注解基礎概念
1.什么是注解編程
指的是在類或者方法上加入特定的注解(@XXX) 完成特定功能的開發
@Component
public classXXX{}
?2.為什么要講注解編程
1.注解開發方便
? ? ? ? 代碼簡潔 開發速度大大提高
2.Spring開發潮流
? ? Spring2.x引入注解 Spring3.x完善注解 Springboot普及 推廣注解編程
3.注解的作用
- 替換XML這種配置形式,簡化配置
- 替換接口,實現調用雙方的契約性
通過注解的方式,在功能調用者和功能提供者之間達成約定,進而進行功能的調用。因為注解應用更為方便靈活
4.Spring注解的發展歷程
1.Spring2.x開始支持注解編程 @Componet @Service @Scope
? ? ? ? 目的:提供這些注解只是為了在某些情況下簡化XML的配置,作為XML開發的有益補充
2.Spring3.x @Configuration @Bean..
? ? ? ? 目的:徹底替換XML,基于純注解編程
3.Spring 4.x Springboot
? ? ? ?提倡使用注解常見開發
5.Spring注解開發的一個問題
Spring基于注解進行配置后,還能否解耦合呢?
Spring框架應用注解時,如果對注解配置的內容不滿意,可以通過Spring配置文件進行覆蓋
Spring基礎注解(Spring2.x)
這個階段注解 僅僅是簡化XML配置 并不能完全替代XML
搭建開發環境
<context:compoent-scan base-package=""/>
作用:讓Spring框架在設置包及其子包中掃描對應的注解 使其生效
?對象創建相關注解
@Component
作用:替換原有Spring配置文件中的<bean>標簽
注意:
? ? ? ? id屬性 component注解 提供了默認的設置方式 首單詞首字母小寫
? ? ? ? class屬性 通過反射獲得class內容
@Component細節
- 如何顯示指定工廠創建對象的id值
@Component("u")
- Spring配置文件覆蓋注解配置內容
applicationContext.xml
@Repository ---->XXXDAO
? ? ? ? ?@Repository
? ? ? ? ? public class UserDao{
}
@Service
? ? ? ? @Service
? ? ? ? public class UserService{
}
@Controller
? ? ? ? @Controller
? ? ? ? public class RegAction{
}
<bean id="和注解一致" class=""/>
id值? class的值 要和 注解中的設置保持一致@Repository
@Service
@Controller
注解:本質上這些衍生注解就是@Component?
? ? ? ? 作用<bean
? ? ? ? 細節 @Service("s")
目的:更加準確的表達這一個類型的作用
注意:Spring整合Mybatis開發過程中 不使用@Repository @Component Dao的實現Spring創建了
?
- @Scope注解
作用:控制簡單對象創建次數
<bean id="" class="" scope="singleton/prototype"/>
?@Lazy注解
作用:延遲創建單例對象
一旦使用@Lazy注解后,Spring會在使用這個對象的時候,進行這個對象的創建
?注入相關注解
@Autowired

@Autowired細節分析
1.Autowired注解基于類型注入
? ? ? ? 基于類型的注入:注入對象的類型,必須與目標成員變量類型想通過或者其子類(實現類)
2.Autowired Qualifier 基于名字進行注入(了解)
? ? ? ? 基于名字的注入:注入對象的id值,必須與Qualifier注解中設置的名字相同
3.Autowired注解放置位置
? ? ? ? a)放置在對應成員變量的set方法上
? ? ? ? b)直接把這個注解放置在成員變量上,Spring通過反射直接對成員變量進行注入(賦值)推薦
4.javaEE規范中類似功能的注解? ? ? ? JSR250 @Resource(name="userDAOImpl") 基于名字進行注入
? ? ? ? @Autowired()
? ? ? ? @Qualifier("userDAOImpl")
? ? ? ? 注意:如果在應用Resource注解時,名字沒有配對成功 那么會繼續按照類型進行注入
????????
?
?@Value注解
@Valye注解
1.設置 xxx.properties
? ? ? ? id=10
? ? ? ? name=gao
2.Spring工廠 讀取這個配置文件
? ? ? ? <context:property-placeholder location=""/>
3.代碼
? ? ? ? 屬性 @Value("${key}")
?@PropertySource
替換Spring配置文件中的<context:property-placeholder>標簽
?@Value注解細節
- @Value注解不能應用在靜態成員變量上
- @Value注解-properties 不能注入集合類型
注解掃描詳解
<context:component-scan base-package="">
? ? ? ? <context:exclude-fliter type="" expression=""/>
? ? ? ?
