在解決螺旋矩陣問題時,我們需要按照順時針螺旋順序遍歷矩陣,并返回所有元素。本文將分享兩種高效的解決方案:邊界收縮法和方向模擬法。
題目描述
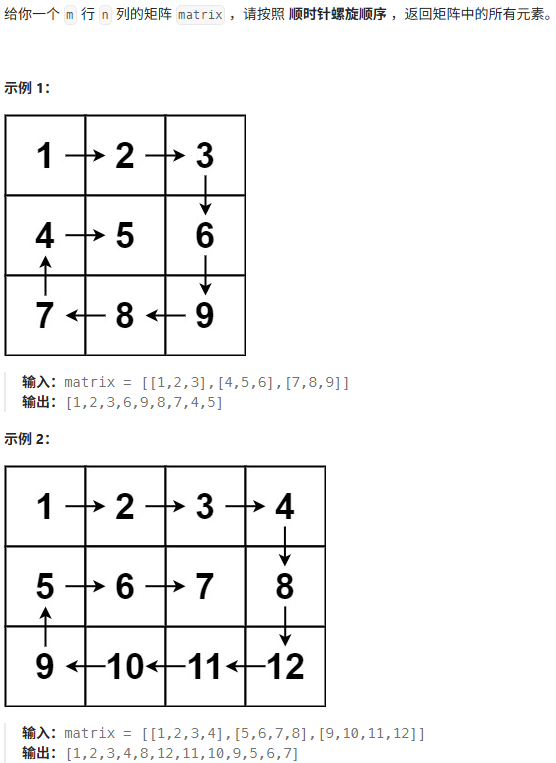
邊界收縮法
邊界收縮法通過定義四個邊界(上、下、左、右)來模擬螺旋遍歷的過程。每完成一個方向的遍歷,就收縮對應的邊界,直到所有元素被訪問完畢。
算法思路
- 初始化邊界:
top = 0,?bottom = m-1(行數-1),?left = 0,?right = n-1(列數-1)。 - 按層遍歷:
- 向右:遍歷上邊界(
top行),從?left?到?right。 - 向下:遍歷右邊界(
right列),從?top+1?到?bottom。 - 向左:遍歷下邊界(
bottom行),從?right-1?到?left+1(需確保存在內層)。 - 向上:遍歷左邊界(
left列),從?bottom?到?top+1(需確保存在內層)。
- 向右:遍歷上邊界(
- 收縮邊界:完成一圈后,將?
top++,?bottom--,?left++,?right--。 - 終止條件:當邊界交錯時停止(
top > bottom?或?left > right)。
代碼實現
class Solution {public List<Integer> spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {List<Integer> result=new ArrayList<Integer>();int x= matrix.length;int y=matrix[0].length;int left=0;int right=y-1;int top=0;int bottom=x-1;while(left<=right&&top<=bottom){for(int i=left;i<=right;i++){result.add(matrix[top][i]);}for(int i=top+1;i<=bottom;i++){result.add(matrix[i][right]);}if(left<right&&top<bottom) {for (int i = right - 1; i > left; i--) {result.add(matrix[bottom][i]);}for (int i = bottom; i > top; i--) {result.add(matrix[i][left]);}}left++;right--;top++;bottom--;}return result;}
}復雜度分析
- 時間復雜度:O(m*n),每個元素被訪問一次。
- 空間復雜度:O(1),僅使用常量額外空間(結果列表不計入)。
方向模擬法(其他解決方案)
方向模擬法通過定義方向數組和記錄訪問狀態來模擬螺旋路徑,適合對邊界條件處理不熟悉的情況。
算法思路
- 初始化:
- 方向數組?
dirs?表示右、下、左、上四個方向。 - 訪問矩陣?
visited?記錄元素是否被訪問。 - 從?
(0,0)?開始,初始方向為右。
- 方向數組?
- 遍歷矩陣:
- 將當前元素加入結果列表,并標記為已訪問。
- 計算下一個位置,若越界或已訪問,則順時針轉向。
- 更新位置并繼續遍歷,直到所有元素被訪問。
代碼實現
class Solution {public List<Integer> spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0) return result;int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;boolean[][] visited = new boolean[m][n];int[][] dirs = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}}; // 右、下、左、上int r = 0, c = 0, d = 0;int total = m * n;for (int i = 0; i < total; i++) {result.add(matrix[r][c]);visited[r][c] = true;// 計算下一個位置int nr = r + dirs[d][0];int nc = c + dirs[d][1];// 若越界或已訪問,則轉向if (nr < 0 || nr >= m || nc < 0 || nc >= n || visited[nr][nc]) {d = (d + 1) % 4; // 順時針轉向nr = r + dirs[d][0];nc = c + dirs[d][1];}r = nr;c = nc;}return result;}
}復雜度分析
- 時間復雜度:O(m*n),每個元素訪問一次。
- 空間復雜度:O(m*n),
visited?矩陣額外占用空間。
總結
- 邊界收縮法:通過動態調整邊界模擬螺旋路徑,無需額外空間,是更優解。
- 方向模擬法:直觀易理解,但需要額外空間記錄訪問狀態,適合快速實現。
兩種方法均能高效解決螺旋矩陣問題,實際應用中推薦優先使用邊界收縮法!
![[嵌入式embed][Qt]Qt5.12+Opencv4.x+Cmake4.x_用Qt編譯linux-Opencv庫 測試](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[嵌入式embed][Qt]Qt5.12+Opencv4.x+Cmake4.x_用Qt編譯linux-Opencv庫 測試)


)






)


)



與標準的 jsonrpc的區別)

