目錄
1.List
1.1 什么是List
1.2 常用的方法
1.3 List的使用
2.?線性表
3. ArrayList 類(順序表)
3.1 順序表定義
3.2 ArrayList鏈表的功能模擬實現
3.3 ArrayList簡介
3.4?ArrayList的構造方法
3.5 ArrayList的遍歷
3.5 ArrayList的具體使用實例
3.5.1 楊輝三角
3.5.2 簡單的洗牌算法
4. LinkedList 類(鏈表)
4.1 鏈表的概念
4.2 無頭單向非循環鏈表的功能模擬實現
4.3 LinkedList鏈表
4.3.1 LinkedList鏈表的概念
4.3.2 LinkedList鏈表的功能模擬實現
4.3.3 LinkedList鏈表的構造方法
4.3.4 LinkedList鏈表的遍歷
4.4 鏈表的練習題
1.List
1.1 什么是List
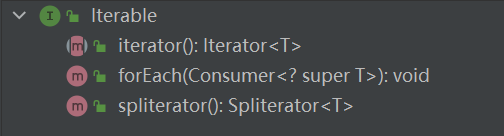
List是一個接口,繼承于Collection,Collection也是一個接口,Collection類繼承于Iterable,Iterable也是一個接口。
Collection接口規范了一些常用的方法。
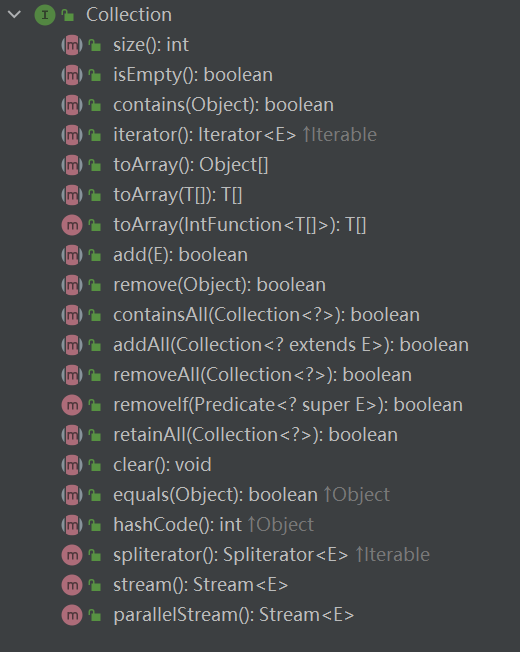
實現Iterable接口的類可以逐個元素遍歷:
在數據結構層次來看,List就是一個線性表,是一組具有相同數據類型的數據的有序序列,在這個有序序列上可以進行增刪改查以及變量等操作。
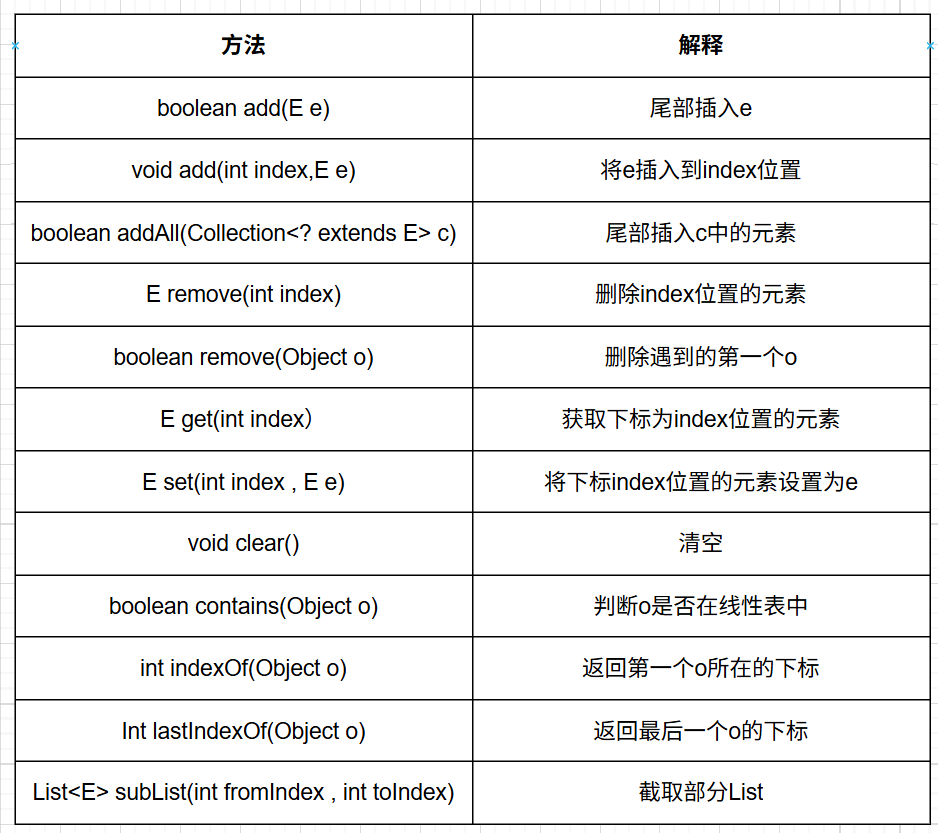
1.2 常用的方法
下面是List類里面常用的方法:
1.3 List的使用
List是一個接口,里面包含了很多抽象方法,要調用這些方法,需要實現該接口,并且要重寫這些方法,比如說ArrayList和LinkedList就實現了List接口。
2.?線性表
線性表是一組具有相同數據類型的數據的有序序列,線性表是一種常用的數據結構,包括:順序表,鏈表,棧,隊列等。
線性表在邏輯上是線性結構,也就是一條連續的直線,但是在物理結構上線性表不一定是連續的,
線性表的主要存儲方式:數組和鏈表。
????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????順序表
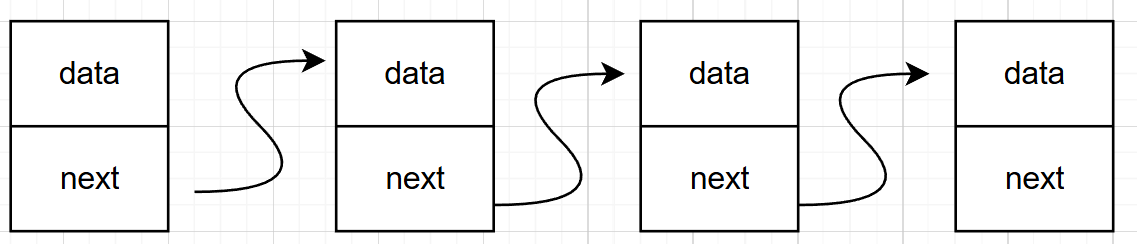
????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????鏈表
3. ArrayList 類(順序表)
3.1 順序表定義
順序表是一組物理地址連續的空間用來存儲數據,一般來說是用數組來存儲,對數組進行增刪改查。
3.2 ArrayList鏈表的功能模擬實現
這里我自己對ArraysList里面的方法進行了實現:
