逐漸成為一個情緒穩定且安靜成長的人
???????????????? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ——24.5.24
線程安全
什么時候發生?
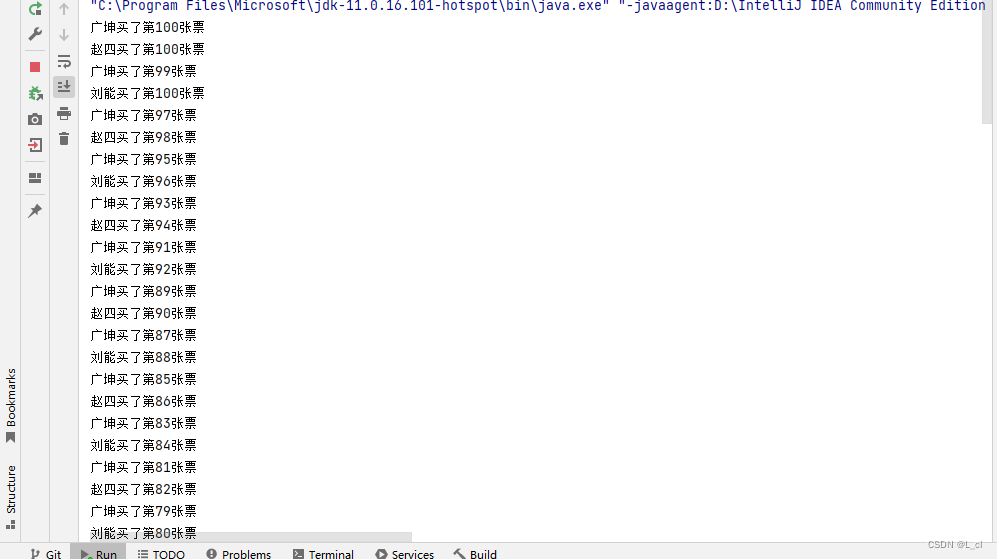
? ? ? ?當多個線程訪問同一個資源時,導致了數據有問題,出現并發問題,數據不能及時更新,導致數據發生錯誤,出現線程安全問題
多線程安全問題示例
package S71ThreadSafe;public class MyTicket implements Runnable{// 定義100章票int ticket = 100;@Overridepublic void run(){while(true){if(ticket>0){System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"買了第"+ticket+"張票");ticket--;}}} }package S71ThreadSafe;public class Demo210Test {public static void main(String[] args) {// new一次,分別傳遞到三個線程對象中去MyTicket myTicket = new MyTicket();Thread th1= new Thread(myTicket, "趙四");Thread th2= new Thread(myTicket, "劉能");Thread th3= new Thread(myTicket, "廣坤");th1.start();th2.start();th3.start();} }
解決線程安全問題方式一:同步代碼塊
synchronized代碼塊 ==?上鎖 可以解決線程安全問題,不保證線程順序
1.格式:
????????synchronized(任意接收對象){
? ? ? ?????????線程要執行的語句;
????????}
2.任意對象:
? ? ? ? 就是我們的鎖對象
3.執行:
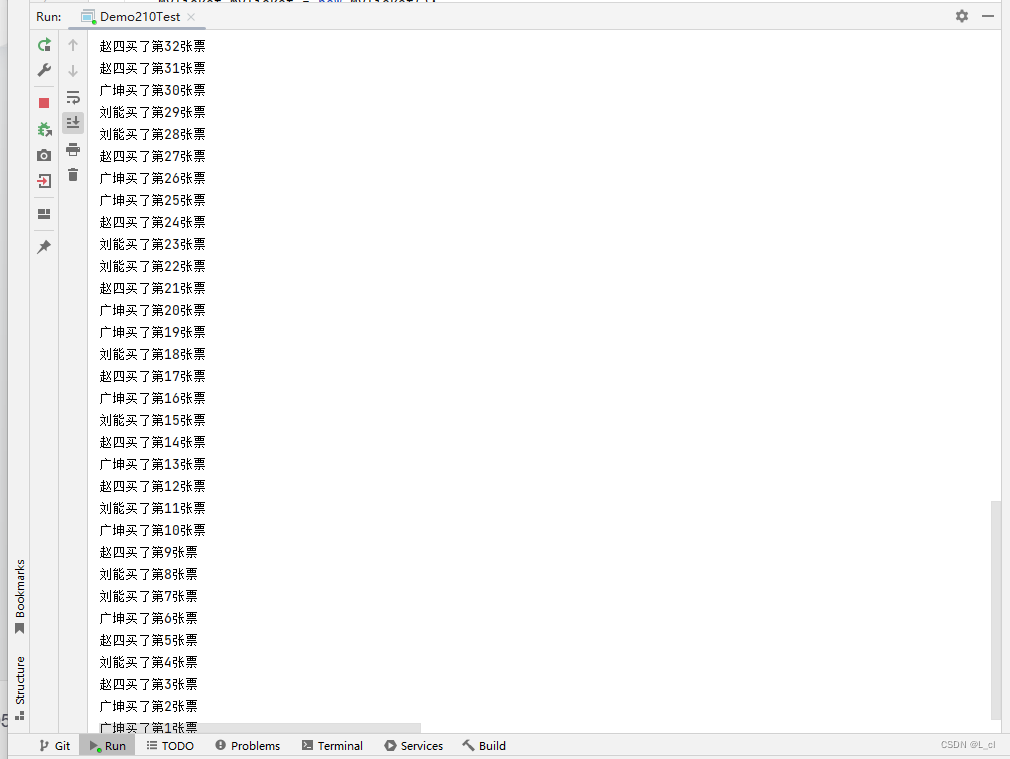
? ? ? ? 一個線程拿到鎖之后,會進入到同步代碼塊中執行,在此期間,其他線程拿不到鎖,就進不去同步代碼塊。需要在同步代碼塊外面等待排隊,需要等待執行的線程執行完畢,出了同步代碼塊,相當于釋放鎖了,等待的線程才能搶到鎖,才能進入到同步代碼塊中執行,上的鎖必須是同一個鎖對象,同一把鎖
package S71ThreadSafe;import java.util.Scanner;public class MyTicket implements Runnable{// 定義100章票int ticket = 100;// 任意new一個對象Object obj = new Object();Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);@Overridepublic void run(){while(true){synchronized (sc) {if (ticket > 0) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "買了第" + ticket + "張票");ticket--;}}}} }package S71ThreadSafe;public class Demo210Test {public static void main(String[] args) {// new一次,分別傳遞到三個線程對象中去MyTicket myTicket = new MyTicket();Thread th1= new Thread(myTicket, "趙四");Thread th2= new Thread(myTicket, "劉能");Thread th3= new Thread(myTicket, "廣坤");th1.start();th2.start();th3.start();} }
解決線程安全問題方式二:同步方法
1.普通同步方法_非靜態
????????在普通方法內用一個同步代碼塊
① 格式:
????????修飾符 synchronized 返回值類型 方法名(參數){
????????????????方法體
????????????????return 結果? ? ? ? }
② 默認鎖:
? ? ? ? this
