在 Kubernetes 集群中,如何在保障應用高可用的同時有效地管理資源,一直是運維人員和開發者關注的重點。隨著微服務架構的普及,集群內各個服務的負載波動日趨明顯,傳統的手動擴縮容方式已無法滿足實時性和彈性需求。
Cluster Autoscaler(簡稱 CA) 作為 Kubernetes 官方提供的自動伸縮組件,通過監控調度器中未能調度的 Pod,并自動調整節點數量,為集群資源的動態調配提供了一種高效解決方案。
Kubernetes 的自動伸縮分為三個維度:
- Pod 級別:Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) 根據 CPU/內存等指標調整 Pod 副本數;
- 節點級別:Cluster Autoscaler (CA) 動態調整集群節點數量;
- 資源粒度:Vertical Pod Autoscaler (VPA) 動態調整 Pod 的 Request/Limit。
本篇文章,就來詳細介紹下 CA 的原理和實踐。
Cluster Autoscaler 工作原理
CA 抽象出了一個 NodeGroup 的概念,與之對應的是云廠商的伸縮組服務。CA 通過 CloudProvider 提供的 NodeGroup 計算集群內節點資源,以此來進行伸縮。
CA 啟動后,CA 會定期(默認 10s)檢查未調度的 Pod 和 Node 的資源使用情況,并進行相應的 Scale UP 和 Scale Down 操作。
CA 由以下幾個模塊組成:
- autoscaler: 核心模塊,負責整體擴縮容功能;
- estimator: 負責評估計算擴容節點;
- simulator: 負責模擬調度,計算縮容節點;
- CA cloud-provider: 與云交互進行節點的增刪操作。社區目前僅支持AWS和GCE,其他云廠商需要自己實現CloudProvider和NodeGroup相關接口。
CA的架構如下:

接下來,我們來看下 CA 的擴縮容時的具體工作流程(原理)。
擴容原理(Scale UP)
當 Cluster Autoscaler 發現有 Pod 由于資源不足而無法調度時,就會通過調用 Scale UP 執行擴容操作。
CA 擴容時會根據擴容策略,選擇合適的 NodeGroup。為了業務需要,集群中可能會有不同規格的 Node,我們可以創建多個 NodeGroup,在擴容時會根據 --expander 選項配置指定的策略,選擇一個擴容的節點組,支持如下五種策略:
- random: 隨機選擇一個 NodeGroup。如果未指定,則默認為此策略;
- most-pods: 選擇能夠調度最多 Pod 的 NodeGroup,比如有的 Pod 未調度是因為
nodeSelector,此策略會優先選擇能滿足的 NodeGroup 來保證大多數的 Pod 可以被調度; - least-waste: 為避免浪費,此策略會優先選擇能滿足 Pod 需求資源的最小資源類型的 NodeGroup。
- price: 根據 CloudProvider 提供的價格模型,選擇最省錢的 NodeGroup;
- priority: 通過配置優先級來進行選擇,用起來比較麻煩,需要額外的配置,可以看Priority based expander for cluster-autoscaler。
如果有需要,也可以平衡相似 NodeGroup 中的 Node 數量,避免 NodeGroup 達到 MaxSize 而導致無法加入新 Node。通過 --balance-similar-node-groups 選項配置,默認為 false。
再經過一系列的操作后,最終計算出要擴容的 Node 數量及 NodeGroup,使用 CloudProvider 執行 IncreaseSize 操作,增加云廠商的伸縮組大小,從而完成擴容操作。
CA 擴容流程
Cluster Autoscaler 的擴容核心在于對集群資源的實時監控和決策,其主要工作流程如下:
- 監控未調度的 Pod: 當 Kubernetes 調度器發現某個 Pod 因為資源不足而無法被調度到現有節點時,CA 會監測到因無法調度而 Pending 的 Pod,進而觸發 CA 擴容操作。CA 擴容的觸發條件如下:
- Pod 因資源不足(CPU/Memory/GPU)無法調度;
- Pod 因節點選擇器(NodeSelector)、親和性(Affinity)或污點容忍(Tolerations)不匹配無法調度;
- 節點資源碎片化導致無法容納 Pod(例如剩余資源分散在不同節點)。
- 節點模板選擇: CA 根據每個節點池的節點模板進行調度判斷,挑選合適的節點模板。若有多個模板合適,即有多個可擴的節點池備選,CA 會調用 expanders 從多個模板挑選最優模板并對對應節點池進行擴容。選擇了 NodeGroup 之后,便會調用云平臺的 API 創建新的節點,并加入到集群中。

- 節點加入與 Pod 調度: 新增節點加入后,調度器重新調度之前未能分配的 Pod,滿足業務需求。
CA ScaleUp 源碼剖析
CA 擴容時調用,ScaleUp 的源碼剖析如下:
func ScaleUp(context *context.AutoscalingContext, processors *ca_processors.AutoscalingProcessors, clusterStateRegistry *clusterstate.ClusterStateRegistry, unschedulablePods []*apiv1.Pod, nodes []*apiv1.Node, daemonSets []*appsv1.DaemonSet, nodeInfos map[string]*schedulernodeinfo.NodeInfo, ignoredTaints taints.TaintKeySet) (*status.ScaleUpStatus, errors.AutoscalerError) {......// 驗證當前集群中所有 ready node 是否來自于 nodeGroups,取得所有非組內的 nodenodesFromNotAutoscaledGroups, err := utils.FilterOutNodesFromNotAutoscaledGroups(nodes, context.CloudProvider)if err != nil {return &status.ScaleUpStatus{Result: status.ScaleUpError}, err.AddPrefix("failed to filter out nodes which are from not autoscaled groups: ")}nodeGroups := context.CloudProvider.NodeGroups()gpuLabel := context.CloudProvider.GPULabel()availableGPUTypes := context.CloudProvider.GetAvailableGPUTypes()// 資源限制對象,會在 build cloud provider 時傳入// 如果有需要可在 CloudProvider 中自行更改,但不建議改動,會對用戶造成迷惑resourceLimiter, errCP := context.CloudProvider.GetResourceLimiter()if errCP != nil {return &status.ScaleUpStatus{Result: status.ScaleUpError}, errors.ToAutoscalerError(errors.CloudProviderError,errCP)}// 計算資源限制// nodeInfos 是所有擁有節點組的節點與示例節點的映射// 示例節點會優先考慮真實節點的數據,如果 NodeGroup 中還沒有真實節點的部署,則使用 Template 的節點數據scaleUpResourcesLeft, errLimits := computeScaleUpResourcesLeftLimits(context.CloudProvider, nodeGroups, nodeInfos, nodesFromNotAutoscaledGroups, resourceLimiter)if errLimits != nil {return &status.ScaleUpStatus{Result: status.ScaleUpError}, errLimits.AddPrefix("Could not compute total resources: ")}// 根據當前節點與 NodeGroups 中的節點來計算會有多少節點即將加入集群中// 由于云服務商的伸縮組 increase size 操作并不是同步加入 node,所以將其統計,以便于后面計算節點資源upcomingNodes := make([]*schedulernodeinfo.NodeInfo, 0)for nodeGroup, numberOfNodes := range clusterStateRegistry.GetUpcomingNodes() {......}klog.V(4).Infof("Upcoming %d nodes", len(upcomingNodes))// 最終會進入選擇的節點組expansionOptions := make(map[string]expander.Option, 0)......// 出于某些限制或錯誤導致不能加入新節點的節點組,例如節點組已達到 MaxSizeskippedNodeGroups := map[string]status.Reasons{}// 綜合各種情況,篩選出節點組for _, nodeGroup := range nodeGroups {......}if len(expansionOptions) == 0 {klog.V(1).Info("No expansion options")return &status.ScaleUpStatus{Result: status.ScaleUpNoOptionsAvailable,PodsRemainUnschedulable: getRemainingPods(podEquivalenceGroups, skippedNodeGroups),ConsideredNodeGroups: nodeGroups,}, nil}......// 選擇一個最佳的節點組進行擴容,expander 用于選擇一個合適的節點組進行擴容,默認為 RandomExpander,flag: expander// random 隨機選一個,適合只有一個節點組// most-pods 選擇能夠調度最多 pod 的節點組,比如有 noSchedulerPods 是有 nodeSelector 的,它會優先選擇此類節點組以滿足大多數 pod 的需求// least-waste 優先選擇能滿足 pod 需求資源的最小資源類型的節點組// price 根據價格模型,選擇最省錢的// priority 根據優先級選擇bestOption := context.ExpanderStrategy.BestOption(options, nodeInfos)if bestOption != nil && bestOption.NodeCount > 0 {......newNodes := bestOption.NodeCount// 考慮到 upcomingNodes, 重新計算本次新加入節點if context.MaxNodesTotal > 0 && len(nodes)+newNodes+len(upcomingNodes) > context.MaxNodesTotal {klog.V(1).Infof("Capping size to max cluster total size (%d)", context.MaxNodesTotal)newNodes = context.MaxNodesTotal - len(nodes) - len(upcomingNodes)if newNodes < 1 {return &status.ScaleUpStatus{Result: status.ScaleUpError}, errors.NewAutoscalerError(errors.TransientError,"max node total count already reached")}}createNodeGroupResults := make([]nodegroups.CreateNodeGroupResult, 0)// 如果節點組在云服務商端處不存在,會嘗試創建根據現有信息重新創建一個云端節點組// 但是目前所有的 CloudProvider 實現都沒有允許這種操作,這好像是個多余的方法// 云服務商不想,也不應該將云端節點組的創建權限交給 ClusterAutoscalerif !bestOption.NodeGroup.Exist() {oldId := bestOption.NodeGroup.Id()createNodeGroupResult, err := processors.NodeGroupManager.CreateNodeGroup(context, bestOption.NodeGroup)......}// 得到最佳節點組的示例節點nodeInfo, found := nodeInfos[bestOption.NodeGroup.Id()]if !found {// This should never happen, as we already should have retrieved// nodeInfo for any considered nodegroup.klog.Errorf("No node info for: %s", bestOption.NodeGroup.Id())return &status.ScaleUpStatus{Result: status.ScaleUpError, CreateNodeGroupResults: createNodeGroupResults}, errors.NewAutoscalerError(errors.CloudProviderError,"No node info for best expansion option!")}// 根據 CPU、Memory及可能存在的 GPU 資源(hack: we assume anything which is not cpu/memory to be a gpu.),計算出需要多少個 NodesnewNodes, err = applyScaleUpResourcesLimits(context.CloudProvider, newNodes, scaleUpResourcesLeft, nodeInfo, bestOption.NodeGroup, resourceLimiter)if err != nil {return &status.ScaleUpStatus{Result: status.ScaleUpError, CreateNodeGroupResults: createNodeGroupResults}, err}// 需要平衡的節點組targetNodeGroups := []cloudprovider.NodeGroup{bestOption.NodeGroup}// 如果需要平衡節點組,根據 balance-similar-node-groups flag 設置。// 檢測相似的節點組,并平衡它們之間的節點數量if context.BalanceSimilarNodeGroups {......}// 具體平衡策略可以看 (b *BalancingNodeGroupSetProcessor) BalanceScaleUpBetweenGroups 方法scaleUpInfos, typedErr := processors.NodeGroupSetProcessor.BalanceScaleUpBetweenGroups(context, targetNodeGroups, newNodes)if typedErr != nil {return &status.ScaleUpStatus{Result: status.ScaleUpError, CreateNodeGroupResults: createNodeGroupResults}, typedErr}klog.V(1).Infof("Final scale-up plan: %v", scaleUpInfos)// 開始擴容,通過 IncreaseSize 擴容for _, info := range scaleUpInfos {typedErr := executeScaleUp(context, clusterStateRegistry, info, gpu.GetGpuTypeForMetrics(gpuLabel, availableGPUTypes, nodeInfo.Node(), nil), now)if typedErr != nil {return &status.ScaleUpStatus{Result: status.ScaleUpError, CreateNodeGroupResults: createNodeGroupResults}, typedErr}}......}......