public class MyArrayList implements IList {public int[] arr;public int arrTrueSize;private static final int ARR_SIZE = 5;public MyArrayList() {arr = new int[ARR_SIZE];}public MyArrayList(int size) {arr = new int[size];}//添加元素到最后一個位置@Overridepublic void add(int data) {//判斷數組是否已滿if(isFull()) {//擴容grow();}arr[arrTrueSize] = data;arrTrueSize++;}//2倍擴容private void grow() {arr = Arrays.copyOf(arr,2*ARR_SIZE);}//在指定pos位置添加元素@Overridepublic void add(int pos, int data) {checkPosOfAdd(pos);//如果數組滿了if(isFull()) {grow();}for(int i = arrTrueSize - 1; i >= pos; i--) {arr[i+1] = arr[i];}arr[pos] = data;arrTrueSize++;}//檢查pos范圍是否正常private void checkPosOfAdd(int pos) {if(pos < 0 || pos > arrTrueSize) {throw new PosOutOfBoundsException("添加元素位置的pos不合法,請重新輸入" + pos);}}//判斷是否包含某元素@Overridepublic boolean contains(int toFind) {for (int i = 0; i < arrTrueSize; i++) {if(arr[i] == toFind) {return true;}}return false;}//查找某個元素對應的下標@Overridepublic int indexOf(int toFind) {for (int i = 0; i < arrTrueSize; i++) {if(arr[i] == toFind) {return i;}}return -1;}//獲取pos位置對應的元素@Overridepublic int get(int pos) {checkPosOfGetOrSet(pos);if(isEmpty()) {throw new ListEmptyException("獲取元素時,順序表為空");}return arr[pos];}//判斷get方法中的pos范圍是否合法private void checkPosOfGetOrSet(int pos) {if(pos < 0 || pos >= arrTrueSize) {throw new PosOutOfBoundsException("獲取或者設置元素位置的pos不合法" + pos);}}//設置pos位置的元素為value@Overridepublic void set(int pos, int value) {checkPosOfGetOrSet(pos);arr[pos] = value;}//刪除第一次出現的元素@Overridepublic void remove(int toRemove) {int index = indexOf(toRemove);if(index == -1) {System.out.println("沒有你要刪除的元素");}for (int i = index; i < arrTrueSize - 