package S73ThreadSafeSolve2;public class Demo212Test {public static void main(String[] args) {// new一次,分別傳遞到三個線程對象中去MyTicket myTicket = new MyTicket();System.out.println(myTicket);Thread th1= new Thread(myTicket, "趙四");Thread th2= new Thread(myTicket, "劉能");Thread th3= new Thread(myTicket, "廣坤");th1.start();th2.start();th3.start();} }package S73ThreadSafeSolve2;import java.util.Scanner;public class MyTicket implements Runnable{// 定義100章票int ticket = 100;Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);@Overridepublic void run(){while(true){try{Thread.sleep(100L);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}// 調用同步方法// method01();method02();}}// 定義一個同步方法public synchronized void method01(){if (ticket > 0) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "買了第" + ticket + "張票");ticket--;}}// 在普通方法內用一個同步代碼塊public void method02(){synchronized (this){System.out.println(this+"————————————————————");if (ticket>0){System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "買了第" + ticket + "張票");ticket--;}}}}? ?????只new了一次對象
2.靜態同步方法
① 格式
????????修飾符 static synchronized 返回值類型 方法名(參數){
????????????????方法體
????????????????return 結果? ? ? ? }
② 默認鎖
????????class對象
package S74ThreadSafeSolve3;import java.util.Scanner;public class MyTicket implements Runnable{// 定義100章票static int ticket = 100;Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);@Overridepublic void run(){while(true){try{Thread.sleep(100L);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}// 調用同步方法method02();}}// 在普通方法內用一個同步代碼塊public static void method02(){synchronized (MyTicket.class){if (ticket>0){System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "買了第" + ticket + "張票");ticket--;}}}}package S74ThreadSafeSolve3;public class Demo213Test {public static void main(String[] args) {// new一次,分別傳遞到三個線程對象中去MyTicket myTicket = new MyTicket();System.out.println(myTicket);Thread th1= new Thread(myTicket, "趙四");Thread th2= new Thread(myTicket, "劉能");Thread th3= new Thread(myTicket, "廣坤");th1.start();th2.start();th3.start();} }StringBuider是線程不安全的,StringBuffer加了死鎖是線程安全,線程同步的




—— 內部類)











)