}
縮容原理(Scale Down)
縮容是一個可選的功能,通過 --scale-down-enabled 選項配置,默認為 true。在 CA 監控 Node 資源時,如果發現有 Node 滿足以下三個條件時,就會標記這個 Node 為 unneeded:
- Node 上運行的所有的 Pod 的 CPU 和內存之和小于該 Node 可分配容量的
50%。可通過--scale-down-utilization-threshold選項改變這個配置; - Node 上所有的 Pod 都可以被調度到其他節點;
- Node 沒有表示不可縮容的
annotaition。
如果一個 Node 被標記為 unneeded 超過 10 分鐘(可通過 --scale-down-unneeded-time 選項配置),則使用 CloudProvider 執行 DeleteNodes 操作將其刪除。一次最多刪除一個 unneeded Node,但空 Node 可以批量刪除,每次最多刪除 10 個(通過 --max-empty-bulk-delete 選項配置)。
實際上并不是只有這一個判定條件,還會有其他的條件來阻止刪除這個 Node,比如 NodeGroup 已達到 MinSize,或在過去的 10 分鐘內有過一次 Scale UP 操作(通過 --scale-down-delay-after-add 選項配置)等等,更詳細可查看 How does scale-down work?。
在決定縮容前,CA 會通過調度器模擬 Pod 遷移過程,確保其他節點有足夠資源接收被遷移的 Pod。若模擬失敗(如資源不足或親和性沖突),則放棄縮容。
CA 縮容流程
- CA 監測到分配率(即 Request 值,取 CPU 分配率和 MEM 分配率的最大值)低于設定的節點。計算分配率時,可以設置 Daemonset 類型不計入 Pod 占用資源;
- CA 判斷集群的狀態是否可以觸發縮容,需要滿足如下要求:
- 節點利用率低于閾值(默認
50%); - 節點上所有 Pod 均能遷移到其他節點(包括容忍 PDB 約束);
- 節點持續空閑時間超過
scale-down-unneeded-time(默認 10 分鐘)。
- 節點利用率低于閾值(默認
- CA 判斷該節點是否符合縮容條件。可以按需設置以下不縮容條件(滿足條件的節點不會被 CA 縮容):
- 節點上有 pod 被 PodDisruptionBudget 控制器限制;
- 節點上有命名空間是 kube-system 的 pods;
- 節點上的 pod 不是被控制器創建,例如不是被 deployment, replica set, job, statefulset 創建;