1; i++) {arr[i] = arr[i+1];}arrTrueSize--;}//獲取順序表里面的數據數量@Overridepublic int size() {return arrTrueSize;}//清空順序表@Overridepublic void clear() {arrTrueSize = 0;}@Overridepublic void display() {for (int i = 0; i < arrTrueSize; i++) {System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");}System.out.println();}//判斷順序表是否滿了@Overridepublic boolean isFull() {return arrTrueSize == arr.length;}//判斷順序表是否為空@Overridepublic boolean isEmpty() {return arrTrueSize == 0;}
}
這里我沒有用泛型的方式來實現,實際上系統的ArraysList是用的泛型類,使用之前需要先進行實例化。
3.3 ArrayList簡介
下面是ArrayList類實現的接口和繼承的抽象類:
綠色是抽象類,粉色是類,其他是接口
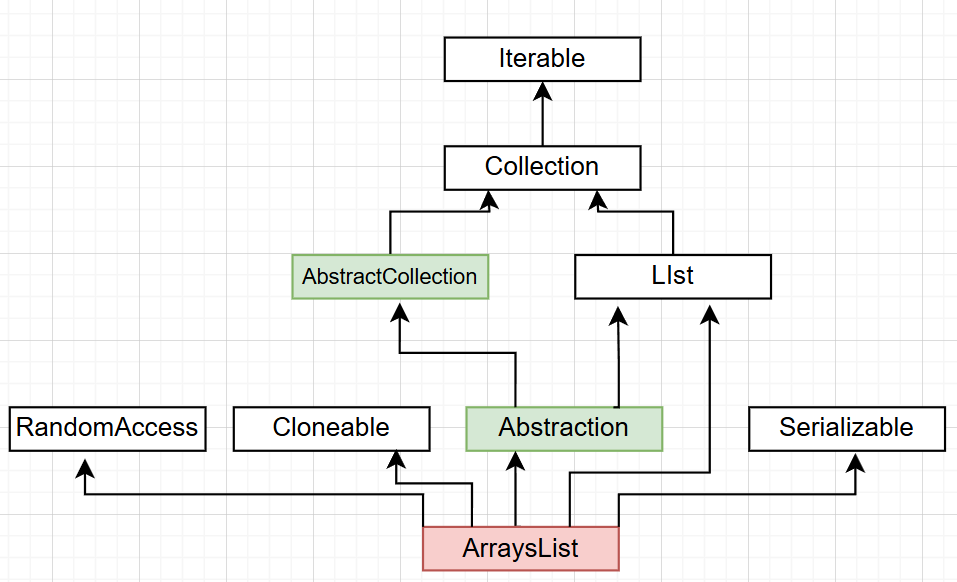
這里ArrayList實現了RandomAccess接口,表明ArraysList支持隨機訪問。
ArrayList實現Cloneable接口,表示ArraysList可以clone。
ArrayList實現Serializable接口,表示ArraysList支持序列化。
ArrayList在單線程下可以使用,在多線程選擇1使用Vector或者CopyOnWriteArrayList
ArrayList底層是一段連續的空間,可以進行動態擴容,是一個動態類型的順序表。
3.4?ArrayList的構造方法
ArrayList存在三個構造方法,構成方法的重載。
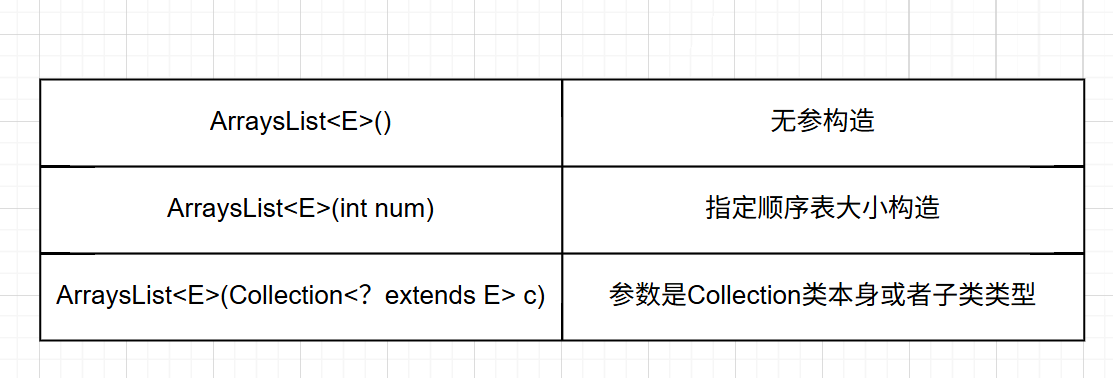
無參數的構造方法源代碼為:
調用空參數的構造方法時,會創建一個空的數組,那么如何add呢

這里我們查看add的底層代碼:
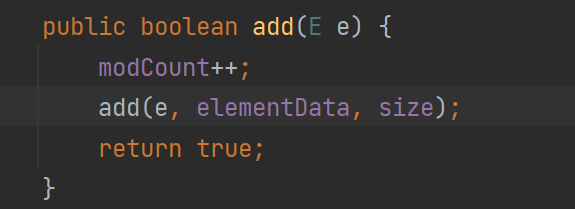
這里又調用了add方法:
下面代碼說明如果數組為空就調用grow方法來擴容。
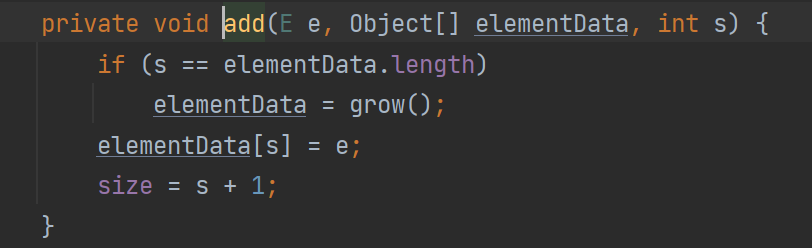
grow方法源碼:
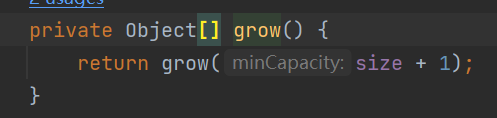
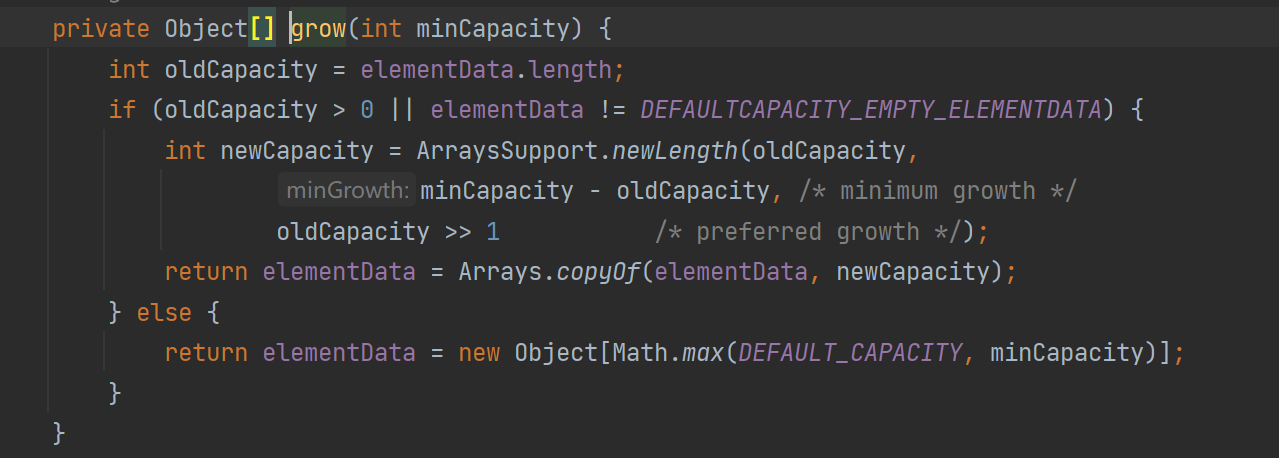
上面代碼意思是當數組大小為0時調用else里面的代碼,創建一個大小為10的數組。當大小為10的數組滿了就1.5倍擴容。
總結:所以調用無參數的構造方法時,首次添加元素時要調用grow方法擴容為10。
參數是一個指定大小的數的構造方法源碼是:
下面會根據你傳入的數據來創建對應大小的順序表。
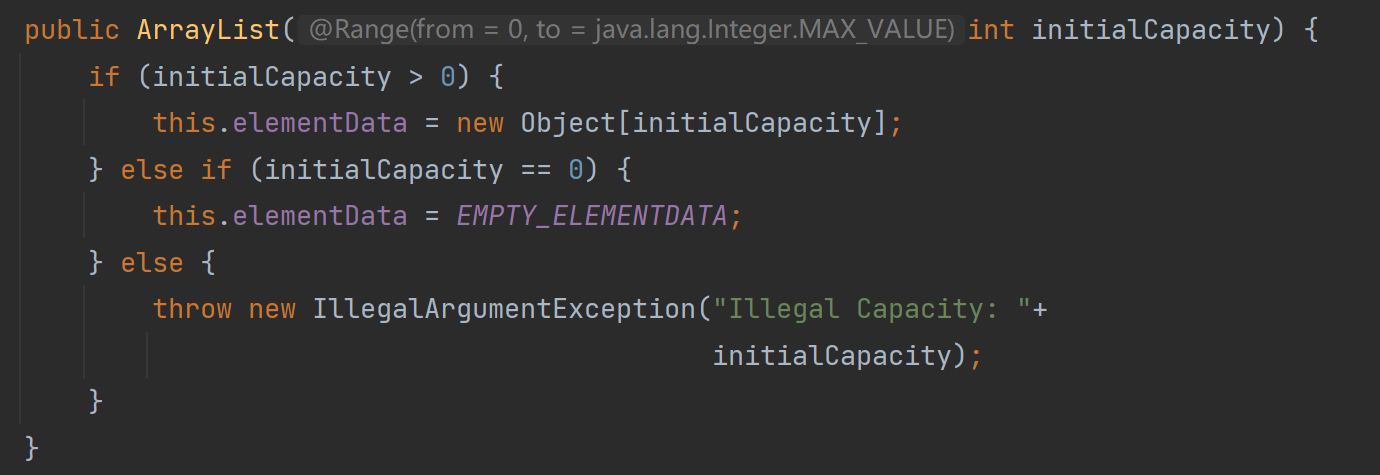
參數是Collection類型或者其子類類型的構造方法的源碼為:
這里面的參數可以是Collection類型或者其子類類型。
