如有問題大概率是我的理解比較片面,歡迎評論區或者私信指正。
?考察線性表,核心圍繞其存儲結構特性、核心操作實現、場景應用選型三大維度,重點檢驗對基礎概念的理解、代碼實現能力及問題分析能力,通常會結合算法設計、復雜度分析和實際場景進行考察。
一、基礎概念與特性辨析
-
核心定義與邏輯結構
-
問題:“什么是線性表?它與非線性結構(如樹、圖)的本質區別是什么?” (考察點:線性表 “一對一” 的邏輯關系,區別于樹的 “一對多” 和圖的 “多對多”)
-
-
兩種存儲結構的核心差異
-
問題:“順序表和鏈表在存儲方式、訪問效率、插入刪除操作上有何本質區別?” (考察點:順序表的連續空間與隨機存取、鏈表的離散空間與指針依賴;插入刪除時 “移動元素” 與 “修改指針” 的效率差異)
-
-
總結
-
順序表 vs 鏈表的本質區別
-
順序表:連續內存、隨機訪問快(O(1)),增刪需移動元素(O(n)),擴容成本高。
-
鏈表:離散內存、增刪快(O(1)),查找需遍歷(O(n)),無擴容問題但存儲密度低。
“數組和鏈表分別適合什么場景?為什么數據庫索引常用B+樹(基于數組)而非鏈表?”
答:數組適合讀多寫少(如索引),鏈表適合頻繁增刪(如操作歷史記錄)。 -
二、核心操作的代碼實現(邊界處理)
(一)順序表操作
插入與刪除
問題1:“編寫函數,在順序表的第 i 個位置插入元素 x,需處理越界、表滿等異常。” (關鍵點:從后往前移動元素(避免覆蓋),表長 + 1;時間復雜度分析)
public class SeqList {private int[] data; // 存儲元素的數組private int maxSize; // 順序表最大容量private int length; // 當前元素個數// 初始化順序表public SeqList(int capacity) {this.maxSize = capacity;this.data = new int[maxSize];this.length = 0;}/*** 在順序表第i個位置插入元素x* @param i 插入位置(位序從1開始)* @param x 插入元素值* @return 操作是否成功*/
public boolean insert(int i, int x) {// 1. 檢查位序有效性if (i < 1 || i > length + 1) {System.err.println("插入位置越界!有效范圍:[1, " + (length + 1) + "]");return false;}// 2. 檢查表滿異常if (length >= maxSize) {System.err.println("順序表已滿!最大容量:" + maxSize);return false;}// 3. 元素后移操作(從后向前移動)for (int j = length-1; j >= i-1; j--) {data[j+1] = data[j]; // 將元素向后移動一位}// 4. 插入新元素data[i - 1] = x; // 數組下標 = 位序 - 1length++; // 更新表長return true;}
}問題2:“刪除順序表中值為 x 的所有元素,要求時間復雜度、空間復雜度
。” (思路:用 k 記錄有效元素個數,遍歷數組時將非 x 元素前移至 k 位置,最后更新表長)
public class OrderedList {private int[] data; // 存儲元素的數組private int length; // 當前元素個數private int capacity; // 列表容量// 初始化順序表public OrderedList(int capacity) {this.capacity = capacity;this.data = new int[capacity];this.length = 0;}/*** 刪除所有值為x的元素(時間復雜度O(n),空間復雜度O(1))* @param x 要刪除的目標值* @return 刪除的元素數量*/public int removeAll(int x) {int k = 0; // 有效元素指針int count = 0; // 刪除計數// 雙指針遍歷for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {if (data[i] != x) {// 保留非x元素data[k] = data[i];k++;} else {// 統計刪除元素count++;}}// 更新表長length = k;return count;}// 輔助方法:添加元素(測試用)public void add(int value) {if (length < capacity) {data[length] = value;length++;}}// 輔助方法:打印當前列表(測試用)public void print() {System.out.print("[");for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {System.out.print(data[i]);if (i < length - 1) System.out.print(", ");}System.out.println("]");}