</context component-scan>
當前包 及其子包
type:assignable 排除特定類型 不進行創建
type="annotation" 排除帶@Service注解類型
type="aspectj" 切入點表達式 只能應用包切入點 類切入點
type ="regex" 正則表達式
type ="custom" 自定義排除策略
第三種常用
---可以多個疊加
?包含方式
基于注解開發的思考
配置互通
Spring注解配置 配置文件配置 互通
ref引用就是UserDaoImpl首字母小寫創建的對象
?什么情況下使用注解 什么情況下使用配置文件
@Component 替換<bean
基礎注解(@Componet @Autowired @Value) 程序員開發類型配置
1.程序員開發的類型上? 可以加入對應注解 進行對象的創建
User UserService UserDao...2應用其它非程序員開發的類型時,還是需要<bean 進行配置的
SqlSessionFactoryBean MapperScannerConfigrue
?Spring的高級注解(Spring3.x及以上)
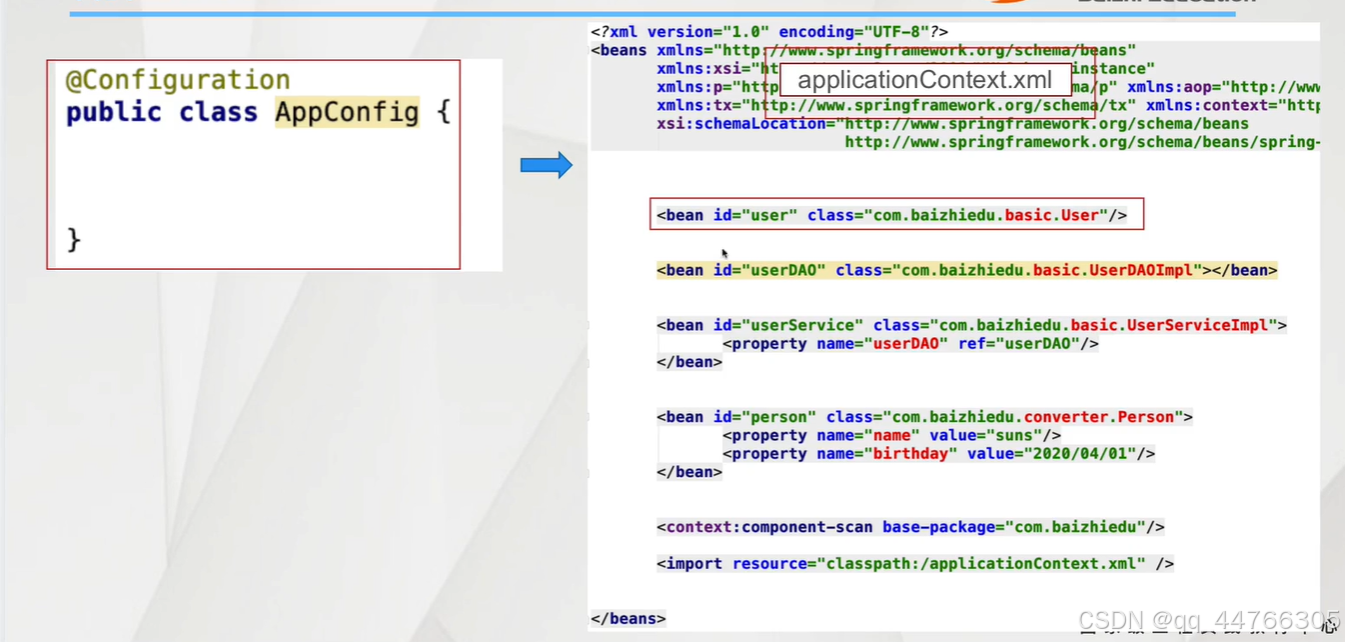
1.配置Bean
Spring在3.x提供新的注解 用于替換XML配置文件
@Configuration
public class AppConfig{
}
?1.配置Bean 替換了XML的什么內容?