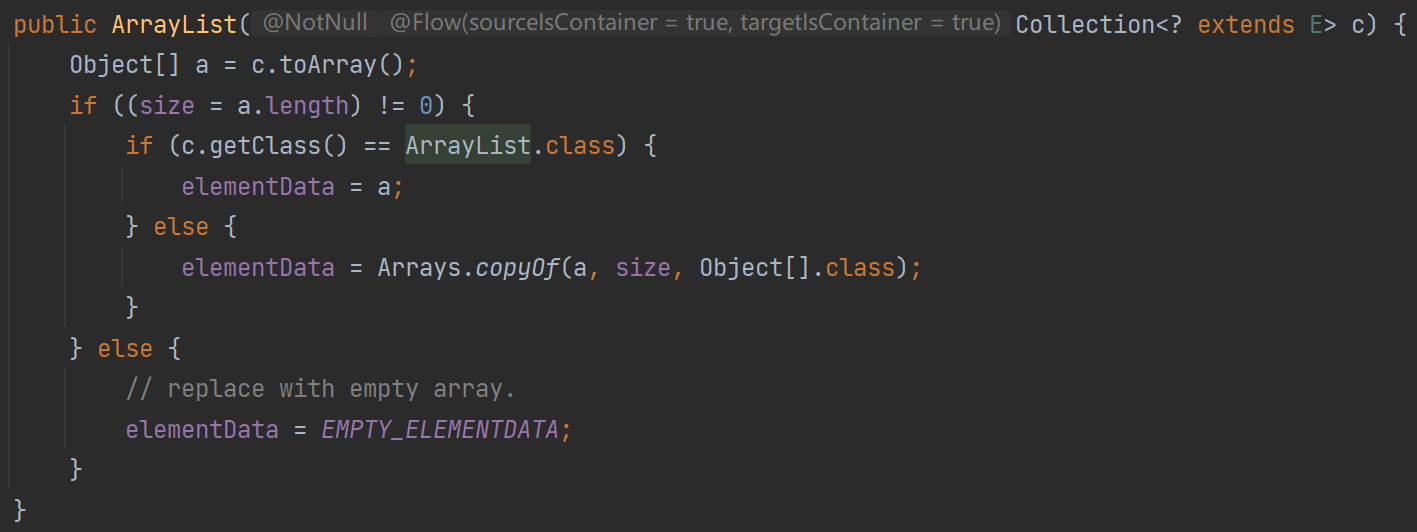
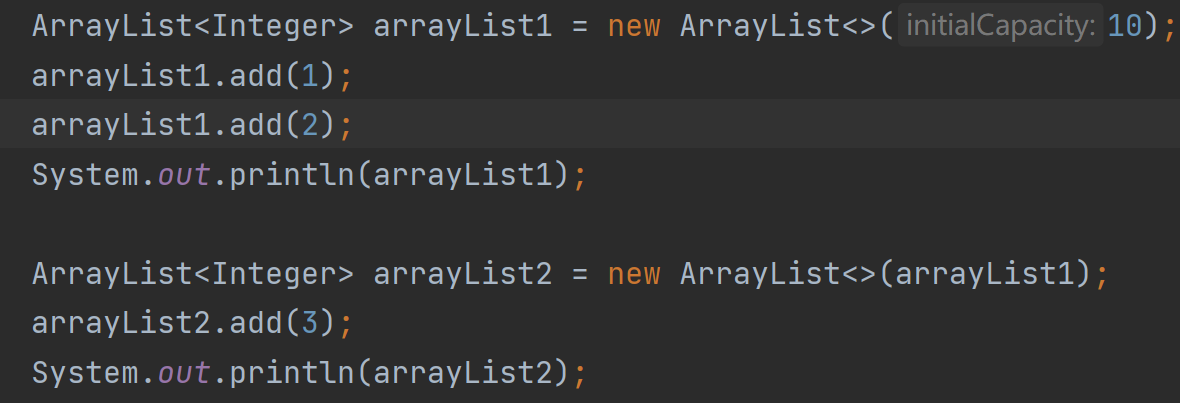
比如說:
輸出結果為:
3.5 ArrayList的遍歷
這里有三種遍歷方式:for循環,for-each循環,迭代器。
代碼如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();arrayList.add(1);arrayList.add(2);arrayList.add(3);//for循環for (int i = 0; i < arrayList.size(); i++) {System.out.print(arrayList.get(i) + " ");}System.out.println();//for-each循環for(Integer integer : arrayList) {System.out.print(integer + " ");}System.out.println();//迭代器Iterator<Integer> it = arrayList.iterator();while(it.hasNext()) {System.out.print(it.next() + " ");}}迭代器相當于將數組里面的元素依次打印出來。
只要是實現了Iterable接口,就可以用迭代器遍歷。
3.5 ArrayList的具體使用實例
3.5.1 楊輝三角
給定一個非負數num(1 <= num <= 30),輸出前num層的楊輝三角。
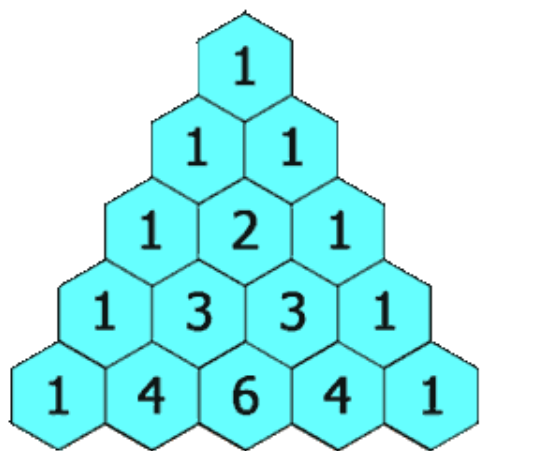
這里我們可以轉換成這樣來看:

這里我們發現除了第一行,其他的每行的第一個元素和最后一個元素都是1,這里我們可以先把第一行設置出來。然后再從第二行開始逐行進行設置,每行的第一個和最后一個為1,
中間的數=該數的上一行的上一列的數+該數上一行的這一列的數,根據此規律寫出中間的數。
最后代碼如下:
public static List<List<Integer>> generate(int num) {List<List<Integer>> list1 = new ArrayList<>();//先處理第一行元素List<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<>();list2.add(1);list1.add(list2);//下面一行一行處理for (int i = 1; i < num; i++) {List<Integer> list3 = new ArrayList<>();//處理第一個元素為1list3.add(1);//處理中間for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) {int a = list1.get(i-1).get(j-1) +list1.get(i-1).get(j);list3.add(a);}//處理最后一個元素為1list3.add(1);list1.add(list3);}return list1;}3.5.2 簡單的洗牌算法
這里我們需要先生成52張牌,然后將牌打亂,再三個人輪流拿五張牌。
我這里打亂是利用最后一張牌跟前面隨機的一張牌交換順序,直到交換到第一張牌停止。
代碼如下:
?
