每一步向前都是向自己的夢想更近一步,堅持不懈,勇往直前!
第一題:36. 有效的數獨 - 力扣(LeetCode)


題目要求我們進行判斷,我們不需要自己填寫,所以要一個標志位,來看當前的值是否在行、列、格中出現過,每當這時候可以考慮使用位掩碼。
class Solution {public boolean isValidSudoku(char[][] board) {int[] line = new int[9];// 行int[] col = new int[9];// 列int[] cell = new int[9];// 9宮格for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {// 如果當前位置沒有數字,不用判斷。if (board[i][j] == '.')continue;//使用位掩碼來記錄數字int shift = 1 << (board[i][j] - '0');// 確定第幾位int k = (i / 3) * 3 + j / 3;// 9宮格的第幾個。// 如果對應的位置只要有一個被標記過,說明有沖突,直接返回false。//&與要求兩邊完全相同才大于0,下面這一步在判斷是否有相同數字出現過if ((col[i] & shift) > 0 || (line[j] & shift) > 0|| (cell[k] & shift) > 0)return false;// 把當前位置所在的行,列以及9宮格都標記為該數字已經存在。//或|只要某一位是1,則都是1,所以不管原來的col[i]等是否為0,//反正判斷的時候還是判斷col[i] & shift,所以下面這樣寫正確//建議自己手動模擬一下col[i] |= shift;line[j] |= shift;cell[k] |= shift;}}return true;}
}第二題:37. 解數獨 - 力扣(LeetCode)


class Solution {//類似于dfs,要找到剛好唯一一組解,可能會涉及到已經放入的值回退的情況//直接使用空間換時間了,不回退直接判斷可不可以放,注意看兩層循環那個//if-for-return的邏輯:如果是'.' 那么能不能放數字,如果放了就繼續,否則return false//再注意看for循環里的邏輯,判斷這個數字放進去滿足數獨不,所以有一個isValidSudoku的判斷函數public void solveSudoku(char[][] board) {solveSudokuHelper(board);}private boolean solveSudokuHelper(char[][] board){for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++){ // 遍歷行for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++){ // 遍歷列if (board[i][j] != '.'){ // 跳過原始數字continue;}for (char k = '1'; k <= '9'; k++){ // (i, j) 這個位置放k是否合適if (isValidSudoku(i, j, k, board)){board[i][j] = k;if (solveSudokuHelper(board)){ // 如果找到合適一組立刻返回//注意這個地方的判斷,潛逃了兩層true的判斷return true;}board[i][j] = '.';}}return false;}}return true;}private boolean isValidSudoku(int row, int col, char val, char[][] board){//分別判斷行列格里是否存在相同元素for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++){if (board[row][i] == val){return false;}}for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++){if (board[j][col] == val){return false;}}int startRow = (row / 3) * 3;int startCol = (col / 3) * 3;for (int i = startRow; i < startRow + 3; i++){for (int j = startCol; j < startCol + 3; j++){if (board[i][j] == val){return false;}}}return true;}
}
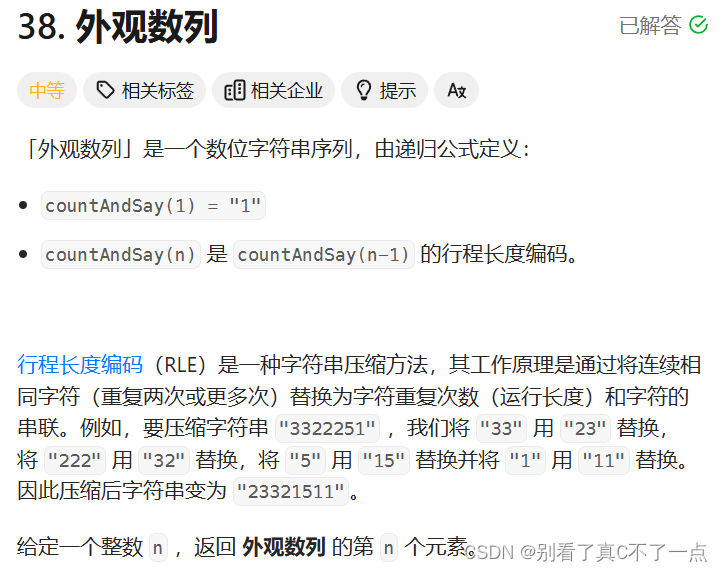
第三題:38. 外觀數列 - 力扣(LeetCode)
public class Solution {// countAndSay 方法用于生成一個特定的字符串序列。// 序列的第 n 項是通過將第 n-1 項字符串中的連續相同字符進行計數和描述來生成的。public static String countAndSay(int n) {// 遞歸出口:如果 n 為 1,則返回字符串 "1",這是序列的第一項。if (n == 1) {return "1";}// 遞歸調用:如果 n 大于 1,則先遞歸調用 countAndSay(n - 1) 生成第 n-1 項,// 然后調用 transfer 方法將第 n-1 項轉換為第 n 項。return transfer(countAndSay(n - 1));}// transfer 方法接受一個字符串 s 作為輸入,并生成下一個字符串。// 它通過計數 s 中連續出現的相同字符,并將計數和字符拼接起來形成新的字符串。public static String transfer(String s) {StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); // 使用 StringBuilder 來構建最終的字符串。int count = 1; // 初始化計數器,用于計數連續相同字符的數量。int length = s.length(); // 獲取輸入字符串的長度。int i;char temp = s.charAt(0); // 初始化臨時變量 temp 為字符串的第一個字符。// 遍歷輸入字符串 s。for (i = 1; i <= length; i++) {// 如果當前字符 temp 與 s.charAt(i) 相同,繼續計數。while (i < length && temp == s.charAt(i)) {count++; // 連續字符計數加 1。i++; // 移動到下一個字符。}// 如果 i < length,說明找到了不同的字符,更新 temp。if (i < length) {temp = s.charAt(i);}// 將當前字符的計數和字符本身添加到 StringBuilder 中。sb.append(count); // 添加計數。sb.append(s.charAt(i - 1)); // 添加字符本身。// 重置計數器,為下一個字符的計數做準備。count = 1; }// 返回構建好的字符串。return sb.toString();}
}第四題:39. 組合總和 - 力扣(LeetCode)