?2.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
1.創建工廠代碼
ApplicationContext ctx=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
2.指定配置文件
? ? ? ? 1.指定配置bean的Class
? ? ? ? ApplicationContext ctx=new AnnotationConfigAplicationContext(AppConfig.class)
? ? ? ? 2,指定配置bean所在的路徑
? ? ? ? ApplicationContext ctx=new AnnotationConfigAplicationContext("包名");
?配置Bean開發的細節分析
引入配置文件log.propertities
@Configuration的本質
@Component的衍生注解
可以應用<context:component-scan 進行掃描
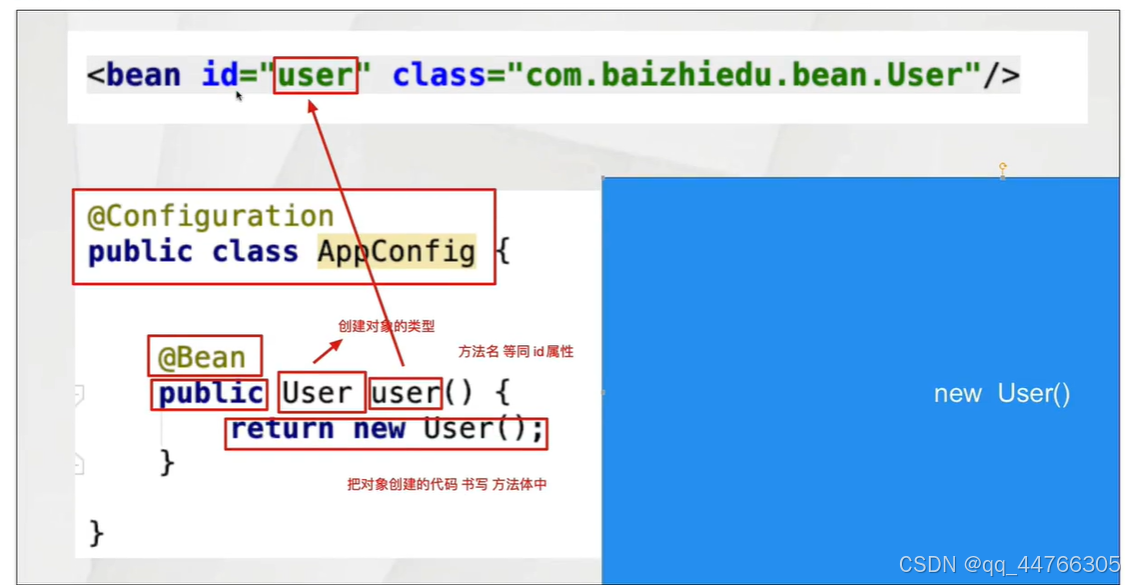
?2.@Bean注解
@Bean注解在配置bean中進行使用,等同于XML配置文件中的<bean>標簽
?1.@Bean注解的基本使用
對象的創建? ? ?
1.簡單對象
? ? ? ? 直接通過new方式創建的對象
?User UserService UserDao
2.復雜對象
? ? ? ? 不能通過new的方式直接創建的對象
? ? ? ? Connection SqlSessionFactory
public class AppConfig {@Beanpublic User user(){return new User();}/*創建一個復雜對象*/@Beanpublic Connection connection() throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/sky_take_out?useSSL=false","root","123456");return connection;}
}
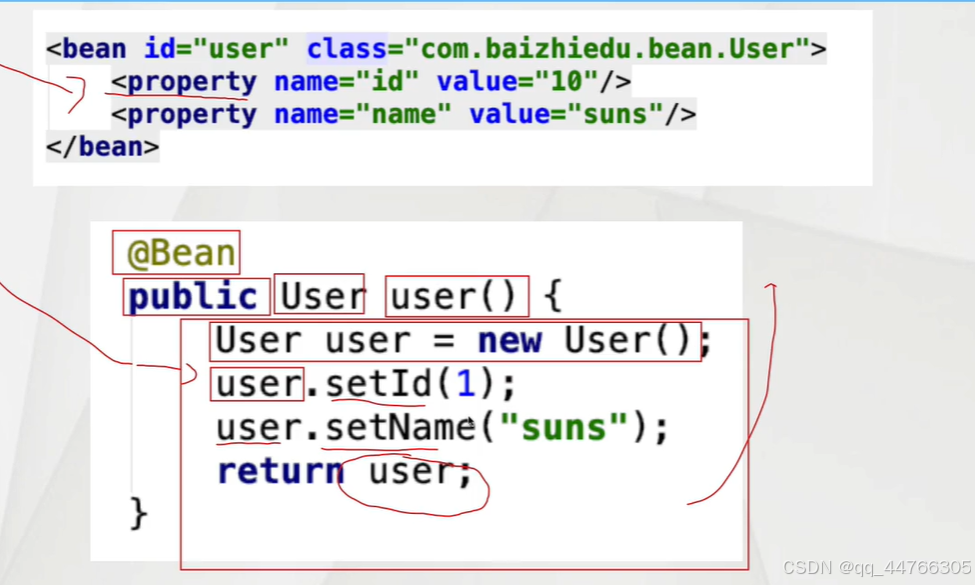
@Bean注解自定義id值
@Bean("u")public User user(){return new User();}/*@Bean控制對象的創建次數
@Bean("u")@Scope("singleton")public User user(){return new User();}@Bean用戶自定義類型注入
package annotationHigh;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;@Configuration
public class AppConfig1 {@Beanpublic User user(){return new User();}@Beanpublic UserDao userDao(){return new UserDaoImpl();}@Beanpublic UserService userService(UserDao userDao){UserServiceImpl userService = new UserServiceImpl();userService.setUserDao(userDao);return userService;}
// @Bean
// public UserService userService(){
// UserServiceImpl userService = new UserServiceImpl();
// userService.setUserDao(userDao());
// return userService;
// }
}@Bean(JDK類型注入)
@BeanJDK類型注入細節分析?