public class Test02 {String[] arr = {"?","?","?","?"};//生成一副牌public List<Card> createCards() {List<Card> cards = new ArrayList<>(52);for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < 13; j++) {String cardShape = arr[i];int cardSize = j;Card card = new Card();card.cardSize = cardSize;card.cardShape = cardShape;cards.add(card);}}return cards;}//打亂牌(將最后一張牌與前面的牌隨機抽取一張交換,從后往前直到第一張牌)private void shuffle(List<Card> cards) {Random random = new Random();for (int i = cards.size() - 1; i > 0; i--) {int n = random.nextInt(i);swap(cards,i,n);}}//交換牌public void swap(List<Card> cards, int a, int b) {Card card = cards.get(a);cards.set(a,cards.get(b));cards.set(b,card);}public static void main(String[] args) {Test02 test02 = new Test02();List<Card> cards = test02.createCards();System.out.println(cards);System.out.println();//打亂牌test02.shuffle(cards);System.out.println(cards);System.out.println();//三個人輪流抓五張牌List<List<Card>> list = new ArrayList<>(3);list.add(new ArrayList<>());list.add(new ArrayList<>());list.add(new ArrayList<>());for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {list.get(j).add(cards.remove(0));}}System.out.println("A:");System.out.println(list.get(0));System.out.println("B:");System.out.println(list.get(1));System.out.println("C:");System.out.println(list.get(2));}
}4. LinkedList 類(鏈表)
4.1 鏈表的概念
鏈表是一種物理存儲結構上非連續的存儲結構。
鏈表結構非常多:
單向或雙向:
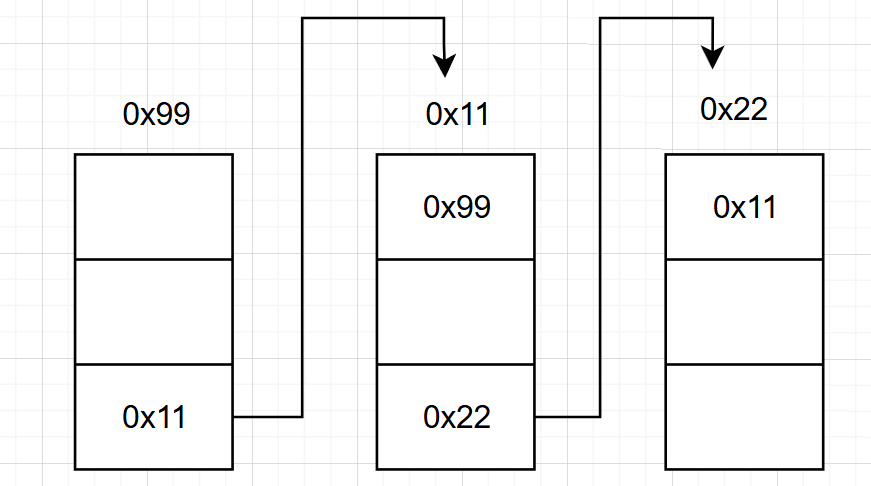
單向
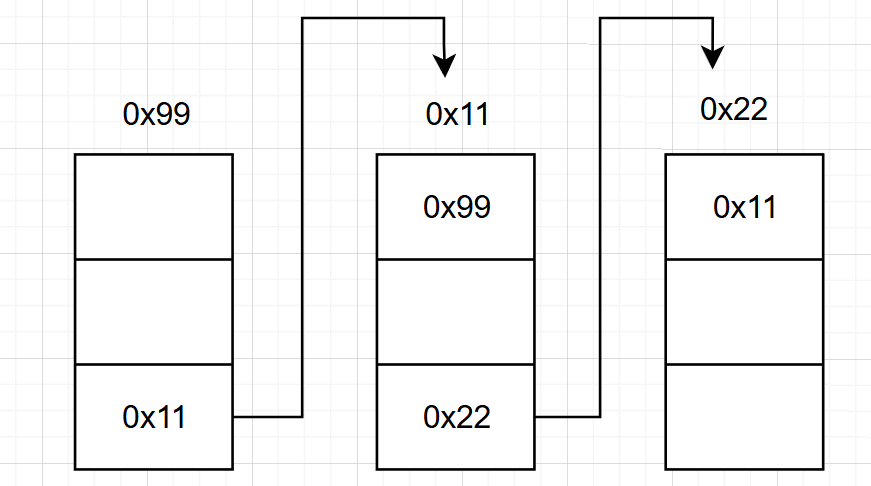
雙向
帶頭或不帶頭:
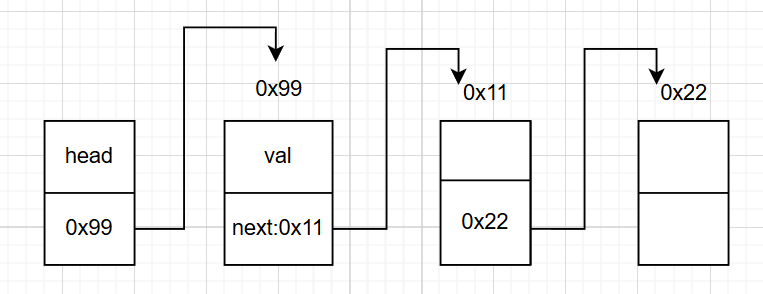
? ? ? ? 帶頭
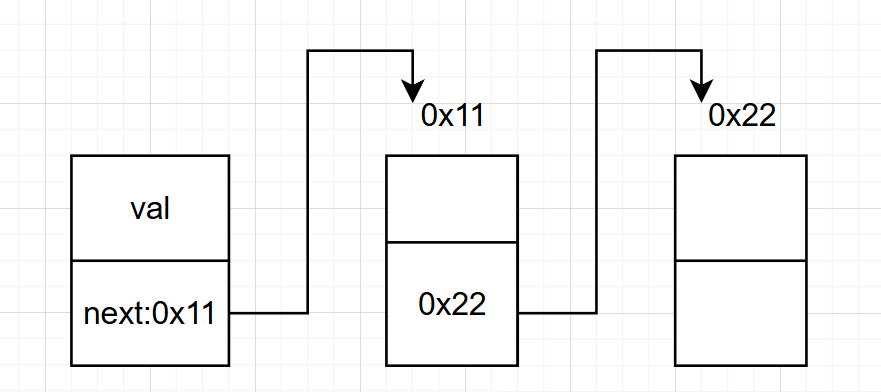
不帶頭
循環或非循環:
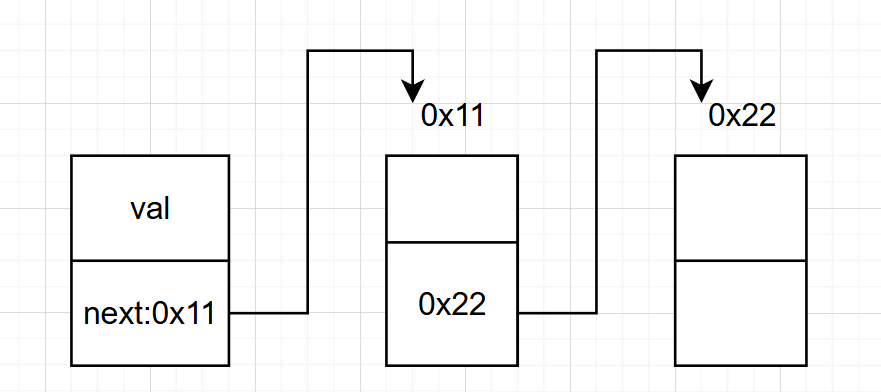
非循環
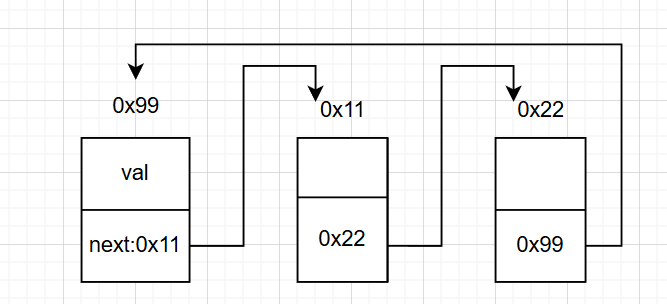
循環
我們主要學習兩種:無頭單向非循環列表 和 無頭雙向循環列表。
無頭雙向循環列表是LinkedList類的實現方式。
4.2 無頭單向非循環鏈表的功能模擬實現
下面是我自己實現的無頭單向非循環鏈表的功能
public class MySingleList {//節點類(靜態內部類)static class ListNode {public int val;public ListNode next;public ListNode(int val) {this.val = val;}}public ListNode head;//創建一個鏈表public void createLinkedList() {ListNode listNode1 = new ListNode(11);ListNode listNode2 = new ListNode(22);ListNode listNode3 = new ListNode(33);ListNode listNode4 = new ListNode(44);listNode1.next = listNode2;listNode2.next = listNode3;listNode3.next = listNode4;this.head = listNode1;}//頭插法public void addFirst(int data){ListNode listnode = new ListNode(data);listnode.next = head;head = listnode;}//尾插法public void addLast(int data){ListNode listNode = new ListNode(data);if(head == null) {head = listNode;}//找到最后一個位置插入ListNode node = head;while(node != null) {if(node.next == null) {node.next = listNode;return;}node = node.next;}}//任意位置插?,第?個數據節點為0號下標public void addIndex(int index,int data){int len = size();if(index < 0 || index > len - 1) {return;}//頭插法if(index == 0) {addFirst(data);return;}//尾插法if(index == len - 1) {addLast(data);return;}//中間插入ListNode node = new ListNode(data);ListNode newHead = head;//獲取插入位置的上一個節點ListNode cur = findBeginList(index);if(cur == null) {return;}node.next = cur.next;cur.next = node;}//找到插入位置的前一個節點private ListNode findBeginList(int index) {int len = size();if(index < 0 || index > len - 1) {return null;}ListNode node = head;int i = 0;while(i != index - 1) {node = node.next;i++;}return node;}//查找關鍵字key是否在單鏈表當中public boolean contains(int key){ListNode node = head;while(node != null) {if(node.val == key) {return true;}node = node.next;}return false;}//刪除第?次出現關鍵字為key的節點public void remove(int key){if(head == null) {return;}if(head.val == key) {head = head.next;return;}ListNode val = findBeginNumList(key);if(val == null) {return;}ListNode cul = val.next.next;head.next = cul;}//查找關鍵字的前驅節點public ListNode findBeginNumList(int key) {if(head == null) {return null;}ListNode node = head;while(node.next != null) {if(node.next.val == key) {return node;}node = node.next;}return null;}//刪除所有值為key的節點public void removeAllKey(int key){if(head == null) {return;}//刪除所有key節點ListNode cul = head;ListNode pex = cul.next;while(pex != null) {if(pex.val == key) {cul.next = pex.next;pex = pex.next;}else {cul = cul.next;pex = pex.next;}}//判斷第一個元素是否需要刪除if(head.val == key) {head = head.next;}}//得到單鏈表的?