}查找與擴容
問題1:“在有序順序表中實現折半查找,返回元素位置;若不存在,返回插入位置。” (考察點:二分法的邊界控制(low <= high)、循環結束時 low 的含義)
/*** 在有序順序表中執行折半查找* * @param arr 有序順序表(升序排列)* @param target 目標元素值* @return 元素位置(從1開始計數),若不存在則返回應插入位置*/
public static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int target) {// 邊界檢查:空表直接返回插入位置1if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {return 1;}int low = 0;int high = arr.length - 1;// 關鍵點1:循環條件必須包含等號(單個元素)while (low <= high) {// 關鍵點2:防止整數溢出的中間值計算int mid = low + ((high - low) >> 1);if (arr[mid] == target) {// 找到目標值,返回位序(索引+1)return mid + 1;} else if (arr[mid] < target) {// 目標在右半區low = mid + 1;} else {// 目標在左半區high = mid - 1;}}// 關鍵點3:循環結束時low指向第一個大于target的元素位置return low + 1;
}問題2:“順序表動態擴容的原理是什么?為什么擴容時通常選擇擴大為原容量的 1.5?倍?” (考察點:避免頻繁擴容導致的時間開銷, amortized 復雜度優化,懶加載策略)
public class ArrayList<E> {/*** 默認初始化空間*/private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;/*** 空元素*/private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};/*** ArrayList 元素數組緩存區*/transient Object[] elementData;private int size;//實際容量// 添加元素觸發擴容public boolean add(E e) {// 步驟1:計算最小所需容量int minCapacity = size + 1;// 步驟2:處理首次添加的特殊情況if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);}// 步驟3:檢查并執行擴容if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) {// 3.1 記錄當前容量int oldCapacity = elementData.length;// 3.2 計算新容量(1.5倍擴容)int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);// 3.3 處理1.5倍不足的情況if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) {newCapacity = minCapacity;}// 3.4 創建新數組并復制數據elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);}// 步驟4:安全添加元素elementData[size++] = e;return true;}
(二)鏈表操作
單鏈表基礎操作
問題1:“帶頭結點的單鏈表中,實現第 i 個位置插入元素;若 i=1,操作和其他位置有何不同?” (關鍵點:頭結點的作用 —— 統一插入邏輯,無需特殊處理 i=1;指針修改順序:先連新結點,再斷原鏈)
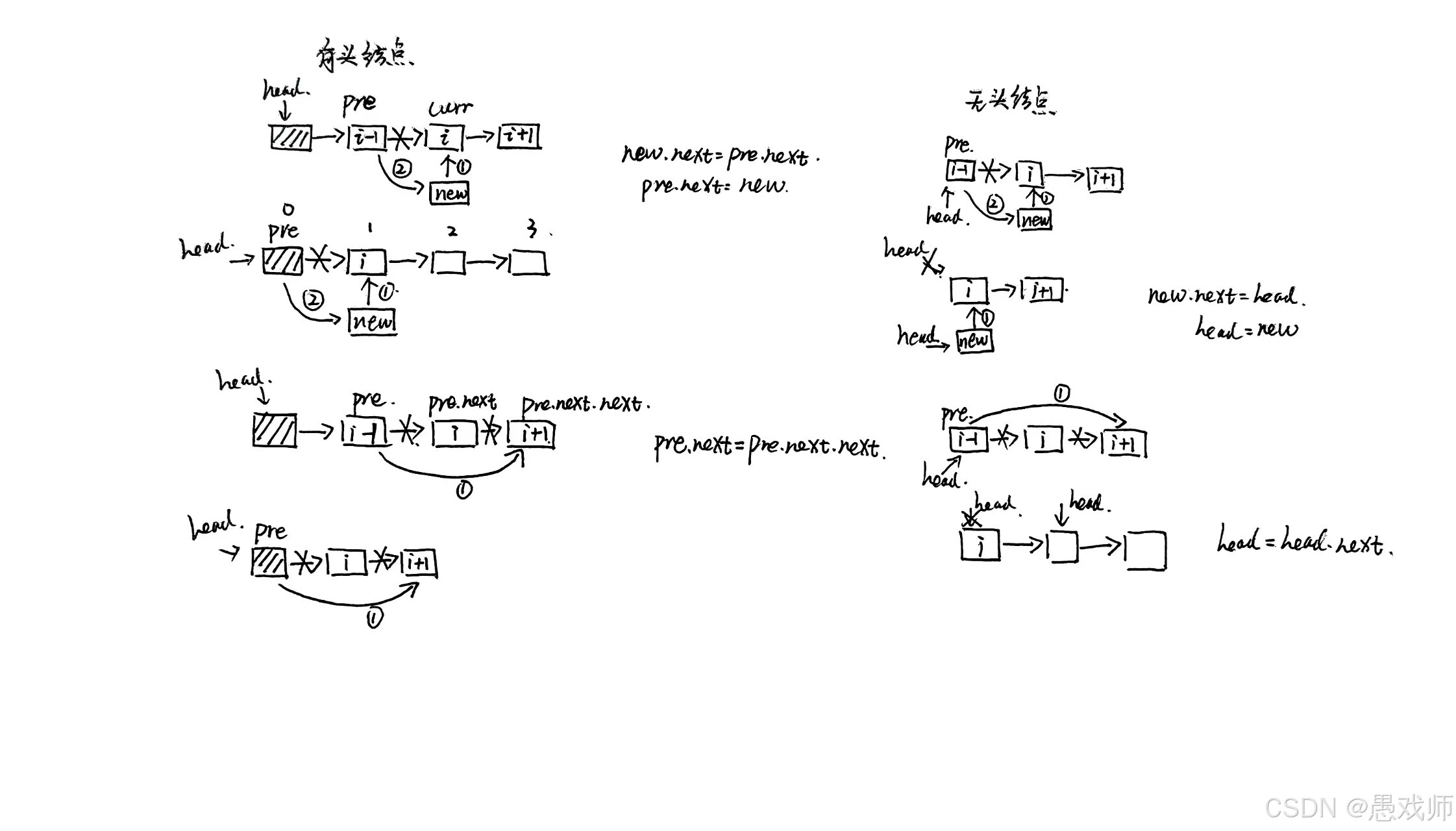