如果直接在代碼中進行set方法的調用 會存在耦合問題
package annotationHigh;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;@Configuration @PropertySource(value = "classpath:init.properties") public class AppConfig1 {@Value("${id}")private Integer id;@Value("${name}")private String name;@Beanpublic User user(){return new User();}@Beanpublic UserDao userDao(){return new UserDaoImpl();}@Beanpublic UserService userService(UserDao userDao){UserServiceImpl userService = new UserServiceImpl();userService.setUserDao(userDao);return userService;} // @Bean // public UserService userService(){ // UserServiceImpl userService = new UserServiceImpl(); // userService.setUserDao(userDao()); // return userService; // }@Beanpublic Customer customer(){Customer customer = new Customer();customer.setId(id);customer.setName(name);return customer;} }
@ComponentScan注解
@ComponentScan注解在配置bean中進行使用,等同于XML配置文件中的<context:component-scan>標簽
目的:進行相關注解的掃描:(@Component @Value ...@Autowired)
?基本使用
@Configuration @ComponentScan(basePackages ="annontation") public class AppConfig2 { }
?排除、包含的使用
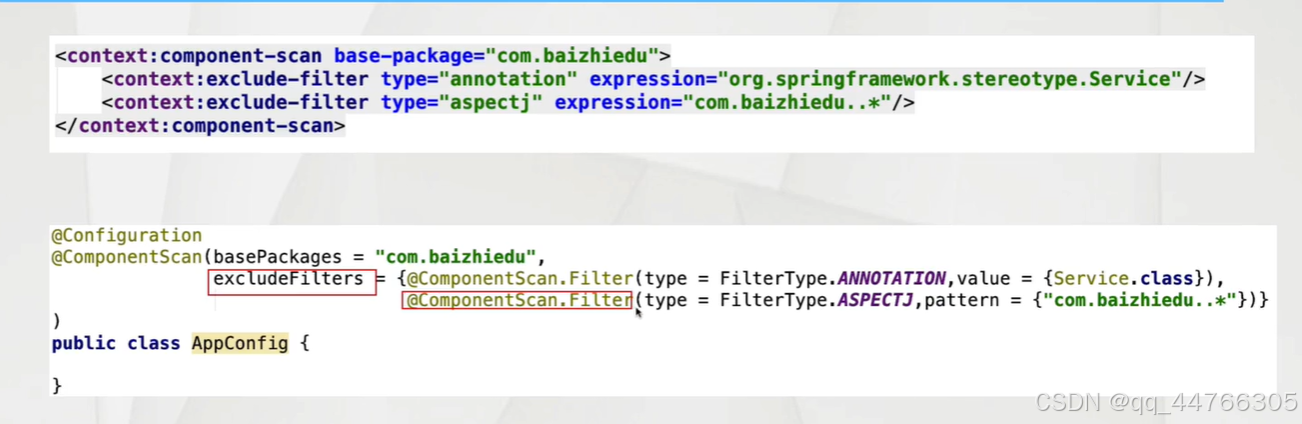
包含
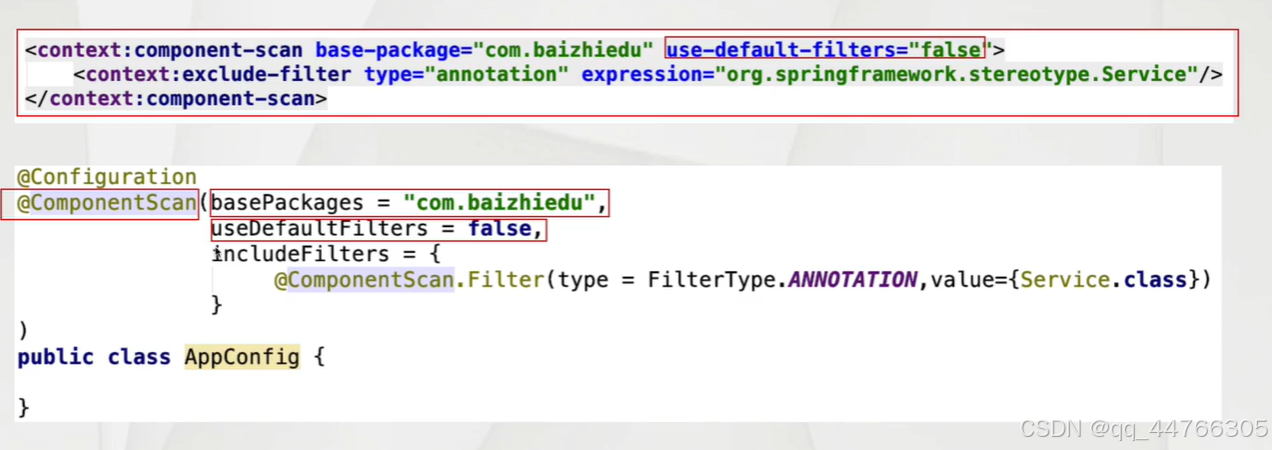
Spring創建工廠的多種方式?
1.多種配置的應用場景

?2。配置優先級
@Component及其衍生注解<@Bean <配置文件bean標簽
優先級高的配置 覆蓋優先級低的配置
@Componentpublic class User{
}
@Bean
public User user(){
? ? ? ? return new User();
}
<bean id="user"class=""/>
注意:id值 應該保持一致
3.解決基于注解進行配置的耦合問題
@Configuration
//@ImportResources("applicationContext.xml")--------也會耦合
public class AppConfig4{
? ? ? ? @Bean
? ? ? ? public UserDao userDao(){
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? return new UserDaoImpl();
????????}
}
applicationContext.xml<bean id="userDao" class=""/>
4.整合多個配置信息
為什么會有多個配置信息
拆分多個配置bean的開發,是一種模塊化開發的形式,也體現了面向對象各司其職的設計思想
?5.多配置信息整合的方式
1.多個配置Bean的整合
2.配置Bean與@Component相關注解的整合
3.配置Bean與SpringXML配置文件的整合
整合洞中配置信息需要關注哪些要點
1.如何使多種配置信息 匯成一個整體
2.如何實現跨配置的注入
1.多個配置Bean的整合
base-package進行多個配置Bean的整合
?@Import
1.可以創建對象
2.多種配置bean的整合
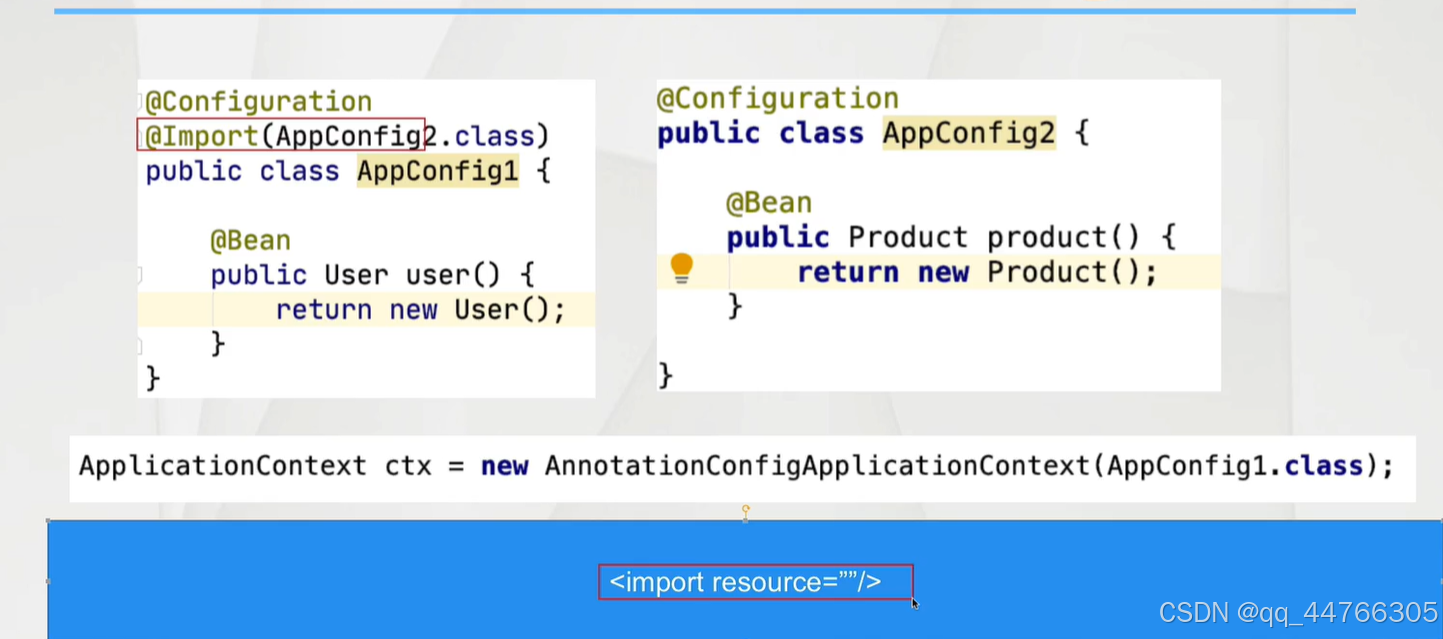
?2.跨配置進行注入
在應用配置Bean的過程中,不管使用哪種方式進行配置信息的匯總,其操作方式都是通過成員變量加入@Autowired注解進行完成
?配置Bean與@Component相關注解的整合
?配置Bean與配置文件的整合
1.遺留系統的整合 2.配置覆蓋
?配置Bean的底層實現原理
四維一體的開發思想?
1.什么是四維一體
Spring開發一個功能的4種形式,雖然開發方式不同,但最終效果是一樣的
1.基于schema
2.基于特定功能注解
3.基于原始<bean
4.基于@Bean注解
2.四維一體的開發案例
1. <context:property-placeholder
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"><context:property-placeholder location="classpath:init.properties"/><bean id="category" class="annontation.Category"></bean><context:component-scan base-package="annontation"></context:component-scan> </beans>package annontation;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;//@Component //@PropertySource(value = "classpath:init.properties") public class Category {@Value("${id}")private Integer