度public int size(){ListNode node = head;int listNum = 0;while(node != null) {listNum++;node = node.next;}return listNum;}public void clear() {}//打印鏈表public void display() {ListNode node = head;while(node != null) {System.out.print(node.val + " ");node = node.next;}System.out.println();}//從指定節點打印鏈表public void display(ListNode listNode) {ListNode node = listNode;while(node != null) {System.out.println(node.val + " ");node = node.next;}System.out.println();}
}
4.3 LinkedList鏈表
4.3.1 LinkedList鏈表的概念
LinkedList鏈表底層是無頭雙向不循環鏈表,利用這種方法對鏈表的增刪查改操作比較方便。
LinkedList 實現了List接口,在任意位置的插入刪除操作效率比較高,時間復雜度為O(1)。
4.3.2 LinkedList鏈表的功能模擬實現
下面是我自己實現的LinkedList類里面的功能:
public class MyLinkedList {static class ListNode {public int val;public ListNode prev;public ListNode next;public ListNode(int val) {this.val = val;}}//標記的頭節點public ListNode head;//標記的尾節點public ListNode last;//頭插法public void addFirst(int data) {ListNode node = new ListNode(data);if(head == null) {head = node;last = node;return;}node.next = head;head.prev = node;head = node;}//尾插法public void addLast(int data) {ListNode node = new ListNode(data);if(head == null) {head = node;last = node;return;}last.next = node;node.prev = last;last = node;}//指定index位置插入public void addIndex(int index, int data) {int size = size();if(index < 0 || index > size) {System.out.println("下標輸入錯誤" + index);return;}//頭插法if(index == 0) {addFirst(data);return;}//尾插法if(index == size) {addLast(data);return;}//中間插入ListNode cul = new ListNode(data);ListNode pex = head;while(index != 0) {pex = pex.next;index--;}cul.next = pex;pex.prev.next = cul;cul.prev = pex.prev;pex.prev = cul;}//查找關鍵字key是否在單鏈表中public boolean contains(int key) {ListNode node = head;while(node != null) {if(node.val == key) {return true;}node = node.next;}return false;}//刪除單鏈表中第一次出現key的節點public void remove(int key) {ListNode node = head;while(node != null) {if(node.val == key) {//判斷是否是刪除第一個節點if(node.prev == null) {if(node.next == null) {head = null;last = null;}else {node.next.prev = null;head = node.next;}}else {//判斷是否刪除最后一個節點if(node.next == null) {node.prev.next = null;last = node.prev;}else {//刪除中間節點node.prev.next = node.next;node.next.prev = node.prev;}}break;}node = node.next;}}//刪除單鏈表中所有的key的節點public void removeAllKey(int key) {ListNode node = head;while(node != null) {if(node.val == key) {//判斷是否是刪除第一個節點if(node.prev == null) {if(node.next == null) {head = null;last = null;}else {node.next.prev = null;head = node.next;}}else {//判斷是否刪除最后一個節點if(node.next == null) {node.prev.next = null;last = node.prev;}else {//刪除中間節點node.prev.next = node.next;node.next.prev = node.prev;}}}node = node.next;}}//打印鏈表public void display() {ListNode node = head;while(node != null) {System.out.print(node.val + " ");node = node.next;}System.out.println();}//求鏈表的長度public int size() {ListNode node = head;int num = 0;while(node != null) {num++;node = node.next;}return num;}//清除單鏈表public void clear() {ListNode node = head;while(node != null) {ListNode nodeN = node.next;node.prev = null;node.next = null;node = nodeN;}head = null;last = null;}
}
4.3.3 LinkedList鏈表的構造方法
LinkedList有兩個構造方法:
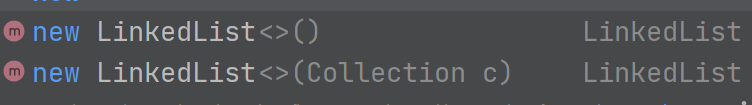
第二個構造方法是利用另一個鏈表來創建鏈表:
LinkedList<Integer> list1 = new LinkedList<>();list1.add(11);list1.add(22);list1.add(33);LinkedList<Integer> list2 = new LinkedList<>(list1);System.out.println(list2);4.3.4 LinkedList鏈表的遍歷