- 節點上有 pod 使用了本地存儲;
- 節點上 pod 驅逐后無處可去,即沒有其他node能調度這個 pod;
- 節點有注解:
"cluster-autoscaler.kubernetes.io/scale-down-disabled": "true"(在 CA 1.0.3 或更高版本中受支持)。
- CA 驅逐節點上的 Pod 后釋放/關機節點。
- 完全空閑節點可并發縮容(可設置最大并發縮容數);
- 非完全空閑節點逐個縮容。
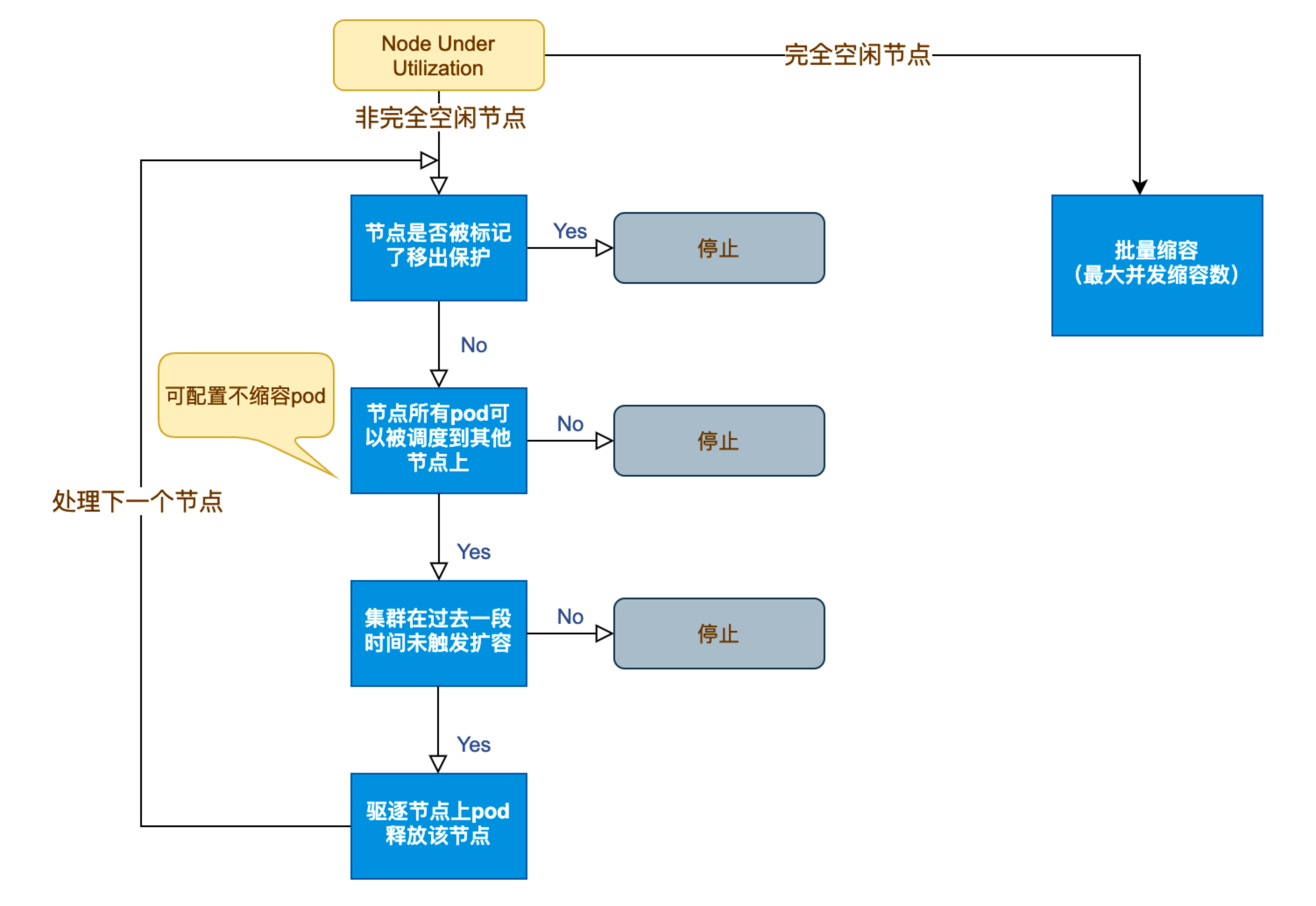
Cluster Autoscaler 在縮容時會檢查 PodDisruptionBudget (PDB),確保驅逐 Pod 不會違反最小可用副本數約束。若 Pod 受 PDB 保護且驅逐可能導致違反約束,則該節點不會被縮容。
與云服務提供商的集成
Cluster Autoscaler 原生支持多個主流云平臺,如 AWS、GCP、Azure 等。它通過調用云服務 API 來實現節點的創建和銷毀。實踐中需要注意:
- 認證與權限: 確保 Cluster Autoscaler 擁有足夠的權限調用云平臺的相關 API,通常需要配置相應的 IAM 角色或 API 密鑰。
- 節點組配置: 集群內通常會預先劃分多個節點組,每個節點組對應不同的資源規格和用途。在擴縮容決策時,Autoscaler 會根據 Pod 的資源需求選擇最合適的節點組。
- 多節點組配置示例(以 AWS 為例):
apiVersion: eksctl.io/v1alpha5
kind: ClusterConfig
nodeGroups:- name: ng-spotinstanceType: m5.largespot: trueminSize: 0maxSize: 10labels: node-type: spot- name: ng-on-demandinstanceType: m5.xlargeminSize: 1maxSize: 5labels:node-type: on-demand
通過標簽區分節點組,CA 可根據 Pod 的 nodeSelector 選擇擴縮容目標組。
- 混合云注意事項: 若集群跨公有云和本地數據中心,需確保 CA 僅管理云上節點組,避免誤刪物理節點。可通過注釋排除本地節點組:
metadata:annotations:cluster-autoscaler.kubernetes.io/scale-down-disabled: "true"
如何實現 CloudProvider?