id;@Value("${name}")private String name;public Category() {}public Category(Integer id, String name) {this.id = id;this.name = name;}/*** 獲取* @return id*/public Integer getId() {return id;}/*** 設置* @param id*/public void setId(Integer id) {this.id = id;}/*** 獲取* @return name*/public String getName() {return name;}/*** 設置* @param name*/public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public String toString() {return "Categpry{id = " + id + ", name = " + name + "}";} }@PropertySource [推薦]
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"><!-- <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:init.properties"/>--> <!-- <bean id="category" class="annontation.Category"></bean>--><context:component-scan base-package="annontation"></context:component-scan> </beans>package annontation;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component @PropertySource(value = "classpath:init.properties") public class Category {@Value("${id}")private Integer id;@Value("${name}")private String name;public Category() {}public Category(Integer id, String name) {this.id = id;this.name = name;}/*** 獲取* @return id*/public Integer getId() {return id;}/*** 設置* @param id*/public void setId(Integer id) {this.id = id;}/*** 獲取* @return name*/public String getName() {return name;}/*** 設置* @param name*/public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public String toString() {return "Categpry{id = " + id + ", name = " + name + "}";} }<bean id="" class="PropertySourcePlaceholderCoonfigure"/>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"><bean id="category" class="annontation.Category"></bean><bean id="propertyholder" class="org.springframework.context.support.PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer"><property name="location" value="classpath:init.properties"></property></bean><context:component-scan base-package="annontation"></context:component-scan> </beans>@Bean? [推薦]
?package annontation;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource; import org.springframework.context.support.PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer; import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;@Configuration @ComponentScan(basePackages = "annontation") public class AppConfig6 {@Beanpublic PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer propertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer() {PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer propertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer = new PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer();propertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer.setLocations(new ClassPathResource("init.properties"));return propertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer;} }