class LinkedListWithHead {private Node head; // 頭指針始終指向頭結點(哨兵結點)public LinkedListWithHead() {head = new Node(-1); // 創建頭結點(哨兵結點),數據域通常無效}// 在位置 i 插入元素public boolean insert(int i, int data) {if (i < 1) return false; // 位置無效檢查Node pre = head; // 從頭結點開始// 尋找第 i-1 個結點(插入位置的前驅)for (int pos = 0; pos < i - 1; pos++) {if (pre.next == null) break; // 提前到達鏈表末尾pre = pre.next;}if (pre == null) return false; // 前驅結點無效Node newNode = new Node(data); // 創建新結點newNode.next = pre.next; // 新結點指向原位置結點pre.next = newNode; // 前驅指向新結點return true;}// 刪除位置 i 的元素public boolean delete(int i) {if (i < 1 || head.next == null) return false; // 位置無效或鏈表為空Node pre = head; // 從頭結點開始// 尋找第 i-1 個結點(刪除位置的前驅)for (int pos = 0; pos < i - 1; pos++) {if (pre.next == null) break; // 提前到達鏈表末尾pre = pre.next;}if (pre.next == null) return false; // 要刪除的結點不存在pre.next = pre.next.next; // 跳過要刪除的結點return true;}// 查找元素public int find(int data) {int position = 1;Node current = head.next; // 從第一個實際結點開始while (current != null) {if (current.data == data) {return position; // 找到元素,返回位置}current = current.next;position++;}return -1; // 未找到}// 獲取鏈表字符串表示public String getListString() {StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("Head → ");Node current = head.next; // 跳過頭結點while (current != null) {sb.append(current.data);if (current.next != null) sb.append(" → ");current = current.next;}sb.append(" → NULL");return sb.toString();}
}class LinkedListWithoutHead {private Node head; // 直接指向第一個實際結點(可能為null)public LinkedListWithoutHead() {head = null; // 初始化為空鏈表}// 在位置 i 插入元素public boolean insert(int i, int data) {if (i < 1) return false; // 位置無效檢查// 特殊處理 i=1 的情況if (i == 1) {Node newNode = new Node(data);newNode.next = head; // 新結點指向原頭結點head = newNode; // 更新頭指針return true;}Node pre = head; // 從第一個結點開始// 尋找第 i-1 個結點for (int pos = 1; pos < i - 1; pos++) {if (pre == null) break; // 提前結束pre = pre.next;}if (pre == null) return false; // 前驅結點無效Node newNode = new Node(data);newNode.next = pre.next; // 新結點指向原位置結點pre.next = newNode; // 前驅指向新結點return true;}// 刪除位置 i 的元素public boolean delete(int i) {if (i < 1 || head == null) return false; // 位置無效或鏈表為空// 特殊處理 i=1 的情況if (i == 1) {head = head.next; // 頭指針指向第二個結點return true;}Node pre = head; // 從第一個結點開始// 尋找第 i-1 個結點for (int pos = 1; pos < i - 1; pos++) {if (pre.next == null) break; // 提前結束pre = pre.next;}if (pre.next == null) return false; // 要刪除的結點不存在pre.next = pre.next.next; // 跳過要刪除的結點return true;}// 查找元素public int find(int data) {int position = 1;Node current = head; // 從第一個實際結點開始while (current != null) {if (current.data == data) return position;current = current.next;position++;}return -1; // 未找到}// 獲取鏈表字符串表示public String getListString() {if (head == null) return "NULL"; // 空鏈表StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();Node current = head;while (current != null) {sb.append(current.data);if (current.next != null) sb.append(" → ");current = current.next;}sb.append(" → NULL");return sb.toString();}
}?單鏈表有無頭節點操作細節總結:
查找:
Node current = head.next; // 從第一個實際結點開始
Node current = head; // 從第一個實際結點開始刪除:
if (i < 1 || head.next == null) return false; // 位置無效或鏈表為空
if (i < 1 || head == null) return false; // 位置無效或鏈表為空 Node pre = head; // 從頭結點開始// 尋找第 i-1 個結點(插入位置的前驅)for (int pos = 0; pos < i - 1; pos++) {if (pre.next == null) break; // 提前到達鏈表末尾pre = pre.next;}if (pre == null) return false; // 前驅結點無效Node pre = head; // 從第一個結點開始// 尋找第 i-1 個結點for (int pos = 1; pos < i - 1; pos++) {if (pre == null) break; // 提前結束pre = pre.next;}if (pre == null) return false; // 前驅結點無效?pre.next = pre.next.next; // 跳過要刪除的結點// 特殊處理 i=1 的情況if (i == 1) {head = head.next; // 頭指針指向第二個結點return true;}pre.next = pre.next.next; // 跳過要刪除的結點插入:
? if (i < 1) return false; // 位置無效檢查Node pre = head; // 從頭結點開始// 尋找第 i-1 個結點(插入位置的前驅)for (int pos = 0; pos < i - 1; pos++) {if (pre.next == null) break; // 提前到達鏈表末尾pre = pre.next;}if (pre == null) return false; // 前驅結點無效if (i < 1) return false; // 位置無效檢查Node pre = head; // 從第一個結點開始// 尋找第 i-1 個結點for (int pos = 1; pos < i - 1; pos++) {if (pre == null) break; // 提前結束pre = pre.next;}if (pre == null) return false; // 前驅結點無效??newNode.next = pre.next; // 新結點指向原位置結點pre.next = newNode; ? ? // 前驅指向新結點// 特殊處理 i=1 的情況if (i == 1) {Node newNode = new Node(data);newNode.next = head; // 新結點指向原頭結點head = newNode; ? ? ?// 更新頭指針return true;}newNode.next = pre.next; // 新結點指向原位置結點pre.next = newNode; ? ? // 前驅指向新結點問題2:“刪除單鏈表中值為 x 的所有結點,如何避免內存泄漏?” (思路:用前驅指針 pre 遍歷,找到目標結點后,pre->next 指向其后繼,釋放當前結點)
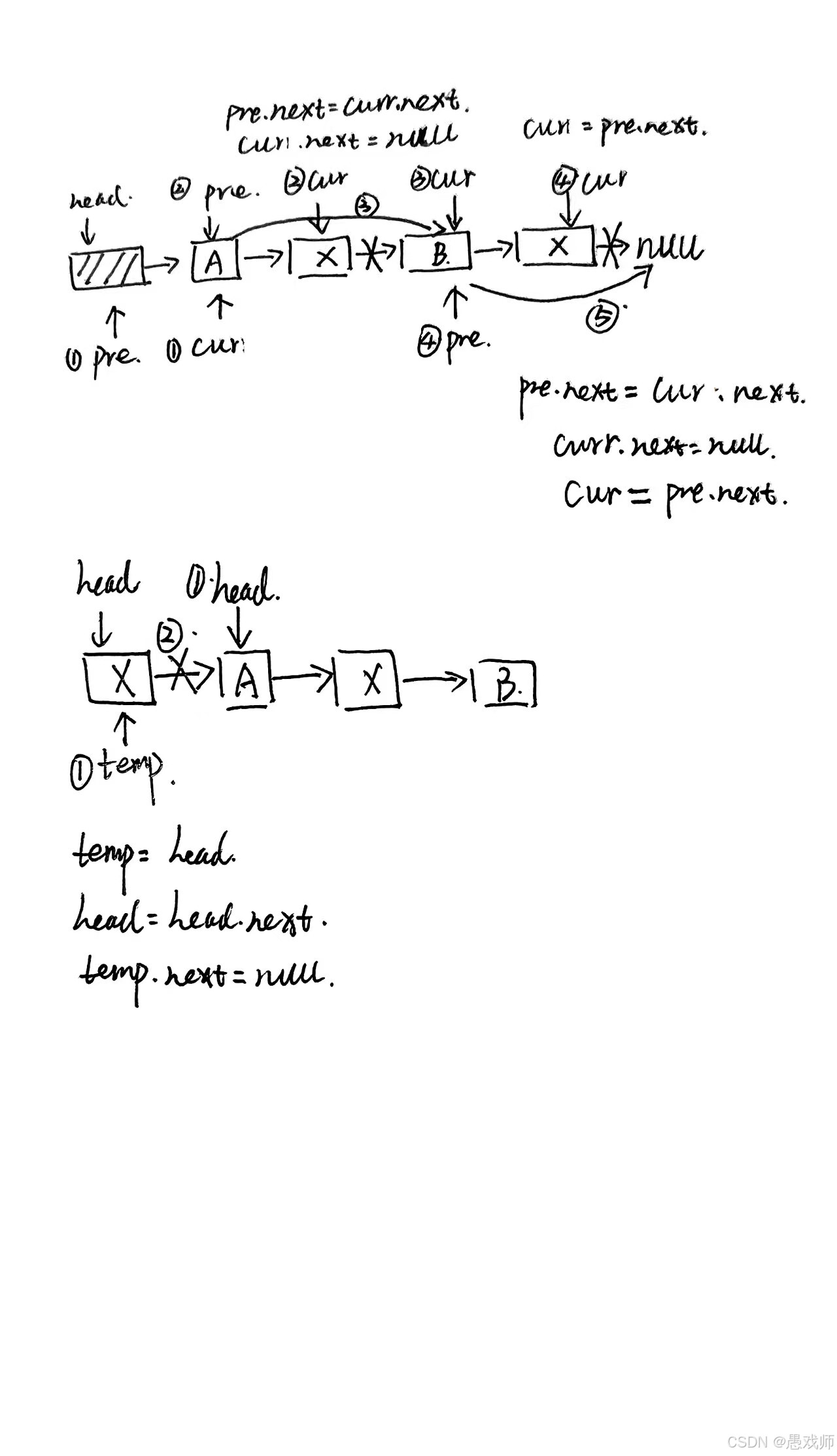
