic EhCacheCacheManager eCacheCacheManager(EhCacheManagerFactoryBean bean) {return new EhCacheCacheManager(bean.getObject());}
}
/*** redis序列化bean* @author asus**/
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {@Beanpublic RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {StringRedisTemplate template = new StringRedisTemplate(factory);//定義value的序列化方式Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);template.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);template.setHashValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);template.afterPropertiesSet();return template;}}






)
:適配器模式——Adapter)










)