純注解AOP開發
package annontation;import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;@Configuration @ComponentScan(basePackages = "annontation") @EnableAspectJAutoProxy public class AppConfig7 { }
package annontation;import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Aspect @Component public class MyAspect {//切入點@Pointcut("execution(* *(..))")public void myPointcut(){};//切面@Around(value="myPointcut()")public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable{System.out.println("before");Object ret=joinPoint.proceed();System.out.println("after");return ret;} }
?細節分析
代理創建方式切換JDK Cglib
@EnableAspectjAutoProxy
切換為cglib
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = True)
純注解版Spring+MyBatis整合
1.連接池
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"><property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db03?useSSL=false"/><property name="username" value="root"/><property name="password" value="123456"/><property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/> </bean>@Bean
public DruidDataSource dataSource(){
? ? ? ? DruidDataSource dataSource=new DruidDataSource();
? ? ? ? dataSource.setDriverClassName("");
? ? ? ? dataSource.setUrl();
? ? ? ? return dataSource;
}
2.SqlSessionFactoryBean<!-- 創建sqlSessionFactory SqlSessionFactoryBean--><bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean"><property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/><property name="mapperLocations"><list><value>classpath:mybatis.mapper/*Mapper.xml</value></list></property></bean>@Bean public SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean(DataSource dataSource){SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();sqlSessionFactoryBean.setDataSource(dataSource);sqlSessionFactoryBean.setMapperLocations(new ClassPathResource("mybatis.mapper/EmpMapper.xml"));return sqlSessionFactoryBean; }
?編碼
1.實體
2.表
3.Dao接口
4.Mapper文件
1. MapperLocations編碼時通配寫法
//設置Mapper文件路徑
ResourcePatternResolver resolver=new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(); Resource[]resources=resolver.getResources("mybatis.mapper/*Mapper.xml"); sqlSessionFactoryBean.setMapperLocations(resources);
?2.配置Bean數據耦合的問題
package mybatis;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component @PropertySource("classpath:mybatis.properties") public class MybatisProperties {@Value("${mybatis.driverClassName}")private String driverClassName;@Value("${mybatis.url}")private String url;@Value("${mybatis.username}")private String username;@Value("${mybatis.password}")private String password;@Value("${mybatis.mapperLocations}")private String mapperLocations;public MybatisProperties() {}public MybatisProperties(String driverClassName, String url, String username, String