// 帶頭結點鏈表中刪除所有值為 x 的結點
public void deleteAll(int x) {Node pre = head; // 前驅指針指向頭結點Node cur = head.next; // 當前指針指向第一個實際結點while (cur != null) {if (cur.data == x) {// 找到目標結點pre.next = cur.next; // 前驅指針跳過當前結點// 釋放內存(在Java中置為null幫助GC,在C++中需要delete)cur.next = null; // 斷開引用cur = pre.next; // 移動當前指針到下一個結點} else {// 非目標結點,雙指針一起移動pre = cur;cur = cur.next;}}
}// 無頭結點鏈表中刪除所有值為 x 的結點
public void deleteAll(int x) {// 特殊情況:刪除開頭連續的目標結點while (head != null && head.data == x) {Node temp = head;head = head.next;temp.next = null; // 斷開引用}if (head == null) return; // 鏈表為空Node pre = head;Node cur = head.next;while (cur != null) {if (cur.data == x) {pre.next = cur.next; // 前驅指針跳過當前結點cur.next = null; // 斷開引用cur = pre.next; // 移動當前指針} else {pre = cur;cur = cur.next;}}
}內存泄漏分析及避免方法
| 操作 | 內存泄漏風險 | 正確做法 |
|---|---|---|
| 未斷開引用 | 被刪除結點仍被其他對象引用 | 將被刪除結點的 next 置為 null |
| 未釋放內存 | 已刪除結點仍占用內存空間 | 在C++中使用 delete,在Java中依賴GC |
| 指針處理錯誤 | 鏈表斷裂,無法訪問后續結點 | 使用雙指針技術確保鏈表連續性 |
| 頭指針處理不當 | 刪除頭結點后未更新頭指針 | 單獨處理鏈表開頭連續的目標結點 |
雙鏈表與循環鏈表
問題1:“雙鏈表中,在 p 所指結點后插入 s 結點,需修改哪些指針?” (步驟:s->next = p->next;p->next->prior = s;s->prior = p;p->next = s)
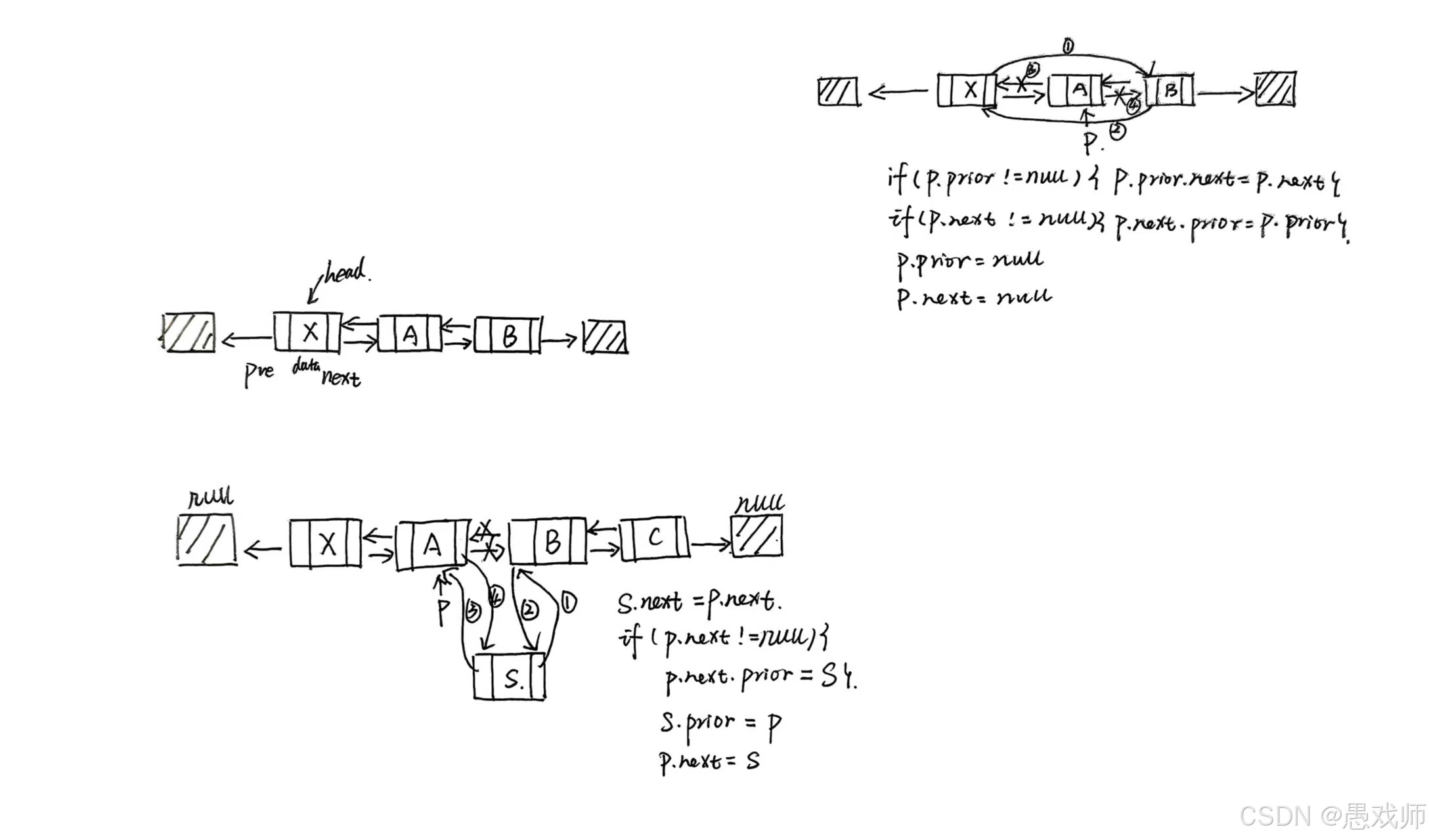
public class DLinkedList<T> {// ... 省略其他代碼/*** 在節點 p 后插入新節點* @param p 目標節點(不能為 null)* @param data 新節點的數據* @return 插入成功返回 true,失敗返回 false*/public boolean insertAfter(DNode<T> p, T data) {if (p == null) return false; // p 無效DNode<T> s = new DNode<>(data); // 創建新節點 s// 核心步驟:s.next = p.next; // 1. s 的 next 指向 p 的原后繼if (p.next != null) {p.next.prior = s; // 2. 如果 p 有后繼,其 prior 指向 s(文檔:p->next->prior=s)}s.prior = p; // 3. s 的 prior 指向 pp.next = s; // 4. p 的 next 指向 sreturn true;}
}public class DLinkedList<T> {// ... 省略其他代碼/*** 刪除節點 p* @param p 要刪除的節點(不能為 null 或頭結點)* @return 刪除成功返回 true,失敗返回 false*/public boolean deleteNode(DNode<T> p) {if (p == null || p == head) return false; // 禁止刪除頭結點或無效節點// 核心步驟:if (p.prior != null) {p.prior.next = p.next; // 1. 前驅節點的 next 指向 p 的后繼}if (p.next != null) {p.next.prior = p.prior; // 2. 后繼節點的 prior 指向 p 的前驅}// 清理引用,避免內存泄漏p.prior = null;p.next = null;return true;}