如果使用上述中已實現接入的云廠商,只需要通過 --cloud-provider 選項指定來自哪個云廠商就可以,如果想要對接自己的 IaaS 或有特定的業務邏輯,就需要自己實現 CloudProvider Interface 與 NodeGroup Interface。并將其注冊到 builder 中,用于通過 --cloud-provider 參數指定。
builder 在 cloudprovider/builder 中的 builder_all.go 中注冊,也可以在其中新建一個自己的 build,通過 go 文件的 +build 編譯參數來指定使用的 CloudProvider。
CloudProvider 接口與 NodeGroup 接口在 cloud_provider.go 中定義,其中需要注意的是 Refresh 方法,它會在每一次循環(默認 10 秒)的開始時調用,可在此時請求接口并刷新 NodeGroup 狀態,通常的做法是增加一個 manager 用于管理狀態。有不理解的部分可參考其他 CloudProvider 的實現。
type CloudProvider interface {// Name returns name of the cloud provider.Name() string// NodeGroups returns all node groups configured for this cloud provider.// 會在一此循環中多次調用此方法,所以不適合每次都請求云廠商服務,可以在 Refresh 時存儲狀態NodeGroups() []NodeGroup// NodeGroupForNode returns the node group for the given node, nil if the node// should not be processed by cluster autoscaler, or non-nil error if such// occurred. Must be implemented.// 同上NodeGroupForNode(*apiv1.Node) (NodeGroup, error)// Pricing returns pricing model for this cloud provider or error if not available.// Implementation optional.// 如果不使用 price expander 就可以不實現此方法Pricing() (PricingModel, errors.AutoscalerError)// GetAvailableMachineTypes get all machine types that can be requested from the cloud provider.// Implementation optional.// 沒用,不需要實現GetAvailableMachineTypes() ([]string, error)// NewNodeGroup builds a theoretical node group based on the node definition provided. The node group is not automatically// created on the cloud provider side. The node group is not returned by NodeGroups() until it is created.// Implementation optional.// 通常情況下,不需要實現此方法,但如果你需要 ClusterAutoscaler 創建一個默認的 NodeGroup 的話,也可以實現。// 但其實更好的做法是將默認 NodeGroup 寫入云端的伸縮組NewNodeGroup(machineType string, labels map[string]string, systemLabels map[string]string,taints []apiv1.Taint, extraResources map[string]resource.Quantity) (NodeGroup, error)// GetResourceLimiter returns struct containing limits (max, min) for resources (cores, memory etc.).// 資源限制對象,會在 build 時傳入,通常情況下不需要更改,除非在云端有顯示的提示用戶更改的地方,否則使用時會迷惑用戶GetResourceLimiter() (*ResourceLimiter, error)// GPULabel returns the label added to nodes with GPU resource.// GPU 相關,如果集群中有使用 GPU 資源,需要返回對應內容。 hack: we assume anything which is not cpu/memory to be a gpu.GPULabel() string// GetAvailableGPUTypes return all available GPU types cloud provider supports.// 同上GetAvailableGPUTypes() map[string]struct{}// Cleanup cleans up open resources before the cloud provider is destroyed, i.e. go routines etc.// CloudProvider 只會在啟動時被初始化一次,如果每次循環后有需要清除的內容,在這里處理Cleanup() error// Refresh is called before every main loop and can be used to dynamically update cloud provider state.// In particular the list of node groups returned by NodeGroups can change as a result of CloudProvider.Refresh().// 會在 StaticAutoscaler RunOnce 中被調用Refresh() error
}// NodeGroup contains configuration info and functions to control a set
// of nodes that have the same capacity and set of labels.