password, String mapperLocations) {this.driverClassName = driverClassName;this.url = url;this.username = username;this.password = password;this.mapperLocations = mapperLocations;}/*** 獲取* @return driverClassName*/public String getDriverClassName() {return driverClassName;}/*** 設置* @param driverClassName*/public void setDriverClassName(String driverClassName) {this.driverClassName = driverClassName;}/*** 獲取* @return url*/public String getUrl() {return url;}/*** 設置* @param url*/public void setUrl(String url) {this.url = url;}/*** 獲取* @return username*/public String getUsername() {return username;}/*** 設置* @param username*/public void setUsername(String username) {this.username = username;}/*** 獲取* @return password*/public String getPassword() {return password;}/*** 設置* @param password*/public void setPassword(String password) {this.password = password;}/*** 獲取* @return mapperLocations*/public String getMapperLocations() {return mapperLocations;}/*** 設置* @param mapperLocations*/public void setMapperLocations(String mapperLocations) {this.mapperLocations = mapperLocations;}public String toString() {return "MybatisProperties{driverClassName = " + driverClassName + ", url = " + url + ", username = " + username + ", password = " + password + ", mapperLocations = " + mapperLocations + "}";} }package mybatis;import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource; import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean; import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource; import org.springframework.core.io.Resource; import org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver; import org.springframework.core.io.support.ResourcePatternResolver;import javax.sql.DataSource; import java.io.IOException;@Configuration @ComponentScan("mybatis") @MapperScan(basePackages = "mybatis") public class MyBatisAutoConfiguration {@Autowiredprivate MybatisProperties mybatisProperties;@Beanpublic DataSource dataSource(){DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();dataSource.setDriverClassName(mybatisProperties.getDriverClassName());dataSource.setUrl(mybatisProperties.getUrl());dataSource.setPassword(mybatisProperties.getPassword());dataSource.setUsername(mybatisProperties.getUsername());return dataSource;}@Beanpublic SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean(DataSource dataSource) throws IOException {SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();sqlSessionFactoryBean.setDataSource(dataSource);ResourcePatternResolver resolver=new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();Resource[]resources=resolver.getResources(mybatisProperties.getMapperLocations());sqlSessionFactoryBean.setMapperLocations(resources);return sqlSessionFactoryBean;}}
純注解版本事務編程?