public static void main(String[] args) {LinkedList<Integer> list1 = new LinkedList<>();list1.add(11);list1.add(22);list1.add(33);//方法1:System.out.println(list1);//方法2:for (int i = 0; i < list1.size(); i++) {System.out.print(list1.get(i) + " ");}System.out.println();//方法3:for(int i : list1) {System.out.print(i + " ");}System.out.println();//方法4(迭代器)正向遍歷:ListIterator<Integer> it = list1.listIterator();while(it.hasNext()) {System.out.print(it.next() + " ");}System.out.println();//迭代器反向遍歷:ListIterator<Integer> itN = list1.listIterator(list1.size());while(itN.hasPrevious()) {System.out.print(itN.previous() + " ");}}4.4 鏈表的練習題
1.刪除鏈表中等于給定值val的所有節點
題目鏈接
解題思路:
這里我利用了兩個下標:cul作為第一個位置的地址,pex作為第二個位置的地址,判斷pex的值是否為刪除的值key, 如果是,則刪除,cur指向pex的下一位,然后pex后移一位,如果不是,則cul和pex統一后移一位再進行判斷。最后再檢查第一位的值是否為key。
代碼實現:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/
class Solution {public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int key) {ListNode newHead = head;if(newHead == null) {return null;}//刪除所有的key元素ListNode cul = newHead;ListNode pex = cul.next;while(pex != null) {if(pex.val == key) {cul.next = pex.next;pex = pex.next;}else {cul = cul.next;pex = pex.next;}}//判斷第一個元素是否是keyif(head.val == key) {head = head.next;}return head;}
}2.?反轉一個單鏈表
題目鏈接
第一種:
解題思路:
這里利用了遞歸的想法,想要n長度的鏈表反轉,必須要后n-1長度鏈表反轉,依次類推直到最后鏈表長度為1,返回最后一個數據的地址,將長度為2的鏈表反轉。
代碼實現:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/
class Solution {public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {if(head == null) {return head;}if(head.next == null) {return head;}ListNode newHead = reverseList(head.next);head.next.next = head;head.next = null;return newHead;}
}第二種:
解題思路:
這里利用了循環的思路,創建一個變量cur作為head的下一個節點,變量pex作為cur的下一個節點,先將第二個節點的next換成第一個節點的地址,然后把三個變量依次后移,循環往復。
代碼實現:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/
class Solution {public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {if(head == null) {return head;}if(head.next == null) {return head;}ListNode cur = head.next;head.next = null;while(cur != null) {ListNode pex = cur.next;cur.next = head;head = cur;cur = pex;}return head;}
}3.?給定一個帶有頭結點head的非空單鏈表,返回鏈表的中間結點。如果有兩個中間結點,則返回第二個中間結點。
題目鏈接
解題思路:這里用到了快慢指針法,設置兩個指針slow和fast,根據相同路程,二倍的速度行駛的距離也是二倍,當fast到達鏈表最后時,slow剛好到達鏈表中間。
代碼實現:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/
class Solution {public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {if(head == null) {return head;}if(head.next == null) {return head;}ListNode slow = head;ListNode fast = head;while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next.next;}return slow;}
}4.?輸入一個鏈表,輸出該鏈表中倒數第k個結點。
題目鏈接
方法1:
解題思路:求倒數第k個節點,也就是求正數第len +1 - k個節點,len是鏈表的長度。
代碼實現:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/
class Solution {public int kthToLast(ListNode head, int k) {ListNode node = head;//求鏈表長度int len = 0;while(node != null) {node = node.next;len++;}for(int i = 1; i < len+1-k; i++) {head = head.next;}return head.val;}
}方法2:
解題思路:
我們可以定義兩個下標slow和fast,讓fast比slow先走k-1步,它們之間距離就差k-1步,這樣當fast走到最后一個節點時候,slow剛好就是倒數第k個節點,因為slow和fast之間的距離不變。
求倒數第k個節點,相當于倒數第k個節點跟最后一個節點差了k-1步。
代碼實現:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/
class Solution {public int kthToLast(ListNode head, int k) {ListNode slow = head;ListNode fast = head;int i = 0;while(i < k-1) {fast = fast.next;i++;}while(fast.next != null) {slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next;}return slow.val;}
}5.?將兩個有序鏈表合并為一個新的有序鏈表并返回。新鏈表是通過拼接給定的兩個鏈表的所有節點組成的。
題目鏈接
解題思路:這里是設置一個中轉節點head,再設置一個節點cul指向head,然后判斷list1.val和list2.val的大小,讓cul指向小的,以此類推,最后返回中間結點的next。
代碼實現:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/