}public class DLinkedList<T> {// ... 省略其他代碼// 后向遍歷(從頭結點后的第一個節點開始)public void traverseForward() {DNode<T> p = head.next; // 跳過頭結點while (p != null) {System.out.print(p.data + " "); // 處理節點(如打印)p = p.next; // 移動到后繼}System.out.println();}// 前向遍歷(需先定位到尾節點,然后從尾到頭)public void traverseBackward() {// 先找到尾節點(需遍歷整個鏈表)DNode<T> tail = head.next;while (tail != null && tail.next != null) {tail = tail.next;}// 從尾節點開始前向遍歷(跳過頭結點)DNode<T> p = tail;while (p != null && p != head) { System.out.print(p.data + " ");p = p.prior; // 移動到前驅}System.out.println();}
}問題2:“循環單鏈表相比單鏈表有何優勢?如何判斷循環鏈表為空或滿?” (考察點:首尾相連,適合環形場景(如約瑟夫問題);判空:頭結點 next 指向自身;判滿:需額外標志或犧牲一個節點)
// 定義鏈表結點類,存儲數據和下一個結點指針
class LNode<T> {T data; // 結點數據LNode<T> next; // 指向下一個結點的指針public LNode(T data) {this.data = data;this.next = null; // 初始化時next為null,在鏈表中會被設置}
}// 定義循環單鏈表類
public class CircularLinkedList<T> {private LNode<T> head; // 頭結點(不存儲數據,用于標記鏈表起始)private int size; // 當前鏈表大小(額外標志,用于判滿)private int maxSize; // 鏈表最大容量(設置判滿條件)// 初始化鏈表:創建頭結點,并使其next指向自身(形成環)public CircularLinkedList(int maxSize) {this.head = new LNode<>(null); // 頭結點data為nullthis.head.next = this.head; // 關鍵:next指向自身,表示空表this.size = 0;this.maxSize = maxSize; // 設置最大容量(用于判滿)}// 判斷鏈表是否為空:頭結點的next指向自身public boolean isEmpty() {return head.next == head;}// 判斷鏈表是否為滿:基于size變量(額外標志)public boolean isFull() {return size >= maxSize; // size達到maxSize時為滿}// 添加結點到鏈表尾部(示例操作,展示環形遍歷)public void append(T data) {if (isFull()) {throw new IllegalStateException("LinkedList is full. Cannot append.");}LNode<T> newNode = new LNode<>(data);if (isEmpty()) {// 空表:新結點next指向頭結點,頭結點next指向新結點newNode.next = head;head.next = newNode;} else {// 非空表:找到尾結點(尾結點的next指向頭結點),插入新結點LNode<T> current = head.next;while (current.next != head) { // 遍歷到尾結點current = current.next;}current.next = newNode; // 尾結點指向新結點newNode.next = head; // 新結點指向頭結點,維持環狀}size++; // 更新大小}// 示例:打印鏈表(展示環形訪問)public void printList() {if (isEmpty()) {System.out.println("LinkedList is empty.");return;}LNode<T> current = head.next;System.out.print("Circular List: ");do {System.out.print(current.data + " -> ");current = current.next;} while (current != head); // 循環直到回到頭結點System.out.println("(head)"); // 表示環閉合}// 主方法:測試判空、判滿和環形場景public static void