class Solution {List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {//為了避免排列的重復情況出現,所以我們先進行排序Arrays.sort(candidates);traversal(0, target, candidates);return res;}private void traversal(int start, int target, int[] candidates){//把滿足條件的提出來if(target == 0){res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));return;}for(int i = start; i < candidates.length; i++){//對于每一個candidate進行遍歷,因為我們升序排列了,所以一旦選過了,//就不會再回去,就避免了排列情況的發生,實際上變為了組合if(target - candidates[i] >= 0){path.add(candidates[i]);traversal(i, target - candidates[i], candidates);//記得回溯path.remove(path.size() - 1);}else{//注意給一個邊界條件,如果不滿足了就退出break;}}}
}?第五題:40. 組合總和 II - 力扣(LeetCode)

class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {Arrays.sort(candidates); // 對數組進行排序List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();//因為每個候選人數字只能出現一次,所以我們與上一題不同的地方是要多加入一個標記數組backtrack(candidates, target, 0, new ArrayList<>(), res, new boolean[candidates.length]);return res;}private void backtrack(int[] candidates, int target, int start, List<Integer> path, List<List<Integer>> res, boolean[] used) {if (target == 0) {res.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); // 找到一種組合return;}for (int i = start; i < candidates.length; i++) {// 本質來說,這題有重復元素的排列導致的結果重復的問題,必須去重// 跳過重復的元素,注意這種去重的方式(避免上一行提到的情況)if (i > start && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]) {continue;}// 如果當前元素大于剩余目標,直接返回//注意邊界條件if (candidates[i] > target) {break;}// 使用當前元素if (!used[i]) {used[i] = true; // 標記為已使用path.add(candidates[i]); // 添加到路徑backtrack(candidates, target - candidates[i], i + 1, path, res, used); // 遞歸調用path.remove(path.size() - 1); // 回溯,移除當前元素used[i] = false; // 重置為未使用}}}
}
sync.Once和)



)




)