class Solution {public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {ListNode newHead = new ListNode(-1);ListNode cul = newHead;while(list1 != null && list2 != null) {if(list1.val < list2.val) {cul.next = list1;list1 = list1.next;}else {cul.next = list2;list2 = list2.next;}cul = cul.next;}if(list1 == null) {cul.next = list2;}if(list2 == null) {cul.next = list1;}return newHead.next;}
}6.?編寫代碼,以給定值x為基準將鏈表分割成兩部分,所有小于x的結點排在大于或等于x的結點之前。
題目鏈接
解題思路:這題可以先創建兩個鏈表,list1用來存儲比x小的節點,list2用來存儲比x大的節點。最后將兩個節點拼接起來。要考慮到所有數都比x大,所有數比x都小,list2節點不為空的話最后一個節點的next是否置為null。
代碼實現:
import java.util.*;/*
public class ListNode {int val;ListNode next = null;ListNode(int val) {this.val = val;}
}*/
public class Partition {public ListNode partition(ListNode pHead, int x) { ListNode list1 = new ListNode(-1);ListNode list2 = new ListNode(-2);ListNode newHead1 = list1;ListNode newHead2 = list2;while(pHead != null) {if(pHead.val < x) {list1.next = pHead;list1 = list1.next;}else {list2.next = pHead;list2 = list2.next;}pHead = pHead.next;}if(newHead1.next == null) {return newHead2.next;}list1.next = newHead2.next;//將最后一個節點的next換為nullif(newHead2 != null) {list2.next = null;}return newHead1.next;}
}7.?鏈表的回文結構。
題目鏈接? ? ? 回文結構是指以中心點為分割線兩邊的數值對稱相等。
解題思路:
這道題我們可以按照先找到鏈表的中間位置,然后將后半部分回轉,再從兩邊向中間靠攏,檢查val是否相同,因為終止條件是左邊的head與右邊的slow相等時終止,但是偶數的話不會相等,我們可以通過判斷它們緊挨著時候上一個節點的next是否等于下一個節點,相等返回true。
代碼實現:
import java.util.*;/*
public class ListNode {int val;ListNode next = null;ListNode(int val) {this.val = val;}
}*/
public class PalindromeList {public boolean chkPalindrome(ListNode head) {if(head == null) {return false;}if(head.next == null) {return true;}//先找到中間位置ListNode slow = head;ListNode fast = head;while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next.next;}//將中間位置后面的節點逆置ListNode cul = slow.next;slow.next = null;while(cul != null) {ListNode pex = cul.next;cul.next = slow;slow = cul;cul = pex;}//從兩邊開始判斷while(head != slow) {if(head.val != slow.val) {return false;}if(head.next == slow) {return true;}head = head.next;slow = slow.next;}return true;}
}8. 輸入兩個鏈表,找出它們的第一個公共結點。
題目鏈接
解題思路:如果兩條鏈表長度不同,我們可以先求出長的鏈表比短的鏈表長多少,讓長的鏈表先走的跟短的鏈表一個起點,然后一起走。
代碼實現:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode(int x) {* val = x;* next = null;* }* }*/
public class Solution {public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {ListNode sho = headA;ListNode lon = headB;int len1 = 0;int len2 = 0;while(sho != null) {sho = sho.next;len1++;}sho = headA;while(lon != null) {lon = lon.next;len2++;}lon = headB;int len = len2 - len1;if(len1 > len2) {sho = headB;lon = headA;len = len1 - len2;}int i = 0;while(i < len) {lon = lon.next;i++;}while(sho != lon) {sho = sho.next;lon = lon.next;}return lon;}
}9.?給定?個鏈表,判斷鏈表中是否有環
題目鏈接
解題思路:這里利用了快慢下標法,設置慢下標slow和快下標fast,slow每次走一格,fast每次走兩格,這樣fast比slow每次多增加一格,這樣的話,如果鏈表有環,則fast和slow不會錯過,鏈表有偶數個數據時,fast!=null,當鏈表有奇數個數據時,fast.next!=null。
代碼實現:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode(int x) {* val = x;* next = null;* }* }*/
public class Solution {public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {ListNode slow = head;ListNode fast = head;while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next.next;if(slow == fast) {return true;}}return false;}
}10.?給定一個鏈表,返回鏈表開始入環的第一個節點。如果鏈表無環,則返回NULL
題目鏈接
解題思路:這里可以證明得從起始點到入口點的距離等于從相遇點到入口點的距離。然后兩個節點分別從起始點和相遇點走,相遇的時候就是入口點。
代碼實現:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode(int x) {* val = x;* next = null;* }* }*/
public class Solution {public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {//判斷是否有環,并找到相遇點的節點ListNode slow = head;ListNode fast = head;while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next.next;if(slow == fast) {break;}}if(fast == null || fast.next == null) {return null;}fast = head;while(fast != slow) {fast = fast.next;slow = slow.next;}return fast;}
}注意:以上題目是博主寫的其中一種解題方法,僅供參考,還有其他方法可以自行去了解。

 --- 子查詢篇)






)








超詳細_Leetcode_20. 有效的括號)