main(String[] args) {// 初始化鏈表,設置最大容量為3(用于判滿)CircularLinkedList<Integer> list = new CircularLinkedList<>(3);// 測試判空System.out.println("Is empty? " + list.isEmpty()); // 輸出: true// 添加結點list.append(1);list.append(2);list.append(3);list.printList(); // 輸出: Circular List: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> (head)// 測試判滿System.out.println("Is full? " + list.isFull()); // 輸出: true// 嘗試添加更多結點(會拋異常)try {list.append(4); // 拋出 IllegalStateException} catch (IllegalStateException e) {System.out.println("Error: " + e.getMessage());}}
}背景:約瑟夫環問題(Josephus problem)是一個著名的理論和計算機科學問題:??n個人圍成一圈,從第一個人開始報數,每數到k的人被淘汰出局,然后從下一個人重新開始報數,如此循環,直到最后剩下一個人為止??。這個幸存者在初始圓環中的位置即為約瑟夫問題的解。
?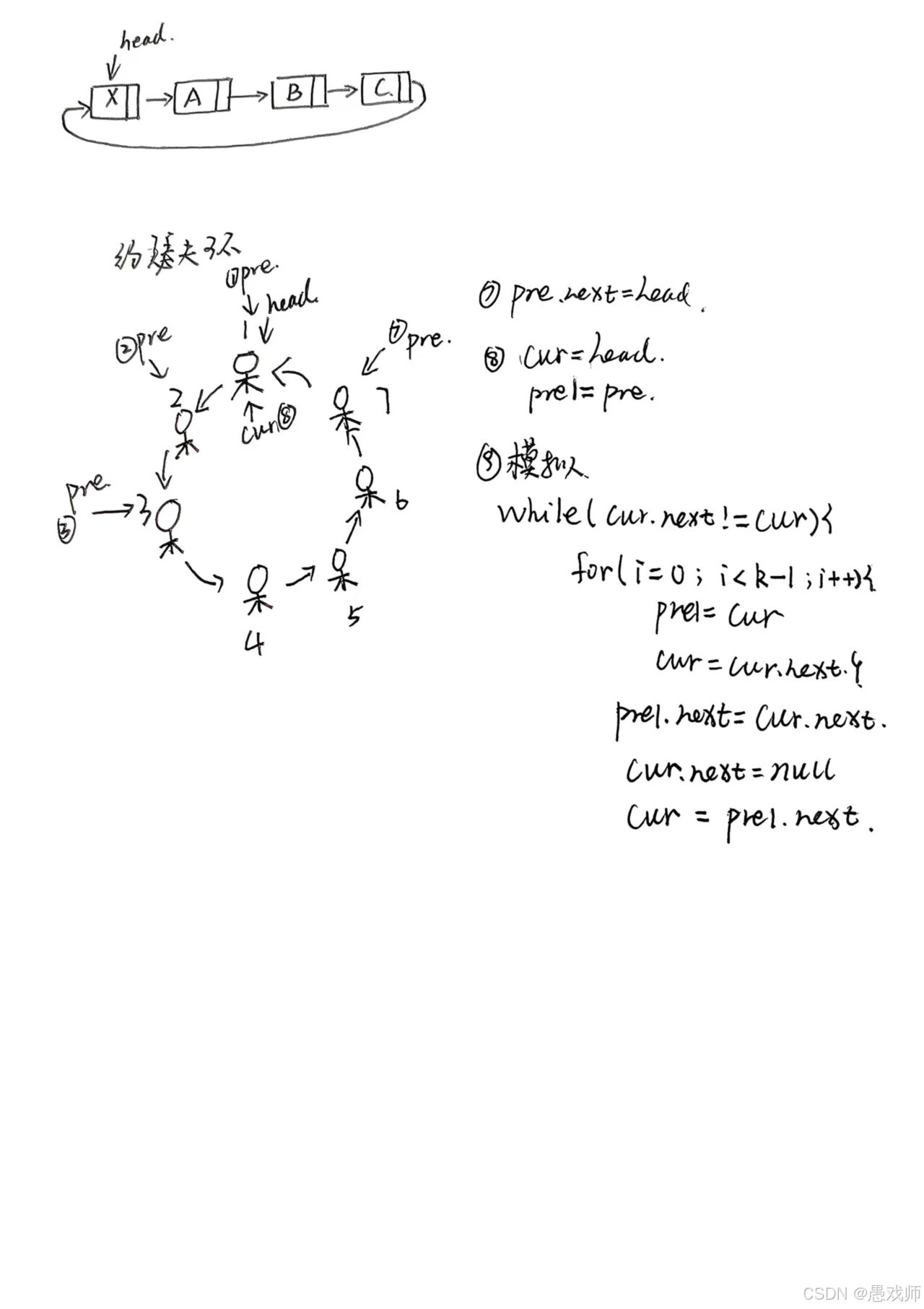
class Node {int data;Node next;public Node(int data) {this.data = data;this.next = null;}
}public class JosephusProblem {public static int josephus(int n, int k) {if (n <= 0 || k <= 0) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("n and k must be positive integers");}// 創建循環鏈表Node head = new Node(1);Node prev = head;for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {prev.next = new Node(i);prev = prev.next;}prev.next = head; // 形成環Node current = head;Node previous = prev; // 前驅節點// 當鏈表中不止一個節點時while (current.next != current) {// 報數:移動k-1步(從1開始計數)for (int i = 0; i < k - 1; i++) {previous = current;current = current.next;}// 移除當前節點previous.next = current.next;current = previous.next; // 從下一個節點重新開始}return current.data; // 最后剩下的節點}public static void main(String[] args) {int n = 7; // 總人數int k = 3; // 報數到k的人出列int survivor = josephus(n, k);System.out.println("最后剩下的人的編號是: " + survivor);}
}鏈表的特殊操作
問題1:“反轉單鏈表(就地逆置),要求空間復雜度。” (思路:用 prev、curr、next 三個指針迭代反轉,避免遞歸棧開銷)
206. 反轉鏈表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
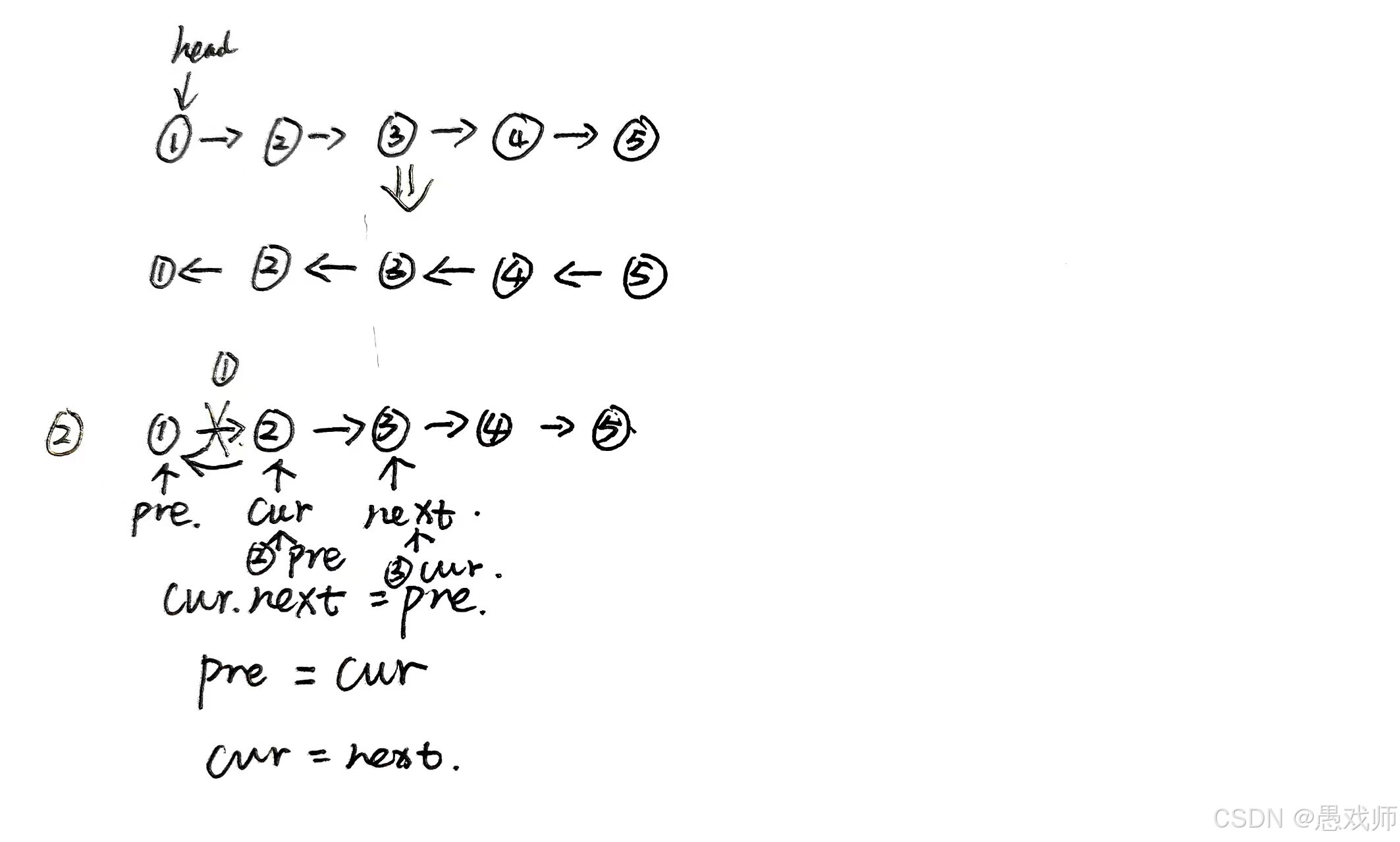
class Solution {public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {ListNode cur=head;ListNode pre=null;ListNode next=null;while(cur!=null){next=cur.next;cur.next=pre;pre=cur;cur=next;}return pre;}
}問題2:“判斷單鏈表是否有環?若有環,如何找到環的入口?” (快慢指針法:快指針每次 2 步,慢指針 1 步,相遇則有環;再從表頭和相遇點同步走,交點即為入口)
141. 環形鏈表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