type NodeGroup interface {// MaxSize returns maximum size of the node group.MaxSize() int// MinSize returns minimum size of the node group.MinSize() int// TargetSize returns the current target size of the node group. It is possible that the// number of nodes in Kubernetes is different at the moment but should be equal// to Size() once everything stabilizes (new nodes finish startup and registration or// removed nodes are deleted completely). Implementation required.// 響應的是伸縮組的節點數,并不一定與 kubernetes 中的節點數保持一致TargetSize() (int, error)// IncreaseSize increases the size of the node group. To delete a node you need// to explicitly name it and use DeleteNode. This function should wait until// node group size is updated. Implementation required.// 擴容的方法,增加伸縮組的節點數IncreaseSize(delta int) error// DeleteNodes deletes nodes from this node group. Error is returned either on// failure or if the given node doesn't belong to this node group. This function// should wait until node group size is updated. Implementation required.// 刪除的節點一定要在該節點組中DeleteNodes([]*apiv1.Node) error// DecreaseTargetSize decreases the target size of the node group. This function// doesn't permit to delete any existing node and can be used only to reduce the// request for new nodes that have not been yet fulfilled. Delta should be negative.// It is assumed that cloud provider will not delete the existing nodes when there// is an option to just decrease the target. Implementation required.// 當 ClusterAutoscaler 發現 kubernetes 節點數與伸縮組的節點數長時間不一致,會調用此方法來調整DecreaseTargetSize(delta int) error// Id returns an unique identifier of the node group.Id() string// Debug returns a string containing all information regarding this node group.Debug() string// Nodes returns a list of all nodes that belong to this node group.// It is required that Instance objects returned by this method have Id field set.// Other fields are optional.// This list should include also instances that might have not become a kubernetes node yet.// 返回伸縮組中的所有節點,哪怕它還沒有成為 kubernetes 的節點Nodes() ([]Instance, error)// TemplateNodeInfo returns a schedulernodeinfo.NodeInfo structure of an empty// (as if just started) node. This will be used in scale-up simulations to// predict what would a new node look like if a node group was expanded. The returned// NodeInfo is expected to have a fully populated Node object, with all of the labels,// capacity and allocatable information as well as all pods that are started on// the node by default, using manifest (most likely only kube-proxy). Implementation optional.// ClusterAutoscaler 會將節點信息與節點組對應,來判斷資源條件,如果是一個空的節點組,那么就會通過此方法來虛擬一個節點信息。TemplateNodeInfo() (*schedulernodeinfo.NodeInfo, error)// Exist checks if the node group really exists on the cloud provider side. Allows to tell the// theoretical node group from the real one. Implementation required.Exist() bool// Create creates the node group on the cloud provider side. Implementation optional.// 與 CloudProvider.NewNodeGroup 配合使用Create() (NodeGroup, error)// Delete deletes the node group on the cloud provider side.// This will be executed only for autoprovisioned node groups, once their size drops to 0.// Implementation optional.Delete() error// Autoprovisioned returns true if the node group is autoprovisioned. An autoprovisioned group// was created by CA and can be deleted when scaled to 0.Autoprovisioned() bool
}
實踐中的常見問題與最佳實踐
部署與配置