1.原始對象 XXX
<bean id="userService" class="xxx">
? ? ? ? <property name="userDao" ref="userDao">
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{
? ? ? ? @Autowired
? ? ? ? private UserDao userDao;
}
2.額外功能
<!----DataSourceTransactionManager>
? ? ? ? <bean id="dataSourceTransactionManager" class="org.spring.framework.jdbc.dataSource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
? ? ? ? <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource">
</bean>
?@Bean public DataSourceTransactionManager dataSourceTransactionManager(){DataSourceTransactionManager dataSourceTransactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager();dataSourceTransactionManager.setDataSource(dataSource);return dataSourceTransactionManager; }3.事務屬性
????????
@Transactional() @Service public class EmpServiceImpl implements EmpService{@Autowiredprivate EmpDao empDao;@Overridepublic void register(Emp emp) {empDao.add(emp);} }4.基于Schema的事務配置
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manage="dataSourceTransactionManage"/>
@EnableTransactionManger--配置Bean
package mybatis;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy; import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;import javax.sql.DataSource;//Mybatis已經配置過掃描了 @Configuration @EnableTransactionManagement public class TransactionAutoConfiguration {//跨配置注入@Autowiredprivate DataSource dataSource;@Beanpublic DataSourceTransactionManager dataSourceTransactionManager(){DataSourceTransactionManager dataSourceTransactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager();dataSourceTransactionManager.setDataSource(dataSource);return dataSourceTransactionManager;} }
?Spring與YAML文件整合
1.什么是YML
YAML是一種新形式的配置文件,比XML更簡單,比Properties更強大
?2.Properties進行配置問題
1.Properties表達過于繁瑣,無法表達數據的內在聯系
2.Properties無法表達對象 集合類型
3.YAML語法簡潔
?1.定義yml文件
xxx.yml xxx.yaml
2.語法
? 1.基本語法
? ? ? ? key:空格value
? ? ? ? name:?suns
? ? ? ? password:123456
? ?2.對象概念
? ? ? ? account:
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? id:1
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? password:123456
? ? 3.定義集合
? ? ? ? service
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? -1111
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? -2222
?4.Spring與YML集成思路分析
1.準備yml配置文件
? ? ? ? init.yml
? ? ? ? name: suns
? ? ? ? password: 123456
2.讀取yml 轉換成 Properties
? ? ? ? YamlPropertiesFactoryBean.setResources(yml配置文件路徑) new ClassPathResources();
? ? ? ? YamlPropertiesFactoryBean.getObject()---->Properties
?3.應用PropertSourcePlaceholderConfigurer
? ? ? ? PropertySourcePlaceholderConfigurer.setProperties();
4.類中@Value注解注入
?5.Spring與YML集成編碼
環境搭建
<dependency><groupId>org.yaml</groupId><artifactId>snakeyaml</artifactId><version>1.29</version> </dependency> 最低版本1.18
編碼?
1.準備yml配置文件
2.配置Bean中操作 完成YAML讀取 與PropertySourcePlaceholderConfigure的創建
3.類 加入@Value注解
account:name: gaopassword: 123456package yml;import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.YamlPropertiesFactoryBean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.support.PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer; import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;import java.util.Properties;@Configuration @ComponentScan(basePackages = "yml") public class YmlAutoConfiguration {@Beanpublic PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer propertySourcePlaceholderConfigurer() {YamlPropertiesFactoryBean yamlPropertiesFactoryBean = new YamlPropertiesFactoryBean();yamlPropertiesFactoryBean.setResources(new ClassPathResource("init.yml"));Properties properties = yamlPropertiesFactoryBean.getObject();PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer configurer = new PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer();configurer.setProperties(properties);return configurer;} }
?集成問題
1.集合處理問題
SpringEL表達式解決
@Value("#{'${list}'/split(',')}")
2.對象類型的YAML進行配置時 過于繁瑣
@Value("${account.name}")SpringBoot @ConfigurationProperties




























 - 多租戶的SAAS版實現(2))
架構方面的設計)

![[Python基礎速成]1-Python規范與核心語法](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[Python基礎速成]1-Python規范與核心語法)





:4A廣告代理公司與行業資質解讀)







)