//雙指針法
public class Solution {public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {ListNode slow=head;ListNode fast=head;while(fast!=null && fast.next!=null){slow=slow.next;fast=fast.next.next;if(slow==fast)return true;}return false;}
}142. 環形鏈表 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {if (head == null) return null;// 步驟1:判斷是否有環并記錄相遇點ListNode slow = head;ListNode fast = head;boolean hasCycle = false;while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next.next;if (slow == fast) {hasCycle = true;break;}}// 無環則返回nullif (!hasCycle) return null;// 步驟2:重置慢指針到鏈表頭slow = head;// 步驟3:同步移動直至相遇while (slow != fast) {slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next; // 快指針改為每次1步}return slow; // 相遇點即環入口
}三、場景應用與選型
1.存儲結構選型
問題:“當需要頻繁按序號訪問元素時,選順序表還是鏈表?當需要頻繁在中間位置插入刪除時,選哪種?為什么?” (考察點:順序表隨機存取O(1)適合高頻訪問;鏈表插入刪除O(1)已知前驅)適合高頻修改)
實際場景設計
問題:“設計一個通訊錄系統,支持添加、刪除、查詢聯系人,應采用順序表還是鏈表?說明理由。” (考察點:通訊錄數據量動態變化(適合鏈表)、查詢頻率(若按姓名查詢,兩種結構差異不大;若按索引,順序表更優))
2. 手寫算法實現
考察目的:考察編碼能力和邊界處理。
? 刪除鏈表中重復元素(有序鏈表)83. 刪除排序鏈表中的重復元素 - 力扣(LeetCode)
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/
class Solution {public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {ListNode cur=head;while(cur!=null && cur.next!=null){if(cur.val==cur.next.val){cur.next=cur.next.next;}else{cur=cur.next;}}return head;}
}關鍵點:雙指針遍歷。
3. 復雜問題與優化
考察目的:考察算法設計思維和優化能力。
(1) 合并兩個有序鏈表(LeetCode 21)21. 合并兩個有序鏈表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
思路:虛擬頭節點簡化邊界處理。
class Solution {public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {//虛擬頭節點ListNode head=new ListNode(-1);ListNode cur=head;while(list1!=null && list2!=null){if(list1.val<=list2.val){cur.next=list1;list1=list1.next;}else{cur.next=list2;list2=list2.next;}cur=cur.next;}cur.next=(list1==null)?list2:list1;return head.next;}
}
4. 場景應用題
考察目的:將線性表應用于實際問題。
Q:設計一個支持高效插入、刪除和隨機訪問的數據結構(LeetCode 380)。
A:使用?哈希表 + 動態數組:
數組存儲元素,支持O(1)隨機訪問。
哈希表存儲元素到數組下標的映射,支持O(1)插入/刪除。



)
8.1)
)





什么意思?有什么用?bmpData.Scan0;什么意思?有什么用?)


)


:自定義實現一個自增的StatefulWidget組件)
![[AI8051U入門第十三步]W5500實現MQTT通信](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[AI8051U入門第十三步]W5500實現MQTT通信)