- 安裝方式: Cluster Autoscaler 可以通過 Helm Chart 或直接使用官方提供的 YAML 清單進行部署。安裝完成后,建議結合日志和監控系統,對其運行狀態進行持續觀察;
- 關鍵參數配置: 根據集群規模和業務需求,合理配置參數非常關鍵。例如:
--scale-down-delay-after-add:設定新增節點后多久開始進行縮容判斷;--max-node-provision-time:控制節點從請求到成功加入集群的最長時間。
- 日志與監控: 建議將 Autoscaler 的日志與集群監控系統(如 Prometheus)集成,以便及時發現和解決問題;
- 關鍵參數詳解:
| 參數 | 默認值 | 說明 |
|---|---|---|
--scale-down-delay-after-add | 10m | 擴容后等待多久開始縮容判斷 |
-scale-down-unneeded-time | 10m | 節點持續空閑多久后觸發縮容 |
--expander | random | 擴容策略(支持 priority, most-pods, least-waste) |
--skip-nodes-with-local-storage | true | 跳過含本地存儲的節點縮容 |
- 資源請求(Request)的重要性: CA 完全依賴 Pod 的
resources.requests計算節點資源需求。若未設置 Request 或設置過低,可能導致:- 擴容決策錯誤(節點資源不足);
- 縮容激進(誤判節點利用率低)。
建議結合 VPA 或人工審核確保 Request 合理。
常見問題
- Pod 長時間處于等待狀態: 可能是由于資源請求過高或節點配置不足,建議檢查 Pod 定義和節點組資源規格是否匹配;
- 節點頻繁擴縮容: 這種情況可能導致集群不穩定。通過調整縮容延遲和擴容策略,可以避免頻繁的節點創建和銷毀;
- 云平臺 API 限額: 在大規模伸縮場景下,需注意云服務商對 API 調用的限額,合理配置重試和等待機制;
- DaemonSet Pod 阻礙縮容: 若節點僅運行 DaemonSet Pod(如日志收集組件),默認情況下 CA 不會縮容該節點。可通過以下注解允許縮容:
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:annotations:cluster-autoscaler.kubernetes.io/daemonset-taint-eviction: "true"
- 僵尸節點(Zombie Node)問題: 若云平臺 API 返回節點已刪除但 Kubernetes 未更新狀態,CA 會持續嘗試縮容。可通過
--node-deletion-retries(默認3)控制重試次數。
最佳實踐
- 與 HPA 結合: 將 CA 與 HPA 聯合使用,可以實現從 Pod 級別到節點級別的全方位自動擴縮,提升資源利用率和集群彈性。HPA 會根據當前 CPU 負載更改部署或副本集的副本數。如果負載增加,則 HPA 將創建新的副本,集群中可能有足夠的空間,也可能沒有足夠的空間。如果沒有足夠的資源,CA 將嘗試啟動一些節點,以便 HPA 創建的 Pod 可以運行。如果負載減少,則 HPA 將停止某些副本。結果,某些節點可能變得利用率過低或完全為空,然后 CA 將終止這些不需要的節點;
- 定期評估和調整配置: 根據實際業務負載和集群運行情況,定期回顧和優化 Autoscaler 的配置,確保擴縮容策略始終符合當前需求;
- 充分測試: 在生產環境部署前,建議在測試環境中模擬高負載和低負載場景,對擴縮容邏輯進行充分驗證,避免意外情況影響業務;
- 成本優化策略:
- 使用 Spot 實例節點組:通過多 AZ 和實例類型分散中斷風險;
- 設置
--expander=priority:為成本更低的節點組分配更高優先級; - 啟用
--balance-similar-node-groups:均衡相似節點組的節點數量。
- 穩定性保障:
- 為關鍵組件(如 Ingress Controller)設置 Pod 反親和性,避免單點故障;
- 使用
podDisruptionBudget防止縮容導致服務不可用:
apiVersion: policy/v1
kind: PodDisruptionBudget
metadata:name: zk-pdb
spec:minAvailable: 2selector:matchLabels:app: zookeeper
案例分享
以某大型電商平臺為例,該平臺在促銷期間流量激增,通過配置 Cluster Autoscaler,實現了在高峰期自動擴容,而在流量恢復正常后及時縮容。實踐中,他們不僅調整了擴縮容相關的時間參數,還結合應用流量監控,提前預估負載變化,確保集群資源始終處于最優狀態。通過這種自動化手段,既保證了業務的高可用性,也大幅降低了運維成本。
- 案例補充: 某金融公司未配置
podDisruptionBudget,導致縮容時 Kafka Pod 同時被驅逐,引發消息堆積。解決方案:- 為 Kafka 設置
minAvailable: 2的 PDB; - 調整
scale-down-delay-after-add至 30 分鐘,避免促銷后立即縮容
- 為 Kafka 設置
- 參數調優示例:
# 生產環境推薦配置(兼顧響應速度與穩定性)
command:- ./cluster-autoscaler- --v=4- --stderrthreshold=info- --cloud-provider=aws- --skip-nodes-with-local-storage=false- --expander=least-waste- --scale-down-delay-after-add=20m- --scale-down-unneeded-time=15m--balance-similar-node-groups=true
總結
Kubernetes Cluster Autoscaler 為集群的自動伸縮提供了一種高效、智能的解決方案。通過對未調度 Pod 的實時監控和云平臺 API 的調用,Cluster Autoscaler 能夠根據實際負載動態調整集群規模,實現資源的按需分配。結合實際生產環境中的部署經驗和最佳實踐,合理配置和調優 Autoscaler,不僅可以提升集群的彈性,還能有效降低運維成本。隨著云原生生態系統的不斷發展,Cluster Autoscaler 也在不斷演進,未來將為更復雜的場景提供更加完善的支持。
未來演進方向:
- 預測性伸縮: 基于歷史負載預測資源需求;
- GPU 彈性調度: 支持動態創建/釋放 GPU 節點;
- 多集群協同: 跨集群資源池化,實現全局彈性。
往期文章回顧
- 帶你從0到1部署一個功能完備、生產可用的Kubernetes集群
- 如何開發一個企業級的 LLMOps(智能體) 平臺?
- 如何在業務開發中引入聲明式 API 編程模式
- 知識星球:云原生AI實戰營。10+ 高質量體系課( Go、云原生、AI Infra)、15+ 實戰項目,P8 技術專家助你提高技術天花板,入大廠拿高薪;
- 公眾號:令飛編程,分享 Go、云原生、AI Infra 相關技術。回復「資料」免費下載 Go、云原生、AI 等學習資料;
- 嗶哩嗶哩:令飛編程 ,分享技術、職場、面經等,并有免費直播課「云原生AI高新就業課」,大廠級項目實戰到大廠面試通關;
)





)



)



)




